The Universe and the Solar System Notes 6th Social Science
The Universe and the Solar System Notes 6th Social Science
6th Social Science Lesson 5 Notes in English
5. The Universe and the Solar System
1. Define Big Bang:
Numerous stars and celestial bodies came into existence by a massive explosion called Big Bang.
2. Define Universe:
These celestial bodies together are called The Universe. It is also referred to as the Cosmos. The stars that you see are so far away that they appear to be small, but they are really huge in size. Universe came into existence after the Big Bang explosion that took place about 15 billion years ago. The universe consists of billions of galaxies, stars, planets, comets, asteroids, meteoroids and natural satellites.
3. Define Cosmology:
The study of the Universe is called Cosmology. The term Cosmos is derived from the Greek word ‘Kosmos’.
4. Define Light Year:
A Light year is the unit used to measure the distance between the celestial bodies.
5. What is Galaxy?
It is a huge cluster of stars which are held together by gravitational force. Most of the galaxies are scattered in space, but some remain in groups.
6. When was Milky way Galaxy Formed?
The Milky Way Galaxy was formed about 5 billion years after the Big Bang explosion. Our solar system is a part of the Milky Way galaxy. Andromeda galaxy is the nearest to the Earth apart from the ‘Magellanic Clouds’ galaxy.
6th Social Book Back Questions
7. What is Solar System?
The word ‘solar’ is derived from the Roman word ‘sol’, which means ‘Sun God’. The solar system is believed to have formed about 4.5 billion years ago.
8. A light-year is the distance traversed by light in a year at a velocity of 300,000 km per second. Sound travels at a speed of 330 m per second.
9. Explain the Nature of The Sun:
The Sun is at the centre of the solar system. Each member of the solar system revolves around the Sun. The Sun is so huge that it accounts for 99.8 percent of the entire mass of the solar system. The Sun is made up of extremely hot gases like Hydrogen and Helium.
10. The Sun is a star, Explain.
It is self-luminous so it gives light on its own. The surface temperature of the Sun is about 6,000° C. It is the source of light and heat energy to the entire solar system. Sunlight takes about 8.3 minutes to reach the Earth.
11. 1.3 million Earths fit inside the Sun. Imagine how big the Sun is.
12. What are Planets ?
The word planet means wanderer. There are eight planets in the solar system. They are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. All the planets rotate anti-clockwise (from west to east) on their own axes except Venus and Uranus.
13. What is Orbit?
The elliptical path in which the planets move around the Sun is known as orbit. The eight planets revolve in their respective orbits because of the gravitational pull of the Sun. They do not move out of their paths or away from the solar system.
14. What are Inner and Outer Planets?
- The four planets nearer to the Sun are called Inner or Terrestrial Planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars). The inner planets are comparatively smaller in size and are composed of rocks. The surface of inner planets has mountains, volcanoes and craters.
- The last four planets are called as Outer Planets or Jovian Planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune). They are also called Gaseous Giants. An asteroid belt is found between Mars and Jupiter.
15. Define the Characteristics of Planet Mercury:
- Mercury is the smallest and closest planet to the Sun.
- It is named after the Roman deity ‘Mercury’, the messenger to the Gods.
- It is an airless and waterless planet. It does not have an atmosphere and so experiences extremes of temperature. It has no natural satellites.
- Mercury can be viewed in the morning and evening with naked eye.
16. Explain Venus:
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is called Earth’s twin, as it is almost the same size as the Earth.
17. Explain the orbit motion of venus:
It has the longest rotation period (243 days) among the planets in the Solar system. It rotates in the opposite direction to all other planets except Uranus. It has no natural satellites like Mercury.
18. Why the name Venus arise?
It is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. It is often visible in the mornings and the evenings and so it is frequently called as the Morning Star and the Evening Star. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky.
19. The distance between the Sun and the Earth is about 150 million kilometre. A flight flying at a speed of 800 km per hour from the Earth would take 21 years to reach the Sun.
20. On 24th September, 2014 Mangalyan (Mars Orbiter Mission – MOM), launched by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), reached the orbit of Mars to analyze its atmosphere and topography. ISRO has now become the fourth space agency to reach Mars after the Soviet Space programme, NASA and the European Space Agency.
21. Explain our planet Earth:
The Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the fifth largest planet in the solar system. It is called ‘blue planet’ or ‘watery planet’ because three-fourth of the Earth is covered by water. The Earth is the only planet in the solar system which is not named after any Greek or Roman deity.
22. Explain the Characteristics of Earth:
It is the only planet known to support life. The polar diameter of the Earth is 12,714 km and the equatorial diameter is 12,756 km. The Earth revolves around the Sun at a speed of about 30 km per second. Life is possible on Earth because of the presence of land, air and water. The only natural satellite of the Earth is the Moon.
23. Explain Mars:
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second smallest planet in the solar system, after Mercury. It is named after the Roman God of war. It appears red in colour due to the presence of iron oxide on its surface. So, it is often described as The Red Planet.
24. Explain the characteristics of Mars:
It has a thin atmosphere. It also has polar ice caps like the Earth. Mars has two natural satellites namely Phobos and Deimos. Many orbiters and rovers have been launched to explore this planet.
25. Explain Jupiter:
Jupiter (the Largest Planet) Jupiter is the fi fth planet from the Sun and the largest planet in the solar system. It is named after the king of the Roman gods. It is the third brightest object in the night sky, after moon and Venus. It is the fastest spinning planet in the solar system. It is called a gas giant planet.
26. Explain the characteristics and satellite of Jupiter:
Its atmosphere is made up of mostly Hydrogen and Helium like the Sun. It has the largest number of natural satellites. Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto are a few large satellites of Jupiter. Saturn (The Ringed planet)
27. What is Saturn?
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest planet in the solar system, after Jupiter. It is named after the Roman god of agriculture. Saturn has many rings around it. These rings are huge and are mostly made up of ice, rocks and dust particles. Saturn has 62 natural satellites around it.
28. Explain Titan:
Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, is the only satellite in the solar system that has clouds and dense atmosphere composed of nitrogen and methane. The specifi c gravity of Saturn is less than that of water.
29. Explain Uranus:
Uranus (The Somersaulting planet) Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It was the fi rst to be discovered with a telescope by the astronomer William Herschel in 1781. It appears green due to the presence of methane. It is named after the Greek god of the sky.
30. Explain the Characteristics of Uranus:
It rotates on its axis from east to west like Venus. Its axis is tilted so much that, it appears to orbit the Sun on its sides like a rolling ball. Uranus has 27 natural satellites, of which Titania is the largest.
31. Explain Neptune:
Neptune (The coldest Planet) Neptune is the eighth and the farthest planet from the Sun. There are strong winds in this planet. It is named after the Roman god of sea. Neptune has 14 natural satellites, the largest being Triton.
32. Why Neptune is the coldest Planet?
Because of its distance from the Sun, Neptune is one of the coldest planets in the solar system. The striking blue and white features of Neptune help to distinguish it from Uranus.
33. Perihelion is the Earth’s closest position to the Sun. Aphelion is the farthest position of the Earth from the Sun.
34. The Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve in the Indian Ocean covers an area of 10,500 sq.km .
35. Explain the Spheres of the Earth:
The Earth is the most suitable planet to support life. It has three major components that we call as the realms of the Earth- lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere. The three components along with suitable climate make life possible on Earth. All living things exist in a narrow zone called the biosphere. Now let us have a close look at each of the spheres.
36. Lithosphere The word lithosphere is derived from the Greek word Lithos, which means rocky. The Lithosphere is the land on which we live. It is the solid outer layer of the Earth consisting of rocks and soils.
37. Hydrosphere The word Hydro means water in Greek. The hydrosphere consists of water bodies such as oceans, seas, rivers, lakes, ice caps on mountains and water vapour in the atmosphere.
38. Atmosphere The word Atmo means air in Greek. Atmosphere is the envelope of air that surrounds the Earth. Different types of gases make up the atmosphere. The major gases are Nitrogen (78%) and Oxygen (21%). The other gases like Carbon dioxide, Hydrogen, Helium, Argon, and Ozone are present in meager amounts.
39. Biosphere The narrow belt of interaction among the lithosphere, the hydrosphere and the atmosphere, where life exists is known as Biosphere. Bio means life in Greek. It consists of distinct zones. Each zone has its own climate, plant and animal life. These zones are known as ecosystems.
40. The Midnight Sun is a natural phenomenon that occurs in the summer months in places north of the Arctic Circle or south of the Antarctic Circle, when the Sun remains overhead 24 hours a day.
41. The velocity of the Earth’s rotation varies from 1670 km per hour at the equator to 845 km per hour at 60° N and S latitudes and zero at the poles.
42. Define Rotation:
It is the spinning movement of the Earth on its axis. The Earth rotates from west to east (anticlockwise) and takes 23 hours 56 minutes and 4.09 seconds to complete one rotation.
43. Define Revolution:
It is the movement of the Earth around the Sun on its elliptical path. The Earth takes 365 ¼ days for it to complete one revolution.
44. What is Terminator Line?
The line which divides the surface of the Earth into a lighted half and a dark half is called the Terminator Line.
45. Define Leap Year:
The remaining quarter day is added once in every four years in the month of February. That is why February has 29 days once in four years. It is called a Leap Year.
46. What is Equinoxes?
- The Northern Hemisphere is inclined towards the Sun for six months from 21st March to 23rd September while the Southern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun.
- From Sep 23rd to March 21st the southern hemisphere is inclined towards the Sun and the northern hemisphere faces away from the Sun.
- The equator faces the Sun directly on 21 March and 23 September. These two days are called Equinoxes, during which the day and night are equal throughout the Earth.
47. Explain Summer and Winter Solstice:
- On 21st June, the Tropic of Cancer faces the Sun. This is known as Summer Solstice. It is the longest day in the Northern Hemisphere and longest night (shortest day) in the Southern Hemisphere.
- On 22nd December, the Tropic of Capricorn faces the Sun. It is called as Winter Solstice. It is the longest day in the Southern Hemisphere and longest night (shortest day) in the Northern Hemisphere.
48. ISRO launched India’s first ever Moon mission, Chandrayaan – 1 in 2008.
49. What are dwarf Planets and Name them?
Dwarf planets are small celestial bodies found beyond the planet Neptune. They are extremely cold and dark. The five dwarf planets of the solar system are Pluto, Ceres, Eris, Makemake and Haumea.
50. Define Moon:
- Satellites are celestial objects, which revolve around the planets.
- The moon is the Earth’s only satellite. It revolves around the Earth once in every 27 days and 8 hours.
- It takes about the same time for it to complete one rotation around its axis. It has no atmosphere.
- The surface of the moon is characterized by craters created by the impact of meteors. The distance between the moon and the Earth is about 3, 84,400 km.
- The size of the moon is one-quarter of the Earth. The Moon is the only celestial body where humans have landed.
51. What are Asteroids?
Asteroids are small solid objects that move around the Sun. They are found as a belt between Mars and Jupiter. They are too small to be called as planets. They are also known as Planetoids or Minor Planets.
52. Define Comets:
A comet is a celestial object made up of a head and a tail. The head of a comet consists of solid particles held together by ice and the tail is made of gases. Halley’s Comet is the most famous comet which comes close to the Earth every 76 years. It last appeared in 1986 and will next appear in 2061.
53. Define Meteors and Meteorites:
A meteor is a stone like or metallic body. When entering into the Earth’s atmosphere, most of them burn. As they often appear as streaks of light in the sky, they are also known as Shooting Stars. Meteors which strike the Earth’s surface are called meteorites.
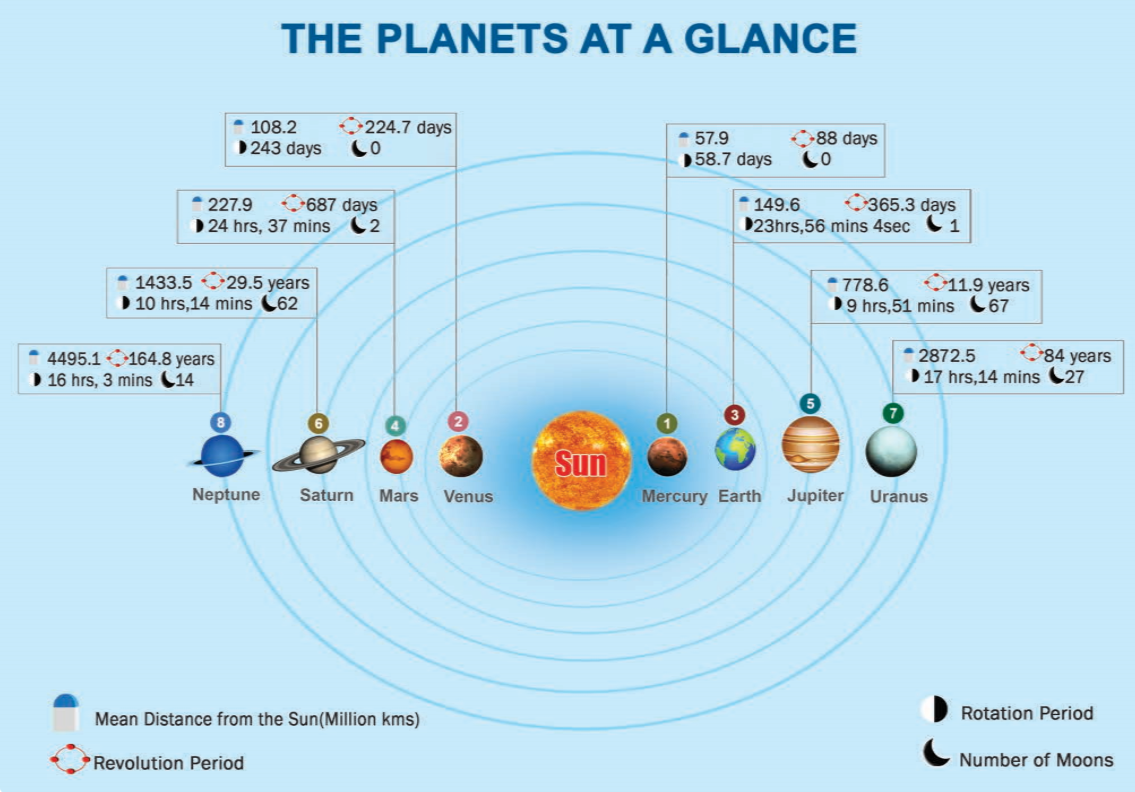
54. Planets at a Glance: