Tamil Nadu Economy 11th Economics Lesson 5 Questions in English
11th Economics Lesson 5 Questions in English
5] Tamil Nadu Economy
1. Assertion (A): In Indian states the social and economic development are uniform.
Reasoning(R): Wide ranges of regional disparities exist in Indian Territory.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The economic and social development of states in India is not uniform. Wide regional disparities exist.
2. Which region is better in the socio-economic development in India?
a) Northern region
b) Western region
c) Eastern region
d) North-East region
Explanation
The western region and southern regions are better off than the other regions.
3. What is the position of Tamil Nadu in India’s total population?
a) 11th
b) 7th
c) 9th
d) 3rd
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is geographically eleventh largest and population wise third largest. Tamil Nadu fares well with many achievements.
4. Tamil Nadu doesn’t rank third position in which of these criteria?
a) GDP
b) Per capita Income
c) Foreign Direct Investment
d) Industrial Output
Explanation
Tamil Nadu stands to second in terms of contribution to GDP, third highest in terms of per capita income, investment, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and industrial output. It has been ranked as the most economically free state by the Economic Freedom.
5. In which of this Tamil Nadu performance is better than national average?
a) Health
b) Higher Education
c) IMR
d) All the above
Explanation
In the social and health sector also Tamil Nadu’s performance is better than many other states and better than national average in terms of health, higher education, IMR and MMR
6. Which of these sectors Tamil Nadu performance has not been improved in recent years?
a) MSME
b) Agriculture sector
c) Poverty alleviation
d) Employment Generation
Explanation
In recent years Tamil Nadu’s performance is outstanding and far ahead of all other states in the spheres of health, higher education, growth of MSMEs, poverty alleviation and employment generation.
7. Which of these states has been ranked in first position in Health index report?
a) Tamil Nadu
b) Bihar
c) Kerala
d) Rajasthan
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is placed third in health index the Tamil Nadu state has come third after Kerala and Punjab in a health index report.
8. Which of these rates of Tamil Nadu are 14 lower than other states in India?
a) Neo Natal mortality rate
b) Employment rate
c) Life expectancy rate
d) Literacy rate
Explanation
The neo natal mortality rate is 14 lower than that of many other states and that the under 5 mortality has dropped from 21 in 2014 to 20 in 2015- Healthy States, Progressive India Report, (2018)
9. Assertion (A): Public Distribution system, Midday meals schemes are complete success relatively in Tamil Nadu.
Reasoning(R): Tamil Nadu extends the social policies to reach all the people.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The reasons for the relative success of Tamil Nadu lie in extending social policies to cover most of the population. For instance the Public Distribution System, midday meals and public health infrastructure have near universal coverage.
10. Tamil nadu accounts for ___ percentage of Water sources and four percentage of ____ area.
a) 4, Textile
b) 3, Agricultural
c) 6, Industrial
d) 3, Land
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is not endowed with rich natural resources compared to other States. It accounts for three per cent of water sources, four per cent of land area against six per cent of population.
11. How many river basins are there in Tamil Nadu?
a) 12
b) 25
c) 17
d) 19
Explanation
North East monsoon is the major source of rainfall followed by South West monsoon. There are 17 river basins in Tamil Nadu. The main rivers are Palar, Cheyyar, Ponnaiyar, Cauvery, Bhavani, Vaigai, Chittar, Tamiraparni, Vellar, Noyyal Siruvaani, Gundar, Vaipar, Valparai etc.
12. Which is the largest water source of irrigation in Tamil Nadu?
a) Tanks
b) Canals
c) Reservoirs
d) Wells
Explanation
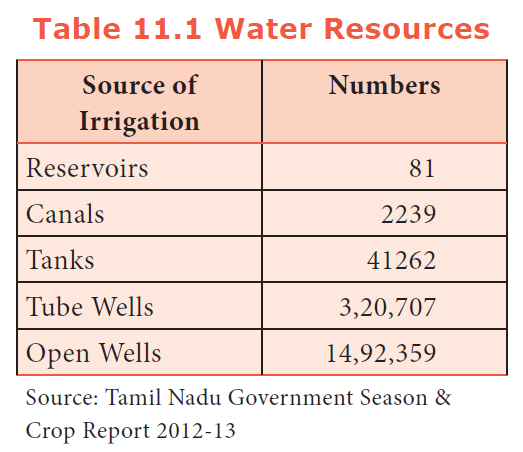
Wells are the largest source of irrigation in Tamil Nadu (56%).
13. Match the water sources of Tamil Nadu
A. Reservoirs i) 2239
B. Open wells ii) 41262
C. Tanks iii) 14, 92,359
D. Canals iv) 81
a) i, iii, ii, iv
b) ii, iii, i, iv
c) iv, iii, ii, i
d) i, iv, iii, ii
Explanation
14. When the Neyveli Lignite Corporation was incorporated by the Indian government?
a) 1983
b) 1956
c) 1942
d) 1965
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has a few mining projects based on Titanium, Lignite, Magnesite, Graphite, Limestone, Granite and Bauxite. The first one is the Neyveli Lignite Corporation that has led development of large industrial complex around Neyveli in Cuddalore district with Thermal power plants, Fertilizer and Carbonization plants. It was incorporated in 1956 and was wholly owned by the government of India. It is under the administrative control of Ministry of Coal.
15. Which of these places are rich in Iron ore?
a) Kanjamalai
b) Nilgiris
c) Anaimalai
d) Kazhugu Malai
Explanation
Magnesite mining is at Salem from which mining of Bauxite ores are carried out at Yercaud and this region is also rich in Iron Ore at Kanjamalai.
16. Which is the only source of molybdenum in India?
a) Warangal
b) Chhotanagpur
c) Dharmapuri
d) Himalayan Belt
Explanation
Molybdenum is found in Dharmapuri, and is the only source in the country.
17. Which of these mineral is having the lowest percentage of national share according to the report of Geology and Mining Department?
a) Magnesite
b) Garnet
c) Zircon
d) Ilmenite
Explanation
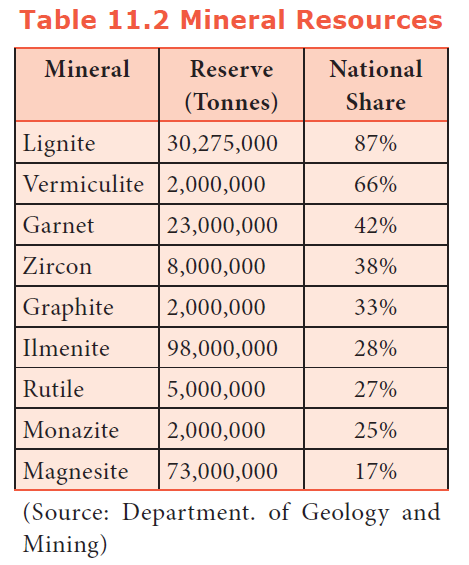
18. What is the position of Tamil Nadu in Indian Population count?
a) Third
b) Seventh
c) Sixth
d) Second
Explanation
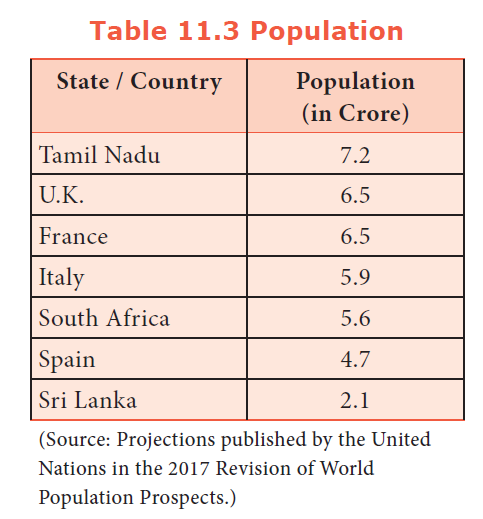
Tamil Nadu stands sixth in population with 7.21 crore against India’s 121 crore as per 2011 census. However, Tamil Nadu’s population is higher than that of several countries according to UN Report.
19. Match the population in terms of crore as per the report of UN, 2017
A. United Kingdom i) 4.7
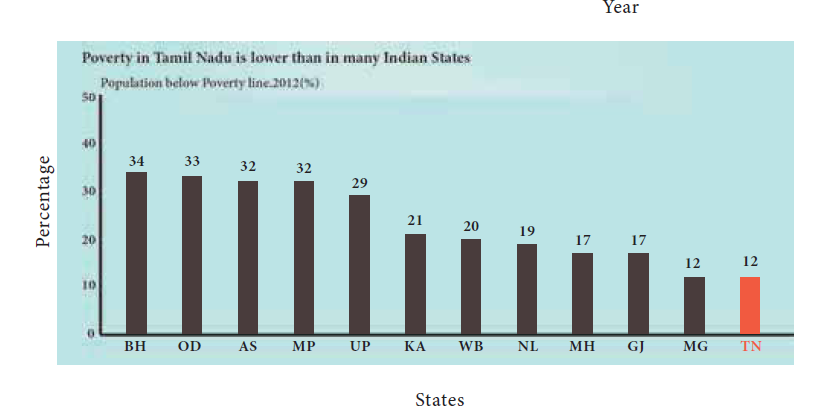
B. South Africa ii) 5.9
C. Spain iii) 5.6
D. Italy iv) 6.5
a) i, iii, iv, ii
b) iv, iii, i, ii
c) ii, iv, iii, i
d) iv, i, iii, ii
Explanation
20. What is the rank of Tamil Nadu in Population density among Indian states?
a) 10th
b) 11th
c) 13th
d) 12th
Explanation
The density of population which measures population per sq.km is 555 (2011) against 480 (2001). Tamil Nadu ranks 12th in density among the Indian States and overall it is 382 for India.
21. What is the urban population percentage of Tamil Nadu?
a) 48.4%
b) 31.5%
c) 94.5%
d) 9.6%
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is the most urbanized state with 48.4% of urban population against 31.5% for India as a whole. The State accounts for 9.61% of total urbanites in India against 6% share of total population.
22. What is the sex ratio in Tamil Nadu as per recent reports?
a) 890
b) 990
c) 995
d) 895
Explanation
Balanced sex ratio implies improvement in quality of life of female population. The sex ratio in Tamil Nadu is nearing balance with 995 which is far better compared to most of the States and all India level.
23. Which of these states position first in the sex ratio?
a) Tamil Nadu
b) Kerala
c) Puducherry
d) Andhra Pradesh
Explanation
Tamil Nadu stands third next only to Kerala state and Puducherry Union Territory in sex ratio.
24. What is the female life expectancy rate of India?
a) 69.6
b) 70.4
c) 65.3
d) 60.8
Explanation
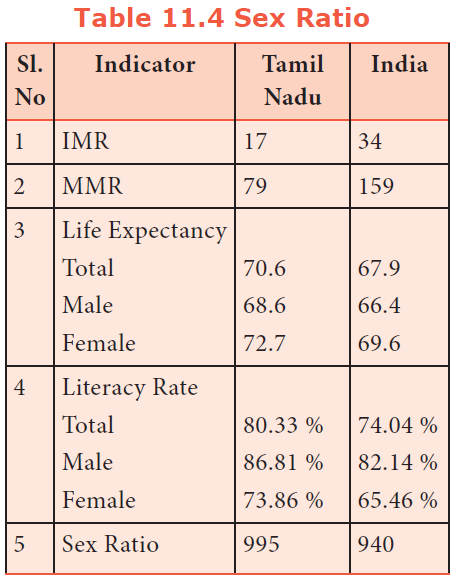
25. Which of the Indicator value of Tamil Nadu is better than India?
a) MMR
b) IMR
c) Life Expectancy rate
d) Urbanization rate
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is well ahead of national average and other states in IMR. According to NITI AAYOG, the IMR is 17 (per 1000) for Tamil Nadu which is just half of national average of 34 as on 2016.
26. What is the MMR rate of Tamil Nadu according to the NITI AAYOG reports?
a) 159
b) 79
c) 61
d) 67
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has a good record of controlling MMR, ranking third with 79 (Kerala 61, Maharashtra 67) against national average of 159 again half of the national average [NITI AAYOG]
27. Assertion (A): The life expectancy rate of India is far better than the most of the developed nations.
Reasoning(R): The total life period of a human in general is known as the Life expectancy.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The average period that a person may expect to live is called life expectancy. However, life expectancy in India still falls short of most developed and developing nations.
28. Define GDP?
a) Production value of Goods in a country
b) Market value of all final goods and services within a Country or state annually.
c) Total value of Services provided by a country or state
d) All the above
Explanation
Just like GDP, the Gross State Domestic Product refers to the total money value of all the goods and services produced annually in the State. The Gross domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time
29. Which of these departments of Tamil Nadu calculates the State GDP?
a) The Commercial Taxes and Registration
b) Planning, Development and Special Initiatives
c) The Directorate of Economics and Statistics
d) The Information and Technology
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is the second largest economy in India with a GSDP of $207.8 billion in 2016-17 according to the Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Tamil Nadu.
30. Which of this country is equated with the GSDP of Tamil Nadu in terms of Purchasing Power parity?
a) South Africa
b) Sri Lanka
c) Spain
d) UAE
Explanation
The GSDP of Tamil Nadu is equal to the GDP of Kuwait on nominal term and GDP of UAE on PPP terms.
31. Assertion (A): Tamil Nadu GSDP is far higher than many countries.
Reasoning(R): Population effect may be the reason for the GSDP of Tamil Nadu.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The GSDP of Tamil Nadu is far higher compared to many countries as shown below. This is mainly due to population effect. Per capita GSDP would be better for inter country or interstate comparisons. Tamil Nadu may go below if per capita GSDP is considered for comparison.
32. What is the GDP of Sri Lanka as per the report of IMF in 2017?
a) 81$
b) 200$
c) 165$
d) 100$
Explanation
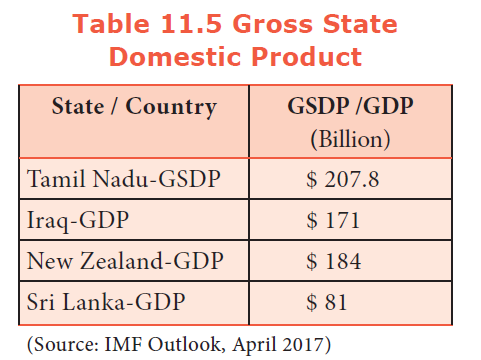
33. Match the sectorial contribution percentage in GSDP of Tamil Nadu.
A. Agriculture i) 64%
B. Service sector ii) 28%
C. Industry sector iii) 8%
a) i, ii, iii
b) ii, iii, i
c) iii, i, ii
d) i, iii, ii
Explanation
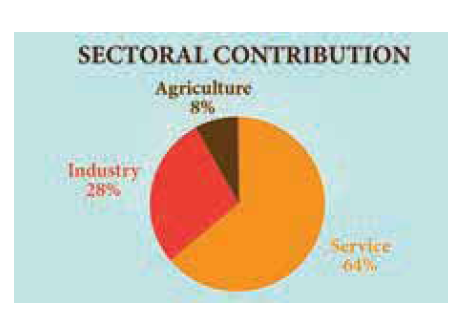
34. Which of these sectors mainly contributes to the GSDP of Tamil Nadu?
a) Tertiary sector
b) Industry sector
c) Agriculture
d) Exports and Imports
Explanation
The tertiary sector (service sector) is the major contributor to Tamil Nadu’s GSDP at 63.70%.
35. State the percentage value of Industry sector in the GSDP of Tamil Nadu.
a) 35%
b) 28%
c) 13%
d) 56%
Explanation
The secondary sector (Industry) contribution is gradually on the rise and now it is 28.5%.
36. Assertion (A): Agriculture sector is having a prominent position in Tamil Nadu’s occupation.
Reasoning(R): The GSDP value of Agriculture sector is gradually increasing in Tamil Nadu.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Agriculture occupies a prominent position in occupation but its contribution to GSDP is declining and now it is just 7.76%.
37. What are the effects of low GSDP contribution of Agriculture sector?
a) Employment rate will be reduced.
b) Sustainable development may not be possible.
c) The GDP of the whole nation may be reduced.
d) It creates the negative impact in the society.
Explanation
Agriculture sector provides employment and food to larger proportion of Indians and Tamils. But, the same sector is growing slowly means it is not good. With this trend sustainable development may not be possible.
38. What is the per capita GSDP rank of Tamil Nadu in India?
a) 10th
b) 2nd
c) 12th
d) 21st
Explanation
The Per capita GSDP of Tamil Nadu also ($ 2,200) which is higher than that of many other States in India. Per capita GSDP of Tamil Nadu is nearly 1.75 times higher than the national average, as per 2018 data. It ranks 10th in per capita GDP in India.
39. What was the per capita income of Tamil Nadu as per the 2017-18 Budget?
a) ₹ 2, 76,899
b) ₹ 1, 88,492
c) ₹ 5, 54,437
d) ₹ 7, 45,342
Explanation
In term of ₹ the per capita income in Tamil Nadu was ₹ 1, 03,600 in 2010-11 and it has increased to ₹ 1, 88,492 in 2017-18 as per the Budget figures 2018.
40. What is the per capita Income of India in US dollars?
a) 1442
b) 2200
c) 1670
d) 729
Explanation
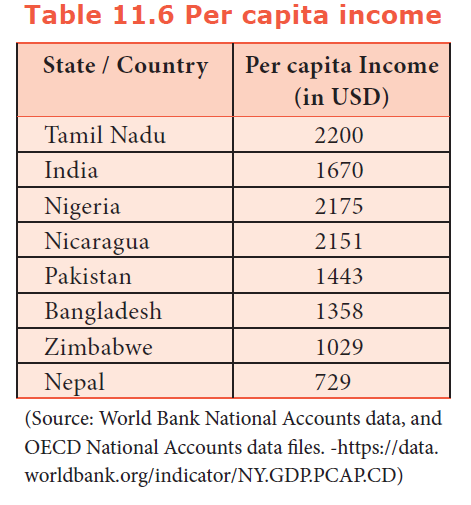
41. Which of these southern states has the highest per capita Income in 2015-16?
a) Telangana
b) Andhra Pradesh
c) Kerala
d) Karnataka
Explanation
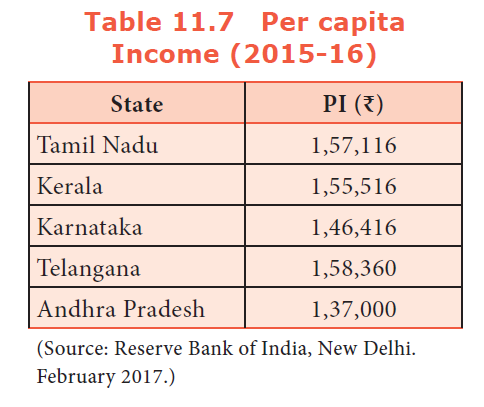
42. How many agro climate zones are available in Tamil Nadu?
a) 3
b) 5
c) 7
d) 4
Explanation
Tamil Nadu, with seven agro climatic zones and varied soil types is better suited for the production of fruits, vegetables, spices, plantation crops, flowers and medicinal plants.
43. Which of this state is the largest producer of fruits in India?
a) Tamil Nadu
b) Andhra Pradesh
c) Telangana
d) Karnataka
Explanation
During the fiscal year 2018, Andhra Pradesh produced the largest fruit share in India, accounting for 15.6 percent. Maharashtra came in second at twelve percent the State of Tamil Nadu is the largest producer of loose flowers and the third largest producer of fruits.
44. Which state leads Tamil Nadu in the rice production?
a) Uttar Pradesh
b) West Bengal
c) Maharashtra
d) Karnataka
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has historically been an agricultural State. At present, Tamil Nadu is the India’s second biggest producer of rice, next only to West Bengal.
45. Which of these are not major produce of Tamil Nadu?
a) Turmeric
b) Groundnut
c) Sugarcane
d) Wheat
Explanation
The state is one of the major producers of turmeric. It is also the leading producer of Kambu, Corn, Groundnut, Oil seeds and Sugarcane.
46. Match the ranks of Tamil Nadu of its various produces.
A. Rubber i) 1
B. Sugarcane ii) 3
C. Plantation crops iii) 4
D. Pepper iv) 2
a) iii, ii, iv, i
b) ii, iv, i, iii
c) iv, iii, i, ii
d) i, iv, iii, ii
Explanation
Tamil Nadu ranks first in production of plantation crops and banana and coconut, second in rubber and cashew nut, third in pepper and fourth in sugarcane.
47. What percentage of area is accounted for the non-food crops in Tamil Nadu?
a) 19%
b) 27%
c) 56%
d) 44%
Explanation
The gross cropped area under all crops was 58.97 lakh hectares in the year 2013-14 in Tamil Nadu. The area under food crops account for 72.9% and that of non-food crops is 27.1%.
48. Which of these food crops is majorly produced in Tamil Nadu?
a) Wheat
b) Paddy
c) Corn
d) Ragi
Explanation
Among the food crops paddy takes a major share in Tamil Nadu and among the non-food crops, groundnut and coconut take a major share.
49. Assertion (A): Tamil Nadu cities are over-crowded and getting congested in recent years.
Reasoning(R): The net sown area has been gradually decreasing in recent years and most of the people are moving towards urban areas.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Net sown area has been gradually declining; and, rural land, labor and capital are moving towards urban projects. As a result, villages are emptied and cities are over-crowded and congested, leading to spatially unbalanced bulging.
50. Which of these food grains are the second most produces in Tamil Nadu?
a) Pulses
b) Millets
c) Rice
d) Jowar
Explanation
Rice production dominates among food grain production with 79.49 lakh tones on 2014-15 followed by millets at 40.79 lakh tons.
51. Which of this production had a drastic increase in recent years of Tamil Nadu?
a) Paddy
b) Pulses
c) Jowar
d) Maize
Explanation
There is significant jump in pulses production from 3.59 lakhs ton in 2011-12 to 7.67 lakh ton in 2014-15.
52. Assertion (A): Tamil Nadu tops in food crops productivity among all states in India.
Reasoning(R): The Tamil Nadu government emphasis on agricultural productivity.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The Government of Tamil Nadu lays emphasis on agricultural production and productivity. As a result, Tamil Nadu tops in productivity, in food crops as well as non-food crops, among the States in India.
53. In which of these Tamil Nadu ranks first In India?
a) Coconut
b) Groundnut
c) Sunflower
d) Rice
Explanation
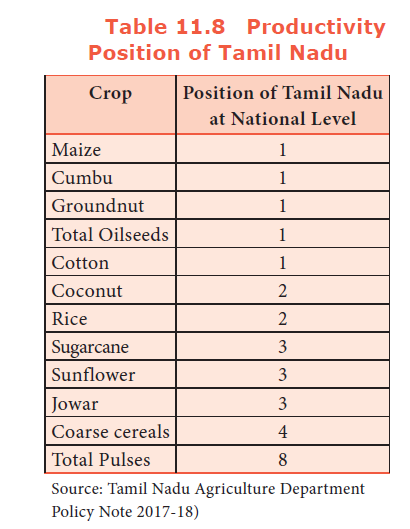
54. Which of these are the other names of Chennai city?
a) Health Capital of India
b) Banking Capital of India
c) Detroit of Asia
d) All the above
Explanation
Chennai is sometimes referred to as the Health Capital of India or the Banking Capital of India, having attracted investments from International Finance Corporations and the World Bank. It is also called as Detroit of Asia.
55. What are the other forms of Industrial parks are available in Tamil Nadu?
a) Apparel Park
b) TICEL for Biotechnology
c) Siruseri IT Park
d) All the above
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has a network of about 110 industrial parks/estates that offer developed plots with supporting infrastructure. Also, the Government is promoting other industrial parks like Rubber Park, Apparel Park, Floriculture Park, and TICEL Park for Biotechnology, Siruseri IT Park and Agro Export Zones.
56. Which of this city is known for the Heavy engineering and Car manufacturing Companies in Tamil Nadu?
a) Chennai
b) Tiruchirappalli
c) Madurai
d) Sivagangai
Explanation
The heavy engineering manufacturing companies are centered on the suburbs of Chennai. Chennai boasts of global car manufacturing giants as well as home grown companies.
57. Which of these places are not involved in Leather industries in Tamil Nadu?
a) Ranipet
b) Salem
c) Ambur
d) Vaniyambadi
Explanation
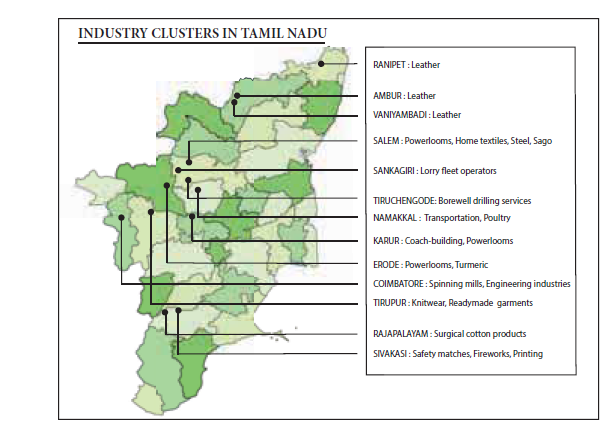
58. Which of this city contributes 80% of south Indian bus body building?
a) Erode
b) Namakkal
c) Karur
d) Pudhukottai
Explanation
Karur is known for its bus body building which contributes 80% of South Indian bus body building.
59. Which is one of the largest ecofriendly paper mills in Asia?
a) Tamilnadu Newsprint & Papers Ltd
b) Ballarpur Industries Ltd
c) Emami Paper Mills Ltd
d) The West Coast Paper Mills Ltd
Explanation
TNPL is the Asia›s largest ecofriendly paper mill.
60. Which of this city is also known as the Steel city?
a) Sivagangai
b) Srivilliputhur
c) Salem
d) Chennai
Explanation
Salem is called as steel city and has many sago producing units and mineral wealth.
61. Choose the Incorrect statements about Sivakasi.
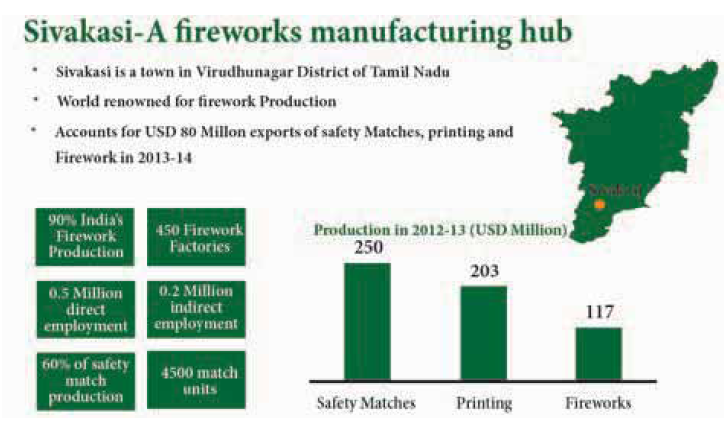
i) Sivakasi is the leader in printing industries in Tamil Nadu.
ii) The Fireworks and safety matching Industries of Sivakasi are the major contributor of India.
iii) About 65% of total fireworks of India is produced in Sivakasi.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Sivakasi is the leader in printing, fireworks, safety matches production in India. It contributes to 80% of India’s total safety matches production and 90% of India’s total fireworks production.
62. Which is the gateway of Tamil Nadu?
a) Chennai
b) Cuddalore
c) Rameshwaram
d) Thoothukudi
Explanation
Thoothukudi is the gateway of Tamil Nadu. It is a major chemical producer next only to Chennai.
63. Which of this state is known as the Yarn Bowl of India?
a) Tamil Nadu
b) Karnataka
c) Rajasthan
d) Uttar Pradesh
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is the largest textile hub of India. Tamil Nadu is known as the “Yarn Bowl” of the country accounting for 41% of India’s cotton yarn production.
64. How much percentage of GDP is contributed by the Textile Industries of India?
a) 35%
b) 4%
c) 24%
d) 10%
Explanation
The textile industry plays a significant role in the Indian economy by providing direct employment to an estimated 35 million people, and thereby contributing 4% of GDP and 35% of gross export earnings.
65. Which of this sector contributes 14% of the manufacturing sector of Tamil Nadu?
a) Steel Industry
b) Textile Industry
c) Car Manufacturing Industry
d) Paper Industry
Explanation
The textile sector contributes to 14% of the manufacturing sector. From spinning to garment manufacturing, entire textile production chain facilities are in Tamil Nadu.
66. Which of these cities has the majority of spinning mills in Tamil Nadu?
a) Salem
b) Coimbatore
c) Vellore
d) Villupuram
Explanation
About half of India’s total spinning mill capacity is in Tamil Nadu. The western part of Tamil Nadu comprising Coimbatore, Tiruppur, Erode, Dindigul and Karur has the majority of spinning mills manufacturing cotton/polyester/blended yarn and silk yarn used by garment units in Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra etc.
67. What is the other name of Tiruppur?
a) Knitting City
b) Detroit of Asia
c) Little Japan
d) Flower City
Explanation
Yarn is also exported to China, Bangladesh etc. Tiruppur known as “Knitting City” is the exporter of garments worth USD 3 Billion.
68. Which city is the main cloth market in South India?
a) Salem
b) Karur
c) Erode
d) Madurai
Explanation
Karur is the major home for textile manufacturing (Curtain cloth, bed linens, kitchen linens, toilet linens, table linens, wall hangings etc.) and export hub in India. Erode is the main cloth market in South India for both retail and wholesale ready-mades.
69. What percentage of leather production is contributed by Tamil Nadu among the Indian states?
a) 30%
b) 45%
c) 70%
d) 60%
Explanation
Tamil Nadu accounts for 30 per cent of leather exports and about 70 per cent of leather production in the country. Hundreds of leather and tannery industries are located around Vellore, Dindigul and Erode. Every year the State hosts the India International Leather Fair in Chennai.
70. Which of this city has emerged the EMS hub of India?
a) Coimbatore
b) Chennai
c) Tiruchirappalli
d) Madurai
Explanation
Chennai has emerged as EMS Hub of India. Many multi – national companies have chosen Chennai as their South Asian manufacturing hub.
71. Identify the Correct match of Tamil Nadu Industries.
A. Automotive Industries i) 28%
B. Trucks segment ii) 45%
C. Passenger cars iii) 42%
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Chennai nicknamed as “The Detroit of Asia “is home to a large number of auto component industries. Tamil Nadu has 28% share each in automotive and auto components industries, 19% in the trucks segment and 18% each in passenger cars and two wheelers.
72. Which state ranks first in the Cement production in India?
a) Andhra Pradesh
b) Rajasthan
c) Tamil Nadu
d) Telangana
Explanation
Tamil Nadu ranks third in cement production in India (First Andhra Pradesh, Second Rajasthan). Among 10 largest cement companies in India as on 2018, Ramco Cement and India Cement find prominent place.
73. What is the rank of Tamil Nadu in the total number of cement plants in India?
a) 3
b) 2
c) 4
d) 7
Explanation
And also Tamil Nadu stands second in number of cement plants with 21 units against 35 units in Andhra Pradesh.
74. Who called Sivakasi as little japan?
a) Jawaharlal Nehru
b) Gandhi
c) Kamaraj
d) Rajagopalachari
Explanation
The town of Sivakasi is a leader in the areas of printing, fireworks, and safety matches. It was fondly called as “Little Japan” by Jawaharlal Nehru. It contributes to 80% of India’s fireworks production. Sivakasi provides over 60% of India’s total offset printing solutions.
75. Which of these places BHEL has its manufacturing units?
a) Tiruchirappalli
b) Ranipet
c) Vellore
d) Both a and b
Explanation
One of the global electrical equipment public sector companies viz BHEL has manufacturing plants at Tiruchirappalli and Ranipet.
76. Where did the Tamil Nadu government own TNPL mill is located?
a) Erode
b) Karur
c) Namakkal
d) Salem
Explanation
The Tamil Nadu State Government owns the Tamil Nadu Newsprint and Papers (TNPL), the world’s biggest bagasse based paper mill in Karur.
77. Which of these places in Tamil Nadu does not have a cement producing plant?
a) Coimbatore
b) Ariyalur
c) Erode
d) Tirunelveli
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is a leading producer of cement in India and with manufacturing units located at Ariyalur, Virudhunagar, Coimbatore and Tirunelveli.
78. Salem is rich in_____.
a) Mineral ores
b) Industries
c) Textile Industries
d) Agro Industries
Explanation
The region around Salem is rich in mineral ores. The country’s largest steel public sector undertaking, SAIL has a steel plant in Salem.
79. Choose the Incorrect statements about Sivakasi.
i) Sivakasi is a town in Madurai district of Tamil Nadu.
ii) 90% of India’s fireworks production is accounted by Sivakasi.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
80. What is the Geographical Indication of Coimbatore?
a) Jewelry
b) Pumps
c) Wet Grinder
d) Cotton
Explanation
Coimbatore is also referred to as “the Pump City” as it supplies two thirds of India’s requirements of motors and pumps. The city is one of the largest exporters of jewelry, wet grinders and auto components and the term “Coimbatore Wet Grinder” has been given a Geographical indication.
81. How much percentage of the total salt of India is produced by Thoothukudi?
a) 75%
b) 30%
c) 10%
d) 50%
Explanation
Thoothukudi is known as “Gateway of Tamil Nadu”. Thoothukudi is the major chemical producer in the state. It produces the 70 per cent of the total salt production in the State and 30 per cent in the country.
82. By which year the MSMED act the enterprises are classified in Tamil Nadu?
a) 2002
b) 2007
c) 2009
d) 2006
Explanation
The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises are defined under the MSMED Act 2006. The enterprises are classified as Manufacturing and Service enterprises based on the investment in plant and machinery and equipment (excluding land and building) the classification of Micro, Small and Medium.
83. How much percentage of MSME enterprises are accounted by Tamil Nadu in India?
a) 12%
b) 27%
c) 15%
d) 35%
Explanation
Tamil Nadu accounts of 15.07% Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in the country( the highest among all States) with 6.89 lakhs registered MSMEs. Producing over 8000 varieties of product for a total investment of more than Rs.32, 008crore.
84. Which of these are the prominent products of the MSME sectors?
a) Electrical
b) Plastics
c) Textiles
d) All the above
Explanation
MSMEs produce a wide variety of products in almost all sectors. The prominent among them are the engineering, electrical, chemicals, plastics, steel paper, matches, textiles, hosiery and garments sector.
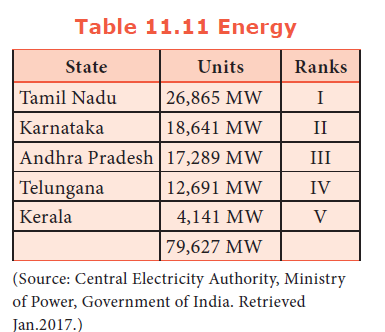
85. How much Megawatt power is contributed by Tamil Nadu?
a) 12,691 MW
b) 18,641 MW
c) 26,865 MW
d) 4,141 MW
Explanation
86. Which of these places has a renewable wind farms?
a) Muppandal
b) Pudhukottai
c) Theni
d) Kancheepuram
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is in the forefront of all other Indian States in installed capacity. Muppandal wind farm is a renewable energy source, supplying the villagers with electricity for work.
87. Which of these cities does not have a Wind farm?
a) Coimbatore
b) Pollachi
c) Villupuram
d) Tuticorin
Explanation
Wind farms were built in Nagercoil and Tuticorin apart from already existing ones around Coimbatore, Pollachi, Dharapuram and Udumalaipettai.
88. How much percentage of total power output of India is contributed by Tamil Nadu wind farms?
a) 5%
b) 2%
c) 12%
d) 10%
Explanation
The Wind farm areas of Tamil Nadu generate about half of India’s 2,000 megawatts of wind energy or two percent of the total power output of India.
89. When the Koodankulam nuclear power plant came into an operational unit?
a) 2002
b) 2007
c) 2003
d) 2001
Explanation
The Kalpakkam Nuclear Power Plant and the Koodankulam Nuclear Power Plant are the major nuclear energy plants for the energy grid. The Koodankulam Construction began on 31 March 2002, with Nuclear Power Corporation of India Ltd (NPCIL) predicting that the first unit would be operational in March 2007, instead of the original target of December 2007.
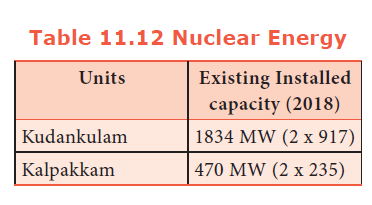
90. How many Megawatt nuclear energy is produced by the Koodankulam plant?
a) 2080 MW
b) 1834 MW
c) 650 MW
d) 1670MW
Explanation
91. Which places does not have thermal power plants in Tamil Nadu?
a) Mettur
b) Coimbatore
c) Ennore
d) Thoothukudi
Explanation
In Tamil Nadu the share of thermal power in total energy sources is very high and the thermal power plants are at Athippattu (North Chennai) Ennore, Mettur, Neyveli and Thoothukudi.
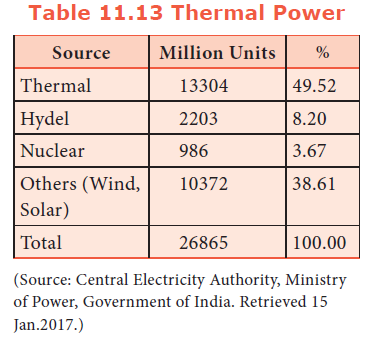
92. How much percentage of Hydel power is contributed to the total power production?
a) 8.2%
b) 40.8%
c) 27%
d) 67%
Explanation
93. How many hydroelectric units are available in Tamil Nadu?
a) 7
b) 32
c) 20
d) 37
Explanation
There are about 20 hydroelectric units in Tamil Nadu. The prominent units are Hundah, Mettur, Periyar, Maravakandy, and Parson Valley etc.
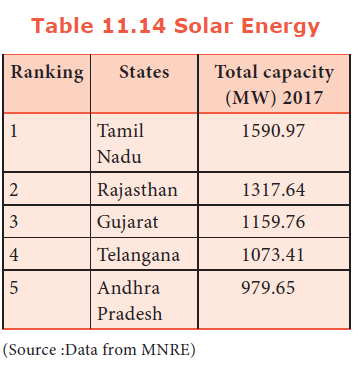
94. Which of these states ranks next to Tamil Nadu in Solar energy?
a) Andhra Pradesh
b) Rajasthan
c) Gujarat
d) Telangana
Explanation
95. Which of these places has been installed with wind energy in Tamil Nadu?
a) Tirunelveli
b) Thoothukudi
c) Rameshwaram
d) All the above
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has the highest installed wind energy capacity in India. The State has very high quality of off shore wind energy potential off the Tirunelveli coast and southern Thoothukudi and Rameshwaram coast.
96. Which of these falls under the service sectors?
a) Insurance
b) Communication
c) Banking
d) All the above
Explanation
Banking, insurance, energy, transport and communication fall under tertiary sector i.e., services.
97. Match
A. State Bank & Associates i) 5%
B. Private Commercial Banks ii) 13%
C. Regional Rural Banks iii) 30%
a) i, iii, ii
b) ii, iii, i
c) ii, i, iii
d) i, ii, iii
Explanation
In Tamil Nadu, Nationalized banks account for 52% with 5,337 branches, Private Commercial Banks 30% (3,060) branches, State Bank of India and its associates 13% (1,364), Regional Rural Banks 5% (537) branches and the remaining 22 foreign bank branches.
98. How much percentage of priority sector advances is accounted in Tamil Nadu?
a) 40%
b) 45.54%
c) 30%
d) 23%
Explanation
The share of Priority Sector Advances stands at 45.54% as against the national average of 40%. The percentage of Agricultural advances to total advances as at the end of March 2017 works out to 19.81% as against the national average of 18%.
99. What is the highest Credit Deposit Ratio of Tamil Nadu?
a) 77.5%
b) 45.8%
c) 119.15%
d) 67.8%
Explanation
Banks in Tamil Nadu have maintained one of the highest Credit Deposit Ratio of 119.15% in the country whereas this ratio is 77.5% at the national level.
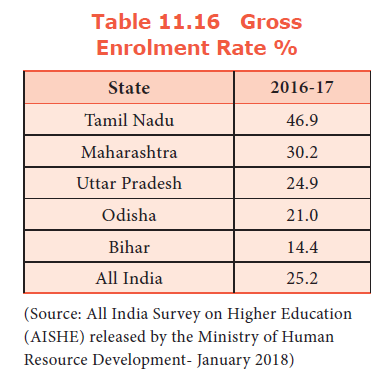
100. Which of these State ranks first in Gross Enrolment Ratio?
a) Kerala
b) Himachal Pradesh
c) Tamil Nadu
d) Andhra Pradesh
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is grouped among high Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) States. It ranks third next only to Kerala (81%) and Himachal Pradesh (74%). The all India average is 43% and the world average is 59%.
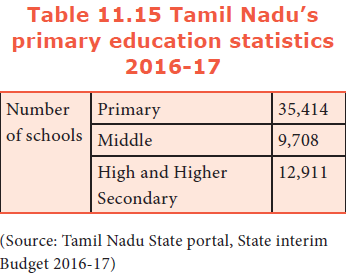
101. How many Middle schools are available in Tamil Nadu?
a) 9708
b) 35,414
c) 12,911
d) 25,645
Explanation
102. Identify the Incorrect match of the GER in Tamil Nadu.
A. Primary Level i) 118.8%
B. Secondary Level ii) 112.3%
C. Higher Secondary Level iii) 49.26%
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Gross Enrolment Ratio is 118.8% for primary level (class 1-5); 112.3% for upper primary level (class 6-8), 62.7% for secondary level (class 9-10), 49.26% at Higher Secondary level (class 11-12). This has been possible mainly due to the supply of free food, cloth, foot-wear, scholarship, laptop etc.
103. Which of these schemes is the major reason for the increase in the GER rate of Tamil Nadu?
a) Free Food scheme
b) Free Laptops
c) Scholarship
d) All the above
Explanation
The GER is 46.9% in Tamil Nadu which is far higher against national average and all other States. This higher GER is thanks to the distribution of free food, cloth, footwear, laptop and scholarship.
104. What is the gross enrolment rate of Higher education in Tamil Nadu among Indian states?
a) 23.5
b) 14.4
c) 46.9
d) 21.0
Explanation
105. Match the educational institutions in Tamil Nadu.
A. Medical College i) 59
B. University ii) 2260
C. Arts and Science College iii) 40
a) i, iii, ii
b) iii, i, ii
c) i, ii, iii
d) ii, i, iii
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has 59 Universities,40 Medical colleges, 517 Engineering colleges, 2,260 Arts and Science colleges, 447 Polytechnics and 20 dental colleges. Tamil Nadu produces nearly four lakh engineering and polytechnic students every year, the highest in the country.
106. What percentage of Education Loan amount is dispersed by the Public Sector Banks in Tamil Nadu?
a) 13%
b) 45%
c) 20%
d) 18%
Explanation
As far as educational loans disbursed by Public Sector Banks under priority sector are concerned, 20.8% of the total amount was disbursed in Tamil Nadu between 2013-14 and 2015-16.
107. Which state ranks third in the Educational Loans dispersal by the Public Sector Banks?
a) Maharashtra
b) Kerala
c) Tamil Nadu
d) Andhra Pradesh
Explanation
Andhra Pradesh was second with 11.2% of the total loan amount followed by Maharashtra (10.2%) by the Public Sector Banks Loan dispersal.
108. Which of these State accounts about 37% of Educational loan by the Private Bank sectors?
a) Andhra Pradesh
b) Tamil Nadu
c) Kerala
d) Telangana
Explanation
Of the total amount of educational loans disbursed by Private Banks during the same period, Kerala accounted for 37.8% followed by Tamil Nadu.
109. Match
A. District Hospitals i) 229
B. Primary Health centers ii) 313
C. Community Health centers iii) 34
D. Sub-divisional Hospitals iv) 1254
a) i, ii, iv, iii
b) ii, iii, i, iv
c) iii, iv, ii, i
d) ii, iv, iii, i
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has a three – tier health infrastructure comprising hospitals, primary health centers, health units, community health centers and subcentres. As of March 2015, the State had 34 district hospitals, 229 sub-divisional hospitals, 1,254 primary health centers, 7,555 Sub-centers and 313 community health centers.
110. Which of this State has the highest number of internet subscribers in India?
a) Maharashtra
b) Andhra Pradesh
c) Karnataka
d) Tamil Nadu
Explanation
Maharashtra has the highest number of internet subscribers in the country at 29.47 million, followed by States like Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
111. How many million internet subscribers are available in India?
a) 342
b) 560
c) 456
d) 778
Explanation
According to government data, India had a total of 342.65 million internet subscribers at the end of March, 2016. Tamil Nadu had 28.01 million subscribers, while its neighbors Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka had 24.87 million and 22.63 million, respectively.
112. Which of these are connected by the extensive road systems of Tamil Nadu?
a) Urban centers
b) Agricultural places
c) Rural Habitations
d) All the above
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is served by an extensive road network in terms of its spread and quality, providing links between urban centers, agricultural market-places and rural habitations in the countryside.
113. Assertion (A): Tamil Nadu has a well-established transportation system connects all parts of the state.
Reasoning(R): The Transportation system is partly responsible for the State investment.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has a well-established transportation system that connects all parts of the State. This is partly responsible for the investment in the State.
114. How many National Highways are there in Tamil Nadu?
a) 28
b) 14
c) 52
d) 72
Explanation
There are 28 national highways in the State of Tamil Nadu covering a total distance of 5,036 km. The State has a total road length of 167,000 km, of which 60,628 km are maintained by Highways Department.
115. How much percentage of total road projects is operated under PPP model in Tamil Nadu?
a) 35%
b) 20%
c) 62%
d) 45%
Explanation
Tamil Nadu ranks second in India with a share of over 20% in total road projects under operation in the public-private partnership (PPP) model.
116. Which of these States is not covered by the Southern Railway network in India?
a) Tamil Nadu
b) Kerala
c) Andhra Pradesh
d) Maharashtra
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has a well-developed rail network as part of Southern Railway, Headquartered at Chennai. The present Southern Railway network extends over a large area of India’s Southern Peninsula, covering the States of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Puducherry, minor portions of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
117. How many Railway stations are there in Tamil Nadu?
a) 690
b) 358
c) 450
d) 560
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has a total railway track length of 6,693 km and there are 690 railway stations in the State. The system connects it with most major cities in India. Main rail junctions in the State include Chennai, Coimbatore, Erode, Madurai, Salem, Tiruchirappalli and Tirunelveli.
118. When did the Metro System become functional in Chennai?
a) 2013
b) 2017
c) 2011
d) 2015
Explanation
Chennai has a well-established Suburban Railway network, a Mass Rapid Transport System and is currently developing a Metro system, with its first underground stretch operational since May 2017.
119. How many major international ports are available in Tamil Nadu?
a) 5
b) 4
c) 3
d) 6
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has four major international airports. Chennai International Airport is currently the third largest airport in India after Mumbai and Delhi. Other international airports in Tamil Nadu include Coimbatore International Airport, Madurai International Airport and Tiruchirappalli International Airport.
120. In which of these places domestic airport is not available in Tamil Nadu?
a) Tuticorin
b) Salem
c) Cuddalore
d) Madurai
Explanation
Tamil Nadu also has domestic airports at Tuticorin, Salem, and Madurai which connect several parts of the country. Increased industrial activity has given rise to an increase in passenger traffic as well as freight movement which has been growing at over 18 per cent per year.
121. How many minor ports are available in Tamil Nadu?
a) 3
b) 54
c) 17
d) 23
Explanation
Tamil Nadu has three major ports; one each at Chennai, Ennore, and Tuticorin, as well as one intermediate port in Nagapattinam, and 23 minor ports.
122. Which is the second principal port of India in handling containers?
a) Mumbai port
b) Kandla port
c) Chennai port
d) Vishakhapatnam port
Explanation
The ports are currently capable of handling over 73 million metric tons of cargo annually (24 per cent share of India). All the minor ports are managed by the Tamil Nadu Maritime Board, Chennai Port. This is an artificial harbor and the second principal port in the country for handling containers.
123. Which of this port is a recently converted major port of Tamil Nadu?
a) Ennore
b) Poombhukar
c) Cuddalore
d) Chennai
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is currently being upgraded to have a dedicated terminal for cars capable of handling 4, 00,000 vehicles. Ennore Port was recently converted from an intermediate port to a major port and handles all the coal and ore traffic in Tamil Nadu.
124. State the annual growth rate of the Tourism industry of Tamil Nadu?
a) 25%
b) 5%
c) 16%
d) 48%
Explanation
Tourism in Tamil Nadu is promoted by Tamil Nadu Tourism Development Corporation (TTDC), a Government of Tamil Nadu undertaking. The State currently ranks the highest among Indian States with about 25 crore arrivals (in 2013). The annual growth rate of this industry stood at 16 per cent. Approximately 28 lakh foreign and 11 crore domestic tourists visit the State.
125. What is the unemployment rate of Tamil Nadu?
a) 42
b) 50
c) 65
d) 35
Explanation
National average of unemployment rate stands at 50 and Tamil Nadu ranks 22nd with unemployment rate of 42 per 1000. There are different kinds of unemployment with different economic implications. All those aspects need to be studied to fully understand the employment situation.
126. What is the main reason for the fastest growth of Tamil Nadu?
a) Agriculture
b) High Population
c) Industrial Development
d) Service sectors
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is one of India’s richest states since 1994; the state has seen a steady decline in poverty. Today, Tamil Nadu has lower levels of poverty than most other States in the country. After 2005, Tamil Nadu was among India’s fastest growing states, with growth being driven mainly by services.
127. Assertion (A): The Tamil nadu economy has a good record of Agricultural growth and industrial development.
Reasoning(R): Tamil nadu is rich in natural resources.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The Tamil Nadu economy which is not rich in natural resources has good record of agricultural growth, industrial progress, infrastructural development and good record of robust growth of service sector especially banking, education, transport and tourism.
128. In which of these general issues Tamil Nadu has a good record?
a) Poverty alleviation
b) Leather imports
c) Employment generation
d) Both a and c
Explanation
Three ranks in health index, education, development of MSMEs. It has a good record of poverty alleviation and employment generation.
129. What are the obstacles for the development in Tamil Nadu?
a) Slum population
b) Beggars and rack pickers
c) Female feticides
d) All the above
Explanation
India in general and Tamil Nadu in particular need to work more to eliminate female feticide, reduce the population living in slums, sleeping on roadsides, beggars and rag pickers. Development is meaningless as long as the above eyesore continues.
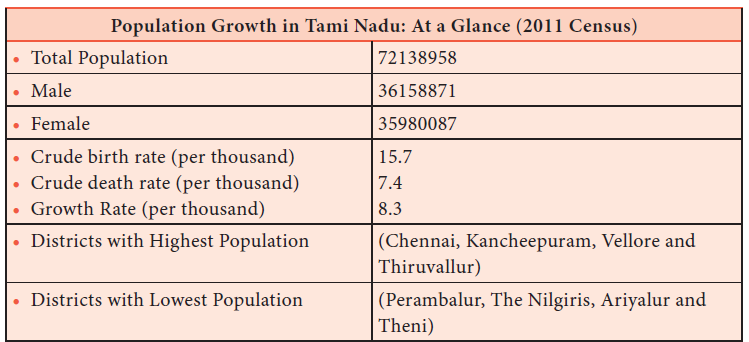
130. Which of these are the highest populated districts in Tamil Nadu?
a) Theni
b) Perambalur
c) Ariyalur
d) Tiruvallur
Explanation
131. What is the population density of Tamil Nadu as per the 2001 Census?
a) 555
b) 480
c) 543
d) 340
Explanation
![]()
![]()
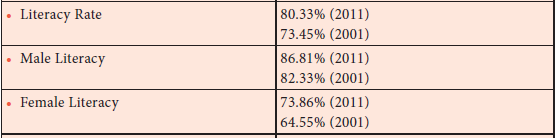
132. Which of these indicators have been increased drastically in the 2001 and 2011 census report of Tamil Nadu?
a) Female Literacy rate
b) Sex ratio
c) Child sex ratio
d) Male literacy rate
Explanation
133. Which age group of children is taken for calculating the child sex ratio?
a) 0-3 years
b) 1-7 years
c) 0-6 years
d) 1-5 years
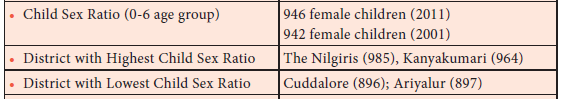
134. Which of this district has the highest child sex ratio?
a) Kanyakumari
b) Coimbatore
c) Cuddalore
d) Ariyalur
Explanation
135. Which of the Indian states are having the highest poverty rate?
a) Madhya Pradesh
b) Karnataka
c) Bihar
d) Odisha
Explanation