Light Online Test 8th Science Lesson 3 Questions in English
Light Online Test 8th Science Lesson 3 Questions in English
Light Online Test 8th Science Lesson 3 Questions in English
Quiz-summary
0 of 54 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
Information
Light Online Test 8th Science Lesson 3 Questions in English
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 54 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 54
1. Question
1. The radiant sky in the morning being filled with___________ colour.
Correct
Explanation
Lofty mountains covered with greenish vegetation, magnificent trees reaching up to the clouds, beautiful streams drifting down the valleys, bluish sea water roaring towards the coast and the radiant sky in the morning being filled with golden red colour, all give delight to our eyes and peace to our mind.
Incorrect
Explanation
Lofty mountains covered with greenish vegetation, magnificent trees reaching up to the clouds, beautiful streams drifting down the valleys, bluish sea water roaring towards the coast and the radiant sky in the morning being filled with golden red colour, all give delight to our eyes and peace to our mind.
-
Question 2 of 54
2. Question
2. Which of the following is not an optical instrument?
Correct
Explanation
Light is a form of energy and it travels in a straight line. You will also study about the laws of reflection and the laws of refraction and some of the optical instruments, such as periscope and kaleidoscope, which work on these principles.
Incorrect
Explanation
Light is a form of energy and it travels in a straight line. You will also study about the laws of reflection and the laws of refraction and some of the optical instruments, such as periscope and kaleidoscope, which work on these principles.
-
Question 3 of 54
3. Question
3. Which of the following statement is correct?
1) We use mirrors in our daily life for various purposes.
2) The mirror is an optical device with a polished surface that reflects the light falling on it
3) They are also used in scientific apparatus, like telescope
Correct
Explanation
We use mirrors in our daily life for various purposes. We use them for decoration. In vehicles, they are used as rear-view mirrors. They are also used in scientific apparatus, like telescope. The mirror is an optical device with a polished surface that reflects the light falling on it.
Incorrect
Explanation
We use mirrors in our daily life for various purposes. We use them for decoration. In vehicles, they are used as rear-view mirrors. They are also used in scientific apparatus, like telescope. The mirror is an optical device with a polished surface that reflects the light falling on it.
-
Question 4 of 54
4. Question
4. Which of the following metal can be used to coated for forming a typical mirror?
1) Silver
2) Mercury
3) Aluminium
Correct
Explanation
A typical mirror is a glass sheet coated with aluminium or silver on one of its sides to produce an image.
Incorrect
Explanation
A typical mirror is a glass sheet coated with aluminium or silver on one of its sides to produce an image.
-
Question 5 of 54
5. Question
5. Which of the following are mirrors are with curved surfaces?
1) Parabolic
2) Ellipsoid
3) Spherical
Correct
Explanation
Mirrors have a plane or curved surface. Curved mirrors have surfaces that are spherical, cylindrical, parabolic and ellipsoid.
Incorrect
Explanation
Mirrors have a plane or curved surface. Curved mirrors have surfaces that are spherical, cylindrical, parabolic and ellipsoid.
-
Question 6 of 54
6. Question
6. Which of the following statement is correct?
1) The shape of a mirror determines the type of image it forms
2) Plane mirrors form the perfect image of an object
3) Curved mirrors produce images that are always enlarged
Correct
Explanation
The shape of a mirror determines the type of image it forms. Plane mirrors form the perfect image of an object. Whereas, curved mirrors produce images that are either enlarged or diminished.
Incorrect
Explanation
The shape of a mirror determines the type of image it forms. Plane mirrors form the perfect image of an object. Whereas, curved mirrors produce images that are either enlarged or diminished.
-
Question 7 of 54
7. Question
7. Which of the following statement about Spherical mirror is correct?
Correct
Explanation
Spherical mirrors are one form of curved mirrors. If the curved mirror is a part of a sphere, then it is called a ‘spherical mirror’. It resembles the shape of a piece cut out from a spherical surface. One side of this mirror is silvered and the reflection of light occurs at the other side.
Incorrect
Explanation
Spherical mirrors are one form of curved mirrors. If the curved mirror is a part of a sphere, then it is called a ‘spherical mirror’. It resembles the shape of a piece cut out from a spherical surface. One side of this mirror is silvered and the reflection of light occurs at the other side.
-
Question 8 of 54
8. Question
8. Which of the following statement about concave mirror is correct?
1) A spherical mirror, in which the reflection of light occurs at its concave surface, is called a concave mirror
2) It diminishes object placed close to them
3) The most common example of a concave mirror is the make-up mirror
Correct
Explanation
A spherical mirror, in which the reflection of light occurs at its concave surface, is called a concave mirror. These mirrors magnify the object placed close to them. The most common example of a concave mirror is the make-up mirror.
Incorrect
Explanation
A spherical mirror, in which the reflection of light occurs at its concave surface, is called a concave mirror. These mirrors magnify the object placed close to them. The most common example of a concave mirror is the make-up mirror.
-
Question 9 of 54
9. Question
9. Which of the following statement is correct?
1) A spherical mirror, in which the reflection of light occurs at its convex surface, is called a convex mirror
2) The image formed by these mirrors is smaller than the object
3) Most common convex mirrors are rear viewing mirrors used in vehicles
Correct
Explanation
A spherical mirror, in which the reflection of light occurs at its convex surface, is called a convex mirror. The image formed by these mirrors is smaller than the object. Most common convex mirrors are rear viewing mirrors used in vehicles.
Incorrect
Explanation
A spherical mirror, in which the reflection of light occurs at its convex surface, is called a convex mirror. The image formed by these mirrors is smaller than the object. Most common convex mirrors are rear viewing mirrors used in vehicles.
-
Question 10 of 54
10. Question
10. In which of the following mirror the below safety warning is labelled: ‘Objects in the mirror are closer than they appear’
Correct
Explanation
Convex mirrors used in vehicles as rear-view mirrors are labelled with the safety warning: ‘Objects in the mirror are closer than they appear’ to warn the drivers. This is because inside the mirrors, vehicles will appear to be coming at a long distance.
Incorrect
Explanation
Convex mirrors used in vehicles as rear-view mirrors are labelled with the safety warning: ‘Objects in the mirror are closer than they appear’ to warn the drivers. This is because inside the mirrors, vehicles will appear to be coming at a long distance.
-
Question 11 of 54
11. Question
11. Assertion(A): A parabolic mirror has a concave reflecting surface
Reason(R): Its surface directs the entire incident beam of light to converge at its focal point.
Correct
Explanation
A parabolic mirror is one type of curved mirror, which is in the shape of a parabola. It has a concave reflecting surface and this surface directs the entire incident beam of light to converge at its focal point.
Incorrect
Explanation
A parabolic mirror is one type of curved mirror, which is in the shape of a parabola. It has a concave reflecting surface and this surface directs the entire incident beam of light to converge at its focal point.
-
Question 12 of 54
12. Question
12. Assertion(A): The light rays reflected by parabolic mirror travel a long distance, without getting Diminished.
Reason(R): Light rays generated by the source placed at this focal point will fall on this surface and they will be diverged in a direction, which is parallel to the principal axis of the parabolic mirror
Correct
Explanation
In the same way, light rays generated by the source placed at this focal point will fall on this surface and they will be diverged in a direction, which is parallel to the principal axis of the parabolic mirror. Hence, the light rays will be reflected to travel a long distance, without getting diminished.
Incorrect
Explanation
In the same way, light rays generated by the source placed at this focal point will fall on this surface and they will be diverged in a direction, which is parallel to the principal axis of the parabolic mirror. Hence, the light rays will be reflected to travel a long distance, without getting diminished.
-
Question 13 of 54
13. Question
13. Which of the following can be collected or projected using Parabolic reflectors?
Correct
Explanation
Parabolic mirrors, also known as parabolic reflectors, are used to collect or project energy such as light, heat, sound and radio waves.
Incorrect
Explanation
Parabolic mirrors, also known as parabolic reflectors, are used to collect or project energy such as light, heat, sound and radio waves.
-
Question 14 of 54
14. Question
14. Which of the following uses Parabolic reflectors?
1) Parabolic Telescope
2) Reflecting Telescope
3) Solar cooker
Correct
Explanation
Parabolic mirrors, also known as parabolic reflectors, used in reflecting telescopes, radio telescopes and parabolic microphones. They are also used in solar cookers and solar water heaters.
Incorrect
Explanation
Parabolic mirrors, also known as parabolic reflectors, used in reflecting telescopes, radio telescopes and parabolic microphones. They are also used in solar cookers and solar water heaters.
-
Question 15 of 54
15. Question
15. The first parabolic mirrors were constructed by______
Correct
Explanation
The principle behind the working of a parabolic mirror has been known since the Greco-Roman times. The first parabolic mirrors were constructed by Heinrich Hertz, a German physicist, in the form of reflector antennae in the year 1888.
Incorrect
Explanation
The principle behind the working of a parabolic mirror has been known since the Greco-Roman times. The first parabolic mirrors were constructed by Heinrich Hertz, a German physicist, in the form of reflector antennae in the year 1888.
-
Question 16 of 54
16. Question
16. ______ is the centre of the sphere from which the mirror is made
Correct
Explanation
Centre of Curvature is the centre of the sphere from which the mirror is made. It is denoted by the letter C in the ray diagrams. A ray diagram represents the formation of an image by the spherical mirror.
Incorrect
Explanation
Centre of Curvature is the centre of the sphere from which the mirror is made. It is denoted by the letter C in the ray diagrams. A ray diagram represents the formation of an image by the spherical mirror.
-
Question 17 of 54
17. Question
17._____ is the geometric centre of the spherical mirror
Correct
Explanation
Pole is the geometric centre of the spherical mirror. It is denoted by the letter P. When a beam of light is incident on a spherical mirror, the reflected rays converge (concave mirror) at or appear to diverge from (convex mirror) a point on the principal axis. This point is called the ‘focus’ or ‘principal focus’. It is also known as the focal point. It is denoted by the letter F in ray diagrams.
Incorrect
Explanation
Pole is the geometric centre of the spherical mirror. It is denoted by the letter P. When a beam of light is incident on a spherical mirror, the reflected rays converge (concave mirror) at or appear to diverge from (convex mirror) a point on the principal axis. This point is called the ‘focus’ or ‘principal focus’. It is also known as the focal point. It is denoted by the letter F in ray diagrams.
-
Question 18 of 54
18. Question
18. The line joining the pole of the mirror and its centre of curvature is called_____
Correct
Explanation
The line joining the pole of the mirror and its centre of curvature is called principal axis. Pole is the geometric centre of the spherical mirror. It is denoted by the letter P.
Incorrect
Explanation
The line joining the pole of the mirror and its centre of curvature is called principal axis. Pole is the geometric centre of the spherical mirror. It is denoted by the letter P.
-
Question 19 of 54
19. Question
19. _____ is the distance between the centre of the sphere and the vertex.
Correct
Explanation
Radius of Curvature is the distance between the centre of the sphere and the vertex. It is shown by the letter R in ray diagrams. (The vertex is the point on the mirror’s surface where the principal axis meets the mirror. It is also called as ‘pole’.)
Incorrect
Explanation
Radius of Curvature is the distance between the centre of the sphere and the vertex. It is shown by the letter R in ray diagrams. (The vertex is the point on the mirror’s surface where the principal axis meets the mirror. It is also called as ‘pole’.)
-
Question 20 of 54
20. Question
20. The distance between the pole and the principal focus is called_____
Correct
Explanation
The distance between the pole and the principal focus is called focal length (f) of a spherical mirror. There is a relation between the focal length of a spherical mirror and its radius of curvature. The focal length is half of the radius of curvature.
Incorrect
Explanation
The distance between the pole and the principal focus is called focal length (f) of a spherical mirror. There is a relation between the focal length of a spherical mirror and its radius of curvature. The focal length is half of the radius of curvature.
-
Question 21 of 54
21. Question
21. The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. Find its focal length
Correct
Explanation
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation

-
Question 22 of 54
22. Question
22. Focal length of a spherical mirror is 7 cm. What is its radius of curvature?
Correct
Explanation
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation

-
Question 23 of 54
23. Question
23. Which of the following statement is correct?
1) Images formed by spherical mirrors are of two types
2) Real images can be formed on a screen
3) Virtual images cannot be formed on a screen
Correct
Explanation
Images formed by spherical mirrors are of two types: i) real image and ii) virtual image. Real images can be formed on a screen, while virtual images cannot be formed on a screen.
Incorrect
Explanation
Images formed by spherical mirrors are of two types: i) real image and ii) virtual image. Real images can be formed on a screen, while virtual images cannot be formed on a screen.
-
Question 24 of 54
24. Question
24. Image formed by a convex mirror is____
1) Erect
2) Real
3) Virtual
4) Diminished
Correct
Explanation
Image formed by a convex mirror is always erect, virtual and diminished in size. As a result, images formed by these mirrors cannot be projected on a screen.
Incorrect
Explanation
Image formed by a convex mirror is always erect, virtual and diminished in size. As a result, images formed by these mirrors cannot be projected on a screen.
-
Question 25 of 54
25. Question
25. Assertion(A): As the object gets closer to a concave mirror, the image gets larger
Reason(R): The characteristics of an image are determined by the location of the object
Correct
Explanation
The characteristics of an image are determined by the location of the object. As the object gets closer to a concave mirror, the image gets larger, until attaining approximately the size of the object, when it reaches the centre of curvature of the mirror.
Incorrect
Explanation
The characteristics of an image are determined by the location of the object. As the object gets closer to a concave mirror, the image gets larger, until attaining approximately the size of the object, when it reaches the centre of curvature of the mirror.
-
Question 26 of 54
26. Question
26. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
1) Concave mirrors form a real image and it can be caught on a screen.
2) Depending on the position of the object in front of the mirror, the position, size and nature of the image will vary
Correct
Explanation
Concave mirrors form a real image and it can be caught on a screen. Unlike convex mirrors, concave mirrors show different image types. Depending on the position of the object in front of the mirror, the position, size and nature of the image will vary
Incorrect
Explanation
Concave mirrors form a real image and it can be caught on a screen. Unlike convex mirrors, concave mirrors show different image types. Depending on the position of the object in front of the mirror, the position, size and nature of the image will vary
-
Question 27 of 54
27. Question
27. In case of convex mirror, when the object is at infinity, image size is_____
Correct
Explanation
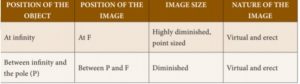 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation

-
Question 28 of 54
28. Question
28. Match the image size with the position of the object in the case of concave mirror:
I. At infinity 1. Highly magnified
II. At C 2. Highly diminished
III. Between C and F 3. Same size as the object
IV. At F 4. Magnified
Correct
Explanation
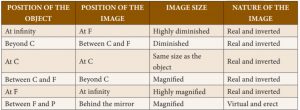 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation

-
Question 29 of 54
29. Question
29. Which of the following is not an application of Concave mirror?
Correct
Explanation
Applications Of Concave Mirrors:
Concave mirrors are used while applying make-up or shaving, as they provide a magnified image.
They are used in torches, search lights and head lights as they direct the light to a long distance.
They can collect the light from a larger area and focus it into a small spot. Hence, they are used in solar cookers.
They are used as head mirrors by doctors to examine the eye, ear and throat as they provide a shadow-free illumination of the organ.
They are also used in reflecting telescopes
Incorrect
Explanation
Applications Of Concave Mirrors:
Concave mirrors are used while applying make-up or shaving, as they provide a magnified image.
They are used in torches, search lights and head lights as they direct the light to a long distance.
They can collect the light from a larger area and focus it into a small spot. Hence, they are used in solar cookers.
They are used as head mirrors by doctors to examine the eye, ear and throat as they provide a shadow-free illumination of the organ.
They are also used in reflecting telescopes
-
Question 30 of 54
30. Question
30. Which of the following statement is correct?
1) Not all the objects can produce the same effect as produced by the plane mirror
2) Light, falling on a body having a shiny, polished and smooth surface alone is bounced back.
3) This bouncing back of the light rays as they fall on the smooth, shiny and polished surface is called reflection.
Correct
Explanation
Not all the objects can produce the same effect as produced by the plane mirror. A ray of light, falling on a body having a shiny, polished and smooth surface alone is bounced back. This bouncing back of the light rays as they fall on the smooth, shiny and polished surface is called reflection.
Incorrect
Explanation
Not all the objects can produce the same effect as produced by the plane mirror. A ray of light, falling on a body having a shiny, polished and smooth surface alone is bounced back. This bouncing back of the light rays as they fall on the smooth, shiny and polished surface is called reflection.
-
Question 31 of 54
31. Question
31. Which of the following statement is correct?
1) Reflection involves two rays: i) incident ray and ii) reflected ray
2) An imaginary line perpendicular to the reflecting surface, at the point of incidence of the light ray, is called the normal.
Correct
Explanation
Reflection involves two rays: i) incident ray and ii) reflected ray. The incident ray is the light ray in a medium falling on the shiny surface of a reflecting body. After falling on the surface, this ray returns into the same medium. This ray is called the reflected ray. An imaginary line perpendicular to the reflecting surface, at the point of incidence of the light ray, is called the normal.
Incorrect
Explanation
Reflection involves two rays: i) incident ray and ii) reflected ray. The incident ray is the light ray in a medium falling on the shiny surface of a reflecting body. After falling on the surface, this ray returns into the same medium. This ray is called the reflected ray. An imaginary line perpendicular to the reflecting surface, at the point of incidence of the light ray, is called the normal.
-
Question 32 of 54
32. Question
32. Which of the following rays are involved in law of reflection?
1) Incident ray
2) Reflected ray
3) Normal ray
Correct
Explanation
The relation between the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal is given as the law of reflection. The laws of reflection are as follows:
The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are always equal.
Incorrect
Explanation
The relation between the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal is given as the law of reflection. The laws of reflection are as follows:
The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are always equal.
-
Question 33 of 54
33. Question
33. ________ metal is the best reflector of light
Correct
Explanation
Silver metal is the best reflector of light. That’s why a thin layer of silver is deposited on the side of materials like plane glass sheets, to make mirrors.
Incorrect
Explanation
Silver metal is the best reflector of light. That’s why a thin layer of silver is deposited on the side of materials like plane glass sheets, to make mirrors.
-
Question 34 of 54
34. Question
34. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
1) The amount of reflection depends on the nature of the reflecting surface of a body
2) Based on the nature of the surface, reflection can be classified as regular and irregular reflection
Correct
Explanation
You have learnt that not all bodies can reflect light rays. Th e amount of reflection depends on the nature of the reflecting surface of a body. Based on the nature of the surface, reflection can be classified into two types namely, i) regular reflection and ii) irregular reflection.
Incorrect
Explanation
You have learnt that not all bodies can reflect light rays. Th e amount of reflection depends on the nature of the reflecting surface of a body. Based on the nature of the surface, reflection can be classified into two types namely, i) regular reflection and ii) irregular reflection.
-
Question 35 of 54
35. Question
35. Which of the following reflection is regular reflection?
1) Reflection of light by a plane mirror
2) Reflection of light from the surface of still water
3) Reflection of light from a wall
Correct
Explanation
When a beam of light (collection of parallel rays) falls on a smooth surface, it gets reflected. After reflection, the reflected rays will be parallel to each other. Here, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection of each ray will be equal. Hence, the law of reflection is obeyed in this case and thus a clear image is formed. This reflection is called ‘regular reflection’ or ‘specular reflection’. Example: Reflection of light by a plane mirror and reflection of light from the surface of still water
Incorrect
Explanation
When a beam of light (collection of parallel rays) falls on a smooth surface, it gets reflected. After reflection, the reflected rays will be parallel to each other. Here, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection of each ray will be equal. Hence, the law of reflection is obeyed in this case and thus a clear image is formed. This reflection is called ‘regular reflection’ or ‘specular reflection’. Example: Reflection of light by a plane mirror and reflection of light from the surface of still water
-
Question 36 of 54
36. Question
36. Which of the following statement about irregular reflection is correct?
1) In the case of a body having a rough or irregular surface, each region of the surface is inclined at different angles
2) Reflection of light from a wall is irregular reflection
3) Irregular reflection is also known as diffused reflection
Correct
Explanation
In the case of a body having a rough or irregular surface, each region of the surface is inclined at different angles. When light falls on such a surface, the light rays are reflected at different angles. In this case, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection of each ray are not equal. Hence, the law of reflection is not obeyed in this case and thus the image is not clear. Such a reflection is called ‘irregular reflection’ or ‘diffused reflection’. Example: Reflection of light from a wall.
Incorrect
Explanation
In the case of a body having a rough or irregular surface, each region of the surface is inclined at different angles. When light falls on such a surface, the light rays are reflected at different angles. In this case, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection of each ray are not equal. Hence, the law of reflection is not obeyed in this case and thus the image is not clear. Such a reflection is called ‘irregular reflection’ or ‘diffused reflection’. Example: Reflection of light from a wall.
-
Question 37 of 54
37. Question
37. The number of images formed, depends on_____
Correct
Explanation
The number of images formed, depends on the angle of inclination of the mirrors. If the angle between the two mirrors is a factor of 360°, then the total number of reflections is finite. If θ (Theta) is the angle of inclination of the plane mirrors, the number of images formed = 360° θ – 1. As you decrease this angle, the number of images formed increases. When they are parallel to each other, the number of images formed becomes infinite.
Incorrect
Explanation
The number of images formed, depends on the angle of inclination of the mirrors. If the angle between the two mirrors is a factor of 360°, then the total number of reflections is finite. If θ (Theta) is the angle of inclination of the plane mirrors, the number of images formed = 360° θ – 1. As you decrease this angle, the number of images formed increases. When they are parallel to each other, the number of images formed becomes infinite.
-
Question 38 of 54
38. Question
38. If two plane mirrors are inclined to each other at an angle of 90°, find number of images formed
Correct
 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 39 of 54
39. Question
39. _____ principle is used in Kaleidoscope
Correct
Explanation
Kaleidoscope is a device, which functions on the principle of multiple reflection of light, to produce numerous patterns of images. It has two or more mirrors inclined with each other.
Incorrect
Explanation
Kaleidoscope is a device, which functions on the principle of multiple reflection of light, to produce numerous patterns of images. It has two or more mirrors inclined with each other.
-
Question 40 of 54
40. Question
40. Which of the following statement is correct?
1) Periscope is an instrument used for viewing bodies or ships, which are over and around another body or a submarine.
2) It is based on the principle of the law of reflection of light.
3) It consists of a long outer case and inside this case mirrors or prisms are kept at each end, inclined at an angle of 60°
Correct
Explanation
Periscope is an instrument used for viewing bodies or ships, which are over and around another body or a submarine. It is based on the principle of the law of reflection of light. It consists of a long outer case and inside this case mirrors or prisms are kept at each end, inclined at an angle of 45°. Light coming from the distant body, falls on the mirror at the top end of the periscope and gets reflected vertically downward.
Incorrect
Explanation
Periscope is an instrument used for viewing bodies or ships, which are over and around another body or a submarine. It is based on the principle of the law of reflection of light. It consists of a long outer case and inside this case mirrors or prisms are kept at each end, inclined at an angle of 45°. Light coming from the distant body, falls on the mirror at the top end of the periscope and gets reflected vertically downward.
-
Question 41 of 54
41. Question
41. Which of the following are the uses of Periscope?
1) It is used in warfare and navigation of the submarine.
2) Photographs of important places can be taken through periscopes without trespassing restricted military regions.
3) Fibre optic periscopes are used by doctors as endoscopes to view internal organs of the body.
Correct
Explanation
Uses of Periscope:
It is used in warfare and navigation of the submarine.
In military it is used for pointing and firing guns from a ‘bunker’
Photographs of important places can be taken through periscopes without trespassing restricted military regions.
Fibre optic periscopes are used by doctors as endoscopes to view internal organs of the body
Incorrect
Explanation
Uses of Periscope:
It is used in warfare and navigation of the submarine.
In military it is used for pointing and firing guns from a ‘bunker’
Photographs of important places can be taken through periscopes without trespassing restricted military regions.
Fibre optic periscopes are used by doctors as endoscopes to view internal organs of the body
-
Question 42 of 54
42. Question
42. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
1) When it falls on a transparent material, it is not reflected completely, but a part of it is reflected and a part of it is absorbed and most of the light passes through it
2) Th rough air, light travels with a speed of 3 × 108 m s-1 , but it cannot travel with the same speed in water or glass
Correct
Explanation
We know that when a light ray falls on a polished surface placed in air, it is reflected into the air itself. When it falls on a transparent material, it is not reflected completely, but a part of it is reflected and a part of it is absorbed and most of the light passes through it. Through air, light travels with a speed of 3 × 108 m s-1 , but it cannot travel with the same speed in water or glass, because, optically denser medium such as water and glass off er some resistance to the light rays.
Incorrect
Explanation
We know that when a light ray falls on a polished surface placed in air, it is reflected into the air itself. When it falls on a transparent material, it is not reflected completely, but a part of it is reflected and a part of it is absorbed and most of the light passes through it. Through air, light travels with a speed of 3 × 108 m s-1 , but it cannot travel with the same speed in water or glass, because, optically denser medium such as water and glass off er some resistance to the light rays.
-
Question 43 of 54
43. Question
43. Which of the following is lesser medium?
Correct
Explanation
Light rays actually travel from the water (a denser medium) into the air (a rarer medium). As you saw earlier, when a light ray travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium, it is deviated from its straight-line path. So, the pencil appears to be bent when you see it through the glass of water.
Incorrect
Explanation
Light rays actually travel from the water (a denser medium) into the air (a rarer medium). As you saw earlier, when a light ray travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium, it is deviated from its straight-line path. So, the pencil appears to be bent when you see it through the glass of water.
-
Question 44 of 54
44. Question
44. Which of the following statement is correct?
1) Refraction of light in a medium depends on the speed of light in that medium.
2) When the speed of light in a medium is more, the bending is more
3) When the speed of light is less, the bending is less
Correct
Explanation
Refraction of light in a medium depends on the speed of light in that medium. When the speed of light in a medium is more, the bending is less and when the speed of light is less, the bending is more.
Incorrect
Explanation
Refraction of light in a medium depends on the speed of light in that medium. When the speed of light in a medium is more, the bending is less and when the speed of light is less, the bending is more.
-
Question 45 of 54
45. Question
45. The amount of refraction of light in a medium is denoted by a term known as____
Correct
Explanation
The amount of refraction of light in a medium is denoted by a term known as refractive index of the medium, which is the ratio of the speed of light in the air to the speed of light in that particular medium.
Incorrect
Explanation
The amount of refraction of light in a medium is denoted by a term known as refractive index of the medium, which is the ratio of the speed of light in the air to the speed of light in that particular medium.
-
Question 46 of 54
46. Question
46. Refractive index =
1) Speed of light in air
2) Speed of light in the medium
3) Speed of light in vacuum
Correct
Explanation
Refractive index, µ is given by
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation
Refractive index, µ is given by

-
Question 47 of 54
47. Question
47. Match the following with their refractive index:
I. Air 1. 1.56
II. Kerosene 2. 1
III. Quartz 3. 1.41
IV. Diamond 4. 2.41
Correct
Explanation
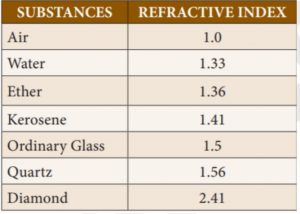 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation

-
Question 48 of 54
48. Question
48. What is the unit of refractive index?
Correct
Explanation
Refractive index is a ratio of two similar quantities (speed) and so, it has no unit. Since, the speed of light in any medium is less than its speed in air, refractive index of any transparent medium is always greater than 1.
Incorrect
Explanation
Refractive index is a ratio of two similar quantities (speed) and so, it has no unit. Since, the speed of light in any medium is less than its speed in air, refractive index of any transparent medium is always greater than 1.
-
Question 49 of 54
49. Question
49. Speed of light in air is 3 × 108 m s-1 and the speed of light in a medium is 2 ×108 ms-1 . Find the refractive index of the medium with respect to air.
Correct
Explanation
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation

-
Question 50 of 54
50. Question
50. Refractive index of water is 4/3 and the refractive index of glass is 3/2. Find the refractive index of glass with respect to the refractive index of water.
Correct
Explanation
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation

-
Question 51 of 54
51. Question
51. Refraction of light obeys___________
Correct
Explanation
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation

-
Question 52 of 54
52. Question
52. Which of the following statement is correct?
1) White light consists of Six colours.
2) Splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours (wavelength), on passing through a transparent medium is known as dispersion of light
Correct
Explanation
White light consists of seven colours. Splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours (wavelength), on passing through a transparent medium is known as dispersion of light.
Incorrect
Explanation
White light consists of seven colours. Splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours (wavelength), on passing through a transparent medium is known as dispersion of light.
-
Question 53 of 54
53. Question
53. Refraction of a light ray is inversely proportional to_______
Correct
Explanation
Dispersion s because, light of different colours-present in white light have different wavelength and they travel at different speeds in a medium. You know that refraction of a light ray in a medium depends on its speed. As each coloured light has a different speed, the constituent-coloured lights are refracted at different extents, inside the prism. Moreover, refraction of a light ray is inversely proportional to its wavelength.
Incorrect
Explanation
Dispersion s because, light of different colours-present in white light have different wavelength and they travel at different speeds in a medium. You know that refraction of a light ray in a medium depends on its speed. As each coloured light has a different speed, the constituent-coloured lights are refracted at different extents, inside the prism. Moreover, refraction of a light ray is inversely proportional to its wavelength.
-
Question 54 of 54
54. Question
54. Which of the following light will deviate less?
Correct
Explanation
Red coloured light, which has a large wavelength, is deviated less while the violet-coloured light, which has a short wavelength, is deviated more.
Incorrect
Explanation
Red coloured light, which has a large wavelength, is deviated less while the violet-coloured light, which has a short wavelength, is deviated more.
Leaderboard: Light Online Test 8th Science Lesson 3 Questions in English
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||