Lithosphere – II Exogenetic Processes 9th Social Science Lesson 20 Questions in English
9th Social Science Lesson 20 Questions in English
20] Lithosphere – II Exogenetic Processes
1. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The Earth is a dynamic system that undergoes various changes due to internal and external processes
- The continuous interaction of these two processes controls the structure of the earth’s surface
- The external processes are the consequence of the earth’s internal heat.
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- 1, 2
- All the above
Explanation
The Earth is a dynamic system that undergoes various changes due to internal and external processes. The continuous interaction of these two processes controls the structure of the earth’s surface. The external processes are the consequence of solar energy and gravitational forces, whereas the internal processes are an outcome of the earth’s internal heat.
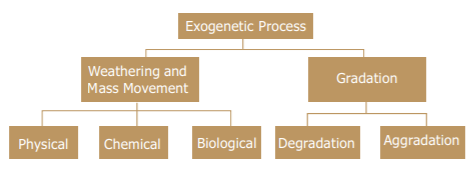
2. Which of the following results in Weathering and Mass Movement?
- Physical
- Chemical
- Aggradation
- Biological
- 1, 2, 3
- 1, 2, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- All the above
Explanation
3. Assertion(A): Weathering is the breaking, disintegration and decomposition of materials of the
earth’s crust by their exposure to atmosphere
Reason(R): There are three types of weathering Physical weathering, Chemical weathering and
Biological weathering
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
Weathering is the breaking, disintegration and decomposition of materials of the earth’s crust by their exposure to atmosphere. There are three types of weathering • Physical weathering, • Chemical weathering and • Biological weathering
4. Which of the following statement about Physical weathering is correct?
- It is the breakdown of rocks without changing their chemical composition, through the action of physical forces.
- The constant freezing and thawing of rocks during the night and day leads to the expansion and contraction of rocks
- Cracks are formed and disintegration occurs eventually.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Physical weathering is the breakdown of rocks without changing their chemical composition, through the action of physical forces. The constant freezing and thawing of rocks during the night and day leads to the expansion and contraction of rocks. Cracks are formed and disintegration occurs eventually. Exfoliation, block disintegration, granular disintegration etc., are the different types of weathering.
5. The peeling of rocks, layer by layer like an onion takes place in_______
- Block disintegration
- Exfoliation
- Granular disintegration
- All the above
Explanation
The alternate heating and cooling on rounded rock surfaces leads to the peeling of rocks, layer by layer like an onion. This is called exfoliation. sheeting and shattering are the other forms of exfoliation.
6. Granular Disintegration takes place in_____
- Sedimentary rocks
- Igneous rocks
- Crystalline rocks
- All the above
Explanation
Granular disintegration takes place in crystalline rocks where the grains of the rocks become loose and fall out. This is due to the action of temperature and frost.
7. Block Disintegration is the result of_____
- Expansion
- Contraction
- Frost
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Repeated expansion and contraction of rocks during day and night respectively causes stress on the joints of the rocks which results in block disintegration.
8. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Disintegration and decomposition of rocks due to chemical reactions is called Chemical Weathering
- Chemical weathering takes place through the processes of oxidation, carbonation, solution, and hydration
- The agents of Chemical weathering are Oxygen, Carbon-dioxide, Hydrogen and water
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Disintegration and decomposition of rocks due to chemical reactions is called Chemical Weathering. This is predominantly high in the hot and humid regions such as the equatorial, tropical and sub-tropical zones. Chemical weathering takes place through the processes of oxidation, carbonation, solution, and hydration. The agents of Chemical weathering are Oxygen, Carbon-dioxide, Hydrogen and water.
9. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Oxygen in the atmosphere reacts with the iron found in rocks, thus leads to the formation of iron oxide
- Carbonation is the mixing of water with the atmospheric carbon-dioxide, forming carbonic acid.
- When the carbonic acid reacts with the carbonate rocks, the rocks get disintegrated
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Oxygen in the atmosphere reacts with the iron found in rocks, thus leads to the formation of iron oxide. This process similar to the rusting of iron, pressure of air and water is known as oxidation, which results in the weakening of rocks. Carbonation is the mixing of water with the atmospheric carbon-dioxide, forming carbonic acid. Carbonation is important in the formation of caves, in limestone region. When the carbonic acid reacts with the carbonate rocks, the rocks get disintegrated. The process of dissolution of rock substances in water result in the loosening of the rock particles. This in-turn breaks down the rocks. Absorption of water into the mineral structure, certain chemicals in the rock enlarge in size in humid conditions. These minerals found in the rock swell and this results in the development of cracks and the rock wears down. This type of weathering is called hydration Biological weathering occurs due to the penetration and expansion of plant roots, earthworms, burrowing animals (rabbits, rats) and some human activities.
10. Which of the following are included in Gradation?
- Erosion
- Transportation
- Deposition
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Gradation is the process of levelling of the land by means of natural agents like rivers, ground water, winds, glaciers, and sea waves. These agents produce various gradational relief features in due course of time. Gradation takes place in two ways: degradation and aggradation Gradation or Denudation is the levelling wearing down of the land surface by various natural agents. Aggradation is building up of landforms due to natural agents. Degradation is eroding of land surface.
Gradation = Erosion + Transportation + Deposition
11. Assertion(A): Rivers originate on higher landforms like, mountains, hills and plateaus that receive water from various sources like the rain, glaciers, springs, lakes, etc.
Reason(R): The work of running water (rivers) is the most extensive among all the other agents
of gradation.
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
The work of running water (rivers) is the most extensive among all the other agents of gradation. Rivers originate on higher landforms like, mountains, hills and plateaus that receive water from various sources like the rain, glaciers, springs, lakes, etc. The place where the river originates is called its source and where it joins the sea is known as its mouth.
12. Based on course rivers are classified into_____ types
- Two
- Three
- Four
- Five
Explanation
Rivers generally originate from mountains and end in a sea or lake. The whole path that a river flows through is called its course. The course of a river is divided into:
i. The upper course
ii. The middle course
iii. The lower course
13. Which of the following land features are carved by a river in its upper course?
- V-shaped valleys
- Gorges
- Ox-bow lakes
- Spurs
- 1, 2, 4
- 1, 3, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- All the above
Explanation
The land features carved by a river in its upper course are Vshaped valleys, gorges, canyons, rapids, pot holes, spurs, and waterfalls.
14. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Erosion is the most dominant action of river in the upper course
- The steep gradient increases the velocity and the river channel performs erosion with great force to widen and deepen its valley.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Erosion is the most dominant action of river in the upper course. In this course, a river usually tumbles down the steep mountain slopes. The steep gradient increases the velocity and the river channel performs erosion with great force to widen and deepen its valley.
15. Which of the following statement about Middle Course is correct?
- The river enters the plain in its middle course
- Deposition also occurs due to the sudden decrease in velocity.
- The river in the middle course develops some typical landforms like alluvial fans, flood plains, meanders, ox-bow lakes etc.,
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The river enters the plain in its middle course. The volume of water increases with the confluence of many tributaries and thus increases the load of the river. Thus, the predominant action of a river is transportation. Deposition also occurs due to the sudden decrease in velocity. The river in the middle course develops some typical landforms like alluvial fans, flood plains, meanders, ox-bow lakes etc.,
16. The river splits into a number of channels called as______
- Tributary
- Distributary
- Deposition
- All the above
Explanation
The river, moving downstream across a broad, level plain is loaded with debris, brought down from its upper and middle courses. Large deposits of sediments are found at the level bed and the river, splits into a number of channels called distributaries. The main work of the river here is deposition and it develops typical landforms like delta and estuary.
17. Which of the following is a Tributary?
- Kaveri
- Bhavani
- Kollidam
- All the above
Explanation

18. Which of the following rivers in India forms deep gorges in India?
- Brahmaputra
- Tethys
- Indus
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
When the river flows through a mountainous region made up of hard rocks, it forms a valley with almost vertical sides called gorge. In India, deep gorges have been formed by Brahmaputra and Indus in the Himalayas. A deep gorge with steep sides that runs for hundreds of kilometres is referred to as canyon e.g. Grand Canyon of the river Colorado in the U.S.A.
19. The highest waterfalls in the world is_______
- Angel Falls
- Jog Falls
- Amazon Falls
- Niagara Falls
Explanation
When a river flows in a region where hard rocks lie over soft rocks horizontally, the soft rocks get eroded quickly and the hard rocks projects outwards. Thus, the river falls vertically from a steep slope to form a waterfall. When the water falls with great force, it erodes the rock material beneath and creates a depression called a plunge pool. Shallow fast flowing water in a stream is called a rapid or river jumps. The highest waterfalls in the world is Angel falls (979 m) in Venezuela.
20. A ‘V’- shaped valley is formed by the____ erosion of the river
- Horizontal
- Vertical
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
A ‘V’- shaped valley is formed by the vertical erosion of the river where the valley is deepened and widened. Due to the river action, cylindrical holes are drilled vertically in the river bed, with varying depth and diameter. These are called pot holes.
21. In which state of India Asia’s largest fresh water ox bow lake located?
- Tamil Nadu
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Bihar
- Himachal Pradesh
Explanation
As the river loaded with debris flows slowly, it forms sweeping loops and bends. It is referred to as meanders. Meanders in due course of time become almost a complete circle with narrow necks. This in turn gets abandoned and forms a lake. This is called an Ox-bow lake. The world’s largest oxbow lake is Lake Chicot is Arkansas of USA. Lake Kanwar in Bihar (India) is Asia’s largest fresh water ox bow lake.
22. Which of the following statement is correct?
- A fan shaped deposition made by the river at the foothills is called an alluvial plain
- Fine sediments are deposited on river banks when a river floods which make the region rich and fertile called as a flood plain
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
A fan shaped deposition made by the river at the foothills is called an alluvial plain. Fine sediments are deposited on river banks when a river flood take place. These sediments make the region rich and fertile. This is called a flood plain. As the height of the river banks gets increases due to continuous deposition of a flooded river, levees are formed.
23. Which of the following about Estuary is correct?
- Deposition of silt by the river is not possible
- Deposition of silt by the river is possible
- Estuary is formed where the rives meets the lake
- None
Explanation
Estuary is formed where the rives meets the sea. Deposition of silt by the river is not possible here in the estuaries like delta as if the waves keep on eroding the deposits. Ex. River Narmada and Tapti.
24. Which of the following statement is correct?
- A triangular shaped low-lying area formed by the river at its mouth is called delta
- Cauvery Delta is located Tamil Nadu and Kerala
- Deltas have fine deposits of sediments enriched with minerals.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
A triangular shaped low-lying area formed by the river at its mouth is called delta. Deltas have fine deposits of sediments enriched with minerals. E.g. Cauvery Delta, Tamil Nadu.
25. ________ is the largest delta in the world
- Ganga- Yamuna Delta
- Ganga-Brahmaputra Delta
- Nile and Yondli Delta
- Cauvery Delta
Explanation
The Greek letter pronounced delta closely resembles the triangular delta of the river Nile. The Ganga-Brahmaputra Delta is the largest delta in the world. Facts The world’s best-known geyser is the Old Faithful geyser in the Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming, U.S.A.
26. Karst topography is formed due to the dissolution of soluble rocks such as_______
- Limestone
- Dolomite
- Gypsum
- All the above
Explanation
As an agent of gradation, underground water creates distinct landforms in limestone regions called Karst Topography. Ground water is an active agent in limestone regions. Karst topography is formed due to the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite and gypsum.
27. Match the Karst Areas in India with their respective states:
- Borra caves 1. Uttarakhand
- Kutumsar 2. Madhya Pradesh
- Robert cave 3. Andhra Pradesh
- Pandav caves 4. Chattisgarh
- 1, 3, 2, 4
- 3, 4, 1, 2
- 3, 1, 2, 4
- 4, 1, 2, 3
Explanation
Limestone topography of Western Slovenia extends for a distance of 480 km in length and 80 km in width which is termed as Karst in the Slavic language. The world’s largest karst area is the Nullarbar located on the Great Australian Coast. Karst regions are also found in Southern France, Spain, Mexico, Jamaica, Western Cuba, Central New Guinea, Sri Lanka and Myanmar.

28. Assertion(A): Rain water and Co2 destroys limestone
Reason(R): When rain water mixes with carbon-di- oxide and enters into a limestone region, it
dissolves and destroys much of the limestone.
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
Most of erosion takes place due to the process of solution. When rain water mixes with carbon-di- oxide and enters into a limestone region, it dissolves and destroys much of the limestone. As a result, landforms such as Terra rossa, Lappies, sinkholes, swallow holes, dolines, uvalas, poljes, caves and caverns are formed.
29. The redness of the soil is due to the presence of______
- Iron
- Iron oxide
- Calcium oxide
- Ferrous sulphate
Explanation
Deposition of red clay soil on the surface of the Earth is due to the dissolution of limestone content in rocks. The redness of the soil is due to the presence of iron oxide. When the joints of limestone rocks are corrugated by groundwater, long furrows are formed and these are called LAPPIES.
30. The average depth ranges between of sinkholes ranges between____
- Two and nine meters
- Three and nine meters
- Three and six meters
- Five and nine meters
Explanation
A funnel shaped depression formed due to dissolution of limestone rock is called sinkholes. Their average depth ranges between three and nine meters. The World’s deepest sinkhole is China’s xianozhai Tienkang at 2172 feet. There are as many as 15000 Sinkholes in Illinois.
31. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Caves and caverns are subterranean features of karst topography.
- Caverns are the caves with irregular floors.
- All types of deposits in the caves and caverns are collectively called speleothems
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Caves and caverns are subterranean features of karst topography. Caves are hollows that are formed by the dissolution of limestone rocks when carbon di oxide in air turns into carbonic acid after its reaction with water. They vary in size and shape. Caverns are the caves with irregular floors. Eg. Guptadham caves in Western Bihar. All types of deposits in the caves and caverns are collectively called speleothems which includes travertines, tufa, dripstones. Swallow Holes, Uvalas, Dolines, Poljis are other erossional Features of karst regions predominant in other parts of the world. Cave insects lose their senses of sight and develop extraordinary long antenna to compensate the loss of sight.
32. When the calcite deposits rise upward like a pillar ________ are formed
- Stalactite
- Stalagmites
- Column
- All the above
Explanation
When the water containing dissolved calcite gradually drips from the ceiling of the caves, water evaporates and the remaining calcite hangs from the ceiling. Thus, Stalactites are formed. When the calcite deposits rise upward like a pillar Stalagmites are formed. Sometimes, Stalactites and Stalagmites meet together to form Columns or Pillars.
33. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Higher the latitude, higher the snowline from sea level.
- A Glacier is a large mass of ice that moves slowly over the land, from its place of accumulation
- It is also known as ‘River of ice’
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
A Glacier is a large mass of ice that moves slowly over the land, from its place of accumulation. It is also known as ‘River of ice’. The place of accumulation is called snowfield. The height above which there is a permanent snow cover in the higher altitude or latitude is called snowline. Higher the latitude, lower the snowline from sea level. Snowline of Alps is 2700 metre whereas the snowline of Greenland is just 600 metre.
34. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The pyramidal peaks formed when three or more cirques meet together (eg) Matterhorns
- Hanging Valley eroded by tributary glacier and that hangs over the main valley
- The glacier erodes the steep side walls of the mountain and forms a bowl-shaped armchair like depression, it is termed as Cirque
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Glaciers are powerful erosive agents. Some of the important erosional landforms are Cirque, Aretes, Matterhorn, U-shaped valley, Hanging valley, Fiords etc., Most of these glacial features are predominantly seen in countries like Switzerland, Norway etc.,
Cirque: The glacier erodes the steep side walls of the mountain and forms a bowl-shaped armchair like depression, it is termed as Cirque
Arete: Aretes are narrow ridges formed when two cirque walls joined together back to back, and forms narrow knife-like ridges.
Pyramidal Peak: The pyramidal peaks formed when three or more cirques meet together (eg) Matterhorns.
U-Shaped Valley: When the glacier moves down along a river valley, the valley further gets eroded deep and wide to form a ‘U’ shaped valley.
Hanging Valley: These are valleys eroded by tributary glacier and that hangs over the main valley.
Fjords are glacial valleys that are partly submerged in the sea.
35. Which of the following statement is correct?
- When air blows vertically at or near the earth’s surface is called wind
- The erosional, transportation and depositional action of wind is predominant in arid regions
- This is called as Aeolian Process.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
When air blows horizontally at or near the earth’s surface is called wind. The erosional, transportation and depositional action of wind is predominant in arid regions. This is called as Aeolian Process.
36. In Which state of India Mushroom Rock are found?
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Tamil Nadu
Explanation
Rocks are made up of hard and soft layers. When a rock’s bottom is soft, the sand-laden winds blow against it and wear it down. By the constant wearing down action of the wind, the bottom gets eroded away to form a mushroom like structure. This is called a mushroom or pedestal rock. Such rocks are found near Jodhpur in Rajasthan.
37. What does the term Inselberg mean?
- island mountain
- group of mountains
- Individual mountain
- Salty mountain
Explanation
Inselberg is a German term which means an island mountain. Certain hard rocks like igneous rocks are more resistant to wind action. Such isolated residual hills rising abruptly from their surroundings are termed as inselbergs. Eg. Uluru or Ayers Rock, Australia
38. Which of the following statement is correct?
- In arid regions, certain rocks have hard and soft layers arranged vertically.
- Barch are isolated, crescent shaped sand dunes.
- Transverse dunes are symmetrical in shape.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
In arid regions, certain rocks have hard and soft layers arranged vertically. When winds blow over these rocks, the soft layers get eroded leaving irregular crests. These are called yardangs.
Sand Dune: In deserts, during sandstorms, wind carries loads of sand. When the speed of wind decreases, huge amount of sand gets deposited. These mounds or hills of sand are called sand dunes. There are different types of sand dunes
Barchan: Barch are isolated, crescent shaped sand dunes. They have gentle slopes on the windward side and steep slopes on the leeward side.
Transverse Dunes: Transverse dunes are asymmetrical in shape. They are formed by alternate slow and fast winds that blow from the same direction.
Longitudinal Dunes (Seif dunes) Longitudinal dunes are long narrow ridges of sand, which extend in a direction parallel to the prevailing winds. These dunes are called Seifs in Sahara
39. The thickest known deposit of loess is found in____
- India
- China
- Australia
- USA
Explanation
The term loess refers to the deposits of fine silt and porous sand over a vast region. Extensive loess deposits are found in Northern and Western China, the Pampas of Argentina, in Ukraine and in the Mississippi Valley of the United States. The thickest known deposit of loess is, 335 metre found in the loess plateau in China.
40. Which of the following are the erosional landforms of sea waves?
- Sea cliff
- Arch
- wave cut platform
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
A steady up (crest) and down (trough) movement of surface water are called waves. Sea waves are the most powerful agents of gradation and their erosional, transportation and depositional processes are confined to a very narrow belt along coastal areas. Some of the erosional landforms of sea waves are sea cliff, sea cave, arch, stack, beach, bar and spit and wave cut platform.
41. Where does sea arch found in India?
- Gujarat
- Andaman and Nicobar
- Tamil Nadu
- West Bengal
Explanation
Sea cliffs are steep rock faces formed when sea waves dash against them. The rocks get eroded to form steep vertical walls. Prolonged wave attack on the base of a cliff erodes rock materials, which result in the formation of caves. When two caves approach one another from either side of a headland and unite, they form an arch. (Eg.) Neil Island, Andaman and Nicobar. Further erosion by waves ultimately leads to the total collapse of the arch. The seaward portion of the headland will remain as a pillar of rock known as stack. Eg the Old man of Hoy in Scotland. Flat surface found at the foot of sea cliffs are called as wave cut platforms. Wave cut platform is also referred as wave cut benches terrace.
42. Match the following:
- Juhu beach 1. Tamil Nadu
- Puri beach 2. Odisha
- Marina beach 3. Maharashtra
- 1, 2, 3
- 2, 1, 3
- 3, 2, 1
- 3, 1, 2
Explanation
Sand and gravel are moved and deposited by waves along the shore to form beaches. This is the most dominant and constructive work of the sea. (Eg.) Juhu beach along Mumbai coast, Puri beach in Odisha and Marina beach in Chennai. A bar is an elongated deposit of sand, shingle or mud found in the sea, almost parallel to the shoreline.
43. In which place a spit is found in India?
- Cochin
- Mumbai
- Kakinada
- Chennai
Explanation
A spit is a ridge or embankment of sediment, attached to the land on one end and terminating in open water on the other end. Spits are common at the mouth of estuaries. Eg. Kakinada spit