Human Organ Systems Notes 6th Science Lesson 12 Notes in English
6th Science Lesson 12 Notes in English
12] Human Organ Systems
Introduction
- Organ systems are formed by the association of organs which are organized from tissues.
- This kind of organization helps the organism to perform various activities more efficiently.
- A group of organs that work together to perform a particular function is known as an organ system. The Human body has eight major organ systems. They are
- Skeletal System
- Muscular System
- Digestive System
- Respiratory System
- Circulatory System
- Nervous System
- Endocrine System
- Excretory System
- In this lesson, let us study more about the structure and function of these organ systems of our body.
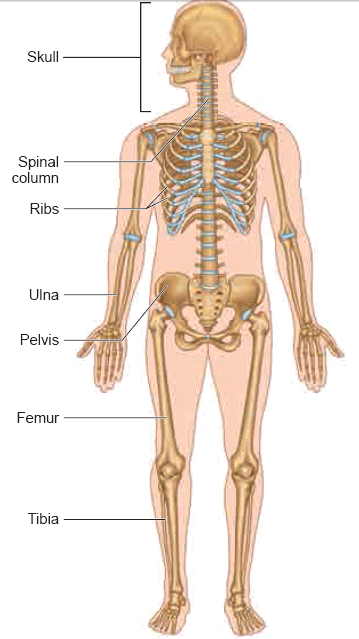
Skeletal System
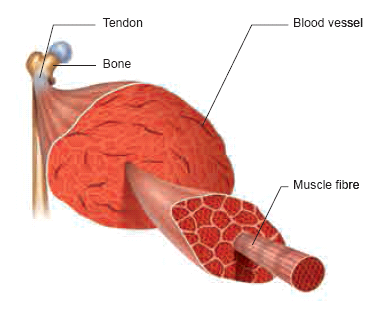
- The skeletal system consists of bones, cartilages and joints. Bones provide a frame work for the body.
- Bones along with muscles help in movements such as walking, running, chewing and dancing etc.,
- The adult human skeletal system consists of 206 bones and few cartilages, ligaments and tendons.
- Ligaments help in connecting bone to bone. Tendons connect bone to muscle. The two major divisions of the skeletal system are Axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton.
- Axial skeleton forms the upright axis of the body which includes
- Skull
- Vertebral column
- Rib cage
- Appendicular skeleton consist of the bones of the limbs along with their pectoral and pelvic girdles.
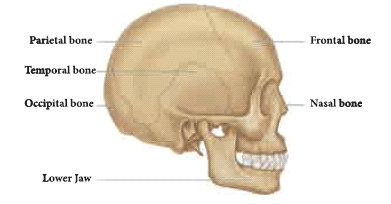
Skull
- The skull is made up of cranial bones and facial bones. It protects the brain and the structures of the face.
- The hyoid bone present at the base of the buccal cavity and the auditory ossicles (Malleus, Incus and Stapes) are also included in the skull. Lower jaw bone is the largest and strongest bone in the human face.
Vertebral Column
Vertebral column extends from the base of the skull. It protects the spinal cord. It is formed by a number of serially arranged small bones called vertebrae (singular : vertebra)
Rib cage
The rib cage is made up of 12 pairs of curved, flat rib bones. It protects the delicate vital organs such as heart and lungs.
Limbs
Man has two pairs of limbs namely upper limbs (fore limbs) and lower limbs (hind limbs). Fore limbs are used for holding, writing etc., while hind limbs are used for walking, sitting etc.,
Skeletal System
Girdles
- The fore limbs and hind limbs are attached to the axial skeleton with the help of pectoral and pelvic girdle respectively.
Muscular System
- In the body, muscular system along with the skeletal and nervous system is responsible for the body movements.
- Muscles can contract and therefore, help in moving other parts of the body. It maintains the posture and body position. There are three types of muscles namely
- Skeletal muscle
- Smooth muscle
- Cardiac muscle
How do muscles work?
- Muscles of the body can only pull and they cannot push. Two muscles are required to move a bone at a joint. When one muscle contracts, the other muscle relaxes.
- For example, to move ‘the lower arm up and down two type of muscles called biceps and triceps are required.
- When we raise our lower hand, the biceps in front become short by contraction and the triceps at the back stretch to pull up the arm.
- When we lower our arm, the triceps at the back contract and biceps stretch to pull the arm down.
Skeletal Muscles
- Skeletal muscles of our body are attached to the bones. They are called Voluntary muscles because they can be controlled by our will. Example: Muscles of arm.
Smooth muscles
- Smooth muscles are found in the walls of the digestive tract, urinary bladder, arteries and other internal organs.
- They are called ‘Involuntary muscles’ because they are not controlled by our will.
Cardiac muscles
- The walls of the heart are made up of cardiac muscles. They are capable of rhythmic, contraction continuously and involuntary in nature.
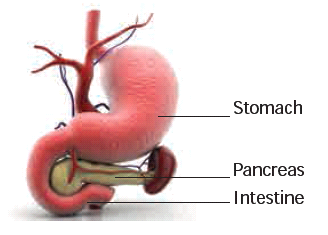
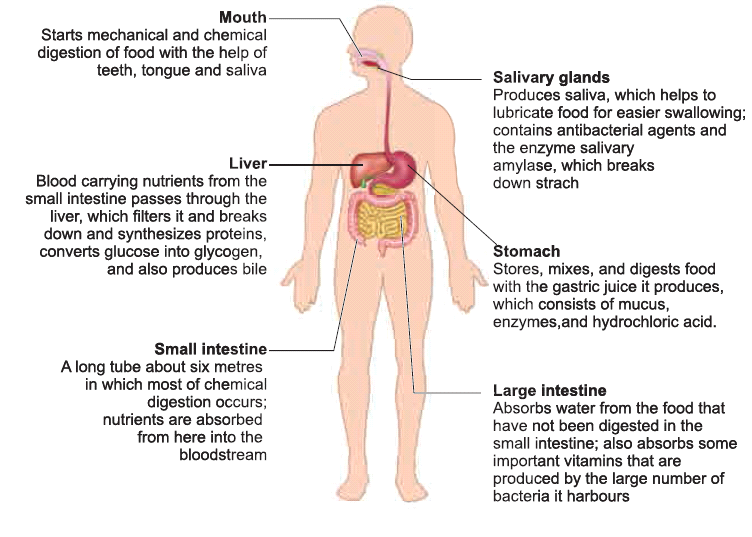
Digestive System
- Digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and associated glands.
- This system is involved in the conversion of complex food substances into simple forms and absorption of digested food.
- The digestive glands associated with the alimentary canal are salivary glands, liver, and pancreas.
- They secrete enzymes which help in the process of digestion of food in the digestive tract or alimentary canal.
- The alimentary canal is about 9 meters long. Stomach is a major organ for digestion of food materials. Absorption of digested food occurs in the small intestine.
Digestive System
Respiratory System
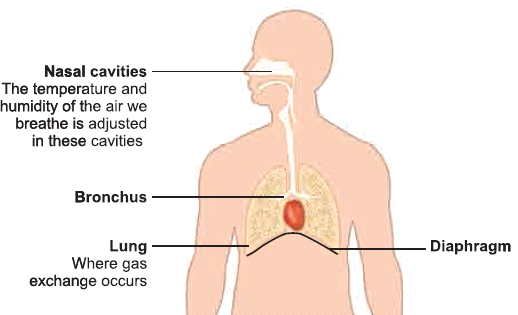
- Respiratory system is involved in exchange of respiratory gases and there by helps us to breathe.
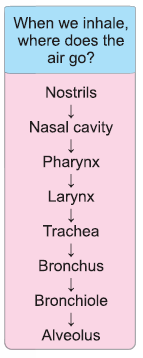
- The human respiratory system consists of nostrils, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs.
- It helps in the movement of air in and out of the body. Exchange of O2 and CO2 occurs between air in the lung and blood. The entry of food into the wind pipe is prevented by a flap like structure called Epiglottis.
Respiratory System
Lungs
- Lungs are the main respiratory organ.
- They are located within the chest cavity. The trachea, commonly called windpipe, is a tube supported by cartilaginous rings that connects the pharynx and larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air.
- The trachea divides into right and left bronchi and enters into the lungs. They divide further and ends in small air sacs called alveoli.
- The lungs are covered by double layered pleura. Diffusion of gases (O2 and CO2) occurs across the alveolar membrane.
Exchange of gases by the respiratory system involves three different processes such as;
1. External Respiration:
- Intake of O2 from the air and releasing of CO2 from the lungs occurs through nostrils.
2. Internal Respiration:
- Taking in of oxygen and giving out CO2.
- The circulatory system transports O2 and CO2 to and from all parts of the body. Hemoglobin in the red blood cells (RBCs) transports O2 and CO2.
3. Cellular Respiration:
- Cells take in O2 and release CO2
Circulatory system
- The circulatory system is one of the important systems consisting of heart, blood vessels and blood.
- It transports respiratory gases, nutrients, hormones and waste materials within the body.
- It protects the body from harmful pathogens and also regulates the body temperature.
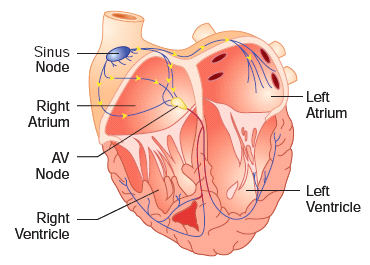
Heart
- Heart is located in the thoracic cavity between the two lungs.
- The heart is four chambered and is surrounded by a double layered membrane called pericardium.
- The heart pumps blood continuously throughout our life time.
Blood vessels
- Three types of blood vessels are present in the body.
- They are arteries, veins and capillaries.
- They form a closed network through which the blood is circulated.
Blood
- Blood is a fluid connective tissue of red colour containing plasma and blood cells.
- There are three types of blood cells namely, Red blood corpuscles (RBCs), White Blood corpuscles (WBCs) and Blood Platelets. RBCs are produced in the bone marrow.
Nervous System
- Nervous system is well developed in human and is composed of neurons or nerve cells. This system includes brain, spinal cord, sensory organs and nerves.
- The two important functions of the nervous system along with the endocrine system are conduction and co-ordination.
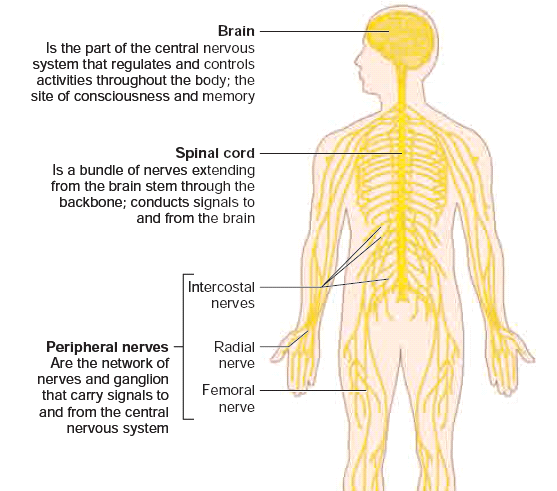
Brain
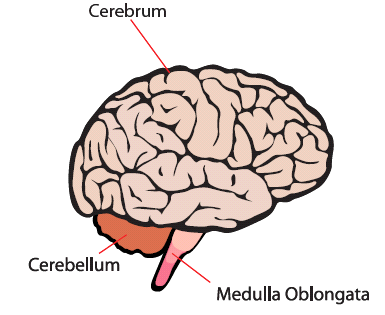
- The brain is a complex organ which is placed inside the cranium. It is protected by a three layered tissue coverings called meninges.
- Brain has three regions namely fore brain, mid brain and hind brain. It is the controlling centre of the body.
Spinal cord
- It is the extension of medulla oblongata of the hind brain and is enclosed within the vertebral column. Spinal cord connects the brain to different part of the body through nerves.
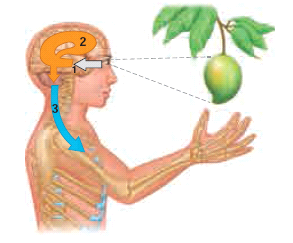
The Functions of the Nervous System
1. Sensory Input
- The conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
2. Integration
- The interpretation of the sensory signals and the formulation of responses.
3. Motor output
- The conduction of signals from the brain and spinal cord to effectors, such as muscle and gland cells.
Sense organs
- Sense organs are like the windows to the outside world. There are five sense organs in our body such as eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin.
- They make us aware of our surroundings. We are able to see, hear, smell, taste and feel, only through sense organs.
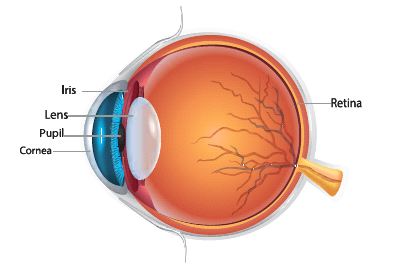
Eyes
- Eyes help us to see things around us i.e., their colour, shape, size whether they are near or far, moving or at rest.
- The eyelids and eyelashes keep the eyes safe. The eye has three main parts namely cornea, iris and pupil.
Ears
- Ears help to hear and differentiate sounds around us.
- The ears also help us in maintaining the balance of the body when we are walking, running or climbing.
- The ear has three major parts, the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear in human beings is made up of an external flap called pinna.
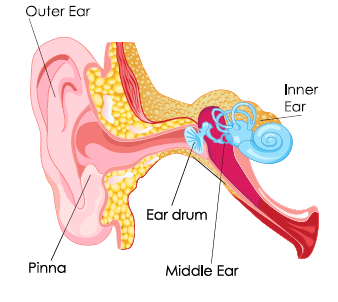
Skin
- Skin is the largest sense organ as it covers the whole body.
- The skin helps to feel the things around us by touching, that is whether they are hot or cold, smooth or rough, dry or wet, hard or soft.
- Skin covers the body and protects it from germs. It also keeps the body moist and regulates the body temperature.
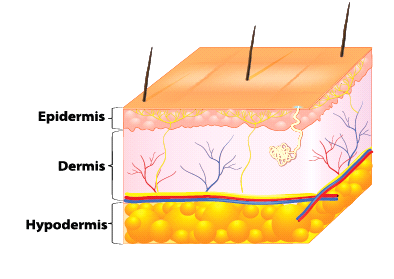
Functions of the skin
1. Skin forms an effective barrier against infection by microbes and pathogens.
2. Skin helps us to synthesize vitamin D using sunlight.
Endocrine System
- Endocrine system regulates various functions of the body and maintains the internal environment.
- Endocrine glands are present in the body, produce chemical substances called hormones.
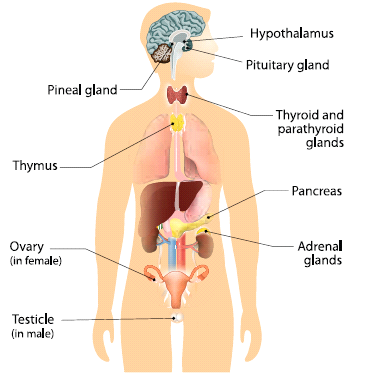
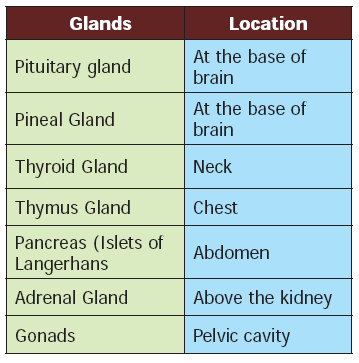
Endocrine System
Excretory System
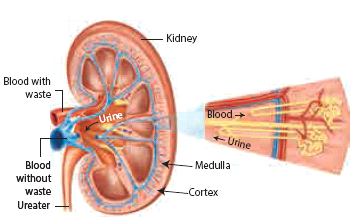
- The nitrogenous wastes are removed from the body by the excretory system. It is composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra.
Kidneys
- These are bean shaped structures present in the abdominal cavity. The functional units of the kidney are called Nephrons which filter the blood and form the urine.

More to know:
- The smallest bone in our body is present inside the ear. It is called Stapes. It is only 2.8 millimeters long (average length). The longest bone in the body is the thigh bone. (Femur)
- A new born baby has more than 300 bones. As the baby grows, some bones are joined together; hence the skeleton of an adult has 206 bones.
- Each lung has about 300 million air sacs or alveoli.
- Yawning helps us to take in more amount of O2 and to give out CO2.