State 11th Political Science Lesson 2 Questions in English
11th Political Science Lesson 2 Questions in English
2] State
1. Which of this study is referred to the Political Science?
a) State c) Economic
b) People d) Cultural
Explanation
Political Science is the systematic study of State. We all live in State. The world is viewed as an embodiment of many States.
2. Which of these the idea of State is not derived from a region?
a) Political c) Economic
b) Religious d) Constitution
Explanation
State as an idea or a concept is derived from a historical process of political, cultural, religious and economic contexts of a region.
3. Choose the correct statements about State.
i) State ensures the people lives and property.
ii) The States law and freedom does not subject to any conditions.
a) i only c) Neither i nor ii
b) ii only d) Both i and ii
Explanation
The law and freedom of State are subjected to certain conditions laid by the State itself. State also ensures that our lives and property are protected.
4. The State is classified under which type of social institution?
a) Natural c) Political
b) Derived d) Constitutional
Explanation
The State is the most universal and most powerful of all social institutions. The State is a natural institution.
5. Who referred Human as a Social Animal?
a) Thomas Hobbes c) Aristotle
b) Woodrow Wilson d) Niccolo Machiavelli
Explanation
Aristotle said ‘Man (Human) is a social animal and by nature s/he is a political being. To him, to live in the State and to be a man were identical.
6. Who was the first person to introduce the term State?
a) Niccolo Machiavelli c) Holland
b) Locke d) Burgess
Explanation
The modern term ‘state’ is derived from the word ‘status’. It was Niccolo Machiavelli (1469 – 1527) who first used the term ‘State’ in his writings.
7. Assertion (A): The State translates the desires and aspirations of Human beings.
Reasoning(R): State is necessary for the basic needs Human beings life.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The state is necessary because it comes into existence out of the basic needs of life. It continues to remain for the sake of good life. The aims, desires, and aspirations of human beings are translated into action through the State.
8. Choose the correct statements regarding the thinkers of the Social Contract Theory.
i) Niccolo Machiavelli was not involved in the Social Contract Theory.
ii) The Thinkers of the Social contract theory disagree that Humans need to be controlled by the State.
iii) The Thinkers agree on the point of control of State on Humans.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
The three main thinkers associated with social contract theory are Thomas Hobbes, John Locke and Jean Jack Rousseau. The three thinkers collectively agree that humans need to be controlled by the State. At the same time, they disagree on to what extent the control can be exercised by the State on humans.
9. Match the thinkers and their opinion on state of nature.
A. Hobbes i) No security or morality
B. Locke ii) A state of war
C. Rousseau iii) Property is not secure
a) iii, i, ii c) i, iii, ii
b) ii, iii, i d) ii, i, iii
Explanation

10. State the definition of Woodrow Wilson of State.
a) A Numerous assemblage of human beings occupying a certain territory.
b) State is people organized for law within a definite territory.
c) Union of families and villages for its self-sufficing life.
d) An Organized unit of mankind in a particular portion.
Explanation
To Woodrow Wilson, “State is people organized for law within a definite territory.
11. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Aristotle defined the State as a union of families alone.
ii) Burgess definition for state says that a particular portion of mankind as an organized unit.
iii) State is a numerous assembly of human beings occupying a certain territory as per Holland’s view.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
Aristotle defined the State as a “union of families and villages having for its end a perfect and self – sufficing life by which it meant a happy and honorable life”. To Holland, the State is “a numerous assemblage of human beings generally occupying a certain territory amongst whom the will of the majority or class is made to prevail against any of their number who oppose it.” Burgess defines the State as “a particular portion of mankind viewed as an organized unit.”
12. By which of these the people of state are united together as per the view of Sidgwick?
a) Politically organized people c) A Central Authority
b) Majority people d) All the above
Explanation
According to Sidgwick “State is a combination or association of persons in the form of government and governed and united together into a politically organized people of a definite territory.”
13. What are the divisions of the State according to Prof.Laski?
a) Government, Subjects c) Laws, Judiciary
b) Society, People d) Security, Defense
Explanation
Prof. Laski defines “State as a territorial society divided into government and subjects whose relationships are determined by the exercise of supreme coercive power.”
14. Which is considered as the limiting agent on the authority of the State?
a) Population c) Constitution
b) People d) Judiciary
Explanation
All modern States have their own Constitution that moderates the freedom and privileges of the citizens of the State with the coercive and unquestionable power of the State. Hence Constitution is considered as a limiting agent on the overwhelming authority of the State.
15. What is the definition of state according to the Montevideo convention, 1933?
a) Permanent Population c) Government
b) Defined Territory d) All the above
Explanation
The Montevideo Convention on Rights and Duties of States held in 1933 gave the fundamental understanding of State. A State must have a permanent population, a defined territory and a government that can control the territory and its people and conducts international relations with other States.
16. Which of this American presided the Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties?
a) John Kennedy c) Harry S.Turman
b) Franklin Roosevelt d) Richard Nixon
Explanation
The Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties of States is a treaty signed at Montevideo, Uruguay, on December 26, 1933, during the Seventh International Conference of American States. The Convention codifies the declarative theory of statehood as accepted as part of customary international law. At the conference, United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt and Secretary of State Cordell Hull declared the Good Neighbor Policy, which opposed U.S. armed intervention in inter-American affairs.
17. Which of these is the cause for the Statelessness?
a) Transfer of territory c) Denationalization
b) Conflict of Laws d) All the above
Explanation
Statelessness may result from a variety of causes, including conflict of laws, the transfer of territory, marriage laws, administrative practices, discrimination, lack of birth registration, denationalization (when a State rescinds an individual’s nationality), and renunciation.
18. Which of this British Viceroy initiated the Census in British India?
a) Lord Mayo c) Lord Lawrence
b) Lord Northbrook d) Lord Lytton
Explanation
The decennial Census of India has been conducted 15 times, as of 2011. While it has been undertaken every 10 years, beginning in 1872 under British Viceroy Lord Mayo, the first complete census was taken in 1881.
19. What was the sex ratio in India according to the 2001 census?
a) 935 c) 940
b) 933 d) 936
Explanation
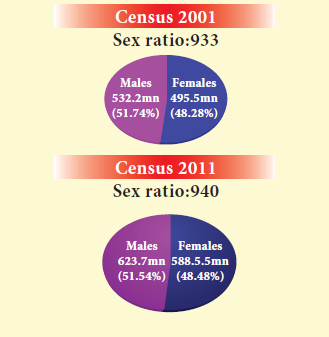
20. Which of these countries population combined to result in India’s population by the 2011 census?
a) USA c) Brazil
b) Indonesia d) All the above
Explanation
The population of India at 121.02 cr is almost equal to the combined population of USA, Indonesia, Brazil, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Japan.
21. Which of this information can be sourced from the Census of a country?
a) Demography c) Sociocultural aspects
b) Standard of Living d) All the above
Explanation
The past-independence census in the country has been conducted once in ten years under the constitutional provisions by notification under the census Act 1948. It is the most credible source of information about demography, literacy, standards of living, urbanization, languages spoken, fertility, mortality and various other economic and sociocultural aspects of the country, which underscores its importance for any government
22. Which of these were focused in the 2011 Indian Census?
a) Cattle Census c) Poverty Census
b) Housing Census d) Literacy Census
Explanation
In the last census, operations conducted in our country in 2011, the enumerators and supervisors has focused on the house listing and housing Census. The type of information gathered on the household, its head, amenities and assets. It also includes the total number of residents, use of the census house and material used for floor, wall and roof.
23. Which of this decade has the lowest population growth rate in India?
a) 1911-21 c) 1931-41
b) 1961-71 d) 1951-61
Explanation
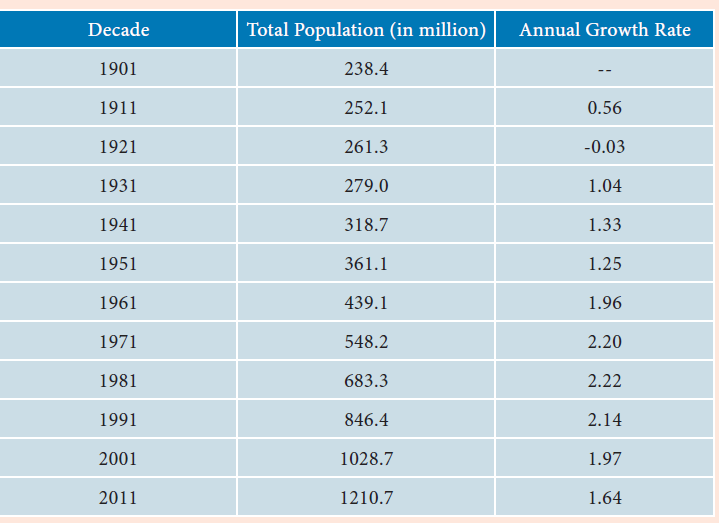
24. Choose the correct statements.
i) The Population of the people is essential for a State.
ii) Aristotle stated that the number of state should be too small to be self-sufficient.
iii) According to Rousseau 25,000 was an ideal number for a state.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
It is the people who make the State. The population is essential for the State. According to Aristotle, the number should be neither too large nor too small. It should be large enough to be self –sufficient and small enough to be well governed. Rousseau determined 10,000 to be an ideal number for a State.
25. Which of these cities were considered for the number view by the ancient thinkers?
a) Rome c) Paris
b) Athens d) Greece
Explanation
Ancient thinkers view on the number was based on the small city – States like Athens and Sparta. The modern States vary in population.
26. What is the significance of the Plato’s ideal number of State?
a) Population can be divided in various columns
b) The number is divisible from 1 to 12.
c) Instructions can be easily given during Emergency situations.
d) All the above
Explanation
According to Plato, the ideal number of State is 5040. The reason is the number 5040 is divisible by numbers from 1 to 12. In the case of 11 the reminder is 2. During the time of emergency the population can be divided in various columns and instructions could be given.
27. Which is essential for the people to organize them socially and politically?
a) Freedom c) Judiciary
b) Territory d) Government
Explanation
People need territory to live and to organize them socially and politically. It may be remembered that the territory of the State includes land, water, and air space.
28. Which of these are referred as the fundamental principle of the Modern State life according to Prof Elliott?
a) Territorial Sovereignty c) Freedom from external control
b) Superiority of State d) All the above
Explanation
Prof. Elliott, “Territorial sovereignty or the superiority of State, overall within its boundaries and complete freedom from external control has been a fundamental principle of the modern State life”.
29. How much percentage does India occupies in terms of global area?
a) 1.8% c) 2.4%
b) 3.7% d) 4.5%
Explanation
India has an area of 32, 87,263 sq. km. approximately India occupies 2.4% of the global area.
30. Who defined the Government as the agency of the State?
a) Ernest Barker c) Prof.A. Appadurai
b) Prof. Elliott d) Harold Laski
Explanation
Government is the working agency of the State. It is the political organization of the State. Indian political scientist Prof.A. Appadurai defined government as the agency through which the will of the State is formulated, expressed and realized.
31. Assertion (A): Government is a fixed structure and a permanent body of a State.
Reasoning(R): The State exists even after the Government leaves the control of the State.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Government is a fixed structure. Political executives who get elected to offices may change but Government as a system is a permanent body of State. The State existed before the people come to power and it will exist after these men and women in power leaves the control of the State.
32. What is the real meaning of the word Sovereignty?
a) Authorized Power c) Final Legal Authority
b) Universal Powers d) Additional Powers
Explanation
The fourth essential element of the State is sovereignty. The word ‘sovereignty” means supreme and final legal authority above. No legal power can exist beyond sovereignty.
33. What are the characteristics of the Sovereignty?
a) Universality c) Exclusiveness
b) Absoluteness d) All the above
Explanation
The concept of “sovereignty” was developed in conjunction with the rise of the modern State. In a traditional understanding, the characteristics of sovereignty are absoluteness, permanence, universality, indivisibility, exclusiveness and inalienability.
34. From which of this word the Sovereignty was derived?
a) Suprema c) Superanum
b) Superanus d) Supreman
Explanation
The term Sovereignty is derived from the Latin word “superanus” which means “supreme”.
35. Who was the father of the Modern theory of Sovereignty?
a) Jean Bodin c) Lord Bryce
b) Prof.A. Appadurai d) C.F. Strong
Explanation
The father of the modern theory of sovereignty was Jean Bodin (1530 – 1597) a French political thinker.
36. Which of these organizations lives in an organized manner?
a) State c) Institutions
b) Society d) Community
Explanation
Families came together under the umbrella of the community for a greater objective of security. The communities so formed made a higher level of organization called society solely to live in an organized manner where each ones’ need is met out by the collective output of the whole.
37. What are the functions of the Government?
a) Law Making c) Law interpretation
b) Implementing the Law d) All the above
Explanation
This control in modern States is done legally through a set of rules and regulations. In a democracy, these rules and regulations are framed by the legislature, enforced by the executive and the judiciary adjudicates the made laws and the implemented laws on the basis of their legality and judiciousness. The function of law making, implementing and interpreting is the function of government.
38. Assertion (A): The Society consists of large number of Individuals and families and Institutions.
Reasoning(R): State is not a form of Society.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The society consists of a large number of individuals, families, groups, and institutions. The early political thinkers considered both State and society as one. The state is a part of society but is not a form of society.
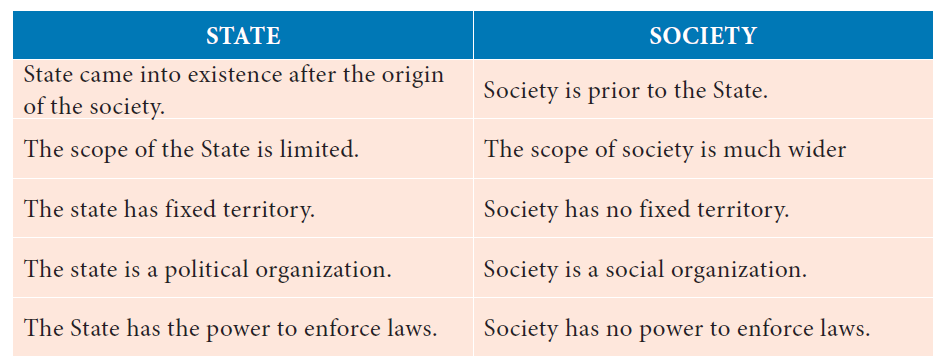
39. State the factors of the Society.
i) The Society has fixed territory.
ii) Society is a social organization.
iii) Society has the power to enforce laws.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
40. Choose the correct statements.
i) The State exists for one great single purpose.
ii) The Society employs a method of voluntary action for controlling the Human.
iii) The multiplicity of the organization of society gives ample opportunity to the members.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
The membership of the State and society are the same. But they differ as regards to their purpose. The State exists for one great but single, purpose; society exists for a number of purposes; some great and some small. The State is a single organization – legal, whereas society comprises within itself many organizations. The State exercises its control over humans by coercion and exact obedience. On the other hand, the society employs a method of voluntary action. The purpose for which society exists makes the persuasive methods necessary. The multiplicity of the organization of society gives ample opportunity to the members to relinquish one association and join another in the event they are subject to any coercion.
41. Assertion (A): The Government can be used as a Synonym for the State.
Reasoning (R): Both the Government and State are same entities.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Government is often used with the ‘State’ as a synonym. But both the government and the State are two different entities. There are differences between the State and the government.
42. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The state consists of population, territory, government and sovereignty.
ii) Powers of the government are original.
iii) The state is permanent and continues forever.
iv) A Government is concrete and is visible.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) iv only
Explanation

43. Which of these were the foundations of the modernity?
a) Equality c) Freedom
b) Individualism d) All the above
Explanation
Modernity laid the foundations of the prioritization of individualism, freedom, equality, fostering of scientific temper in every walk of life and thus modernity led humans from agrarianism towards industrialization, urbanization, and secularization.
44. Which of this War was ended by the Treaty of Westphalia?
a) Thirty years War c) European wars of Religion
b) Seven Years War d) Both a and c
Explanation
The rational foundation of modern State is often argued to be the treaty of Westphalia signed in the year 1648. The Peace of Westphalia was a series of peace treaties that were signed between May and October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabruck and Munster. They largely ended the European wars of religion, including the Thirty Years’ War.
45. Which of these exported the idea of Modern State throughout the world?
a) First World War c) Socialism
b) European Colonization d) Industrialization
Explanation
The idea of modern State was exported throughout the world during the nineteenth century by the process of European Colonization. The South Asian States that became independent from colonial control after Second World War can be brought under the umbrella of post-colonial States.
46. Which of this Economic structure is integrated in the State’s society?
a) Micro Economic Structure c) Mixed Economic Structure
b) Macro Economic Structure d) Market Economic Structure
Explanation
The State should strive to keep its people secure and safe. The State should ensure that its borders are sealed and protected. The market needs to be integrated into the society by a well-knit macroeconomic structure.
47. What should be the Motto of all the activities of the Modern State?
a) Industrial Development c) Improvising Life Style
b) Citizen First d) Increasing the Trade activities
Explanation
Citizen first’ should be the motto of all the activities of the State. The sole principle of governance of modern State is whether the action of the State leads to the promotion of the welfare of its people.
48. What are the main functions of the Modern State?
a) Security and Defense c) Economic conditions
b) Essential Service d) All the above
Explanation
It is largely accepted that the modern State focuses on three main functions. Security and Defense, Economic, Provision of Essential Services.
49. Who introduced the idea of perpetual peace for the States of the world?
a) Immanuel Kant c) C.F. Strong
b) Harold J. Laski d) Jean Bodin
Explanation
Terms like Human Security have emerged to put citizens first. Inspired by the philosopher Immanuel Kant’s idea of perpetual peace, the States of the world came together as ‘league of nations’ and later as the ‘United Nations Organization and have been debating the terms security and defense in terms of promoting peace.
50. Which of these are included in the Economic functions of the Modern State?
a) Investing in no profit areas c) Protecting Consumers
b) Protecting Weaker Sections d) All the above
Explanation
Protecting consumers, weaker sections, investing in areas where there is no profit are those included in the economic functions of the modern state.
51. Which is not the responsibility of the Modern State?
a) Providing basic needs c) Providing Education
b) Fund Allocation d) Social Security
Explanation
The fundamental needs such as food, clean drinking water, providing education, healthcare, and social security for the population are the responsibilities of the modern state.
52. In Which year the Nutritious meal scheme was introduced in Tamil Nadu schools?
a) 1985 c) 1965
b) 1982 d) 1993
Explanation
The noon meal scheme and the nutrition’s meal schemes in all Government schools initiated by the Government of Tamil Nadu and adopted in different parts of the country is one such example of the welfare state. The Nutritious Meal program was introduced in Tamil Nadu in the year 1982.
53. State the new concept of the Modern state?
a) Citizen First c) Welfare State
b) Essential Service d) Self Sufficient State
Explanation
The modern State strived for the welfare of its people and hence another concept came into existence called ‘Welfare State’.
54. Which of these is described as the Novel Features of the Indian Constitution by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar?
a) Fundamental Duties c) Dual Citizenship
b) Fundamental Rights d) Directive Principles of State Policy
Explanation
Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) are mentioned in the Part 4 of the Indian constitution from articles 36 to 51. DPSPs are taken from the Constitution of the Ireland. Dr. B R Ambedkar described these principles as ‘novel features’ of the Constitution.
55. From which of this Country the Part IV of the Indian Constitution is derived?
a) Canada c) South Africa
b) Ireland d) USSR
Explanation
The principles have been inspired by the Directive Principles given in the Part IV of Indian Constitution of Ireland which are related to social justice, economic welfare, foreign policy, and legal and administrative matters.
56. Which of these countries are known for their excellence in Welfare States?
a) Scandinavian c) British
b) Canada d) South Asian
Explanation
It is a reality that the abundance of resources with a minimal population has been the main reason for the successful functioning of welfare State model. The Scandinavian countries are excellent examples of welfare State.
57. Assertion (A): The Welfare state concept was originated in the Western Europe countries.
Reasoning(R): Human development and Protection of wellbeing of Citizens are the key concepts of Welfare state.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The concept of welfare State has its origin in Western Europe after the Second World War. The main idea of welfare State is that the government of welfare State plays a vital role in human development. The role of the welfare State extends to the protection and promotion of the wellbeing of its citizens.
58. Which of these factors are the basic principles of Social well-being of the Citizens?
a) Public Responsibility c) Equal distribution of wealth
b) Equality of Opportunity d) All the above
Explanation
The economic and social well-being of the citizens is based on the principle of equality of opportunity, equitable distribution of wealth, Public responsibility for those who cannot afford themselves the minimal provisions for leading a good life.
59. Which of these countries was the inspiration for the Welfare state in the Indian constitution?
a) Eastern Model c) Western Model
b) Westminster Model d) Monarchy Model
Explanation
India before independence was a Colonial State under British rule. Indians were subjects of the English crown. Once India attained Independence, we had our Constitution that has been deeply inspired by the western model of welfare State.
60. Which of these factors were limiting the Asian states according to Karl Gunnar?
a) Societal Indiscipline c) Poverty
b) Monarchy d) Developing nature
Explanation
Nobel Laureate Karl Gunnar Myrdal identified what he called as societal indiscipline in the Asian States when compared to the western countries.
61. What are the main characteristics of a Soft state?
a) Weak law enforcement c) Social Indiscipline
b) Corruption d) All the above
Explanation
Societal indiscipline is the characteristics of soft State. Social indiscipline, corruption and weak law enforcement are the main characteristics of a soft State.
62. When was the Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques (PCPNDT) Act, 1994 was amended in the Indian Constitution?
a) 1997 c) 2003
b) 2001 d) 1998
Explanation
Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques (Regulation and Prevention of Misuse) Act, 1994 (PNDT), was amended in 2003 to The Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques (Prohibition Of Sex Selection) Act (PCPNDT Act) to improve the regulation of the technology used in sex selection.
63. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The Post-colonial states are categorized as Soft States.
ii) A soft state can refine their democratic values.
iii) The Inability to adhere the standards and maintain discipline is the factor of the Soft state.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
The post-colonial developing States are generally categorized as soft States where their institutions of governance are not fully developed. Our inability to adhere to standards and to enforce law and maintain discipline makes our country as a soft State. A soft State cannot advance further in refining its democratic values.
64. Assertion (A): The Governance crisis of Pakistan and Bangladesh are explained in terms of over developed state.
Reasoning(R): Over developed state is the effectiveness of the functioning similar of bureaucratic Governance after Independence.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Hamza Alawi explains the case of the governability crisis of Pakistan and Bangladesh using the concept of Over Developed State. Overdeveloped State is an explanation offered to the in effectiveness of the functioning of post-colonial States that operate with the similar structure of bureaucratic governance before and after their independence.
65. Which of these economic factors are known for the Modern State?
a) Supports Industries c) Eliminates Poverty
b) Intervenes the economic functions d) Secure the people in the territory
Explanation
The modern state is supposed to intervene in the economic functions of the political system. The State needs to support the people, make them realize their potential for their betterment.
66. Assertion (A): The State gets modernized when the society and its economy are lagging without modernization.
Reasoning(R): This Modernization lag divides the People and the State apparatus.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The State gets increasingly modernized when the society and its economy are lagging behind without modernization the State and the society grossly mismatched each other. This creates a divide between the people and the State’s apparatus.
67. Which of these countries have a Military Bureaucracy Oligarchy according to Hamza Alawai?
a) Bangladesh c) South Korea
b) Pakistan d) Both a and b
Explanation
In the case of Pakistan and Bangladesh, Hamza Alawai coins the word ‘military bureaucracy oligarchy’ that is similar to the license raj of India and over-centralization as a continuation of colonial legacy that has been constantly addressed by the government of India.
68. Which of these are termed for the Post-Colonial states?
a) Decolonized States c) Under Developed States
b) Well Developed States d) Developmental States
Explanation
Post-colonial State is the name of new nation States that have emerged out of the process of decolonization after the Second World War. Post-colonial State is used synonymously with developmental State.
69. Which of these factors are exhibited by the post-colonial states?
a) Political Instability c) Governance crisis
b) Poverty d) All the above
Explanation
In general, post-colonial States exhibit a high degree of poverty, political instability and the crisis of governance. The mismatch between the society with its traditional power structure overlapping with modern States has largely resulted in such a situation.
70. Which of these are the major challenges faced by the Colonial countries after their Independence?
a) Societal indiscipline c) Poverty
b) National Identity d) Industry Development
Explanation
It is obvious that the Colonial powers that ventured into newer worlds destroyed the main parts of native traditions and cultures and further constantly replaced them with their own ones. This cultural import led to conflicts as and when they became independent as they suddenly faced the challenge of developing a new national identity and self-confidence.
71. Which of this Article declares the Part IV of Indian Constitution as a Fundamental Right?
a) Article 51 c) Article 21
b) Article 32 d) Article 44
Explanation
According to the Indian Constitution Part IV does not trigger enforceable rights but the free legal aid has been upheld by the Supreme Court as a fundamental right under Article 21 of the Constitution.
72. Assertion (A): The Asylum seeker and the Refugees differ in their definitions.
Reasoning(R): An asylum seeker requests the international protection whose claim for refugee status has not been determined.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
An asylum seeker is someone who is seeking international protection but whose claim for refugee status has not yet been determined. In contrast, a refugee is someone who has been recognized under the 1951 Convention relating to the status of refugees to be a refugee. The definition of ‘refugee’ does not cover other individuals or groups of people who leave their country only because of war or other civil disturbance, famine, natural disasters or in order to seek a better life.
73. Which of these proclaims India as a Sovereign state in the Indian Constitution?
a) 42nd Amendment c) Part IV
b) The Preamble d) Fundamental Rights
Explanation
The Preamble proclaims that India is a Sovereign State. ‘Sovereign’ means that India has its own independent authority and it is not a dominion or dependent state of any other external power. The Legislature of India has the powers to enact laws in the country subject to certain limitations imposed by the Constitution.
74. What is breakdown of constitutional machinery in the Indian Constitution?
a) Article 356 c) Article 360
b) Article 370 d) Article 243
Explanation
Under the breakdown of the constitutional machinery of any state can impose constitutional emergency. Article 356 deals with Constitutional emergency. This situation arises when a situation in a state reaches to a place, that it can no longer rule according to the provisions of the constitution.
75. Choose the correct statements regarding Sovereign in the Indian Constitution.
i) India is a Sovereign Democratic Republic country.
ii) Sovereign defines the independent authority of a State.
iii) In republic Countries the elected representatives of the people has the authority for the sovereignty.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
Sovereign means the independent authority of a State. It means that it has the power to legislate on any subject; and that it is not subject to the control of any other State / external power. According to the preamble, the constitution of India has been pursuance of the solemn resolution of the people of India to constitute India into a ‘Sovereign Democratic Republic’, and to secure well-defined objects set forth in the preamble. Sovereignty denotes supreme and ultimate power. It may be real or normal, legal or political, individual or pluralistic. In republican form of governments, which mostly prevail in the contemporary world, sovereignty is shifted to the elected representatives of the people.