Monetary Economics 12th Economics Lesson 5 Questions in English
12th Economics Lesson 5 Questions in English
5] Monetary Economics
1. Who quoted that inflation is taxation without legislation?
a) Milton Friedman
b) Fisher
c) Daznavatti
d) Marshall
Explanation
Inflation is taxation without legislation.-Milton Friedman
2. Which of these money functions are analyzed by the monetary economics?
a) Medium of exchange
b) Store of value
c) Unit of account
d) All the above
Explanation
Monetary Economics is a branch of economics that provides a framework for analyzing money and its functions as a medium of exchange, store of value and unit of account.
3. Which of these are not examined by the monetary economics?
a) Regulation of money
b) Banking rates
c) Financial Institutions regulation
d) Monetary systems effects
Explanation
It examines the effects of monetary systems including regulation of money and associated financial institutions.
4. Assertion (A): Money is accepted as payments for goods and services.
Reasoning(R): Medium of Exchange is widely accepted as means of payments.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Money is anything that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts and that serves as a medium of exchange. A medium of exchange is anything that is widely accepted as a means of payments.
5. Which is the basis of credit?
a) Cheques
b) Bills
c) Money
d) None of the above
Explanation
In recent years, the importance of credit has increased in all the countries of the world. Credit instruments are used on an extensive scale. The use of cheques, bills of exchange, etc. has gone up. It should however, be remembered that money is the basis of credit.
6. Choose the correct statements.
i) Walker quoted that Money can be anything acceptable as means of exchange.
ii) Crowther view on Money is what money does.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
“Money is, what money does”- Walker.
“Money can be anything that is generally acceptable as a means of exchange and at the same time acts as a measure and a store of value”.–Crowther
7. Which of this system was pioneer in trade and services?
a) Gold Coins
b) Barter System
c) Copper coins
d) None of the above
Explanation
The introduction of money as a medium of exchange was one of the greatest inventions of mankind. Before money was invented exchange took place by Barter that is commodities and services were directly exchanged for other commodities and services.
8. Which of these goods were exchanged in the Barter system?
a) Skins
b) Rice
c) Utensils
d) All the above
Explanation
Goods like furs, skins, salt, rice, wheat, utensils, weapons, etc. were commonly used as money.
Such exchange of goods for goods was known as “Barter Exchange” or “Barter System”.
9. Who introduced the Barter system in the world history?
a) Babylonians
b) Mesopotamia Tribes
c) Sumerian Tribes
d) Harappa Civilization
Explanation
The history of Barter system starts way back in 6000 BC. Barter system was introduced by Mesopotamia tribes.
10. Which of these people developed an improved barter system?
a) Phoenicians
b) Mesopotamians
c) Babylonians
d) Romans
Explanation
Phoenicians adopted bartering of goods with various other cities across oceans. Babylonian’s also developed an improved barter system, where goods were exchanged for goods.
11. Which of this standard was the premier in the barter system?
a) Paper currency
b) Metallic standard
c) Goods
d) All the above
Explanation
Among these, metallic standard is the premier one. Under metallic standard, some kind of metal either gold or silver is used to determine the standard value of the money and currency.
12. Assertion (A): Standard coins were made out of the metals.
Reasoning(R): The face value of the standard coins was equal to their intrinsic metal value.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Standard coins made out of the metal are the principal coins used under the metallic standard. These standard coins are full bodied or full weighted legal tender. Their face value is equal to their intrinsic metal value.
13. Choose the correct statements.
i) Gold standard value is directly linked with the value of gold.
ii) The Monetary unit is defined in terms of a certain weight of gold.
iii) Purchasing power of a unit of money is equal to the value of fixed weight of gold.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Gold Standard is a system in which the value of the monetary unit or the standard currency is directly linked with gold. The monetary unit is defined in terms of a certain weight of gold. The purchasing power of a unit of money is maintained equal to the value of a fixed weight of gold.
14. Assertion (A): The Silver standard monetary systems are the standard unit of account of fixed weight of silver.
Reasoning(R): The Government of a country allows conversion of its currency into fixed amount of silver.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The silver standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is a fixed weight of silver. The silver standard is a monetary arrangement in which a country’s Government allows conversion of its currency into fixed amount of silver.
15. Which of these government institution issues the paper currency?
a) The Finance Ministry
b) The Central Bank
c) The Treasury
d) Both b and c
Explanation
The paper currency standard refers to the monetary system in which the paper currency notes issued by the Treasury or the Central Bank or both circulate as unlimited legal tender.
16. Choose the correct statements.
i) Paper currency is not convertible into any metal.
ii) The value of the paper currency is dependent of the value of gold.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Paper currency is not convertible into any metal. Its value is determined independent of the value of gold or any other commodity.
17. Which is referred as the paper standard?
a) Managed Currency standard
b) Money Circulatory
c) Commodity standard
d) Stable control
Explanation
The paper standard is also known as managed currency standard. The quantity of money in circulation is controlled by the monetary authority to maintain price stability.
18. Which of these is the recently evolved form of money?
a) Paper Currency
b) Plastic Money
c) Digital Currency
d) None of the above
Explanation
The latest type of money is plastic money. Plastic money is one of the most evolved forms of financial products. Plastic money is an alternative to the cash or the standard “money”.
19. Which is not a form of Plastic money?
a) Credit Cards
b) Forex Cards
c) Bit coins
d) Smart Cards
Explanation
Plastic money is a term that is used predominantly in reference to the hard plastic cards used every day in place of actual bank notes. Plastic money can come in many different forms such as Cash cards, Credit cards, Debit cards, Pre-paid Cash cards, Store cards, Forex cards and Smart cards. They aim at removing the need for carrying cash to make transactions.
20. What are the techniques used to regulate the units of currency digitally?
a) Encryption Techniques
b) Digital Conversion
c) Decryption Techniques
d) All the above
Explanation
A digital currency in which encryption techniques are used to regulate the generation of units of currency and verify the transfer of funds operating independently of a Central Bank.
21. Bit coins are the one of the form of______.
a) Paper Currency
b) Crypto Currency
c) Smart Currency
d) Invisible Currency
Explanation
Decentralized crypto currencies such as Bit coin now provide an outlet for Personal Wealth that is beyond restriction and confiscation.
22. How many functions are classified as the main function of the money?
a) 8
b) 7
c) 4
d) 3
Explanation
The main functions of money can be classified into four categories:
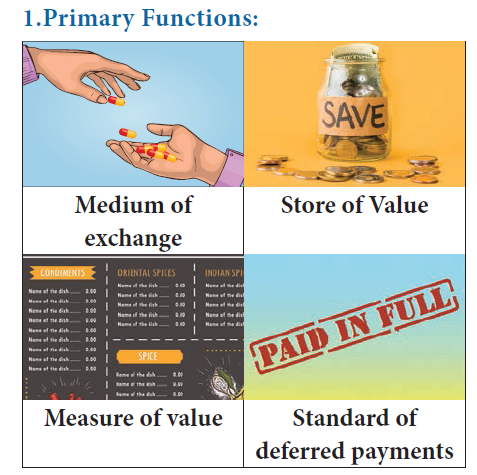
23. Which is not a primary function of the Money?
a) Medium of Control
b) Standard of Deferred payments
c) Store Value
d) Measure Value
Explanation
Primary Functions:
24. What is the basic function of Money?
a) Measure Value
b) Store Value
c) Medium of Exchange
d) Basis of credit system
Explanation
Money as a medium of exchange: This is considered as the basic function of money. Money has the quality of general acceptability, and all exchanges take place in terms of money
25. What are the types of transaction of money?
a) Credit, Sale
b) Debit, Purchase
c) Value, Measure
d) Sale, Purchase
Explanation
On account of the use of money, the transaction has now come to be divided into two parts. First, money is obtained through sale of goods or services. This is known as sale. Later, money is obtained to buy goods and services. This is known as purchase.
26. What is referred as the measure value of money?
a) Price of all goods and services
b) Production value of currency
c) Circulatory value of Money
d) All the above
Explanation
The second important function of money is that it measures the value of goods and services. In other words the prices of all goods and services are expressed in terms of money.
27. Assertion (A): Money is a single measure of value.
Reasoning(R): The rate of exchange between various types of goods is very hard to determine in terms of money.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Money is thus looked upon as a collective measure of value. Since all the values are expressed in terms of money, it is easier to determine the rate of exchange between various types of goods in the community.
28. Which of these function of money made the savings easy?
a) Store of Value
b) Capital
c) Standard of Deferred payments
d) Credit System
Explanation
Money as a Store of value: Savings done in terms of commodities were not permanent. But, with the invention of money this difficulty has now disappeared and savings are now done in terms of money.
29. Assertion (A): Money serves as an easily available store of wealth.
Reasoning(R): Money can be converted into various marketable assets.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Money also serves as an excellent store of wealth, as it can be easily converted into other marketable assets, such as, land, machinery, plant etc.
30. State the difficulty in the Barter system.
a) Borrowing and Lending
b) Measurement
c) Payment structure
d) All the above
Explanation
Borrowing and lending were difficult problems under the barter system. In the absence of money, the borrowed amount could be returned only in terms of goods and services.
31. Which of these money function simplified the borrowing and lending process?
a) Money as the basis of the Credit System
b) Money as a Means of Transferring Purchasing Power
c) Money as a Standard of Deferred Payments
d) Money as a Store of value
Explanation
Money as a Standard of Deferred Payments: The modern money-economy has greatly facilitated the borrowing and lending processes. In other words money now acts as the standard of deferred payments.
32. State the usage of Money as a means of Transferring Purchasing Power.
a) To extend the usage of money to distant land.
b) Develop the global economy.
c) To have a standard Money.
d) All the above
Explanation
Money as a Means of Transferring Purchasing Power: The field of exchange also went on extending with growing economic development. The exchange of goods is now extended to distant lands. It is therefore, felt necessary to transfer purchasing power from one place to another.
33. Assertion (A): Business transactions are either cash or on credit.
Reasoning(R): Money is the basis of the Credit system.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Money is the basis of the Credit System. Business transactions are either in cash or on credit. For example, a depositor can make use of cheques only when there are sufficient funds in his account.
34. On what basis the commercial banks create credit?
a) Adequate Cash reserve
b) Liquidity of Cash
c) Repo rate
d) None of the above
Explanation
The commercial banks create credit on the basis of adequate cash reserves. But money is at the back of all credit.
35. In what ways money is distributed by the national income?
a) Income
b) Wages
c) Interest
d) All the above
Explanation
The task of distribution of national income was exceedingly complex under the barter system. But the invention of money has now facilitated the distribution of income as rent, wage, interest and profit.
36. How the consumer can obtain maximum utility of money?
a) By incurring expenditure on various commodities
b) By decreasing Marginal utilities
c) By paying wages and rent
d) High Interest rates
Explanation
Consumer can obtain maximum utility only if he incurs expenditure on various commodities in such a manner as to equalize marginal utilities accruing from them.
37. Assertion (A): Money helps to equalize the marginal productivities of various factors of production.
Reasoning(R): The prices of all commodities are expressed in terms of money.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
In equalizing these marginal utilities, money plays an important role, because the prices of all commodities are expressed in money. Money also helps to equalize marginal productivities of various factors of production.
38. Which form of money is the mostly used form of capital?
a) Liquid form
b) Store Value
c) Credit values
d) Mutual Funds
Explanation
Money is the most liquid form of capital. In other words, capital in the form of money can be put to any use. It is on account of this liquidity of money that capital can be transferred from the less productive to the more productive uses.
39. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Money possesses the quality of general acceptability.
ii) Every firm has assets in the form of liquid cash for the repayment capacity.
iii) Except the Government all other institutions may have some liquid money to maintain their repayment capacity.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Money possesses the quality of general acceptability. To maintain its repayment capacity, every firm has to keep assets in the form of liquid cash. The firm ensures its repayment capacity with money. Likewise, banks, insurance companies and even governments have to keep some liquid money to maintain their repayment capacity.
40. Assertion(A): Money should be used only for the purpose for which it has been served.
Reasoning(R): Purchasing Power in terms of money can be used for various purposes.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Money represents Generalized Purchasing Power: Purchasing power kept in terms of money can be put to any use. It is not necessary that money should be used only for the purpose for which it has been served.
41. Which is the most preferred form of Capital?
a) Liquid Money
b) Crypto Currency
c) Assets
d) Mutual Funds
Explanation
Money is the most liquid form of capital. It can be put to any use.
42. Choose the correct statements regarding money.
i) Money supply means the circulating amount of money in an economy.
ii) Money supply determines the price level and interest rates.
iii) Money supply at a given point of time is a flow.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Money supply means the total amount of money in an economy. It refers to the amount of money which is in circulation in an economy at any given time. Money supply plays a crucial role in the determination of price level and interest rates. Money supply viewed at a given point of time is a stock and over a period of time it is a flow.
43. Which of these Ministry of Indian Government is involved in the issuing of currency?
a) Ministry of Home Affairs
b) Ministry of Commerce and Industry
c) Ministry Of Finance
d) Ministry of Planning
Explanation
In India, currency notes are issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and coins are issued by the Ministry of Finance, Government of India (GOI).
44. What is the other term for the currency notes?
a) Fiat money
b) Credit
c) Standard exchange
d) None of the above
Explanation
The balance is savings, or current account deposits, held by the public in commercial banks are also considered money. The currency notes are also called fiat money and legal tenders.
45. How many alternative measures of money supply are approved by the RBI?
a) 5
b) 7
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation
Money supply is a stock variable. RBI publishes information for four alternative measures of Money supply namely M1, M2, M3 and M4.
46. In which year the new symbol of rupee was approved by the Union cabinet?
a) 2008
b) 2010
c) 2012
d) 2013
Explanation
The new symbol designed by D.Udaya Kumar, a post graduate of IIT Bombay was finally selected by the Union cabinet on 15th July, 2010.
47. Which of these language combinations are used in the new symbol of rupee?
a) Devanagiri, Roman
b) Sanskrit, Sumerian
c) Urdu, Sanskrit
d) Hindi, Roman
Explanation
The new symbol is an amalgamation of Devanagiri ‘Ra’ and the Roman ‘Without the stem. The symbol of India rupee came into use on 15thJuly, 2010.
48. Which of these was the first country to accept a unique currency symbol?
a) Britain
b) The United States
c) Japan
d) India
Explanation
After America, Britain, Japan, Europe Union. India is the 5th country to accept a unique currency symbol.
49. What happens if there is an increase in CDR?
a) Decrease in money multiplier
b) Increase in Cash credit
c) Probability of Inflation
d) None of the above
Explanation
Currency Deposit Ratio (CDR); It is the ratio of money held by the public in currency to that they hold in bank deposits.
50. Which of these are included in the Reserve deposit ratio?
a) Bank deposits with RBI
b) Vault cash in banks
c) Public Currency
d) Both a and b
Explanation
Reserve deposit Ratio (RDR); Reserve Money consists of two things (a) vault cash in banks and (b) deposits of commercial banks with RBI.
51. Which is termed as the fraction of the deposits the banks must keep with RBI?
a) Reserve deposit Ratio
b) Cash Reserve Ratio
c) Statutory Liquidity Ratio
d) Currency Deposit Ratio
Explanation
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR); It is the fraction of the deposits the banks must keep with RBI.
52. State the SLR ratio of India at present?
a) 12.8
b) 10.8
c) 13.2
d) 19.5
Explanation
Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR); It is the fraction of the total demand and time deposits of the commercial banks in the form of specified liquid assets.
53. Which of this relationship are explained by the Quantity theories?
a) Quantity and value of money.
b) Liquidity and Reserve ratio of Money
c) Credit and Debit ratio of Money
d) None of the above
Explanation
Quantity theories of money explain the relationship between quantity of money and value of money. Here, we are given two approaches of Quantity Theory of Money, viz. Fisher’s Transaction Approach and Cambridge Cash Balance Approach.
54. When the quantity theory of money was propounded by the economist Davanzatti?
a) 1522
b) 1732
c) 1588
d) 1642
Explanation
The quantity theory of money is a very old theory. It was first propounded in 1588 by an Italian economist, Davanzatti.
55. Who gave the quantitative equation form for the theory of money?
a) Irving Fisher
b) Davanzatti
c) Marshall
d) Coulbourn
Explanation
The credit for popularizing this theory in recent years rightly belongs to the well-known American economist, Irving Fisher who published his book, ‘The Purchasing Power of Money” in 1911.He gave it a quantitative form in terms of his famous “Equation of Exchange”.
56. What does the T represents in the Fisher equation?
a) Price Level
b) Money Supply
c) Volume of Transaction
d) Velocity of Money
Explanation
The general form of equation given by Fisher is MV = PT
Where M = Money Supply/quantity of Money
V = Velocity of Money
P = Price level
T = Volume of Transaction
57. Which of these was included in the Fishers equation for the modern economy?
a) Bank deposits and velocity
b) Liquidity ratio
c) Cash reserve ratio
d) Assets of the Banks
Explanation
The Fishers equation considers only currency money. But, in a modern economy, bank’s demand deposits or credit money and its velocity play a vital part in business. Therefore, Fisher extended his original equation of exchange to include bank deposits M1 and its velocity V1.
58. State the revised Fishers equation.
a) PT = MV + M1V1
b) T= MM1 + VV1 / P
c) PT = MM1 * VV1
d) P= MV / M1V1
Explanation
From the revised equation, PT = MV + M1V1
P = MV + M1V1 / T
It is evident that the price level is determined by
(a) The quantity of money in circulation ‘M’
(b) The velocity of circulation of money ‘V’
(c) The volume of bank credit money M1
(d) The velocity of circulation of credit money V1 and the volume of trade (T)
Supply of Money = Demand for Money
59. Which of this approach is analyzed by the Marshalls equation?
a) Price Balance
b) Cash Balance
c) Purchasing Power Balance
d) Income Balance
Explanation
Cambridge Approach (Cash Balances Approach)
i) Marshall’s Equation
The Marshall equation is expressed as: M = KPY
Where, M is the quantity of money
Y is the aggregate real income of the community
P is Purchasing Power of money
K represents the fraction of the real income which the public desires to hold in the form of money. Thus, the price level P = M/KY or the value of money (The reciprocal of price level) is 1/P = KY/M
60. Which of these factors influence the value of money in the Marshall’s equation?
a) M
b) K
c) Y
d) Both a and b
Explanation
According to Marshall’s equation the value of money is influenced not only by changes in M but also by changes in K.
61. State the equation of Keynes.
a) n = p + k
b) p = nk
c) n = p – k
d) p = n / k
Explanation
Keynes’ Equation Keynes equation is expressed as: n = pk (or) p = n / k
Where n is the total supply of money
p is the general price level of consumption goods
k is the total quantity of consumption units the people decide to keep in the form of cash
62. Which of this value is a real balance in the equation of Keynes?
a) K
b) P
c) r
d) n
Explanation
Keynes indicates that K is a real balance, because it is measured in terms of consumer goods. According to Keynes, peoples’ desire to hold money is unaltered by monetary authority. So, price level and value of money can be stabilized through regulating quantity of money by the monetary authority.
63. Which of these is expressed by the term ‘r’ in the Keynes equation?
a) Total money supply
b) Price Level of Consumer Goods
c) Cash reserve ratio
d) Total money deposit in Banks
Explanation
Keynes extended his equation in the following form: n = p (k + rk’) or p = n/(k + rk’)
Where, n = total money supply
p = price level of consumer goods
k = peoples’ desire to hold money in hand (in terms of consumer goods) in the total income of them
r = cash reserve ratio
k’ = community’s total money deposit in banks, in terms of consumers goods.
64. Which of these factors are changed directly to the volume of money in the extended Keynes equation?
a) P
b) k
c) k’
d) r
Explanation
In the extended equation also Keynes assumes that, k, k’ and r are constant. In this situation, price level (P) is changed directly and proportionately changing in money volume (n).
65. Assertion (A): Inflation is a consistent rise in the general price level.
Reasoning (R): The price level is increased with the decrease in the purchasing power of currency is called as Inflation.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Inflation is a consistent and appreciable rise in the general price level. In other words, inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising and consequently the purchasing power of currency is falling.
66. Who defined Inflation as Too much of Money chasing too few goods”?
a) Coulbourn
b) Gregorye
c) Irving Fisher
d) Davanzatti
Explanation
Definition of Inflation
“Too much of Money chasing too few goods”- Coulbourn
“A state of abnormal decrease in the quantity of purchasing power”- Gregorye
67. How many types of Inflation are categorized on the basis of speed?
a) 3
b) 5
c) 4
d) 7
Explanation
(i) Creeping inflation (ii) Walking inflation (iii) Running inflation and (iv) Galloping inflation or Hyper inflation.
68. Choose the correct statements about the Creeping Inflation.
i) Creeping inflation is moderate price increase of the goods.
ii) The price rise is rapid at a rate of speed of 10%-20%.
iii) It is also known as Mild Inflation and Moderate Inflation.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Creeping Inflation: Creeping inflation is slow-moving and very mild. The rise in prices will not be perceptible but spread over a long period. This type of inflation is in no way dangerous to the economy. This is also known as mild inflation or moderate inflation.
69. Assertion (A): Moderate price raise causes the Running Inflation.
Reasoning(R): Walking Inflation is caused by the 10%-20% price increase per annum.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
When prices rise moderately and the annual inflation rate is a single digit ( 3% – 9%), it is called walking or trolling inflation. Running Inflation: When prices rise rapidly like the running of a horse at a rate of speed of 10% – 20% per annum, it is called running inflation.
70. Which of this inflation is caused by the increase in price rates of goods at two or three digits per annum?
a) Galloping Inflation
b) Creeping Inflation
c) Demand-pull Inflation
d) Running Inflation
Explanation
Galloping inflation: Galloping inflation or hyperinflation points out to unmanageably high inflation rates that run into two or three digits. By high inflation the percentage of the same is almost 20% to 100% from an overall perspective.
71. Which of this country faced the first hyperinflation of the 21st century?
a) Brazil
b) Cuba
c) Nepal
d) Zimbabwe
Explanation
The first hyperinflation of the 21st century Zimbabwe’s annual inflation rate surged to an unprecedented 3714 percent at the end of April 2007.
72. Assertion (A): Demand and supply decides the inflation levels of a society.
Reasoning(R): Demand for a product is low and the supply is high causes the Demand-pull Inflation.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Demand-Pull Inflation: Demand and supply play a crucial role in deciding the inflation levels in the society at all points of time. For instance, if the demand is high for a product and supply is low, the price of the products increases.
73. Which of these does not cause the Cost-push Inflation?
a) Increase in cost of raw materials
b) Increase in labor wages
c) Inputs cost increase
d) Increase in goods
Explanation
Cost-Push Inflation: When the cost of raw materials and other inputs raises inflation results. Increase in wages paid to labor also leads to inflation.
74. Match
A. Credit Inflation i) Excess supply of money
B. Deficit induced Inflation ii) Liberal bank credits
C. Currency Inflation iii) The Central Bank
a) i, iii, ii
b) ii, iii, i
c) i, ii, iii
d) iii, i, ii
Explanation
Currency inflation: The excess supply of money in circulation causes rise in price level. Credit inflation: When banks are liberal in lending credit, the money supply increases and thereby rising prices.
Deficit induced inflation: The deficit budget is generally financed through printing of currency by the Central Bank. As a result, prices rise.
75. Which of this inflation is a result of higher profit aim of firms?
a) Tax induced inflation
b) Deficit induced inflation
c) Profit induced inflation
d) Scarcity induced inflation
Explanation
Profit induced inflation: When the firms aim at higher profit, they fix the price with higher margin. So prices go up.
76. Which of this country experienced the scarcity induced inflation in the year 2019?
a) Venezuela
b) Angola
c) Iran
d) Sudan
Explanation
Scarcity induced inflation: Scarcity of goods happens either due to fall in production (eg. farm goods) or due to hoarding and black marketing. This also pushes up the price. This has happened is Venezuela in the year 2018.
77. Which of these causes the Taxflation?
a) Increase in Excise duty and custom duty
b) Decrease in Direct taxes
c) Reduced rate of people savings rate
d) All the above
Explanation
Tax induced inflation: Increase in indirect taxes like excise duty, custom duty and sales tax may lead to rise in price (eg. petrol and diesel). This is also called taxflation.
78. In which of this condition the inflation rate will be increased?
a) Lower GDP rate
b) Higher developmental activities
c) Higher growth rate of the nominal money supply
d) Lower disposable income rate of the people
Explanation
Increase in Money Supply: Inflation is caused by an increase in the supply of money which leads to increase in aggregate demand. The higher the growth rate of the nominal money supply the higher is the rate of inflation.
79. What are the causes for increase in the disposable income of the people of a nation?
a) Rise in national income
b) Reduction in taxes
c) People savings reduction
d) All the above
Explanation
When the disposable income of the people increases, it raises their demand for goods and services. Disposable income may increase with the rise in national income or reduction in taxes or reduction in the saving of the people.
80. Assertion (A): Cheap money policy raises the demand for goods and services in the economy.
Reasoning(R): Expanding government activities in developmental and social welfare programs reduces the price.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Government activities have been expanding due to developmental activities and social welfare programs. This is also a cause for price rise. Cheap money policy or the policy of credit expansion also leads to increase in the money supply which raises the demand for goods and services in the economy.
81. Which of these increase the demand for goods and services?
a) Hire purchase
b) Installment basis
c) High Margin
d) Both a and b
Explanation
The demand for goods and services increases when they are given credit to buy goods on hire-purchase and installment basis.
82. Define Deficit Financing.
a) Decrease the demand to aggregate supply
b) Printing more currencies
c) Government borrows from public
d) Both b and c
Explanation
In order to meet its mounting expenses, the government resorts to deficit financing by borrowing from the public and even by printing more notes. This raises aggregate demand in relation to aggregate supply, thereby leading to inflationary rise in prices.
83. Assertion (A): Black marketing increases the aggregate demand and the prices.
Reasoning(R): People spend black money lavishly.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The existence of black money and black assets due to corruption tax evasion etc., increase the aggregate demand. People spend such money lavishly. Black marketing and hoarding reduces the supply of goods. These trends tend to raise the price level further.
84. What happens when the government repays its internal debt to the Public?
a) Increase the money supply with the public.
b) Decrease the price for goods and services.
c) Increase the investors
d) Inflation is moderate.
Explanation
Whenever the government repays its past internal debt to the public, it leads to increase in the money supply with the public. This tends to raise the aggregate demand for goods and services.
85. How many categories are classified under the effects of Inflation?
a) 3
b) 2
c) 5
d) 4
Explanation
The effects of inflation can be classified into two heads :(1) Effects on Production and (2) Effects on Distribution.
86. Assertion (A): If the Inflation is high it acts as an incentive to traders and producers.
Reasoning(R): The Business class increases their investments due to the price rise.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
When the inflation is very moderate it acts as an incentive to traders and producers. This is particularly prior to full employment when resources are not fully utilized. The profit due to rising prices encourages and induces business class to increase their investments in production leading to generation of employment and income.
87. Choose the correct statements.
i) During inflation debtors are the losers and the creditors are the gainers.
ii) Debtors repay the loans when the purchasing power of money is low.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Debtors and Creditors: During inflation, debtors are the gainers while the creditors are losers. The reason is that the debtors had borrowed when the purchasing power of money was high and now repay the loans when the purchasing power of money is low due to rising prices.
88. Which sector people is worst affected by the inflation?
a) Share Holders
b) Fixed Income groups
c) Entrepreneurs
d) All the above
Explanation
The fixed incomes groups are the worst hit during inflation because their incomes being fixed do not bear any relationship with the rising cost of living. Examples are wage, salary, pension, interest, rent etc.
89. Assertion (A): Inflation is the boon to the entrepreneurs and Businessmen.
Reasoning(R): Business enterprises experience windfall gains as the prices of stocks are increased.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Inflation is the boon to the entrepreneurs whether they are manufacturers, traders, merchants or businessmen, because it serves as a tonic for business enterprise. They experience windfall gains as the prices of their inventories (stocks) suddenly go up.
90. Assertion (A): During Inflation the investors invented in bonds and securities lose much.
Reasoning(R): The people invented in shares gain by rich dividends in inflation period.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The investors who generally invest in fixed interest yielding bonds and securities have much to lose during inflation. On the contrary those who invest in shares stand to gain by rich dividends and appreciation in value of shares.
91. How many measures are suggested by Keynes and Milton to control of inflation?
a) 5
b) 3
c) 7
d) 8
Explanation
Keynes and Milton Friedman together suggested three measures to prevent and control of inflation. (1) Monetary measures (2) Fiscal measures (J.M. Keynes) and (3) Other measures.
92. Which of these measures are not adopted by the Central Bank of the country?
a) Sale of Private securities in the Open Market
b) Increase in Bank rate
c) Higher Margin Requirements
d) CRR and SLR
Explanation
These measures are adopted by the Central Bank of the country. They are (i) Increase in Bank rate (ii) Sale of Government Securities in the Open Market (iii) Higher Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) (iv) Consumer Credit Control and (v) Higher margin requirements (vi) Higher Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate.
93. Which of these is the major anti-inflationary fiscal measure?
a) Reduction of Government Expenditure
b) Public Borrowing
c) Enhancing Taxation
d) All the above
Explanation
Fiscal policy is now recognized as an important instrument to tackle an inflationary situation. The major anti-inflationary fiscal measures are the following: Reduction of Government Expenditure, Public Borrowing and Enhancing taxation.
94. Which is referred as the short term measure to control inflation?
a) Rationing
b) Monetary measures
c) Fiscal measures
d) Accelerating economic growth
Explanation
Short-term measures can be in regard to public distribution of scarce essential commodities through fair price shops (Rationing). In India whenever shortage of basic goods has been felt the government has resorted to import so that inflation may not get triggered.
95. What are the features of Deflation?
a) Falling prices
b) Reduced money supply
c) Unemployment
d) All the above
Explanation
Deflation: The essential feature of deflation is falling prices, reduced money supply and unemployment. Though falling prices are desirable at the time of inflation, such a fall should not lead to the fall in the level of production and employment. But if prices fall from the level of full employment both income and employment will be adversely affected.
96. Assertion (A): Disinflation is the slowdown rate of inflation by controlling the amount of credit.
Reasoning(R): It is also referred as the process of reversing inflation with unemployment.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Disinflation is the slowing down the rate of inflation by controlling the amount of credit (bank loan, hire purchase) available to consumers without causing more unemployment. Disinflation may be defined as the process of reversing inflation without creating unemployment or reducing output in the economy.
97. Which of these are combined to form the stagflation?
a) High Economic Growth, Low inflation, High Unemployment
b) High Unemployment, High Inflation, stagnant economic growth
c) High inflation, Low Employment, Decreased Economic growth
d) Low Employment, Low Inflation, Low stagnant economic growth
Explanation
Stagflation: Stagflation is a combination of stagnant economic growth, high unemployment and high inflation.
98. Which is not referred to the study of the economic activity periods?
a) Business Cycle
b) Capitalist Cycle
c) Trade Cycle
d) Industrial Fluctuation
Explanation
The economic activity in a capitalist economy will have its periodic ups and downs. The study of these ups and downs is called the study of Business cycle or Trade cycle or Industrial Fluctuation.
99. Which of these economic factors are referred by a Trade cycle?
a) Employment
b) Income
c) Output
d) All the above
Explanation
A Trade cycle refers to oscillations in aggregate economic activity particularly in employment, output, income, etc. It is due to the inherent contraction and expansion of the elements which energize the economic activities of the nation. The fluctuations are periodical, differing in intensity and changing in its coverage.
100. Assertion (A): The Periods of trade cycle is composed of Good trade and Bad trades.
Reasoning(R): The Good trade is characterized by rising prices and low unemployment percentages.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
“A trade cycle is composed of periods of good trade characterized by rising prices and low unemployment percentages altering with periods of bad trade characterized by falling prices and high unemployment percentages”.- J.M. Keynes
101. Which is not a phase of Trade cycle?
a) Boom
b) Growth
c) Recession
d) Depression
Explanation
The four different phases of trade cycle is referred to as (i) Boom (ii) Recession (iii) Depression and (iv) Recovery.
102. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Boom period is characterized by the full employment and the movement beyond that.
ii) The demand for the bank credit increases during the Boom period.
iii) There is a slow economic activity during this boom period.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The full employment and the movement of the economy beyond full employment is characterized as boom period. During this period, there is hectic activity in economy. Money wages rise, profits increase and interest rates go up. The demand for bank credit increases and there is all-round optimism.
103. Assertion (A): Recession happens after the returning point from boom condition.
Reasoning (R): Liquidity preference of the people decreases and money market becomes easier.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Recession: The turning point from boom condition is called recession. This happens at higher rate, than what was earlier. Generally, the failure of a company or bank bursts the boom and brings a phase of recession. Investments are drastically reduced, production comes down and income and profits decline. There is panic in the stock market and business activities show signs of dullness. Liquidity preference of the people rises and money market becomes tight.
104. State the result of depression.
a) Loss in firms
b) Business closure
c) Unemployment
d) All the above
Explanation
During depression the level of economic activity becomes extremely low. Firms incur losses and closure of business becomes a common feature and the ultimate result is unemployment.
105. Which is the extreme point of depression?
a) Trough
b) Revival
c) Growth
d) Prosperity
Explanation
Depression is the worst phase of the business cycle. Extreme point of depression is called as “trough” because it is a deep point in business cycle.
106. Who advocated that the autonomous investment of the government only can end the depression?
a) Davanzatti
b) Irving Fisher
c) Marshall
d) J.M.Keynes
Explanation
An economy fell down in trough could not come out from this without external help. Keynes advocated that autonomous investment of the government alone can help the economy to come out from the depression.
107. What is the ending point of depression?
a) Recovery
b) Recession
c) Growth
d) Prosperity
Explanation
After a period of depression recovery sets in. This is the turning point from depression to revival towards upswing. It begins with the revival of demand for capital goods. Autonomous investments boost the activity.
108. By which of this process recovery may be initiated?
a) Innovation
b) Government Expenditure
c) Autonomous Investment
d) All the above
Explanation
Recovery may be initiated by innovation or investment or by government expenditure (autonomous investment).
109. Which of these are termed as Narrow money by the RBI?
a) M1, M4
b) M2, M4
c) M1, M2
d) M3, M2
Explanation
Money supply is a stock variable. RBI publishes information for four alternative measures of Money supply namely M1, M2, M3 and M4. M1 and M2 are known as narrow money. M3 and M4 are known as broad money. The gradations are in decreasing order of liquidity.
110. Which of this currency has the lowest value globally?
a) Iranian Rial
b) Kuwaiti Dinar
c) Indonesian Rupiah
d) Paraguayan Guarani
Explanation
The Iranian Rial is the least valued currency in the world. It is the lowest currency to USD.