Understanding Diversity Notes 6th Social Science
Understanding Diversity Notes 6th Social Science
6th Social Science Lesson 7 Notes in English
7. Understanding Diversity
1. Define Civilisation:
India is a home to a civilisation that is 5,000 years old. Different groups of people from different parts of the world were attracted towards India over the years because of its wealth.
2. How India has Rich Diversity:
Some came for trade with the local people and others were keen on invading its territory. So diverse races of people migrated into India by land and sea routes over time.
3. Define Diversity :
We come from different backgrounds, belong to different cultures, worship in different ways, yet we live together. This is known as diversity.
4. Explain India is a Sub Continent:
A continent is a very large area of land with various physical features such as mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers and seas and various types of weather patterns. India has all of them. India is known as a sub-continent.
5. Explain the Economic Activities of a Region:
Physical and climatic features determine the economic activities of a region.
- People living in the plains thrive on agriculture, while people in the coastal areas take to fishing for their livelihood.
- In mountainous regions, rearing of animals is undertaken.
- Hilly landscapes are supported by favourable climatic conditions for the cultivation of coffee and tea.
6th Social Book Back Questions
6. Define the Flora and Fauna of India:
Diversity in landforms also impacts the flora and fauna of a region. The plant and animal wealth of a place depends upon the natural habitat and the climate that prevails in that region. Food, clothing, occupation and livelihood of the people is closely connected with the region’s natural surroundings and climate.
7. Mawsynram located in Megalaya, is the land of highest rainfall.
8. Jaisalmer located in Rajasthan, is the land of lowest rainfall.
9. Define Community:
A community is a place where people live together with a common interest or heritage.
10. Which forms the fundamentals of Society :
Families constitute the fundamental unit of a society. There are two types of families: joint families and nuclear families.
11. How family form a city:
Families live in a harmonious neighbourhood. Hundreds of neighbourhoods collectively form a village and thousands of them group together in a city.
12. How people are united socially?
The needs of people and the interdependence of communities for amenities such as water, food, electricity, education, housing and so on bring us together to live in harmony. Though we are diverse in our cultural practices, we are united and interdependent socially.
13. Name the religion that born in India:
India is the birth place of many religions and has become the home of many others. Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, Jainism and Zoroastrianism flourish in India.
14. Various Festivals of India:
The wide variety of festivals celebrated in India is a true manifestation of its rich culture and traditions. Festivals like Pongal, Deepavali, Holi, Vijayadhasami, AyudhaPuja, Navaratri, Durga Puja, Dussehra, Ganesh Chaturthi, Bihu, Kumbamela, Onam, Miladi Nabi, Ramzan, Christmas, Buddha Poornima, Mahavir Jayanthi, Guru Nanak Jayanthi and Rakshabandhan are some of the festivals that denote the cultural diversity of India.
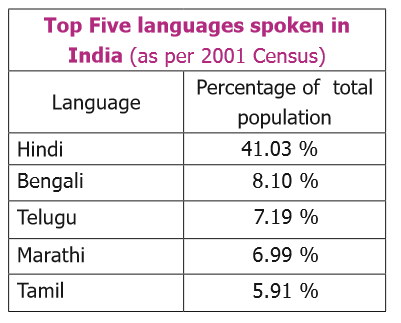
15. How many Languages are there in India?
According to census of India 2001, India has 122 major languages and 1599 other languages.
16. Name the Major Languages?
Four major Indian language families are Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Austroasiatic and Sino Tibetian. Tamil is the oldest Dravidian language.
17. Name the various countries that ruled India:
Historically, the Portuguese, the Dutch, the British, the Danish and the French came to India for trade and their occupation of India or some parts of it has left behind a certain impact upon the culture and language of the people.
18. Mention the Importance of English:
In due course, English has emerged as an important language and a medium of instruction in schools and colleges. It is widely used in official communication and daily life.
19. The Constitution of India recognises twenty-two languages as official languages. The Government of India has declared Tamil as the first classical language in 2004. Apart from Tamil, five other Indian languages have been declared as the classical languages, by the Goverment of India.
20. Various Languages in India:
21. Define Culture:
The term ‘culture’ refers to customs and practices of people, their language, their dress code, cuisine, religion, social habits, music, art and architecture.
22. Which is called as the Integral Part of Community?
Art and architecture are an integral part of every community. It develops as a part of culture and tradition of a community.
23. About 60 percent of the total epigraphical inscriptions found by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) are from Tamil Nadu, and most of these are in the Tamil script.
24. Explain the cultural richness of India:
In ancient times, dance was considered as a way to celebrate, worship and also as a gesture of thanks giving and joy. Dances of India reflect its cultural richness.
25. Various Music and Dance style of India:
The Hindustani music, Karnatic music, Classical Tamil Music, Folk Music, Lavani, Ghazl are some of them.
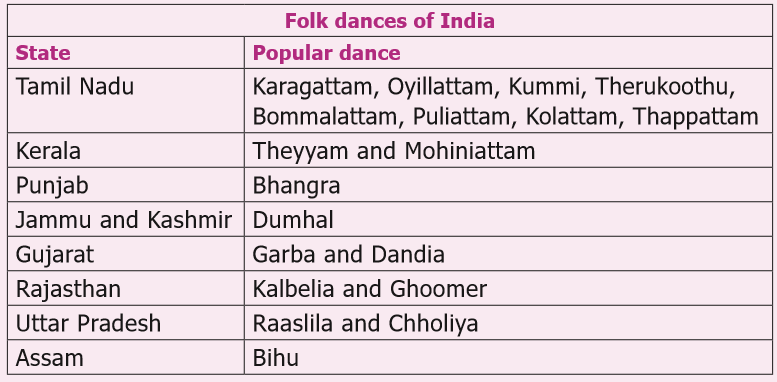
26. Various folk dances of India:
27. V.A. Smith called India as an ‘Ethnological museum’, as a great variety of racial types exist.
28. India is known for ‘unity in diversity’. This phrase was coined by Jawaharlal Nehru, the first Prime Minister of independent India, in his book Discovery of India.
29. Explain Unity in Diversity:
- Though diversity is visible in every aspect of life in India, we are united by the spirit of patriotism.
- Symbols such as the National Flag and National Anthem remind us of our great nation and the need to stay united.
- Celebration of landmark events such as Independence Day, Republic Day and Gandhi Jayanthi every year brings us together and keeps the spirit of one nation alive within us.
30. India has a multi-cultural society: Explain.
India evolved as a single nation through common beliefs, customs and cultural practices. The freedom struggle and the drafting of our Constitution stands as ample evidence to the spirit of unity of India.