Science Notes
Magnetism Notes 6th Science Lesson 13 Notes in English
6th Science Lesson 13 Notes in English
13] Magnetism
Discovery of Magnets
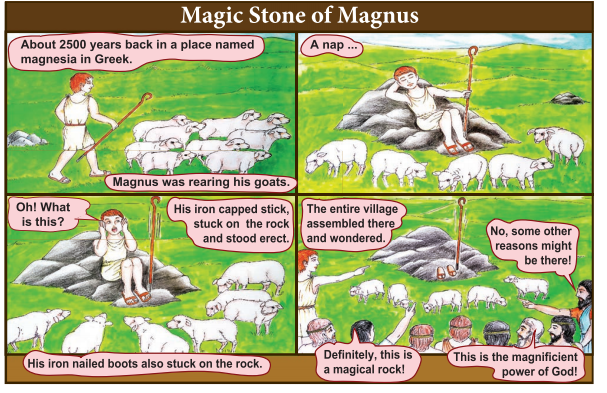
- People wondered about this incident, each and everyone expressed their views.
- What might be the reason for the stick, to get stuck on the rock?
- Yes, you are right. That is a magnetic rock. People found it attracting not only for the stick of Magnus, but also for all the materials made of iron.
- The more rocks of these kinds were found worldwide.
- These magnetic rocks were named ‘Magnets’ and the ore is called as ‘Magnetite’ after the name of the boy Magnus.
- The name is also supposed to come after the name of the place (Magnesia) in which it was found.
- Magnetite was the ore with attracting property found in that region. Magnetites are natural magnets. They are called magnetic stones.
- Natural magnets do not have a definite shape.
- Since, they are used for finding direction, they are also called ‘leading stones’ or ‘lode stones’.
Magnet of different shapes


- After learning the method of changing the piece of iron into magnet (magnetization) we have been making and using several kinds of magnets.
- Such man-made magnets are called artificial magnets.
- Bar-magnet, Horseshoe magnet, Ring magnet and Needle magnet are generally used artificial magnets
- Oval-shape, Disc shapes Cylindrical and magnets are also available.
Magnetic and Non Magnetic Materials

- Substances which are attracted by magnet are called magnetic substances. Iron, cobalt, nickel are magnetic substances.
- Substances which are not attracted by magnet are called non-magnetic substances. Paper, plastic are called non- magnetic substances.
Magnetic Poles
- Place some iron filings on a paper. Place a bar magnet horizontally in the filings and turn it over a few times.
- Now lift the magnet.
- What do you see?
- Which part of the magnet has more iron filings sticking to it?
- Which part of the magnet has almost no filings sticking to it?
- The parts of the magnet those attract the largest amount of iron filings are called as its poles.
- The attractive force of the magnet is very large near the two ends. These two ends are called its poles.
- If you have a horseshoe magnet, or any other type of magnet at home, find the position of its poles by this experiment.
- In experiments with magnets you will need to use iron filings again and again.
- You can do this by placing a magnet in a pile of sand and turning it around in the sand.
- The small pieces of iron present in the sand will stick to the magnet. If you cannot find sand you can look for iron pieces in clayey soil as well.
- If you don’t have iron filings, you can collect small pieces of iron and they will serve the purpose as well.
Finding directions with a magnet
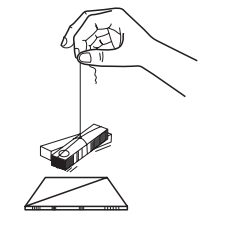
- Tie a piece of thread to the centre of a bar magnet and suspend it. Note, in which direction the magnet stops.
- Draw a line on a sheet of cardboard or the table along the direction in which the bar magnet stops
- This is roughly the north-south direction. The end of the magnet that points to the north is called the North Pole.
- The end that points to the south is called the South Pole.
- A freely suspended magnet always comes to rest in north-south direction.
- The directive property of magnets has been used for centuries to find directions.
- Around 800 years ago, the Chinese discovered that a suspended lode stone stops in the north-south direction.
- Chinese used these lode stones to find directions.
- The navigators of that country used to keep a piece of lode stone suspended in their boats and during a storm or mist, they used the lode stone to locate directions.
Magnetic compass

- A compass is an instrument which is used to find directions.
- It is mostly used in ships and airplanes.
- As a rule, mountaineers also carry a compass with them so that they do not lose their way in unknown places.
- The compass has a magnetic needle that can rotate easily. The marked end of the needle is the North Pole of the magnet.
- Can you use magnetic compass to find west direction?
- Ask your teacher to help you in using magnetic compass.
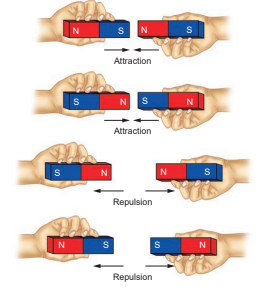
Properties of Magnets
Attraction or Repulsion
- Take two similar magnets, place them in four different ways as shown in Figure.
- Do magnets lose their properties? When?
- Magnets lose their properties if they are heated or dropped from a height or hit with a hammer.
- Magnets lose their properties when they are placed near Cellphone, Computer, DVDs. These objects will also get affected by magnetic field.
Storage of Magnets
- Improper storage can also cause magnets to lose their properties.
- To keep them safe, bar magnets should be kept in pairs with their unlike poles on the same side.
- They must be separated by a piece of wood and two pieces of soft iron should be placed across their ends.

- For a horse-shoe magnet a single piece of soft iron can be used as a magnetic keeper across the poles.
Usage of Magnets

- We use various equipment with magnets in day to day life.
- Discuss with your friends about the usage of the magnets in the following instances.
Science Today – Bullet Trains
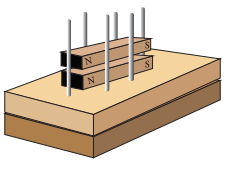
- We know that like poles of the magnets repel each other.
- keep two Bar magnets as shown in figure.
- By using repulsion we can levitate a magnetic object. Let us make a toy and enjoy magnetic levitation.
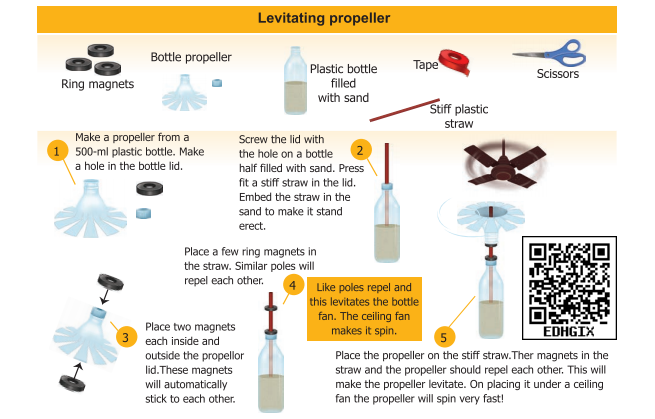

How does the electromagnetic train work?
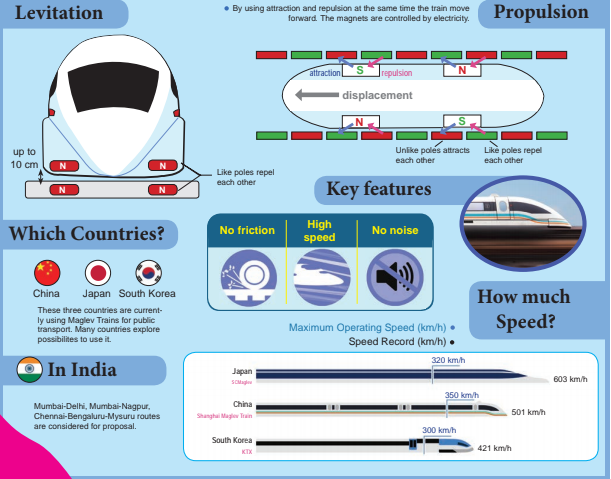
- Electromagnets are used in Electromagnetic train.
- Electromagnets are magnetised only when current flows through them.
- When the direction of current is changed the poles of the electromagnets are also changed.
- Like poles of the magnets which are attached at the bottom of the train and rail track repel each other. So, the train is lifted from the track up to a height of 10 cm.
- We know that we can move any magnetic object with the force of attraction or repulsion properties of magnets.
- This train also moves with the help of the magnets attached on the sides of track and the magnets fitted at the bottom sideway of the train.
- By controlling the current we can control the magnets and movement of the train.
- As there are no moving parts, there is no friction. So, the train can easily attain a speed of 300 km per hour. These trains are capable of running up to 600 km/ hour.
- They do not make any noise.
- They require less energy and they are eco-friendly.
- Even though, many countries have taken effort to use these trains, such trains are used for public transport only in China, Japan and South Korea.
- In India the possibilities of introducing these trains are under consideration.