India’s International Relations 10th Social Science Lesson 21 Questions in English
10th Social Science Lesson 21 Questions in English
21] India’s International Relations
1. Who quoted the statement as “we live in a world of Interdependence”?
a) Jawaharlal Nehru c) Mount Batten
b) Rajendra Prasad d) Gandhi
Explanation
The first Prime Minister of India Jawaharlal Nehru stated “We can neither be absolutely dependent or independent, but we live in a world of interdependence.”
2. Assertion (A): Independent India has been fostering world peace.
Reasoning(R): India abjured in military alliances from Independence.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Independent India has been consistently fostering world peace and international cooperation.India abjured military alliances but has been active in cooperating and co-coordinating with other nations for peace and economic development.
3. What was India’s objective in International relations?
a) Peace c) Money Policy
b) Good Business relations d) Exchange policy
Explanation
India would prefer a peaceful, wealthy neighborhood responsive to its own needs and wishes. India has always been known as a peace-loving country and has strived hard to champion the cause of peace in the world.
4. Choose the correct statements regarding India’s foreign relations.
i) India is a highly populated country.
ii) India’s neighbors had been part of a homogenous culture in the subcontinent for many years.
a) i only c) Both a and b
b) ii only d) None of the above
Explanation
Being a country with a huge population, India is surrounded by many neighboring countries with whom she has traditionally tried to maintain friendly and good neighborly relations. India’s neighbors had been a part of a homogenous culture prevailing in the Indian subcontinent for last five thousand years.
5. Which country does not belong to the North boundary of the India?
a) China c) Bhutan
b) Nepal d) Pakistan
Explanation
India is a vast country with Pakistan and Afghanistan to the north-west and China, Nepal, Bhutan to the north.
6. Which separates Maldives from India?
a) Indian Ocean c) Palk Strait
b) Bay of Bengal d) Rann of Kutch
Explanation
Sri Lanka from south-east and Maldives from south-west are two countries that lie close to India separated by the Indian Ocean. India has cordial historical, religious, economic, ethnic and linguistic relationship with all of these countries.
7. Match
A. South East i) Bangladesh
B. East ii) Afghanistan
C. North West iii) Maldives
D. South West iv) Sri Lanka
a) iv, iii, ii, i c) iv, i, ii, iii
b) ii, iv, i, iii d) i, ii, iv, iii
Explanation
India is a vast country with Pakistan and Afghanistan to the north-west and China, Nepal, Bhutan to the north, Bangladesh to the east, Myanmar to the Far East. Sri Lanka from south-east and Maldives from south-west are two countries that lie close to India separated by the Indian Ocean.
8. Which of these country share most number of neighbors in its borders?
a) Russia c) France
b) India d) Germany
Explanation
The countries that share the most number of neighbors touching its borders are China and Russia.
9. Assertion (A): Indo-Afghan relation was strengthened by the SPA agreement.
Reasoning(R): The SPA provides assistance to rebuild Afghan infrastructures.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Indo-Afghan relation was strengthened by the Strategic Partnership Agreement (SPA). SPA provides assistance to re-build Afghan’s infrastructure, institutions, agriculture, water, education, health and providing duty-free access to the Indian market.
10. Which Afghan dam was constructed with the help of India?
a) Salma Dam c) Kajaki Dam
b) Darunta Dam d) Grishk Dam
Explanation
India helped Afghans in the construction of Salma Dam in the Heart Province.
11. Which of these King of ancient India sent religious missionaries to Afghanistan?
a) Harsha c) Asoka
b) Kanishka d) Akbar
Explanation
During the reign of Kanishka a large number of Indian missionaries went to China, Central Asia and Afghanistan to preach their religion.
12. Name the Afghanistan leader participated in Indian freedom struggle?
a) Jinnah c) Abul Kalam Azad
b) Ali brothers d) Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan
Explanation
Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan of Baluchistan a border province in today’s Pakistan was a prominent leader of the Indian Independence movement and active supporter of the Indian National Congress.
13. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the Indo-Afghan relations.
i) India announced scholarships for children of Martyrs of Afghan Security Forces.
ii) India supports the Public health sectors of Afghanistan.
iii) All large Scale Industries of Afghanistan were promoted by Indian investments.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
India announced 500 scholarships for the children of the martyrs of Afghan Security Forces in school and colleges both in Afghanistan and in India. India is also supporting Afghanistan to improve its public health and small-scale industries.
14. In which sector Indian companies planned to make a huge investment?
a) Agriculture c) Shipping Industry
b) Mining sector d) Textile Industries
Explanation
India is at the forefront of the promotion of investment in Afghanistan and a consortium of public and private Indian companies has been selected to make one of the biggest investments in the mining sector.
15. Name the Cricket stadium which proves the Indian-Afghan collaboration?
a) Rawalpindi Cricket Stadium c) Kandahar International Cricket Stadium
b) Gadaffi Stadium d) Arbab Niaz Stadium
Explanation
To harness India’s sports potential India has built Kandahar International Cricket Stadium in Afghanistan.
16. In what way India supports Afghanistan for its development?
a) Monetary Aids c) Funds
b) Manpower d) both a and c
Explanation
India is contributing proactively to the development of Afghanistan in the form of monetary aids and funds.
17. Which country was acknowledged as an independent country by India?
a) Bangladesh c) Japan
b) Pakistan d) Nepal
Explanation
India was the first nation to acknowledge Bangladesh the former East Pakistan as an independent country.
18. Bangladesh formerly belonged to which part of these countries?
a) West Pakistan c) West Afghanistan
b) East Nepal d) East Pakistan
Explanation
Bangladesh was known as East Pakistan is an independent country.
19. State the correct distance shared by Bangladesh and India border?
a) 6045.5 km c) 5132.4 km
b) 4096.7 km d) 7890.6 km
Explanation
India and Bangladesh share the longest land boundary of 4096.7 kilometers.
20. Which of these cities of India and Bangladesh are proposed for a new Railway connectivity?
a) Agartala-Akhaura c) Shillong- Sylhet
b) Kohima- Dhaka d) Imphal – Khulna
Explanation
India has plans to implement the proposed rail connectivity between Agartala, India and Akhaura, Bangladesh.
21. Under which agreement India shares a Road transit facility with Bangladesh?
a) BBIN-MVA c) SASEC
b) SCO d) Chabahar Agreement
Explanation
Bangladesh has granted India road transit facility through its territories from Kolkata to Agartala via Dhaka under BBIN-MVA Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, and Nepal Motor Vehicle Agreement.
22. When the Farakka accord was signed between India and Bangladesh?
a) 1976 c) 1977
b) 1987 d) 1956
Explanation
The Farakka accord on sharing of Ganga waters signed in 1977 is a historic agreement between India and Bangladesh.
23. Assertion (A): India shares Ganga water with Bangladesh according to the Farakka Accord.
Reasoning(R): India and Bangladesh shares about 15 common rivers.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
India and Bangladesh share 54 common rivers and a bilateral Joint River Commission is working to maximize benefits from common river systems. The Farakka accord on sharing of Ganga waters signed in 1977 is a historic agreement between India and Bangladesh.
24. Which of these are constructed by India under Aid to Bangladesh?
a) Laboratories c) Deep tube wells
b) Dispensaries d) All the above
Explanation
The Government of India provides grant assistance for project under ‘Aid to Bangladesh’ for the construction of buildings, laboratories, dispensaries and deep tube wells.
25. Which organ of India grants scholarships to the Bangladesh students every year?
a) ICCR c) AICTE
b) HECI d) MHRD
Explanation
The scholarships are granted by ICCR (Indian Council for Cultural Relations) every year to students from Bangladesh and it has initiated a Tagore Chair in University of Dhaka.
26. In which of this Universities India has initiated a Tagore Chair for the benefit of the Bangladesh students?
a) The University of Dhaka c) The Banaras Hindu University
b) The University of Delhi d) The Bangladesh University
Explanation
The scholarships are granted by ICCR (Indian Council for Cultural Relations) every year to students from Bangladesh and it has initiated a Tagore Chair in University of Dhaka.
27. In which city of Bangladesh, India inaugurated a pipeline construction from Siliguri?
a) Dhaka c) Parbatipur
b) Rajshahi d) Khulna
Explanation
The India and Bangladesh jointly inaugurated the construction of 130-kilometre Friendship Pipeline between Siliguri in West Bengal and Parbatipur, Bangladesh.
28. When India leased the Teen Bigha to Bangladesh?
a) 2010 c) 2012
b) 2011 d) 2014
Explanation
The Teen Bigha Corridor is a strip of land belonging to India on the West Bengal–Bangladesh border, which was leased to Bangladesh in 2011.
29. State the other name of Bhutan?
a) Land of Mountains c) Land of Himalaya
b) Land of Rivers d) Land of Thunderbolt
Explanation
Bhutan a small Himalayan kingdom popularly known as a land of thunderbolt is one of the poorest countries of the world.
30. When and where did India appoint its resident representative in Bhutan?
a) 1986, Pura c) 1968, Thimphu
b) 1967, Jakar d) 1956, Gelephu
Explanation
The diplomatic relations between India and Bhutan were established in 1968 with the appointments of a resident representative of India in Thimphu.
31. Which of the access of Bhutan id dependent on India?
a) Railway Line c) Sea Access
b) Airline d) None of the above
Explanation
Bhutan is a landlocked nation. So it is highly dependent on India for access to sea.
32. Assertion (A): The Bilateral trade relation between India and Bhutan is known as Bharat to Bhutan.
Reasoning(R): India is the principal contributor to the economic development of Bhutan.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
India is the principal contributor in the economic development of Bhutan. India declared the bilateral trade relation known as ‘Bharat to Bhutan’ (B2B).
33. Which of these was constructed with the help of India for the benefit of Bhutan Students?
a) Primary Schools c) Colleges
b) Digital library d) University
Explanation
India provides scholarship to Bhutanese students to study in prestigious institutions of higher learning and offered help in setting up a digital library in Bhutan.
34. Choose the correct statements.
i) The Bhutanese students are provided scholarship for studying in prestigious Institutions.
ii) Nehru-Wangchuk Scholarship is awarded to the Indian students.
a) i only c) Both a and b
b) ii only d) neither a nor b
Explanation
The prestigious Nehru-Wangchuk Scholarship is being awarded to deserving and talented Bhutanese nationals to undertake studies in selected premier Indian educational institutions. India provides scholarship to Bhutanese students to study in prestigious institutions of higher learning.
35. How many hydroelectric projects have been constructed by India in Bhutan?
a) 2 c) 4
b) 6 d) 3
Explanation
The Hydro power sector represents one of the main indicators of bilateral co-operation between India and Bhutan. So far, Government of India has constructed three hydroelectric projects in Bhutan.
36. Assertion (A): The Hydro Electric power sector is the main bilateral co-operation between India and Bhutan.
Reasoning(R): The Government of India has constructed Hydro power stations in Chukha, Kurichchu and Tala.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The hydropower sector represents one of the main indicators of bilateral co-operation between India and Bhutan. So far, Government of India has constructed three hydroelectric projects in Bhutan in Chukha, Kurichchu and Tala.
37. State the main sectors of Bhutan in which India had played a major part in development?
a) Telecommunication c) Bridges
b) Hospitals d) all the above
Explanation
India has helped Bhutan in developing that country’s infrastructure by establishing telecommunication and in the construction of hospitals, roads and bridges.
38. Which Indian saint played a major role in spreading Buddhism in Bhutan?
a) Guru Padmasambhava c) Guru Nandhikasyapa
b) Guru Sariputra d) Guru Upali
Explanation
Guru Padmasambhava a Buddhist saint who went to Bhutan from India played an influential role in spreading Buddhism and cementing traditional ties between people of both nations.
39. Which of this country share a common geographic and civilizational depth with India?
a) Bangladesh c) Afghanistan
b) Pakistan d) China
Explanation
In terms of geographic and demographic dimension, skilled manpower and civilizational depth China is the only country in the region which qualifies for comparison with India.
40. In what ways India and China share similar ideas and views in World forum?
a) World Trade Organization c) Reforms of the World Bank
b) International Climate change d) All the above
Explanation
India and China share similarity of view on many fronts like World Trade Organization, international climate change talks and reforms of the World Bank.
41. Which of this Chinese organization gave the observer status to India?
a) Shanghai Cooperation c) BRICS
b) SAARC d) The World Bank
Explanation
Shanghai Cooperation Organization, which was China’s initiative, has granted the observer status to India while SAARC had granted the observer status to China.
42. In which of these ways India and China developed their relations.
a) Both countries established more dialogue mechanisms covering diverse sectors.
b) Bilateral trade has developed enormous growth.
c) A Common educational exchange program was signed between these two countries.
d) All the above
Explanation
Both sides of China and India have established more dialogue mechanisms covering diverse sectors. Bilateral trade has registered enormous growth. India and China have signed an educational exchange program. Under this agreement, scholarships are awarded to 25 students by both sides in recognized institutions of higher learning in each other’s country.
43. What is the boundary line between the territories of India and China?
a) Radcliffe line c) Durand Line
b) McMahon line d) Palk Strait
Explanation
McMahon Line is the boundary line between India and China, east of Bhutan.
44. In which year the McMahon line was determined?
a) 1912 c) 1916
b) 1910 d) 1914
Explanation
McMahon line was determined 1914 at a conference of representatives of British India, Tibet and China. The Secretary of State for India in British Cabinet, Arthur Henry McMahon represented British India at the Conference.
45. Which of these Countries representatives were involved in the 1914 Conference?
a) British India c) Tibet
b) China d) All the above
Explanation
McMahon line was determined 1914 at a conference of representatives of British India, Tibet and China. The Secretary of State for India in British Cabinet, Arthur Henry McMahon represented British India at the Conference.
46. Which country is located at the South of Lakshadweep Island?
a) Sri Lanka c) Maldives
b) Malaysia d) Oman
Explanation
Maldives is located south of Lakshadweep Islands in the Indian Ocean.
47. Which of these factors are being developed between India and Maldives?
a) Trade c) Tourism
b) Industries d) both a and c
Explanation
The relationship with Maldives is important for India given its strategic location and geographical proximity. Trade and tourism are being developed between the two countries.
48. Assertion (A): India and Maldives share a common Linguistic, Cultural and religious links.
Reasoning(R): Both Countries have agreed to strengthen the cooperation to enhance Maritime Security in the Indian Ocean region.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
India and Maldives share ethnic, linguistic, cultural, religious and commercial links steeped in antiquity and enjoy cordial and multi-dimensional relations. Both countries have agreed to Strengthen cooperation to enhance maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region through Coordinated patrolling and aerial surveillance and exchange of information.
49. When did Burma change its name as Myanmar?
a) 1987 c) 1990
b) 1989 d) 1986
Explanation
India’s second largest border is shared with Myanmar known as Burma till 1989.
50. Which of these Indian states does not share their borders with Myanmar?
a) Arunachal Pradesh c) Mizoram
b) Nagaland d) Assam
Explanation
Four North-Eastern Indian states Arunachala Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram also share their borders with Myanmar.
51. Myanmar is the India’s gateway of _________ Asia.
a) North-East c) South-East
b) South-West d) North-West
Explanation
Myanmar is India’s gateway to South East Asia.
52. Which of these connects the Kolkata to Sittwe in Myanmar?
a) Kaladan Multi Model Transit Transport
b) Pancheshwar project
c) Strategic Partnership Agreement
d) BBIN-MVA Agreement
Explanation
India is building the Kaladan Multi-Model Transit Transport a road-river-port cargo transport project to link Kolkata to Sittwe in Myanmar.
53. Which source of energy of Myanmar is shared for the needs of India?
a) Petroleum c) Solar Power
b) Iron d) Minerals
Explanation
Myanmar is an important partner in India’s energy needs for petroleum and natural gas.
54. Which of these Indian sectors have invested in Myanmar’s energy sector?
a) ESSAR c) GAIL
b) ONGC d) All the above
Explanation
The Indian companies such as Essar, GAIL and ONGC, Videsh Ltd. had invested in Myanmar’s energy sector.
55. Which country acts as a Natural buffer between India and China?
a) Tibet c) Bhutan
b) Nepal d) Myanmar
Explanation
Nepal is a natural buffer between India and China.
56. Assertion (A): Nepal depends on India for Economic support and Transit facilities.
Reasoning(R): Nepal is a small landlocked country.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Nepal being a small landlocked country depends on India for economic support and transit facilities.
57. Which of these Indian States share its borders with Nepal?
a) Sikkim c) Bihar
b) West Bengal d) All the above
Explanation
India shares borders in five Indian states Sikkim, West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand with Nepal.
58. Which of the Nepal city is connected by the Mahendra Raj Marg link of India?
a) Kathmandu c) Janakpur
b) Pasupathi d) Varanasi
Explanation
India built the 204-kilometre long Mahendra Raj Marg to link Kathmandu and India.
59. What is the capacity of the Pancheshwar project took by the Indian Government?
a) 1000MW c) 3600MW
b) 5600MW d) 10500MW
Explanation
Nepal is endowed with fast-flowing rivers and its terrain is ideal for hydroelectric power generation. India has taken up the work of 5600 MW Pancheshwar project which remained stalled for 18 years after agreement.
60. Name the traditional centers in Nepal?
a) Pasupathi c) Janakpur
b) Kathmandu d) Both a and c
Explanation
Nepali and Indian people visit each other’s country for religious pilgrimage. Pashupati and Janakpur are traditional centers in Nepal whereas Varanasi and the four Dhaams Badrinath, Puri, Dwaraka and Rameshwaram are important pilgrimage destinations in India.
61. In which schedule of the Indian Constitution the Nepalese language has been added?
a) Sixth schedule c) Eighth schedule
b) Seventh schedule d) Fifth Schedule
Explanation
The bond of friendship further increased when India included Nepalese language in the VIII schedule of the Constitution.
62. On which of this river a joint Hydropower project between Nepal and India has been built?
a) Shardha c) Yamuna
b) Ganges d) Brahmaputra
Explanation
A joint hydropower project is being built on the Sharda River. This power plant helps both India and Nepal with respect to electricity production and irrigation facilities.
63. How many twinning cities have been signed between India and Nepal?
a) 2 c) 4
b) 3 d) 5
Explanation
The governments of India and Nepal have signed three sister-city agreements for twinning of Kathmandu-Varanasi, Lumbini-Bodhgaya and Janakpur-Ayodhya.
64. When the territory of India was bifurcated to form Pakistan?
a) 1946 c) 1945
b) 1947 d) 1948
Explanation
The bifurcation of territory demarcated India and Pakistan in 1947.
65. Assertion (A): Pakistan has been antagonistic in maintain the relations with India.
Reasoning(R): India has made extreme efforts to improve and stabilize the relations with Pakistan.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Pakistan has been antagonistic when maintaining relations with India. But India has made extreme efforts to improve and stabilize relations with Pakistan.
66. When the Ceasefire line was renamed as the Line of Control?
a) 1972 c) 1976
b) 1949 d) 1947
Explanation
The Ceasefire line determined in 1949 was called the LoC after 1972.
67. Match
A. Shimla Agreement i) Sri Lanka
B. Radcliffe Line ii) Pakistan
C. Brandix iii) 1947
D. Pakistan Partition iv) 1972
a) ii, i, iv, iii c) i, iv, iii, ii
b) iii, iv, ii, i d) iv, ii, i, iii
Explanation
The boundary agreed between India and Pakistan under the Shimla Agreement of 1972. It was called Radcliffe Line at the time of partition in1947. The Sri Lankan investments in India include Brandix garment city in Vishakhapatnam.
68. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the India-Pakistan relationship.
i) Kashmir is the bone of contention between India and Pakistan.
ii) Cross border terrorism is the major irritant between these two countries.
iii) India never tried to bring a positive change in the relationship with Pakistan.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
Kashmir is the bone of contention between India and Pakistan which has brought the two countries into an open clash many times. Cross-border terrorism is a major irritant. India tried to bring a positive change in the relationship of the two countries.
69. Which of these agreements made efforts to improve the relationship between India and Pakistan?
a) Shimla Agreement c) Panchaseela policies
b) Lahore Declaration d) Both a and b
Explanation
India tried to bring a positive change in the relationship of the two countries through bilateral agreements such as Shimla Agreement and Lahore Declaration.
70. Which separates India and Sri Lanka?
a) Radcliffe Line c) Bay of Bengal
b) Indian Ocean d) Palk Strait
Explanation
India has cultural, historical and religious ties with Sri Lanka separated by the narrow expanse of the Palk Strait.
71. By which of these India and Sri Lanka develop trade agreements?
a) SAARC c) BRICS
b) G-7 d) Common Wealth
Explanation
India and Sri Lanka have shared excellent trade relations committing to each other in both bilateral free trade agreements as well as developing interactions through SAARC.
72. Which of these Statements is true regarding the India Sri Lanka relationship?
i) India and Sri Lanka has conventionally close to each other.
ii) India is among the top investors in Sri Lanka.
iii) India has Cultural, historical and religious ties with Sri Lanka.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
The relationship between India and Sri Lanka can generally be termed as friendly. India and Sri Lanka has conventionally close to each other. India is among the top investors in Sri Lanka and its investments are in diverse areas. India has cultural, historical and religious ties with Sri Lanka.
73. In which of these sectors India made its Investments in Sri Lanka?
a) Petroleum Retail c) Real estate
b) Tourism d) All the above
Explanation
India is among the top investors in Sri Lanka and its investments are in diverse areas including petroleum retail, IT, real estate, telecommunication and tourism.
74. Which country is a partner in Nalanda University Project in India?
a) Bhutan c) Bangladesh
b) Sri Lanka d) China
Explanation
India offers scholarship slots annually to deserving Sri Lankan students. Sri Lanka is also a partner in Nalanda University Project of India.
75. Which ancient King conquered the northern part of Ceylon?
a) Ashoka c) Vijayalaya Chozhan
b) Harsha d) Rajendra I
Explanation
Ashoka had sent his son Mahinda and daughter Sangamitra to Ceylon or Sri Lanka for the propagation of Buddhism. Chola kings Rajaraja I and Rajendra I conquered the northern part of Ceylon.
76. Which of these are categorized as the developed countries?
a) USA c) Australia
b) Japan d) All the above
Explanation
A developed country is a sovereign state that has a highly developed economy and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations such as USA, Japan, Australia and European countries.
77. Which of these factors is an explanation of a developed country?
a) Highly developed economy c) Major exports
b) Huge Military forces d) High GDP
Explanation
A developed country is a sovereign state that has a highly developed economy and advanced technological infrastructure.
78. Match
A. COMCASA i) Australia
B. AUSINDEX ii) Japan
C. MAHSR iii) USA
a) iii, i, ii c) ii, i, iii
b) ii, iii, i d) i, ii, iii
Explanation
India and the United States of America have signed a Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA). Mumbai–Ahmedabad High Speed Railway MAHSR is another area of co-operation of Japan’s Shinkansen system. It is a highest class of high-speed railway system with safety and accuracy. Australia and India are committed to working together to enhance maritime co-operation with India’s bilateral naval exercise, AUSINDEX.
79. What is the significance of the COMCASA agreement between India and United States of America?
a) Military agreement c) Information Technology Agreement
b) Trade Agreement d) Industrial Sectors
Explanation
India and the United States of America have signed a Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA) that will lead to a new generation of bilateral military partnership. It is valid for a period of 10 years.
80. Which of these countries Launch pads are used by ISRO?
a) German c) Russia
b) France d) Britain
Explanation
There has been a significant progress in all areas particularly the growing cooperation and exchanges include defense, counterterrorism, nuclear energy and space. French space launch pads are used by ISRO.
81. Which of these smart cities are developed by India and France cooperation?
a) Chandigarh c) Pondicherry
b) Nagpur d) All the above
Explanation
India and France are cooperating on developing smart cities Chandigarh, Nagpur and Pondicherry.
82. Assertion (A): The Australian India Council broadens the relationship between India and Australia.
Reasoning(R): India and Australia have built strategic trust over years slowly and steadily.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The Australia India Council broadens the relationship between Australia and India raising awareness and promoting exchanges. India and Australia have built strategic trust over the years slowly yet steadily.
83. To which sector Japan’s Shinkansen system is related?
a) Naval System c) High speed Railway System
b) Military System d) Solar power system
Explanation
India decided to introduce the Japan’s Shinkansen system. It is a highest class of high-speed railway system with safety and accuracy.
84. How many number of seats has been offered by Japan to Indian Nationalist in the University of Japan?
a) 50 c) 25
b) 20 d) 10
Explanation
The Government of Japan has offered 20 seats per year to Indian nationals for a master’s degree course in the University of Japan for serving the Indian Railways.
85. Which of these Institutes provide the Japan manufacturing skills to Indian people?
a) JIM c) MAHSR
b) Shinkansen System d) COMCASA
Explanation
In the manufacturing sector Japan announced its co-operation of training 30,000 Indian people in the Japan India Institute of Manufacturing (JIM) providing Japanese style manufacturing skills to enhance India’s manufacturing industry base and contribute to ‘Make in India’ and ‘Skill India’ initiatives.
86. Which of these Indian states has the JIM’s?
a) Gujarat c) Rajasthan
b) Karnataka d) All the above
Explanation
In 2017 the first four JIMs were started in the states of Gujarat, Karnataka, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu.
87. In which State of India the Japanese Endowed Courses were included in the Engineering Colleges?
a) Tamil Nadu c) Rajasthan
b) Andhra Pradesh d) Gujarat
Explanation
The two Japanese Endowed Courses in engineering colleges, JEC was established in Andhra Pradesh.
88. Which of these Countries are included in the West Asia?
a) Japan c) Afghanistan
b) South Korea d) Turkey
Explanation
West Asia includes Egypt, the Arabian Peninsula, Turkey and Iran. India and West Asia enjoy pre-historical ties.
89. Assertion (A): India and West Asian countries enjoy pre-historical ties.
Reasoning(R): Trade relations were established between the Indus Valley and Mesopotamia
Civilizations.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
India and West Asia enjoy pre-historical ties. Trade relations were established between the civilizations of Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley.
90. Which of the countries signed the Chabahar Agreement to establish the transit using the Chabahar port?
a) India, Afghanistan, Iran
b) Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan
c) Afghanistan, Japan, India
d) India, Iran, Saudi Arabia
Explanation
A trilateral agreement called the Chabahar Agreement was signed between India, Afghanistan and Iran, which has led to the establishment of transit and transport corridor among three countries using Chabahar port.
91. Which of this ancient Indian place was connected with ancient Sumeria?
a) Meluha c) Lothal
b) Multan d) Sindh
Explanation
One of the oldest maritime trading routes ran from ancient Sumeria via Bahrain to the Indus Civilization called Meluha.
92. Assertion (A): India is a potential super power and has a growing International Influence around the World.
Reasoning(R): India is a newly industrialized country.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
India is a potential superpower and has a growing international influence all around the world. Being a newly industrialized country, India has a great history of collaboration with several countries.
93. Which of these Countries does not included in BRICS Organizations?
a) Brazil c) China
b) Russia d) Singapore
Explanation
Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa are leading emerging economies and political powers at the regional and international level.
94. Find the Headquarters of the BRICS organization?
a) New Delhi c) Hong Kong
b) Shanghai d) Beijing
Explanation
The BRICS organization’s headquarters is in Shanghai, China.
95. Assertion (A): The BRICS organization opened a possibility of countries of the Global North to
Challenge the Global South.
Reasoning(R): India is an active member of BRICS which helps to build a Global profile.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
BRICS opened up a possibility for countries of the Global South to challenge the Global North. India is an active member and this collaboration paves way for India to build its global profile.
96. What were the reasons for forming the BRICS?
i) To be an alternative to World Bank and IMF.
ii) To challenge the supremacy of the Western Countries.
iii) To Dominate the Economic power globally.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
Reason for the formation of BRICS
- To be an alternative to World Bank and IMF
- To challenge U.S. supremacy
- To provide self-owned and self-managed organizations to carry out developmental and
- Economical plans in its member nations
97. State the Objectives of BRICS.
a) To Challenge the Supremacy of USA.
b) To achieve Regional development.
c) To Overcome the Economic Burdens of the associated Nations.
d) To Fund the Development projects in the associated countries.
Explanation
The Objectives of BRICS are achieving regional development; it acts as a bridge between developed and developing countries.
98. Who coined the acronym BRICS?
a) Jim O’Neil c) Friedrich Hayek
b) Alan Greenspan d) Ernst Fehr
Explanation
The acronym BRICS was coined by Jim O’Neill, a famous British economist. He Predicted that by year 2050 Brazil, Russia, India and China would become bigger than the six most industrialized nations in dollar terms and would completely change the power dynamics of the last 300 years.
99. Which provides a framework for protecting against the Global liquidity pressures of the BRICS countries?
a) IMF c) NDB
b) UN d) CRA
Explanation
The Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) is a framework for providing protection against global liquidity pressures which includes currency issues.
100. In which year BRICS summit a payment system was initiated as an alternative for SWIFT system?
a) 2011 c) 2013
b) 2015 d) 2017
Explanation
At the 2015 BRICS Summit, ministers from the BRICS nations initiated consultations a payment system that would be an alternative to the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) system.
101. Which of this country does not belong to OPEC’s Founder members?
a) Kuwait c) Saudi Arabia
b) Iran d) Austria
Explanation
Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela are the OPEC’s Founder Members.
102. How many categories of memberships are followed among the OPEC nations?
a) 2 c) 4
b) 3 d) 5
Explanation
OPEC the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries is a group of oil producing Nations. It is an intergovernmental organization founded in Baghdad, Iraq, and headquartered in Vienna, Austria. There are three categories of memberships: Founder Members, Full Members and Associate Members.
103. When the OPEC Logo was finalized by an international competition?
a) 1965 c) 1956
b) 1973 d) 1969
Explanation
The OPEC LOGO is the result of an international design competition held in 1969. An Austrian designer Svoboda won the competition with her design, which combined the different letters of the organization’s name in a rounded design.
104. Which is not a mission of OPEC?
i) To coordinate oil policies in its member countries.
ii) An efficient and regular supply of oil to consuming nations.
iii) To setup oil markets in new countries.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) all the above
Explanation
The OPEC’s mission
- To coordinate oil policies in its member countries
- Help stabilize oil markets
- To secure fair and stable income to petroleum producers
- An efficient, economic and regular supply of oil to consuming nations
- A fair return on capital to those investing in the petroleum industry
105. Choose the correct statements regarding OPEC.
i) OPID is an institution that helps poor countries to start up new Oil markets.
ii) OPEC has an Information center open to the oil producing countries and its members.
iii) OPID helps finance projects with low interest loans.
iv) The information center of OPEC is used by the researchers and students.
a) i, ii, iv only c) ii, iii, iv only
b) ii, iv only d) iii, iv only
Explanation
The OPEC Fund for International Development (OPID) is an institution that helps finance projects with low interest loans. OPEC has an Information Centre with over 20,000 volumes including books, reports, maps and conference proceedings related to petroleum, energy and the oil market. The Information Centre is open to the public and is often used by researchers and students.
106. Assertion (A): India is one of the biggest producers of crude oil.
Reasoning(R): OPEC has vested interest in India’s economic growth.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
India is one of the biggest consumers of crude oil. OPEC obviously has vested interest in India’s economic growth.
107. Choose the correct statements regarding India’s position in OPEC
i) India has enough oil resources.
ii) India is a great partner for OPEC because of its high oil produce.
iii) Devoid of necessary oil reserves in India strongly focuses on agriculture and Industrial production.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) All the above
Explanation
India has been identified as a great partner for OPEC mainly because of its high oil demand. India doesn’t have enough oil reserves. India can’t produce oil. Devoid of necessary oil reserves India strongly focuses on agriculture, and industrial production.
108. Which of these countries is not included in IBSA?
a) India c) Afghanistan
b) Brazil d) South Africa
Explanation
The IBSA consists of India, Brazil, and South Africa which focuses on agriculture, education, energy, trade, culture and defense among others.
109. What does C stands for in the BCIM organization?
a) China c) Cuba
b) Chile d) Canada
Explanation
The Members of the BCIM are Bangladesh, China, India, and Myanmar.
110. Which of this organization was initiated to create infrastructural facilities in the Ganga-Mekong basin?
a) RCEP c) IBSA
b) MGC d) BIMSTEC
Explanation
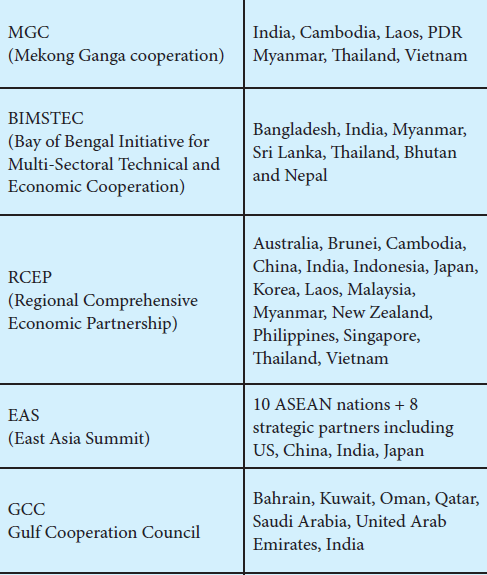
The Mekong Ganga cooperation was created to develop necessary infrastructural facilities in the Ganga Mekong basin. India, Cambodia, Laos, PDR, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam are the active members of this organization.
111. State the countries included in the BIMSTEC organization?
a) Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka
b) Sri Lanka, China, India, Australia
c) Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Indonesia
d) Malaysia, India, Singapore, Nepal
Explanation
The BIMSTEC, Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectorial Technical and Economic Cooperation has Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Bhutan and Nepal as its members.
112. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the RCEP organization.
i) New Zealand is one of the members in the RCEP organization.
ii) Technical cooperation and dispute settlements are also objectives of RCEP.
iii) To achieve modern high quality in goods and trade of service.
a) i only c) iii only
b) ii only d) None of the above
Explanation
The members of RCEP are Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. The main objective of RCEP are to achieve modern high quality and mutually beneficial agreement that covers trade in goods, trade in service, investments, technical cooperation dispute settlement and other issues.
113. What does RCEP stands for?
a) Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership
b) Regional Cooperation in Economic Partnership
c) Reuse Carbon Ecofriendly Partners
d) Resolution for Cooperative Economic profile
Explanation
The RCEP stands for Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.
114. Which of these organization aims for the energy development among its members?
a) BBIN c) EAS
b) SCO d) GCC
Explanation
The BBIN consists of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, and Nepal as its members and the objective of this organization is for energy development.
115. Which of these countries does not belong to GCC nations?
a) Bahrain c) Nepal
b) Kuwait d) Qatar
Explanation
The members of GCC, Gulf Cooperation Council are Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates and India.
116. When the Shanghai Cooperation Organization was formed?
a) 1991 c) 1990
b) 1996 d) 1993
Explanation
The SCO was founded on 26 April 1996 with five nations as it initial members.
117. Assertion (A): India and China are active members of SCO.
Reasoning(R): SCO aims to resolve border issues and countering terrorisms.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The Shanghai cooperation Organization members are India, Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. It aims for security-related concerns, resolving border issues, intelligence sharing and countering terrorism.
118. Which of this organization promotes peace and stability in Asia?
a) SCO c) MGC
b) EAS d) RCEP
Explanation
The EAS, East Asia Summit objective is to promote peace and stability.
119. Where did the 19th SCO summit held?
a) Bishkek c) Astana
b) Tashkent d) Ufa
Explanation
The 19th SCO summit meeting was held on June 13, 2019 at Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan and the participating countries signed 14 agreements.
120. Match the member countries with the Organization.
A. MGC i) Bahrain
B. EAS ii) Bhutan
C. GCC iii) Cambodia
D. BIMSTEC iv) Japan
a) iii, i, ii, iv c) i, ii, iv, iii
b) iii, iv, i, ii d) ii, iii, i, iv
Explanation