Science Notes
Changes Around Us Notes 6th Science Lesson 9 Notes in English
6th Science Lesson 9 Notes in English
9] Changes Around Us
Introduction
What is a change?
- Change is the Law of Nature. In our day – to – day life we see many changes around us.
- Weather changes periodically (daily/seasonly), Seasons changes periodically. A paper burns readily while it takes a few days for an iron nail to rust.
- It takes a few hours for milk to turn into curd but vegetables get softened in a few minutes when cooked.
- The said changes are accompanied by change in properties like shape, colour, temperature, position and composition.
- Some changes can be observed while some are not possible to notice.
Classification of Changes
- There are different types of changes observed in nature that occurs around us.
- Some changes take place very quickly while others take hours, days or even years.
- Some changes are temporary while some others are permanent.
- Some changes produce new substances while others do not. Some changes are natural while others are made by human beings.
- Some changes are desirable to us but some changes are not desirable.
We shall now try to classify changes on the basis of certain similarities and differences.
- slow and fast
- reversible and irreversible
- physical and chemical changes
- desirable and undesirable
- natural and man – made
Slow and Fast changes
Slow changes
- Changes which take place over a long period of time (hours / days / months / years ) are known as Slow changes.
- Examples: growth of nail and hair, change of seasons, germination of seed.
Fast Changes
- Changes which take place within a short period of time (seconds or minutes) are known as fast changes.
- Examples: Bursting of balloon, breaking of glass, bursting of fire crackers, burning of paper.
Reversible and Irreversible changes
Reversible change
- Changes which can be reversed (to get back the original state) are known as reversible changes.
- Examples: Touch me not plant (Responding to touch), stretching of rubber band, melting of ice.

Irreversible change
- Changes which cannot be reversed or to get back the original state are known as Irreversible changes.
- Examples: Change of milk into curd, digestion of food, making idly from batter.
Physical and Chemical Changes
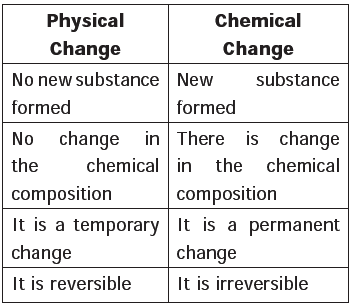
Physical changes
- Physical changes are the temporary changes in which there is change in the physical appearance of the substance but not in its chemical composition.
- Here no new substance is formed.
- Example: Melting of ice, the solution of salt or sugar, stretching of rubber band.
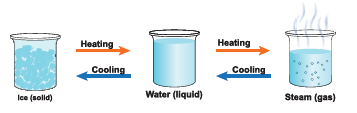
- Let us now understand the physical changes that take place in water.
- You already know that water exists in three states as solid, liquid and gas.
- Change of state takes place either by heating or cooling. By heating energy is supplied and by cooling energy is taken away. These are the reasons for the changes.
- Let us name a few processes connected with the changes in states of water.
Dissolution
The spreading of the solid particles (broken into individual molecules) among the liquid molecules is called as dissolution.
- Solvent is a substance that dissolves the solute.
- Solute is a substance that is dissolved in a solvent to make a solution.
- When solute is dissolved in a solvent it forms a solution.
![]()
Chemical changes
- Chemical changes are the permanent changes in which there is change in the chemical composition and new substance is formed.
- Examples: Burning of wood, Popping of popcorn, Blackening of silver ornaments, and Rusting of iron.
Desirable and Undesirable Changes
Desirable changes
- The changes which are useful, not harmful to our environment and desired by us are known as desirable changes.
- Examples: Ripening of fruit, growth of plants, cooking of food, milk changing to curd.
Undesirable changes
- The changes which are harmful to our environment and not desired by us are known as Undesirable changes.
- Examples: Deforestation, decaying of fruit, rusting of iron.
Natural and human made changes
Natural changes
- Changes which take place in nature on their own and are beyond the control of human beings are known as Natural changes.
- Examples: Rotation of the earth, changing phases of the Moon, Rain.
Human made or artificial changes
- The changes which are brought about by human beings are known as human made or artificial changes. They will not happen on their own.
- Examples: Cooking, Deforestation, Cultivating crops, construction of buildings.
More to know:
- The change of state from solid to gas directly is called Sublimation. Example : Camphor
- Water is known as the universal solvent. It dissolves a wide range of substance.