The Living World Of Plants Notes 6th Science Lesson 4 Notes in English
6th Science Lesson 4 Notes in English
4] The Living World Of Plants
Introduction
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure and functions. The living world comprises of plants and animals. Plants can prepare food itself, grow in size, and reproduce. Various parts of the plants are used as food, medicine, wood, and shelter.
Plant forms and functions:
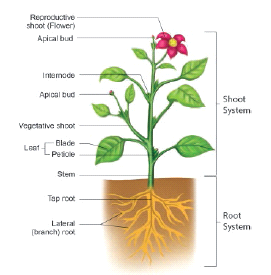
Our body is made up of many organs. Similarly the plant body is also made up of several organs such as root, stem leaves and flowers.
Plants are of many forms and many colours, yet they are alike in some manner. That is, they all have stems and leaves above the ground which we can see easily and roots below the ground.
As shown in the picture, a flowering plant consists of two main parts. They are,
1. Root system.
2. Shoot system.
Let us learn about these in detail.
Root system
Root
- The underground part of the main axis of a plant is known as root. It lies below the surface of the soil.
- Root has no nodes and internodes.
- It has a root cap at the tip.
A tuft of root hairs is found just above the root tip. Roots are positively geotropic in nature. Plants root system is classified into two types.
1. Tap root system
2. Fibrous root system
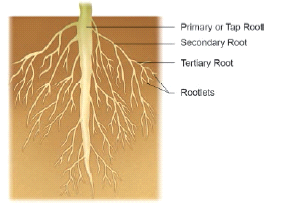
1. Tap root system
It consists of a single root, called taproot, which grows straight down into the ground.
Smaller roots, called lateral roots arise from the taproot. They are seen in dicotyledonous plants.
Example: Bean, Mango, Neem.
2. Fibrous root system
- It consists of a cluster of roots arising from the base of the stem. They are thin and uniform in size.
- It is generally seen in monocotyledonous plants. Example: Grass, Paddy, Maize.
Functions of the Root
- Fixes the plant to the soil.
- Absorbs water and minerals from the soil.

Fibrous Root of Grass
- Stores food in some plants like Carrot and beet root.
2. Shoot system
Stem
- The aerial part of the plant body above the ground is known as the shoot system. Main axis of the shoot system is called the stem.
- The shoot system consists of stem, leaves, flowers and fruits. Stem grows above the soil, and it grows towards the sunlight.
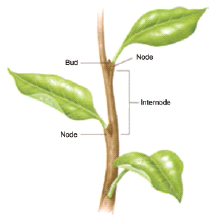
- It has nodes and internodes. Nodes are the parts of stem, where leaf arises. The part of the stem between two successive nodes is called internode.
- The bud at the tip of the stem is known as apical or terminal bud, and the buds at the axils of the leaves are called auxiliary buds.
Functions of the stem
The stem,
- Supports the branches, leaves, flowers and fruits.
- Transports water and minerals from roots to upper aerial plant parts.
- Transports the prepared food from leaves to other parts through stem.
- Stores food as in the case of sugarcane.
Structure of a leaf
- The leaf is a green, flat expanded structure borne on the stem at the node.
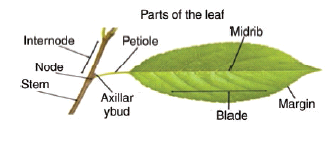
- A leaf has a stalk called petiole.
- The flat portion of the leaf is called leaf lamina or leaf blade. On the lamina, there is a main vein called midrib. Other veins are branch out from mid rib.
- The portion of the leaf connected in the nodal region of the stem is known as the leaf base.
- Leaves of some plants possess a pair of lateral outgrowth on the base, on either side of auxiliary bud. These are called stipules.
- The green colour of the leaf is due to the presence of green coloured pigment called chlorophyll. On the lower side of the leaf there are tiny pores or openings known as stomata.
Functions of the leaf
The green leaves
- Prepare food by the process of photosynthesis.
- Helps in respiration.
- Carry out transpiration.
Types of Habitat
Let us study the two major types of habitat with the help of following:

Aquatic habitat:-
- When we visit a pond, we see some plants appear to float on water. One of the common plants is the lotus plant. Its leaves float on the water.
- There is a small frog sitting on a leaf. It is ready to catch the insects flying/fluttering around the flowers.
- The stem of the plant is seen to be inside (submerged) the water. Its roots are found within the muddy floor of the pond. As this plant grows in water, shall we call it an aquatic plant?
- Aquatic habitat includes areas that are permanently covered by water and surrounding areas that are occasionally covered by water.
- There are two types namely Fresh water habitat and Marine water habitat.
Fresh water Habitat:-
- Rivers, lakes, ponds and pools are the fresh water habitat.
- Water hyacinth, water lily and lotus are seen in the fresh water habitat.
- In these plants roots are very much reduced in size. Stem and leaves have air chambers that allow aquatic plants to float in water.

Marine water habitat:-
- From outer space earth looks like an awesome blue marble, that’s because most of earth’s surface, more than 70% is covered by oceans.
- Oceans also support the growth of plants. Marine plants perform about 40% of all photosynthesis that occurs on the planet.
- Example: Marine Algae, Sea grasses, Marsh grass, Phytoplanktons.

Terrestrial habitat:
- Terrestrial habitats are the ones that are found on land like forest, grassland and desert. It also includes man-made habitats like farms, towns and cities.
- They can be as big as a continent or as small as an island. They make up about 28% of the entire world habitat. Example: Rubber tree, teak tree and Neem tree.

- Terrestrial habitat is classified into three types such as
a. Desert
b. Grassland
c. Forest
a. Desert habitat
- A habitat without much water is called deserts.
- Desserts are the driest place on earth; they get fewer than 25cm of rainfall annually. Deserts cover atleast 20% of the earth.
- The plants which grows in this habitat have thick leaves that store water and minerals.
- The plants like cactus store water in their stem and the leaves are reduced to spines.
- They have long roots that go very deep in the soil in the search of water.

b. Grassland habitat
- Grassland is an area where the Vegetation is dominated by grasses. Grasses ranges from short to tall. Eg. Savanna Grassland

c. Forest habitat
Forest is a large area dominated by trees. There are three types of forests and are: –
- Tropical forests, temperate forests and mountain forest. Annual rain fall ranges from 25-200 cm.

Plant Adaptations and Modifications.
- Adaptations are special features in plants which help them to survive in the habitats they live in over a long period.
- Plants in a specific environment have developed special features which help them to grow and live in that particular habitat.
- some adaptations like tendril, twiners and thorns. These adaptations are seen in plants which live in terrestrial and desert habitat.
Tendril Climber:-
- Tendril is a twining climbing organ of some weak stemmed plants like peas and bitter gourd. Tendril coils round a support and help the plant to climb. Example:
- Sweet Peas – Leaflets are modified into tendrils.
- Bitter Gourd – Axillary buds are modified into tendril which helps the plant to climb.

Twiners:-
- Some plants have weak stems. They cannot stand straight on their own. They must climb on any support to survive. Example: Clitoria and Jasmine

Clitoria
Thorns:-
- Leaves of some plants become wholly or partially modified into sharp pointed structures called “thorns or spines” for defensive purpose.
Example:
1. Agave – the leaf apex and margins are modified into thorns
2. Opuntia – the leaves are modified into spines.
3. Bougainvillea – the stem has sharp thorns.

Agave

Opuntia
More to know:
- Victoria amazonica, the leaves of this plant grow up to 3 metres across. A mature Victoria leaf can support an evenly distributed Load of 45 Kilograms or apparently young person.
- Nile is the longest river in the world. It is 6650 Km long. The Longest River in India is Ganges River. It is 2525 Km long.
- Air spaces in stems and petioles of lotus are useful for floating in water
- The first land plants appeared around 470 million years ago. They were mosses and liverworts.
- The Amazon Rain Forest in South America produces half of the world’s oxygen supply.
- Thar Desert, also called Great Indian Desert, is an arid region of rolling sand hills on the Indian subcontinent. It is located partly in Rajasthan state, north-western India, and partly in Punjab and Sindh (Sind) provinces, eastern Pakistan.
- World habitat day is observed on 1st Monday of October.
- Bamboo is one of the fast growing plants, during active growth phase.