International Organizations 12th Political Science Lesson 11 Questions in English
12th Political Science Lesson 11 Questions in English
11] International Organizations
1. When the League of Nations was established?
a) 1919
b) 1920
c) 1932
d) 1902
Explanation
International Organizations, it is often considered as a twentieth century phenomenon that began with the establishment of the League of Nations in 1919.
2. Which of these is not a part of the United Nations System?
a) The International Telecommunication Union
b) The Universal Postal Union
c) The International Monetary Fund
d) The International Telegraph Union
Explanation
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) established in 1865 (originally called the International Telegraph Union), and the Universal Postal Union which was established in 1874. Both of these systems are today part of the United Nations system.
3. Where did the International Peace Conference held in 1899?
a) Geneva
b) Hague
c) Paris
d) New york
Explanation
The International Peace Conference held in The Hague in 1899 elaborated the instruments for settling crises peacefully preventing wars and codifying rules of warfare.
4. Which of these was the predecessor of the International Court of Justice?
a) The International Criminal Tribunals
b) The International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea
c) The International Peace Conference
d) The Permanent Court of Arbitration
Explanation
The Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA) which began its work in 1902. It is the predecessor of the United Nations International Court of Justice (ICJ).
5. Which of these events exposed the limitations of the International mechanisms?
a) First World War
b) Economic Crisis
c) Second World War
d) Colonialism
Explanation
The outbreak of World War I in August 1914, and the destruction that followed, exposed the limitations of these international mechanisms.
6. Which of this system was ended to prevent Europe from the source of war?
a) The United Nations
b) Concert of Europe
c) International Peace Conference
d) None of the above
Explanation
It was also followed by the end of an international system called the Concert of Europe that had prevented the continent from the scourge of war since the Napoleonic adventures a century earlier.
7. In which of these years Europe witnessed the worst human loss in history?
a) 1914-18
b) 1902-12
c) 1909-19
d) 1890-95
Explanation
Between the years 1914-18, Europe witnessed the worst human loss in its history where around twenty million people lost their lives.
8. Which of these nations were not formed by the collapse of the Empires?
a) Germany
b) Czechoslovakia
c) Finland
d) Estonia
Explanation
Empires collapsed (the Ottoman, the Austro-Hungarian and temporarily the Russian) and new nations such as Czechoslovakia, Estonia, and Finland were born, radical revolutions took place in Russia and Germany.
9. Which of these were not included in the Wilson’s Fourteen Points?
a) Open diplomacy
b) Limitations on Turkey
c) Establishment of independent India
d) Adjustment of Colonial Claims
Explanation

10. In which year the President Woodrow Wilson outlined the idea of the League of Nations?
a) 1917
b) 1912
c) 1918
d) 1923
Explanation
Amidst the carnage, President Woodrow Wilson in January 1918 outlined his idea of the League of Nations which received widespread support given the utter devastation caused by World War I.
11. Assertion (A): The United States joined the League of Nations.
Reasoning(R): The President Woodrow Wilson chaired the Versailles Peace Conference Commission.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Although the United States failed to join the League of Nations, President Woodrow Wilson chaired the Versailles Peace Conference’s commission on the establishment of an international Organization.
12. When the League started its operations in Geneva?
a) 1934
b) 1920
c) 1914
d) 1923
Explanation
The League being housed temporarily in London, commenced operation in the year 1920 in Geneva, Switzerland.
13. Match
A. Iraq i) Upper Silesia
B. Germany ii) Aland Islands
C. Finland iii) Mosul
a) ii, iii, i
b) ii, i, iii
c) iii, i, ii
d) i, ii, iii
Explanation
Initially it had some success when it settled disputes between Finland and Sweden over Aland Islands, between Germany and Poland over Upper Silesia and between Iraq and Turkey over the city of Mosul.
14. Which of these are the models for the United Nations?
a) The Permanent Court of International Justice
b) International Labor Organization
c) The United League
d) All the above
Explanation
The League acted as an umbrella Organization for agencies such as the International Labor Organization (ILO) and the Permanent Court of International Justice and it later became a model for the future United Nations (UN).
15. Which of the two countries formed the League of Nations along with France and Great Britain?
a) Japan and Italy
b) Austria and Germany
c) Poland and Finland
d) China and Germany
Explanation
The League of Nations was dominated by the victors of World War I that included France and Great Britain along with Japan and Italy as the other two permanent members of the League Council.
16. How many founding members were part of General Assembly which included most of Europeans and Latin Americans?
a) 29
b) 35
c) 28
d) 15
Explanation
There were twenty eight founding members who were represented in the General Assembly who were mostly from Europe and Latin America. The League of Nations was one that was Eurocentric
17. Which of the following are the reasons behind the failure of League of Nations?
a) Absence of United States
b) Germany and Soviet Union undermined the significance of the organization
c) Option (a) & (b)
d) None of the above
Explanation
The reasons for the League of Nations to fail were multiple. The absence of the United States was a significant factor in rendering the League ineffectual. Its importance was further minimized when Germany and the Soviet Union who were briefly members had undermined the significance of the Organization.
18. Which of the following country joined League of Nations in 1926 and excited in 1933 when Nazis came to power?
a) Germany
b) Soviet Union
c) Japan
d) Italy
Explanation
Germany joined in 1926 and exited after the Nazis came to power in 1933.
19. Which is the only nation to be expelled from League of Nations following their attack on Finland in 1939?
a) Germany
b) Soviet Union
c) Japan
d) Italy
Explanation
In the year 1933 Soviet Union entered the League and was expelled following their attack on Finland in 1939 which also made the USSR the only nation to be expelled from the League.
20. Which of the following two countries left the League of Nations after the criticism for their occupation of Manchuria and Ethiopia respectively?
a) Germany and Soviet Union
b) Japan and Italy
c) Poland and Finland
d) China and Austria
Explanation
Japan left the League in 1933 following criticism by the league of its occupation of Manchuria and Italy too was equally dismissive of its membership obligations after its occupation of Ethiopia.
21. Due to which of the event that happened in 1930s countries including France and Britain were not willing to fight distant wars?
a) The Global Economic Crisis
b) Floods
c) Pandemic Diseases
d) Droughts and Famine
Explanation
The global economic crisis of 1930s certainly curbed the enthusiasm of others and more particularly France and Britain who were not willing to fight distant wars that would not have an immediate effect on their national security.
22. Which of the following country has been dismantled as a result of agreement between Britain and France at the Munich Conference in 1938?
a) Japan
b) Soviet Union
c) Germany
d) Czechoslovakia
Explanation
In 1938 at the Munich Conference, Britain and France agreed to the dismantling of Czechoslovakia by agreeing to the addition of Sudetenland to Hitler’s Reich.
23. Which of the following event reduced the hopes of League of Nations as it was not capable of imposing sufficient pressure on the aggressor nations?
a) US’s attack on Japan
b) Germany’s attack on Poland
c) Soviet Union’s attack on Italy
d) Germany’s attack on Austria
Explanation
Germany attacked Poland after concluding pact with the Soviet Union in 1939 which dashed all hopes that were placed on the League of Nations. The League of Nations was not capable of applying sufficient pressure on the aggressor nations as it could only impose verbal or economic sanctions against them and these methods failed to intervene militarily.
24. Which of the following two countries supplied Military troops to League of Nations as it did not have an army for its own?
a) Japan and Soviet Union
b) Germany and China
c) France and Britain
d) Poland and Italy
Explanation
The League of Nations did not have authority beyond its member nations and this made it possible for countries suffering from the pressure of economic sanctions to trade with non-members. Additionally, since the League did not have an army of its own, military intervention meant that member states (France and Britain) would have to supply necessary troops.
25. The Nations of League failed to become which of the following ‘hope’ that President Woodrow Wilson had?
a) ‘Definite guarantee of Peace’
b) ‘Definite guarantee of Power’
c) ‘Guarantee of success’
d) ‘Guarantee of Peace and Power’
Explanation
The League expelled the Soviet Union in 1939, and it was known widely that the League had failed and did not become what President Woodrow Wilson had hoped as a ‘definite guarantee of Peace’.
26. Which of the following Organization was formed as a result of 72 million casualties due to Second World War?
a) League of Nations
b) United Nations
c) WHO
d) G8 and SAARC
Explanation
With the end of the Second World War which witnessed around 72 million casualties, the idea of the United Nations was born. World leaders who had collaborated to bring the war to an end felt a strong need for a mechanism that would ensure lasting peace and prevent future wars. It was also felt that this was possible only through a global Organization where all nations would work together.
27. Who coined the name ‘United Nations’?
a) Franklin D. Roosevelt
b) Theodore Roosevelt
c) Woodrow Wilson
d) Harry S. Truman
Explanation
The name ‘United Nations’ was coined by the then United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt
28. In which year the United Nations was officially used?
a) 1938
b) 1952
c) 1949
d) 1942
Explanation
United Nations was first officially used in 1942.
29. How many nations signed the declaration by United Nations to continue to fight together against the axis powers?
a) 28
b) 25
c) 26
d) 27
Explanation
Representatives from twenty-six nations signed the Declaration by United Nations to continue to fight together against the axis powers in order to obtain just peace.
30. In which year did delegates from China, Soviet Union, United Kingdom and the United States, met in Dumbarton Oaks to draw the basic blueprint for the new International Organization?
a) 1944
b) 1942
c) 1932
d) 1943
Explanation
In August 1944, delegates from China, Soviet Union, United Kingdom and the United States, met in Dumbarton Oaks to draw the basic blueprint for the new International Organization and by October the outline of the United Nations Charter was ready.
31. Which of the following is not included in four main purposes of United Nations?
a) Military Security
b) Economic and Social Progress
c) Fight against terrorism
d) Upholding of human rights
Explanation

32. Following which countries surrender in 1945 the Charter was signed by the representatives from fifty countries?
a) Soviet Union
b) Japan
c) Italy
d) Germany
Explanation
Following the surrender of Germany in the year 1945, representatives from fifty countries met in San Francisco on June 26, 1945 and signed the Charter.
33. After which event did United Nations came into existence
a) The conclusion of the Pacific war
b) The conclusion of American Civil wars
c) The conclusion of American Revolution war
d) The conclusion of Spanish – American war
Explanation
The conclusion of the Pacific war in October 24, 1945, the United Nations officially came into existence. While making the UN Charter, the drafters faced the same issue that the League of Nations faced which was to lay the foundation of an international Organization that would guarantee peace.
34. What was the solution that the UN came with, to make sure that Countries do not walk out from the UN?
a) Acceptance power
d) Veto Power
c) Voting
d) Signature of members
Explanation
How could one draft a Charter that would effectively deal with the fact that some countries were more equal than others? How could one make sure that one country could not simply walk out when it did not like the decisions of the UN, as Japan had done earlier in the 1930s. The simple solution that the drafters came up with was the veto power.
35. Which of the following country is not included in the five founding members of UN?
a) China
b) France
c) Great Britain
d) Japan
Explanation
Veto power was granted to the five founding members of the UN – China, France, Great Britain, the United States and the Soviet Union who are also known as the Permanent Five (P-5).
36. Which was the key Goal of both UN and League of Nations?
a) Promotion of International Security
b) Peaceful settlement of Disputes
c) Option (a) & (b)
d) None of the above
Explanation
The founders of the UN were keenly aware of the failures of the League of nations, most of its ideals constituted the core element of the UN Charter. Most evidently, the UN Charter and the League of Nations Covenant had promotion of international security and the peaceful settlement of disputes as its key goals, however, the Charter included two more elements that were also given importance.
37. Which of this Article of the UN Charter includes social and economic progress?
a) Article 23
b) Article 29
c) Article 14
d) Article 7
Explanation
Although it was reflected briefly in article 23 of the League of Nations Covenant, the UN Charter included social and economic progress into its key goals. The emphasis laid on social and economic progress was rooted in the inter-war years.
38. What were the main reasons for the establishment of the UN?
a) Global economic crisis of 1930
b) Rise of Ultra-nationalism
c) Second World War
d) All the above
Explanation
The global economic crisis of the 1920s to the 1930s as the root cause of political upheavals that led to the rise of ultra-nationalism and acts of aggression resulted in the Second World War. Thus the UN was created to be an active participant in world affairs.
39. How many major organs were present in the UN in the year 1945?
a) 6
b) 7
c) 3
d) 8
Explanation
In 1945, the six major organs of the UN were (i) the General Assembly, (ii) The Security Council, (iii) Economic and Social Council (iv) Trusteeship Council, (v) International Court of Justice and (vi) the Secretariat.
40. Which is not a special organ of the UN?
a) FAO
b) UNDP
c) WHO
d) UNESCO
41. How many permanent members are provided with the Veto power in the Security Council?
a) 10
b) 3
c) 7
d) 5
Explanation

42. Identify the correct match
A. General Assembly i) Parliament of the UN
B. Security Council ii) Executive committee
C. The Secretariat iii) Advisory Committee
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
All organs of the UN meet regularly and members vote to make decisions, issue declarations and discuss issues that are of prime importance. Yet the functions of the organs differ significantly vis-à-vis each other. While the General Assembly is the Parliament of the UN, the Security Council is its executive committee; the secretariat is the operational body or the bureaucracy that runs the UN.
43. Assertion (A): The General Assembly is the main deliberative organ of the UN.
Reasoning(R): Each of the Member states has vote based on the influence and size.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The General Assembly is the main deliberative organ of the UN which is comprised of Member States and each one has a vote no matter its influence or size.
44. Which of these issues are decided by the two-thirds of majority members of the UN?
a) UN Charter
b) International Peace
c) Admitting new members states
d) All the above
Explanation
Discussions often include issues arising under the UN Charter, decisions on international peace and security, admitting new member states and the UN budget is decided by two-thirds majority.
45. The Resolutions of the General Assembly represents,
a) Economically strong countries opinion
b) World-wide Leaders views
c) Commands and rules to the member states
d) Views of the Majority people of the world
Explanation
Resolutions taken by the General Assembly are only recommendations to the member states, but since they represent the views of majority of the world, it carries with it a heavy moral weight and often leads countries to join international agreements called treaties, conventions, protocols, etc.,
46. In which of these months the General Assembly session begins every year?
a) December
b) September
c) March
d) June
Explanation
The General Assembly’s sessions begin in September every and most resolutions are made between September and December. Requests for special sessions may be initiated by the Security Council or if a majority of its members make a request.
47. How long the general debate will happen before the regular session of General Assembly?
a) 20 Days
b) one week
c) 30 days
d) Two weeks
Explanation
At the beginning of each regular session, the General Assembly has a two-week general debate in which heads of State present their views on a wide range of issues such as terrorism, war, poverty, hunger and disease.
48. Which of the following continent is not a part of UN Peacekeeping Operations?
a) Africa
b) Europe
c) Asia
d) Antarctica
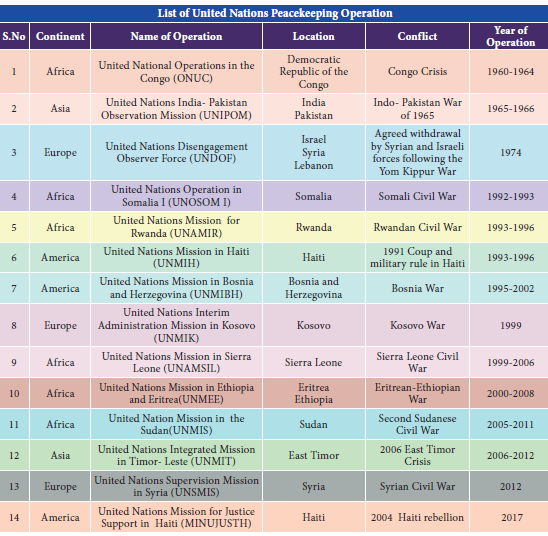
48. Who quoted as saying that India has been one of the most significant votaries of shaping the UN agenda on behalf of the developing world?
a) Kofi Annan
b) Ban Ki-Mon
c) Antonio Guterres
d) Boutros Ghali
Explanation
India has always seen itself as a champion, a ‘moralistic force’ of the so called Third World, the developing states. Former Secretary General Kofi Annan has been quoted as saying that India has been one of the most significant votaries of shaping the UN agenda on behalf of the developing world.
50. Which country was criticized by United states by lone Vetoes of resolutions in UN?
a) Japan
b) Israel
c) Finland
d) Italy
Explanation
The veto power has been criticized for its undemocratic nature. A single country can prevent a majority of the Security Council from taking any action. For example, the United States routinely casts lone vetoes of resolutions criticizing Israel. The permanent members also veto resolutions that criticize their own actions.
51. Who wrote “The veto is an anachronism. In the twenty-first century, the veto has come to be almost universally seen as a disproportionate power and an impediment to credible international action to crises.”?
a) Cummings
b) William Slater Brown
c) Laurance Stallings
d) Peter Nadin
Explanation
Peter Nadin writes that “The veto is an anachronism. In the twenty-first century, the veto has come to be almost universally seen as a disproportionate power and an impediment to credible international action to crises.” The “enormous influence of the veto power” has been cited as a cause of the UN’s ineffectiveness in preventing and responding to genocide, violence, and human rights violations.
52. Which of the following Country proposed limitations over Veto power?
a) African Union
b) Soviet Union
c) American Union
d) None of the above
Explanation
Various countries outside the P5, such as the Non-Aligned Movement and African Union have proposed limitations on the veto power. Reform of the veto power is often included in proposals for reforming the Security Council.
53. When did A/RES/377 A adopted in UN to not prevent UNGA from taking any action to restore international peace and security?
a) 3 November 1950
b) 5 September 1950
c) 10 October 1950
d) 4 November 1950
Explanation
By adopting A/RES/377 A, on 3 November 1950, over two-thirds of UN Member states declared that, according to the UN Charter, the permanent members of the UNSC cannot and should not prevent the UNGA from taking any and all action necessary to restore international peace and security, in cases where the UNSC has failed to exercise its “primary responsibility” for maintaining peace
54. For which of the following did UNGA was awarded for the matters of international peace and security by UN charter?
a) Secondary responsibility
b) Initial responsibility
c) Final responsibility
d) None of the above
Explanation
UNGA as being awarded “final responsibility”—rather than “secondary responsibility”—for matters of international peace and security, by the UN Charter. Various official and semi-official UN reports make explicit reference to the Uniting for Peace resolution as providing a mechanism for the UNGA to overrule any UNSC vetoes; thus rendering them little more than delays in UN action, should two-thirds of the Assembly subsequently agree that action is necessary.
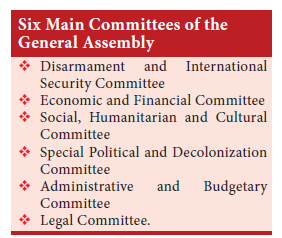
55. Which of the following is not included in six main committees of General Assembly?
a) Disarmament and International Security Committee
b) Economic and Financial Committee
c) Legal Committee
d) Health and wellbeing committee
Explanation
56. Which of the following Council under UN charter has the responsibility to maintain international peace and security?
a) Peace Council
b) Political Council
c) Legal Council
d) Security Council
Explanation
Under the UN Charter the Security Council has the responsibility to maintain international peace and security. Unlike the General Assembly which has regular meetings, the Security Council does not have such meetings and can be convened at any time whenever there is a threat to international peace.
57. How many members do Security Councils consists of?
a) 20
b) 25
c) 10
d) 15
Explanation
The Security Council has fifteen members which includes five permanent members (P-5). The other ten members are elected by the General Assembly on rotation basis for a period of two years.
58. How many votes are required In order to pass a resolution in the Security Council?
a) 10 out of 15
b) 9 out of 15
c) 15 out of 15
d) 13 out of 15
Explanation
In order to pass a resolution in the Security Council nine out of fifteen votes is required. However, if any one of the P-5 Members votes ‘No’, often referred as Veto, the resolution does not pass.
59. How many years does the central body of the UN serve?
a) 4
b) 3
c) 2
d) 5
Explanation
The Economic and Social Council of the UN which has fifty-four members who are chosen for equal geographical representation and serve a three-year term is the central body of the UN for coordinating the economic and social work of the UN and the UN system.
60. Over how many percent of the UN System is devoted to promoting higher standards of living, alleviating poverty through full employment; economic and social progress; and development?
a) 70%
b) 80%
c) 90%
d) 60%
Explanation
Over seventy percent of the UN System is devoted to promoting higher standards of living, alleviating poverty through full employment; economic and social progress; and development. It promotes economic growth in developing countries, supports human rights, and fosters world cooperation to alleviate poverty and under-development.
61. Which of the following is not a specialized agency of UN?
a) Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
b) The World Health Organization (WHO)
c) The UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO),
d) National Security Agency (NSA)
Explanation
To address specific needs of the council, it has established a number of specialized agencies such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), The World Health Organization (WHO), the UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), UN Development Programme (UNDP), UN Children’s Fund (UNICEF), and the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR).
62. Which council was assigned to monitor the administration of eleven former colonies?
a) Trusteeship Council
b) Legal Council
c) Security Council
d) Peace Council
Explanation
Under the UN Charter, the Trusteeship Council was assigned to monitor the administration of eleven Trust Territories – former colonies. At the end of the Second World War, this system was created for the advancement of the inhabitants of those dependent territories for their progressive development towards self-governance or independence.
63. Which of the trust territories was the last to become independent?
a) Western Samoa
b) Palau
c) New Guinea
d) Togoland
Explanation
In 1994, Palau became the last Trust Territory to become independent and subsequently the council decided to suspend operations and meet when occasion might require.
64. Which country is not a part of permanent members of the UN Security Council comprise the Trusteeship Council?
a) China
b) France
c) United Kingdom
d) Japan
Explanation
China, France, United Kingdom, the Russian Federation and the United States who are permanent members of the UN Security Council comprise the Trusteeship Council.
65. Which is UN’s main judicial organ?
a) International Court of Justice (ICJ)
b) General Assembly
c) Security Council
d) Economic and Social Council
Explanation
The UN’s main judicial organ is the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and is located in The Hague, Netherlands.
66. In which year did The ICJ or World Court was established?
a) 1947
b) 1952
c) 1945
d) 1950
Explanation
The ICJ or World Court was established in 1945. It’s predecessor was the Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA).
67. In which year did The ICJ or World Court started its functions?
a) 1945
b) 1946
c) 1952
d) 1942
Explanation
The ICJ or World Court began it functions in 1946.
68. How many Judges does the ICJ or World Court consists of?
a) 20
b) 15
c) 10
d) 5
Explanation
The court is presided by fifteen judges elected for nine year terms, each belonging to a different nation. The judges are selected by both the General Assembly and the Security Council.
69. Where do the International Court of Justice and its offices located?
a) Peace Palace
b) Legal Palace
c) Security Palace
d) Justice Palace
Explanation
The court and its offices occupy the ‘Peace Palace’ which was constructed by the Carnegie Foundation which a non-profit Organization to serve as the headquarters of the Permanent Court of International Justice under the League of Nations. The UN makes an annual contribution to the Foundation for the use of the building. UNSC refer cases to the ICJ.
70. Which of the following administers the programs and the policies laid out by the other principal organs of the UN?
a) The UN Secretariat
b) The UN Security council
c) The General Assembly
d) None of the above
Explanation
The UN Secretariat administers the programs and the policies lay out by the other principal organs of the UN. The Secretary General heads the Secretariat and is appointed by the General Assembly on the recommendations of the Security Council
71. For a term of how many years do the Secretary General is appointed as the head of UN Secretariat?
a) 10
b) 5
c) 3
d) 2
Explanation
The Secretary General is appointed for a five-year term which is renewable. As the chief administrative officer of the UN the Secretary General directs the work of other staff in the Organization who is known as international civil servants.
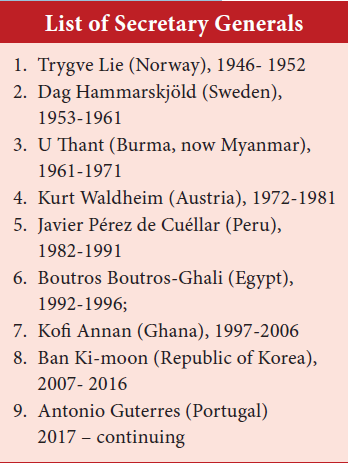
72. Match the following
Secretary Generals Years
- Trygve Lie i) 1961-1971
- Dag Hammarskjold ii) 1946 -1952
- U Thant iii)1953-1961
a) ii, iii, i
b) i, iii, ii
c) iii, i, ii
d) i, iii, ii
Explanation
73. Where is the headquarters of UN SECRETARIAT?
a) Moscow
b) Washington
c) New York
d) Geneva
Explanation
The Secretariat is headquartered at New York and has its offices at Geneva, Vienna, Nairobi, Addis Ababa, Beirut, Santiago and Bangkok.
74. Which of the following is not a duty of Secretariat?
a) Peacekeeping operations
b) Providing military support to needed countries
c) Mediating international disputes
d) Surveying social and economic trends
Explanation
These duties are varied and range from peacekeeping operations, mediating international disputes, surveying social and economic trends to laying the groundwork for international agreements and organizing international conferences. Th e role of the Secretariat which is multi-faceted is under constant pressure from the dyad of nation- state imperatives and universal goals.
75. Where does the Secretary-General bring to the attention in case of disturbances to international peace and security?
a) Security Council
b) General Assembly
c) The UN Secretariat
d) Legal Council
Explanation
The Secretary-General may bring to the attention of the Security Council matters that may in his opinion disturb international peace and security. He can also use his good offices to prevent conflicts or promote peaceful settlements of disputes between nations. The Secretary General can also act upon his own discretion to deal with humanitarian or any other problem that might require special importance.
76. Which of the following is a temporary body in UN SECRETARIAT?
a) UNHCR
b) UNICHEF
c) UNESCO
d) WHO
Explanation
New bodies were added on a regular basis while some were made to be temporary bodies such as the UNHCR; they have nevertheless become permanent organs.
77. Which of the following article made it possible for the UN to work with NGOs in conflict zones?
a) Article 77
b) Article 88
c) Article 86
d) Article 76
Explanation
Envisioned in 1945 in article 77 of the UN Charter, it states explicitly that the UN ‘may make suitable arrangements for consultation with nongovernmental Organizations which are concerned with matters within its competence’. This made it possible for the UN to work with hundreds of NGOs to undertake humanitarian work in conflict zones.
78. How many NGOs issued an open letter to the Secretary General to pressurize Sudan’s government to permit a Joint African Union/United Nations Peacekeeping force?
a) 35
b) 37
c) 32
d) 31
Explanation
In 2007, thirty-two NGOs issued an open letter to the Secretary General to pressurize Sudan’s government to permit a Joint African Union/United Nations Peacekeeping force to enter the conflict-ridden Darfur region.
79. Which of the following under the UN mandate coordinates the economic and social work of the UN and the UN family of Organizations?
a) UNHCR
b) UNICHEF
c) UNESCO
d) ECOSOC
Explanation
The ECOSOC under the UN mandate coordinates the economic and social work of the UN and the UN family of Organizations. It therefore plays a key role in fostering international cooperation for development.
80. Which commission monitors the observance of human rights across the world?
a) Political
b) Legal
c) Human Rights
d) Peace and Security
Explanation
The ECOSOC although a relatively powerless body of the UN structure, oversees a number of functional and regional commissions. The Commission on Human Rights monitors the observance of human rights across the world.
81. Which of the following is not one of the three sisters of global economic power?
a) World Bank
b) The International Monetary Fund
c) The world Trade Organization
d) The UNICEF
Explanation
The true global economic power in fact lays with the so called three sisters (i) the World Bank (ii) The International Monetary Fund and (iii) the World Trade Organization.
82. How the World Bank was originally known as?
a) International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD).
b) International Bank for Reconstruction and Deformation (IBRD).
c) International Bank for Reservation and Development (IBRD).
d) International Bank for Remuneration and Development (IBRD).
Explanation
The World Bank which is based in Washington was originally known as the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD).
83. When did the term “world bank” was first used in reference to IBRD in an article in the Economist?
a) July 21, 1944
b) July 22, 1944
c) June 22, 1944
d) June 21, 1944
Explanation
The term “world bank” was first used in reference to IBRD in an article in the Economist on July 22, 1944, in a report on the Bretton Woods Conference.
84. Which of the following is primary focus of the World Bank
a) Reduce poverty
b) Increase economic growth
c) Increase the quality of life by using its financial resources and its extensive experience
d) All the above
Explanation
The primary focus of the Bank is to work with the poorest people and the poorest countries through its five institutions to reduce poverty, increase economic growth and increase the quality of life by using its financial resources and its extensive experience. The World Bank is managed by its member countries who are lenders, borrowers or donors.
85. Which of the following actors does World Bank works with?
a) Government agencies
b) Civil society Organizations
c) Aid agencies and the private sector.
d) All the above
Explanation
Many developing countries in the world use the World Bank’s assistance ranging from loans and grants to technical assistance and policy advice. The Bank works with a wide range of actors that includes government agencies, civil society Organizations, other aid agencies and the private sector.
86. Which is the fundamental mission of the World Bank?
a) Reducing poverty and improving the quality of life
b) Providing financial support to developing countries
c) Providing financial support to developed countries
d) Providing Loan to industrial investors
Explanation
The fundamental mission of the World Bank is reducing poverty and improving the quality of life has not changed, in recent times it is adjusting its approaches and policies to the needs of developing countries in the new economic context.
87. Which country occupies the additional seat in the Board of Directors that made world bank to influence developing and transition countries that are in the Bank Group?
a) India
b) Iran
c) Sub-Saharan Africa
d) Iraq
Explanation
With an additional seat in the Board of Directors for Sub-Saharan Africa and an increase in voting power of developing countries, the Bank seeks to elevate the representation and influence of developing and transition countries that are in the Bank Group.
88. Which is the key concern of World Bank along with the Governance?
a) Unemployment
b) Poverty
c) Inflation
d) Anticorruption
Explanation
Among its key concerns, the Bank has governance and anticorruption across sectors and countries. This is based on the mandate to reduce poverty – a capable and accountable state creates opportunities for all to develop.
89. Which of these is not an institution of the World Bank?
a) The International Development Association
b) World Trade Center
c) International Finance Corporation
d) The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
Explanation

90. Assertion (A): The World Bank provides more information on project and programs in recent years.
Reasoning(R): The ability to access information policy of the World Bank to share its knowledge
with wide audience.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The Bank’s ability to access information policy provides opportunities for the Bank to share its knowledge and experience with a wide audience in order to enhance its quality of operations by providing more information about projects and programs than ever before.
91. How many members were involved with World Bank in the year 1946?
a) 75
b) 21
c) 58
d) 38
Explanation
The beginning of operations in 1946 with thirty-eight members, there has been a dramatic change in the number of members and the conditions in the world. As many nations became independent from colonial rule, they gradually joined the institution and subsequently the bank and the development needs of member states expanded.
92. What is the objective of IBRD?
a) Reduce Unemployment
b) Reduce poverty in middle-income countries
c) Improve Entrepreneurship
d) None of the above
Explanation
The main objective of the IBRD is to reduce poverty in middle-income countries and credit worthy low income by promoting sustainable development through loans, guarantees and analytical and advisory services. It was established in 1945 and has 184 members. Its net income and allocable income for the fiscal year in June 2018 amounted to $698 billion.
93. When the International Development Association was established?
a) 1960
b) 1942
c) 1923
d) 1974
Explanation
The International Development Association: It supports country-led initiatives for poverty reduction in the poorest countries with interest-free credits and grants with money received from contributions made by members. It was established in the year 1960 and its total commitment amounted to $24 billion in the fiscal year June 2018.
94. Assertion (A): The International Finance Corporation was established in the year 1945.
Reasoning (R): This provides loans to the Public Sectors to promote economic development in developing countries.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The International Finance Corporation: It provides loans to the private sector to promote economic development in developing countries. It was established in 1956 with 176 members and its investments in the year 2018 amounted to $23.3 billion.
95. How many members were involved in the International center for settlement of Investment Disputes in 1966?
a) 120
b) 100
c) 140
d) 180
Explanation
The International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes: It encourages foreign investment in developing countries by providing facilities for arbitration of investment disputes. It was established in 1966 with 140 members.
96. By which of this conference the International Monetary Fund was conceived?
a) Geneva Conference
b) Bretton Woods Conference
c) Paris Conference
d) Tokyo Conference
Explanation
The International Monetary fund or the Fund is the world’s largest premier international financial institution. It was conceived at the Bretton Woods conference in 1944 as a global response to the great economic depression of the 1930s.
97. Choose the correct statements.
- The International Monetary Fund provides long term finance to member countries.
- The Member countries does not rely on competitive devaluation and protectionist trade policies
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The International Monetary fund was established to provide short term and medium term finance to member countries facing balance of payments difficulties so that they could pursue policies of economic adjustment that did not rely on competitive devaluation and protectionist trade policies.
98. Assertion (A): The International monetary Fund is a dependent Organization of the United Nations.
Reasoning(R): The Member countries provide capital for the IMF.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an independent international Organization with 185 member countries with the objective to promote economic stability and growth. The member countries are the shareholders in the cooperative and provide capital for the International Monetary Fund through quota subscription.
99. State the significance of the International Monetary Fund
a) Regularly examines the economic conditions all countries in the world virtually.
b) Provides loan for the economic development of countries.
c) Promotes economic stability of all countries.
d) All the above
Explanation
Surveillance of Members’ Economic Policies: nations who are members agree to pursue economic policies that are consistent with the objectives of the IMF and the articles of agreement confer on the IMF the legal authority to oversee compliance with this obligation which makes the IMF the only Organization that has the mandate to examine regularly the economic conditions of virtually all countries in the world
100. How many initiatives are made by the IMF to provide debt relief?
a) 4
b) 6
c) 8
d) 2
Explanation
The IMF participates in two international initiatives to provide debt relief (i) Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) and (ii) Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative (MDRI).
101. What is the international asset issued by the IMF?
a) Special Drawing Right
b) Derivative Fund
c) Special Economical asset
d) Contingent Fund
Explanation
If there is a global need to supplement existing reserves, the IMF has the authority to issue an international asset called the Special Drawing Right (SDR). These SDRs belong to the net international reserves of members and can be exchanged for convertible currencies.
102. How the MDB’s are categorized into various institutions?
a) Population
b) Economic Stability
c) Regional Coverage
d) Poverty level
Explanation
MDBs belong to a complex set of public institutions that can be categorized as (i) global, (ii) regional and (iii) Sub-regional. Categorizations of all MDBs are done by taking into consideration their regional coverage.
103. Which of these fall under the MDB categories?
a) Asian Development Bank
b) Inter-American Development Bank
c) Islamic Development Bank
d) All the above
Explanation
Most MDBs fall in the above mentioned three categories and directly target a particular continent such as the Asian Development Bank, the African Development Bank, Asian Infrastructure and Investment Bank, New Development Bank, Inter-American Development Bank, Islamic Development Bank, European Investment Bank, etc.
104. Assertion (A): The American Economist John Maynard Keynes addressed economic and social needs in the post-war period.
Reasoning(R): Henry Dexter played a key role in envisioning the set of institutions created by John Maynard Keynes.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The prominent British economist John Maynard Keynes addressed economic and social needs that emerged in the post-war period. Harry Dexter White- an American economist was a key figure in envisioning the set of institutions that were to be created as envisioned by John Maynard Keynes.
105. Which of this country is not a member of MDB?
a) Germany
b) Cuba
c) India
d) Brazil
Explanation
Almost all countries in the world with the exception of Cuba and North Korea are members of MDBs. All countries with membership in MDBs contribute to the institution since they are affiliated to and avail loans from them.
106. When the ADB was founded?
a) 1923
b) 1978
c) 1966
d) 1982
Explanation
The Asian Development Bank is a regional multilateral finance institution that is dedicated to the realization and reduction of poverty in Asia and the Pacific. The ADB was founded in1966 and has 62 member countries and most of them belong to the region
107. What is the central component of the long-term framework of the ADB?
a) Economic stability
b) Increasing Trade activities
c) Increasing Global economy
d) Poverty Reduction Strategy
Explanation
The ADB’s Poverty Reduction Strategy (PRS) is the central component of its Long-Term Strategic Framework (LTSF 2001 – 2015). This fifteen-year agenda of the ADB subscribed to the United Nations Millennium Development Goals to achieve the target of halving the number of people living in poverty worldwide.
108. How many Geographic regions are operated by the ADB?
a) 7
b) 3
c) 5
d) 4
Explanation
The ADB now operates through five geographically contiguous areas which addresses country and sector themes. The groupings are (i) East and Central Asia, (ii) the Mekong, (iii) the pacific, (iv) South Asia and (v) South-East Asia
109. Which of this country have the largest shares in the ADB?
a) India
b) China
c) The United States
d) Pakistan
Explanation
The ADB receives resources from its shareholders. Japan and the United States have the largest shares among the 62 country members that amounts to 15.9 percent of shares.
110. Assertion (A) : India refused to endorse the BRI initiative in the Qingdao declaration.
Reasoning(R): India coined secure strategy in the SCO region.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Shanghai Cooperation Organization, Qingdao declaration: India refused to endorse the ambitious Chinese Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). India coined SECURE strategy for comprehensive security in the SCO region.
111. Which is the Headquarters for the SCO organization?
a) Beijing
b) Seoul
c) Wuhan
d) Japan
Explanation
Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO): It is a Eurasian political, economic, and security Organization formed in 2001 and headquartered in Beijing.
112. When the Shanghai Five forum was founded?
a) 1992
b) 1996
c) 1990
d) 1987
Explanation
The SCO owes its origin to its predecessor Shanghai Five (a multilateral forum founded by 5 countries China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan in Shanghai in 1996).
113. The Shanghai Spirit includes,
a) Respect for other cultures
b) Non-interference in internal affairs of others
c) Harmony
d) All the above
Explanation
Its driving philosophy is known as the “Shanghai Spirit” which emphasizes harmony, working by consensus, respect for other cultures, non-interference in the internal affairs of others, and non-alignment.
114. How many member states are involved in the SCO organization?
a) 6
b) 9
c) 3
d) 8
Explanation
SCO comprises eight-member states, India, Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyz Republic, Pakistan, Russian, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
115. In which year India became full time members of the SCO organization?
a) 2012
b) 2006
c) 2017
d) 2010
Explanation
2018 year SCO meet is India’s first participation in the summit as a full-time member. India, along with Pakistan, became full-time members during the Astana summit in Kazakhstan in June 2017.
116. Define OPEC Asian Premium.
a) The Actual selling charge of oil to Asian countries.
b) The Annual amount collected by the OPEC countries.
c) The Extra charge collected by the OPEC countries from Asian countries.
d) None of the above
Explanation
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) Asian Premium: It is the extra charge being collected by OPEC countries from Asian countries when selling oil.
117. Identify the Incorrect Match.
A. Brent i) European Market
B. WTI ii) South Asian Market
C. Dubai iii) Middle East Market
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
There are 3 important benchmarks in global market, representing the cost of oil produced in respective geographies. Brent: Light sweet oil representative of European market, West Texas Intermediate (WTI): US market, Dubai/Oman: Middle East and Asian Market.
118. Assertion (A): Dubai/Oman countries do not have derivative trading in the oil market.
Reasoning(R): The United States and Europe markets and oil prices is based on future trading.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The US and Europe had an advantage because their markets and prices were based on future trading and reflected every trend in the crude market. On the other hand, Asia represented by Dubai/Oman do not have any derivative trading, doesn’t have that edge.
119. Choose the Correct statements.
i) The Price differential between Asian Countries and Europe is termed as the Asian Premium.
ii) The Oil price charged from Asian Countries is slightly lower than the Europe countries.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The Oil price charged from Asian countries remained $1-$2 dollar higher than that from Europe and the US. This price differential is termed as ‘Asian Premium’.
120. Which country is not a founding member of the OPEC?
a) Iran
b) India
c) Kuwait
d) Saudi Arabia
Explanation
OPEC is headquartered at Vienna, Austria. It was set up at the 1960 Baghdad Conference with Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela as founding members.
121. When the IAEA was set up in the United Nations system?
a) 1952
b) 1957
c) 1951
d) 1959
Explanation
International Atomic Energy Agency: It is the world’s central intergovernmental forum for scientific and technical cooperation in the nuclear field. This organization within the United Nations system set up in July 1957 through its own international treaty, the IAEA Statute
122. Assertion (A): IAEA is an autonomous international Organization.
Reasoning(R): The IAEA reports both the United Nations General Assembly and the Security Council.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
IAEA is an autonomous international Organization within the United Nations system set up in July 1957 through its own international treaty, the IAEA Statute. The IAEA reports to both the United Nations General Assembly and Security Council.
123. Which of these is the Headquarters of IAEA?
a) Vienna
b) Geneva
c) Denmark
d) Iceland
Explanation
The objective of IAEA Safeguards is to deter the spread of nuclear weapons by the early detection of the misuse of nuclear material or technology. It is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
124. To which country India ratified a protocol with the IAEA agreements?
a) Russia
b) United States
c) Germany
d) Israel
Explanation
In 2014, India ratified an Additional Protocol (as part of its commitments under US-India Nuclear Deal) to its safeguards agreements with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
125. How many states member are included in the BIMSTEC organization?
a) Six
b) Three
c) Five
d) Seven
Explanation
BIMSTEC is a regional Organization comprising seven Member States lying in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal including Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Myanmar and Thailand.
126. Where the secretariat of the BIMSTEC organization is located?
a) Dhaka
b) Bandung
c) Bangkok
d) New Delhi
Explanation
The BIMSTEC sub-regional Organization came into being on 6 June 1997 through the Bangkok Declaration. Its Secretariat has been established at Dhaka.
127. In which of this Conference the SSC was formed in the year 1955?
a) Bandung
b) Seoul
c) Tokyo
d) Chile
Explanation
South- South Cooperation (SSC) is defined as the exchange and sharing of developmental solutions among countries in the global south. The formation of SSC can be traced to the 1955 Bandung Conference.
128. Which of these countries are involved in the IBSA?
a) India, Bangladesh, Sudan
b) India, Belgium, South Africa
c) India, Brazil, South Africa
d) India, Brazil, Sri Lanka
Explanation
IBSA: It is an international tripartite grouping for promoting international cooperation of India, Brazil and South Africa.
129. When was IBSA formally established by the Brasilia Declaration?
a) 2003
b) 2009
c) 2001
d) 2006
Explanation
IBSA was formally established by the Brasilia Declaration of 6 June 2003 by external affairs ministers of India, Brazil and South Africa. IBSA Mechanism for Development Cooperation -IBSA Fund for the Alleviation of Poverty and Hunger.
130. What is the contribution of the member countries to the IBSA fund annually?
a) $ 1 Million
b) $ 10 Million
c) $ 5 Million
d) $ 2 Million
Explanation
Each member country contributes $1 Million annually to the IBSA fund. The IBSA Fund is managed by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).
131. The North Atlantic Treaty organization provides security against which of this Country?
a) Soviet Union
b) Israel
c) Pakistan
d) North Korea
Explanation
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization was created in 1949 by the United States, Canada, and several Western European nations to provide collective security against the Soviet Union.
132. Assertion (A): NATO was the first peacetime military alliance of the United States outside the Western hemisphere.
Reasoning(R): The Western Europe nations want to assure the United States would intervene automatically in the event.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
NATO was the first peacetime military alliance the United States entered into outside of the Western Hemisphere. The nations of Western Europe wanted assurances that the United States would intervene automatically in the event of an attack.
133. When the North Atlantic Treaty was signed between the Nations?
a) 1932
b) 1987
c) 1949
d) 1952
Explanation
The North Atlantic Treaty was signed in 1949. In this agreement, the United States, Canada, Belgium, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxemburg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, and the United Kingdom agreed to consider attack against one an attack against all, along with consultations about threats and defense matters.
134. Which of this agreement ensures the better serve needs of the Member states in International Terrorism?
a) NATO
b) The North Atlantic Treaty
c) Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
d) UN Global Counter-Terrorism Coordination Compact
Explanation
UN Global Counter-Terrorism Coordination Compact: It is an agreement between the UN chief, 36 Organizational entities, the International Criminal Police Organization (INTERPOL) and the World Customs Organization, to better serve the needs of Member States when it comes to tackling international terrorism.
135. Choose the correct statements.
i) The Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban is a multilateral treaty bans all nuclear explosions for military purposes only.
ii) The Treaty was negotiated in the Geneva Conference on Disarmament.
iii) CTBT treaty was opened for signature on December 1992.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty: It is a multilateral treaty banning all nuclear explosions for both military and civilian purposes. It was negotiated at the Conference on Disarmament in Geneva and adopted by the United Nations General Assembly. It was opened for signature on 24 September 1996.
136. Where the CTBT organization was established by the treaty?
a) Geneva
b) Austria
c) Vienna
d) Paris
Explanation
The Treaty establishes a CTBT organization (CTBTO), located in Vienna, to ensure the implementation of its provisions, including provisions for international verification measures.
137. Assertion (A): India did not support the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty in 1996.
Reasoning(R): The CTBT of the year 1996 did not address the complete disarmament with the UNSC members.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
India did not support the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty in 1996 and still does not due to following reasons: CTBT does not address complete disarmament (supported by India), discriminatory in nature with permanent UNSC members.
138. Which of these countries are not included in the NON-Proliferation Treaty of Nuclear Weapons, 1968?
a) United States of America
b) England
c) France
d) Israel
Explanation
Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) 1968
Its objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy and to further the goal of achieving nuclear disarmament and general and complete disarmament. India, Israel, North Korea, Pakistan and South Sudan are not parties to this treaty.
139. Choose the correct statements.
- INGO work with intergovernmental Organizations and donor agencies.
- INGO’s make efforts to the change the trade and investment patterns.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
INGOs often work with intergovernmental organizations and donor agencies and can have tremendous sway in certain policy domains. Recently the work of INGOs has been linked with their efforts to changes in trade and investment patterns and decisions in terms of humanitarian intervention, economic sanctions and aid allocation.
140. When did the League nations form a Federation in Geneva?
a) 1901
b) 1929
c) 1940
d) 1932
Explanation
In the year 1910, a group of 132 organizations came together to form the Union of International organizations. In 1929 a group of organizations that regularly attended the League meetings and formed the Federation of Private and Semi-Official International organizations established in Geneva.
141. Which of this Conference made provision for the formal relations of organizations with ECOSOC?
a) San Fransico
b) Sweden
c) Paris
d) Geneva
Explanation
When the UN Charter was finalized, the San Francisco Conference agreed to make provision for both intergovernmental organizations and private organizations to have formal relations with the ECOSOC.
142. Assertion (A): The Specialized agencies were introduced by the Article 53 in the UN charter.
Reasoning(R): Article 71 introduced the non-governmental organizations in the UN Charter.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Under Article 57, a new term Specialized Agencies was introduced to define inter-governmental organizations. Under Article 71, a new second term was introduced – non-governmental Organizations
143. Assertion (A): The Amnesty International is the largest governmental organization across the globe.
Reasoning(R): It works to promote the environmental protection campaign movement worldwide.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Amnesty international is one of the largest international non-governmental organization that works for the rights of humans across the globe. Its work is a worldwide campaign movement that seeks to promote all human rights that are established in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) and other international human rights instruments.
144. Which institution was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in the year 1977?
a) The Amnesty International
b) UDHR
c) ECOSOC
d) The Human Rights Watch
Explanation
In the year 1977, the Amnesty International was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for its campaign against torture.
145. When the Human Rights Watch was founded?
a) 1972
b) 1923
c) 1978
d) 1980
Explanation
The Human Rights Watch was founded in 1978 with the founding of its Europe and Central Asia Division then known as the Helsinki Watch.
146. The Human Rights Watch is known for its,
i) Accurate Findings
ii) Effective Media usage
iii) Targeted Advocacy
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The Human Rights Watch is known for its accurate findings, impartial reporting, effective usage of media and targeted advocacy often in partnership with local human rights groups.
147. In which year the Human Rights Watch won the United Nations Award?
a) 2008
b) 2001
c) 2003
d) 2005
Explanation
Human Rights Watch has won the 2008 United Nations Prize for Human Rights, in recognition of the vital role played by the Human Rights movement in trying to end abuses over the past 60 years.
148. The Human Rights award bestowed in New York was given every ____.
a) 3 Years
b) 2 Years
c) 5 Years
d) 6 Years
Explanation
The award given every five years was bestowed in New York on December 10, 2008, the 60th anniversary of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
149. Assertion (A): Human Rights Watch is an independent, non-partisan institution.
Reasoning(R): Human Rights Watch runs by the direct government funds.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Human Rights Watch in order to maintain it independence claims that it does not accept government funds directly or indirectly or support from any private funder that could compromise its objectivity and independence. It also does not embrace any political cause and is non-partisan and strives to main neutrality in situations of armed conflict.
150. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The United Nations Human Rights Commission was setup in the year 2002.
ii) The Council members are elected for three years by direct and secret voting method.
iii) India was elected with highest number of votes to the General Assembly for UNHRC.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation

151. In which of these places the international coordinating body of the Greenpeace is located?
a) Amsterdam
b) Geneva
c) New york
d) Paris
Explanation
Greenpeace is a non-governmental environmental Organization with offices in over 39 countries and an international coordinating body in Amsterdam.
152. When the Netherlands Greenpeace was established by environmental activists?
a) 1923
b) 1967
c) 1971
d) 1945
Explanation
The Netherlands Greenpeace was founded in 1971 by Irving Stowe and Dorothy Stowe Canadian and US ex-pat environmental activists.
153. Which of these issues are focused by the Greenpeace?
a) Climate Change
b) Terrorism
c) Commercial Whaling
d) Genetic-Engineering
Explanation
Greenpeace states its goal is to “ensure the ability of the Earth to nurture life in all its diversity” and focuses its campaigning on worldwide issues such as climate change, deforestation, overfi shing, commercial whaling, genetic engineering, and anti-nuclear issues.
154. Greenpeace is a founding member of the ________.
a) FAO
b) WHO
c) UNESCO
d) INGO
Explanation
Greenpeace has a general consultative status with the United Nations Economic and Social Council and is a founding member of the INGO Accountability Charter, an international non-governmental Organization that intends to foster accountability and transparency of non-governmental Organizations.
155. Assertion (A): International Organizations have been increasing in recent years.
Reasoning(R): The International politics is more institutionalized by the treaties among states.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
International Organizations have become an increasingly common phenomenon in international life. The proliferation of international Organizations and treaty arrangements among states represents the formal expression of the extent to which international politics is becoming more and more institutionalized.