Population and Settlement Notes 7th Social Science
Population and Settlement Notes 7th Social Science
7th Social Science Lesson 5 Notes in English
5. Population and Settlement
1. What is Population Geography?
Population Geography is a study of demographic phenomena which includes natality, morality, growth rates etc., through both space and time. Increase (or) decrease in population indicates population distribution and growth.
2. Define Migration:
The study of movements and mobility of population is called migration. Among the human people from place to place the ancient origin is grouped under major races such us language and religion.
3. What are Races?
- Race has been defined as a biological grouping within the human species.
- The race is a group of people with more (or) less permanent distinguishing characteristics that are inherited.
4. How do the Races Vary?
The most widely found human racial types are based on visual traits such as head shape, facial features nose shape, eye shape and colour, skin colour, stature, blood groups etc.
7th Social Book Back Questions
5. What are the Major Human Races of World?
The major world Human races are
- Caucasoid (European)
- Negroid (African)
- Mongoloid (Asiatic)
- Australoid (Australian)
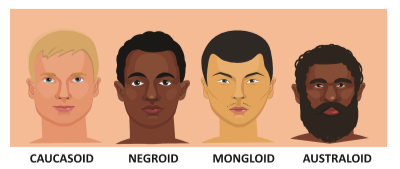
6. Define Causasoid:
The Caucasoid is known as European race. This group is the one with fair skin and dark brown eyes, wavy hair and narrow nose. The Caucasoid are also found in Eurasia.
7. Human geography is the study of Man and his surroundings to the natural environment
8. Define Negroid:
Negroid have the dark eyes, Black skin, black wooly hair, wide nose, long head, and thick lips. They are living in different parts of Africa.
9. Define Mongoloids:
The mongoloid race is commonly known as the Asian-American race. The mongoloid have the light yellow to brown skin, straight hair, flat face, broad head and medium nose. Such people are found in Asia and Arctic region
10. Define Australoids:
Australoids have wide nose, curly hair dark skin, and short in height. They are living in Australia and Asia.
11. Races of India:
India is said to be one of the cradle lands of human civilization. The ancient Indus valley civilization in India was believed to have been of Dravidian origin in northern India.
12. Importance of Dravidian People:
- The Dravidian people were pushed south when the Indo-Aryan came in later.
- South India was dominated by the three Dravidian kingdoms of the chera, the cholas, and the pandyas.
- The Dravidian languages are Tamil, Telugu, kannada, Malayalam and Tulu almost all the Dravidians live in the southern part of India.
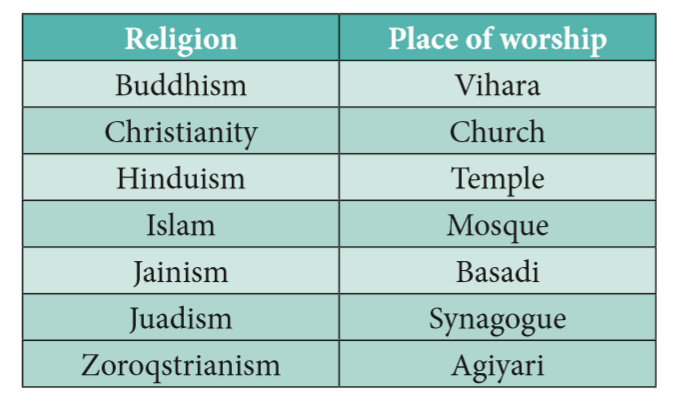
13. What is Religion?
Religion means a particular system of faith and worship, which brings human being with human society. Religion, is a symbol of group identity and a cultural rallying point.
14. What are the Classification of Religion?
a) Universalizing Religions
Christianity, Islam and Buddhism.
b) Ethnic Religions
Judaism, Hiduism and Japanese Shintoism.
c) Tribal or Traditional Religions
Animism, Shamanism and Shaman.
15. Define Language:
- Language is a great force of socialization.
- Language, either in the written or oral form, is the most common type of communication.
- Language promotes the transmission of ideas and the functioning of political, economic, social and religious systems.
16. Mention the Languages of India:
India has many languages and culture. Each state has its own language though the national language is Hindi, 22 major language were spoken by about 97 percent population of the country.
17. Various Languages followed in India:
- India follows, kashmiri Urdu Punjabi, Hindi Rajasthani, Gujarati, Bengali and Assamese etc., these language are followed in North India.
- The main language of the Dravidian family are Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam etc., These languages are mainly spoken in southern India.
18. What is Settlement?
Settlement is a place where people live and interact through activities such as agriculture, trading and entertainment.
19. What is Rural Settlement?
A rural settlement is a community, involved predominantly in primary activities such as agriculture, lumbering, fishing and mining.
20. What is Urban Settlement?
An urban settlement engages in predominantly in secondary and tertiary activities, such as industries, trade and banking.
21. How the Settlements Vary?
Site and situation refers to the location of the actual settlement. The initial choice of a site for a settlement depends on how it is useful for meeting our daily needs, like water supply, availability of farmland, building material and fuel etc.
22. What are the Patterns of Settlements?
Settlements also be classified into Compact settlements and Dispersed settlement.
23. Define Compact settlements:
- Compact settlement is also known as nucleated settlement.
- In this type large a number of houses are built very close to each other such settlement develop along the river valleys and fertile plains.
- In India compact settlements are found in the northern plains and the coastal plains of peninsular India.
24. Define Dispersed Settlements:
- Dispersed settlements are generally found in the areas of extreme climate, hilly tracts, thick forests, grasslands, areas of extensive cultivation.
- In these settlements, houses are spaced far apart and after interspersed with fields.
25. Where Dispersed settlements are found in India?
In India this type of human settlement is found in the northern kosi tract, the Ganga delta, the Thar Desert of Rajasthan and the foot hills of Himalayas and the Niligris.
26. What are Rural Settlement?
- Rural settlements are predominantly located near water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and springs where water can be easily available.
- People choose to settle near fertile lands suitable for agriculture, along with the provision of other basic needs.
- Hence, they prefer to live near low lying river valleys and coastal plains suited for cultivation.
- The availability of building materials like wood, stone and clay near settlements is another advantage, for settlements to be built.
27. Factors Influencing Rural Settlement:
- Nature of topography
- Local weather Condition
- Soil and water resources
- Social organization
- Economic condition
28. Pattern of Rural Settlement:
- The pattern of settlement has been defined as the relationship between a house or building to another.
- A rural settlement pattern is a function of relief, climate, water supply and socio-economic factor.
- It is broadly classified under the following patterns, such as Linear, Rectangular, Circular, Star like pattern etc.
29. What is Linear Settlement?
In a Linear settlement, houses are arranged along the either side of a road, railway line, river (or) canal, the edge of a valley, etc., e.g. the Himalayas the Alps, the Rockies.
30. Define Rectangular Settlement:
The rectangular settlements are almost straight, meeting each other at right angles. Such a Settlement is found in plain areas (or) inter montane plain. E.g.,Sutlej.
31. Define Circular Settlement:
Houses built around a central area are known as Circular pattern of settlements. Such Settlement develop around lakes and tanks.
32. What is Star like Pattern?
The Star like pattern of settlement develops on the sites and places where several roads converge and houses spread out along the sides of roads in all directions. e.g. The Indo – Ganga plains of Punjab and Haryana.
33. Define Pilgrim settlement:
Pilgrim settlement may come up around a place of worship (or) any spot with a religious significance. E.g. Thiruverkadu in Tamil Nadu.
34. Define Wet Point Settlement:
A wet point is a site with reliable supply of water from wells, tank, river, spring (or) pond in an area.
35. Define Dry Point Settlement:
- A dry Point settlement is located in low lying areas in the regions of excessive dampness.
- Dry point settlements are not affected by flooding, due to the landscape and the source of water.
- Such settlements are found in the coastal plains of Kerala and deltas along the east coast of India.
36. What is an Urban Settlement?
- The settlements in which most of the people are engaged in secondary and tertiary activities are known as urban settlements.
- In other words, urban is related to cities and towns.
- The word urban is often used in terms of town, city, mega city, conurbation, megalopolis.
37. Classification of Urban Settlements:
The definition of urban area varies from are country to another. Some of the common basis of classification are
- Size of population
- Occupational structure
- Administration
38. Define Town:
- Town is a general name for an urban place, usually a settlement meeting a prescribed minimum population threshold.
- Population more than 5000 people.
- Based on the function that cities perform they can be classified into the following types of towns, such as administrative, cantonment, academic etc.,
39. What does a City Contain?
- The term City is generally applied to large urban places with no strict definitions to separate if from smaller town.
- City is a nucleated settlement which multifunctional in character, including an established central business district.
40. How Many people will live in city?
In India an urban place with more than one lakh population is considered as a city (Population more than 1,00,000).
41. What is a Mega city?
- A mega city is a very large city typically with a population of more than 10 million people.
- A mega city can be a single metropolitan area.
- E.g. Canton, Tokyo, Delhi, Mumbai are some of the examples of megacities.
42. Define Megalopolis:
- The word megalopolis is given for a large conurbation, when two or more large cities whose total population exceeds ten million.
- The region made up of cities between Boston and Washington D.C is a well-known megalopolis.
43. What are the Megapolis in India?
In India, Kolkata is the largest urban area which is a megalopolis. Gandhinagar, Surat, Vadodara, Rajput in Gujarat are the important megalopolis cities in India.
44. Define Conurbation:
A Conurbation is a region comprising of a number of cities, large town, and other urban areas that through population growth and physical expansion have merged to form one continuous urban (or) industrially developed area.
45. Various Examples of Conurbation:
West Midland in England, the Ruhr in Germany, Randstad in the Netherlands are example of conurbations. Mumbai in Maharashtra, Gurgaon, Faridabad in Haryana, Noida in Uttar Pradesh are the conurbation cities of India.
46. World Health Organization (WHO) suggests that among other things a healthy city must have
- A Clean” and “Safe” environment
- Meets the basic needs of “All” its inhabitants
- Involves the “Community” in local government
- Provides easily accessible “Health service.
47. What is a Satellite Town?
- A satellite town is a town designed to house the over population of a major city, but is located well beyond the limits of that city.
- Satellite towns are generally located outside the rural urban fringe. In India most satellite towns are purely residential in character.
48. Various Satellite Towns?
Satellite towns occasionally present a look of twin towns such as Dehri and Dalmianager in Rohtas district of Bihar. They may be connected with roads. For e.g. Patna, Barauni, Varanasi and Hajipur.
49. What is a Smart City?
In an urban region, a city which is very much advanced in terms of infrastructure, real estate, communication and market availability is called a Smart City.
50. What are the first ten smart cities of India?
The first ten smart cities of India are Bhubaneshwar, Pune, Jaipur, Surat, Ludhiana, Kochi, Ahmedabad, Solapur, New Delhi and Udaipur.
51. What the cities in Tamil Nadu under smart city Project?
Tamil Nadu has 12 major cities to be transformed as smart cities. They are Chennai, Madurai, Tirunelveli, Tiruchirappalli ,Thanjavur, Tiruppur, Salem, Vellore, Coimbatore, Thoothukudi, Dindugul and Erode.
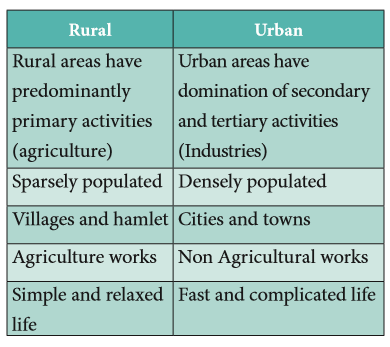
52. Difference Between Rural and Urban Settlement:
53. Define hierarchy of settlements:
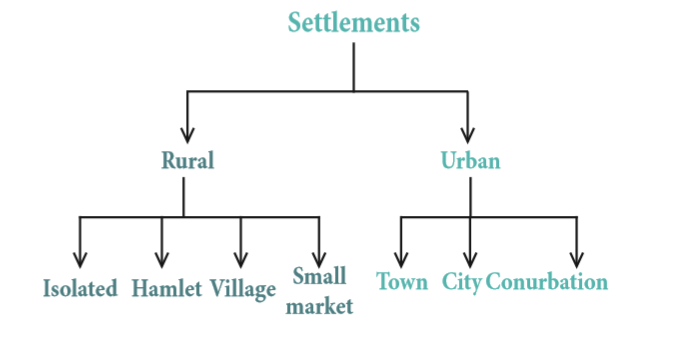
54.
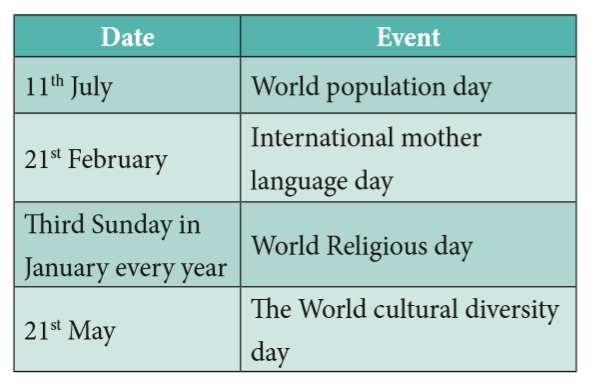
55. Major Religion and their Worship Places: