Democracy Notes 6th Social Science
Democracy Notes 6th Social Science
6th Social Science Lesson 22 Notes in English
22. Democracy
1. Do you know what kind of society did the early man live in?
In the beginning, they were hunters and gathered food. Later, they settled near rivers and practised agriculture.
2. Democracy is ‘Government of the people, by the people, for the people’ – Abraham Lincoln
3. What is Democracy?
The citizens of a country select their representatives through elections. Thus, they take part in the direct governance of a country. This is termed Democracy
4. Major types of Democracy:
Among those, direct democracy and representative democracy are the most popular forms of government.
5. The birth place of democracy is Greece.
6th Social Book Back Questions
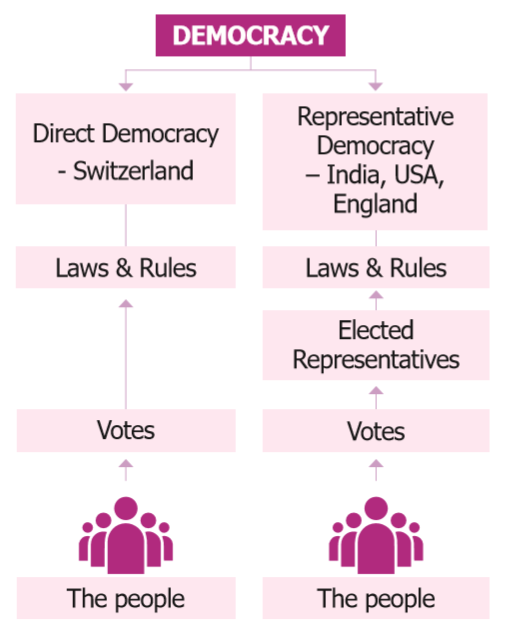
6. What is Direct Democracy?
In a Direct Democracy, people have the power to frame laws. In a Direct Democracy, only the citizens can make laws. All changes have to be approved by the citizen. The politicians only rule over parliamentary procedure. Switzerland has had a long history of a successful direct democracy.
7. What is Representative Democracy?
On behalf of the other members, they obtain the power to take decisions in a democratic manner. This is termed as Representative Democracy.
8. What is meant by democratic decision making?
In the system of democracy, the power to take decisions does not lie with the Head. On the contrary, a group holds the power, but adheres to the rules and regulations. All the members of the group hold open discussions and take final decisions only when everyone is convinced. This is called democratic way of decision making.
9. When was the International Day of Democracy?
In 2007, the UNO General Assembly resolved to observe 15th September as the International Day of Democracy.
10. What are the rights given in our Constitution?
Our Constitution ensures freedom, equality and justice to everyone.
11. What other features are found in our constitution?
- It defines the political principles, the structure of the government institutions and methods to follow these rules and regulations, the powers and responsibilities.
- And also, it fixes the Rights and Duties and the Directive Principles of the citizens. Thus our constitution provides a structure to us.
12. Is the constitution of India such a detailed one?
Indian Constitution is the longest written constitution in the world. It is drafted by the Drafting Committee of the Constituent Assembly headed by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar. That is why we call him the ‘Chief Architect of our Constitution.
13. Aims of Democracy:
- Democracy is defined as “Government of the people, for the people and by the people.”
- In a democracy, the power is vested in the hands of the people. For that, the people should have rights to take decisions.
- Everyone cannot participate in decision making. So, the representative government elected by the people to form a democratic system, all those who attain the age of 18 are given the voting rights to elect the representatives.
- At the same time, the representatives have the responsibility to protect the welfare of the people.
14. Which is the First Country to allow women to vote?
New Zealand is the first country to allow women to vote (1893).
15. Various Countries Voting Rights:
- Voting rights to women were given in 1918 and 1920 in the UK and USA respectively. At the same time, the wealthy alone were given the voting rights in India.
- Many leaders like Mahatma Gandhi kept insisting on giving voting rights to all. Now in India, all the people above 18 years of age enjoy Universal Adult Franchise.
16. The world statistical data on democracy declares that 79% of the Indian citizens have faith in the democratic system. Hence, India ranks first among the democratic countries of the world.
17. Illustrate the types of Democracy:
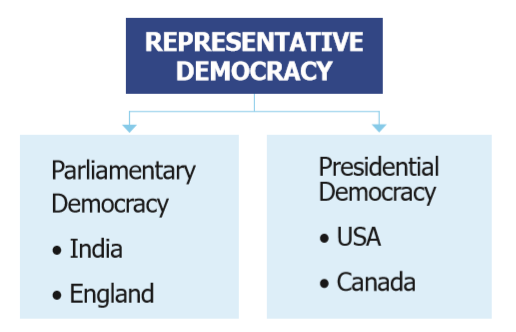
18. Show the Representative Democracy with its types:
19. Various oldest Democracies in the World:
