Cell Biology Notes 7th Science Lesson 10 Notes in English
7th Science Lesson 10 Notes in English
10] Cell Biology
Introduction:
Sona had a dinner, some hour later, she experienced a stomach pain and went to a clinic. After examination, the Doctor told Sona that she had eaten food contaminated with a type of bacteria which might have caused food poisoning. Bacteria are micro-organisms that can be seen only under microscope and not seen through naked eyes. Salmonella species is a bacteria that can cause food-borne infection.

Salmonella bacteria
Our earth is a beautiful place where in different types of organisms happily coexists. From minute mosses to huge conifers, invisible bacteria to huge blue whale, all have a basic unit called Cell. Let us study about the cell.
Cell as a fundamental unit of life:
The building wall is made up of numerous bricks. In the similar manner, a bee hive is composed of numerous hexagonal units. Some of the organisms are represented by a single cell. Therefore, they show a simple organization. The basic functional unit of an organism is called, a cell. Structure of a cell represent the arrangement of parts or organells in a cell. Function is the activity of each part or organell in a cell. Cells are the basic building blocks of an organism. You learnt that atoms are the basic building blocks of matter in chapter three. Likewise, human body is made up of animal cell and plant is made up of plant cell.

Unicellular organisms:
Some simple organisms, are made up of only one cell. They are called unicellular organisms, which can be seen with the help of a microscope. There are many single – celled microscopic organisms.
Have a look at the image. Chlamydomonas and an Amoeba, a single cell organisms which carryout entire functions. The body of all organisms are made up of tiny building blocks called, cells. Bacteria are also one celled unicellular organisms.


Multicellular Organism:
The cells are organized into tissues, organs and organ systems in a multicellular organism. Macroscopic organisms are visible and consists of many cells. The body of macroscopic organisms involves various functions. You can see cells of onion and human through a microscope. Onion and man are examples for multicellular organism.

Onion Human
Cell to organism:
Many cells function together to form tissues, different tissues combined together to form an organ and different organs to form an organ system, which leads to form an organism.
Organisms:
Many types of organ systems function together in a body, e.g. respiratory system,digestive system, excretory system circulatory system etc.
Organ System:
Many organs together form an organ system, which is concerned with a specific function. For example, Respiratory system, which has organs like nostrils, nasal chamber, wind pipe and lungs that helps in the process of respiration. In a plant, the root system consists of primary root, secondary root and tertiary root, which does the function of conduction of water, mineral and also fixation.

Organ:
A collection of different tissues worked together to perform a specific function or functions is called an organ. Human body has different organs like stomach, eye, heart, lungs etc., are made up of different type of tissues. Plant have organs such as leaves, stems, and roots.
Tissue:
Tissue is a group of cells, organized for a specific function. Tissues have following features like same shaped cells or different shaped cells to perform a common function. Human and other animals are made up of nervous, epithelial, connective and muscle tissues. Plants have transport, protective and ground tissues.
Cell:
The cell is a basic structural and functional unit of life. Cell is the building unit of living organisms. You can see in a hand, how many types of cells are there to work together to perform its functions. So, cell is known as the basic unit of life.

Plant and Animal cell comparison:
Why do plant cells differ from animal cells? They differ from each other because they have to perform different functions.
Now you know that there are many main similarities between plant and animal cells.
Human cells related to functions:
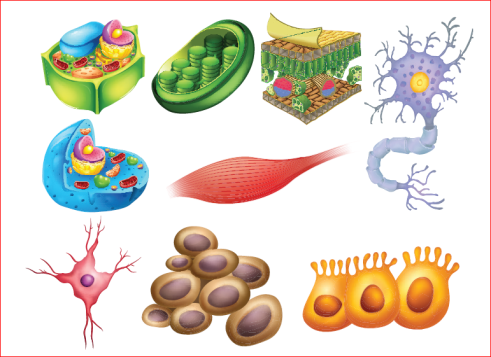
Different types of cells:
Our body is made up of many different kinds of cells. Each type of cell is specialized to perform a specific function. Depending on the function, cell has specific shape, size and may have some components which other type of cells do not have. Have a look at the differences between nerve cells and red blood cells in the images. Even though there are many different types of cells, there are some components common to all type of cells. Let us take a look at this in the next section.
What’s inside a cell?
Inside a cell, there are many tiny structures called cell organelles. These organelles are responsible for providing needs of the cell. They work to bring in food supplies, get rid of waste, protection and repair of the cell, and help it to grow and reproduce. Each one has a specific function to do for the cell. And, if any Find out major organs that are part of the circulatory system of a human body and list out their functions one organelle stops its function, then the cell is programmed to die.
Cell Structure:
As we have mentioned before, all cells have some common structure. These are
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus (In most eukaryotic cells).
The structure of a typical plant and animal cell shows following peculiarities:
Cell membrane:
The boundary of an animal cell is the plasma membrane, which is also called as cell membrane.
Cell wall – “Supporter and Protector”:
All animal and plant cells are enclosed or surrounded by a cell membrane as you learned before. However, as you might have noticed previously that, animal cells often have an irregular shape, whereas plant cells have a much more regular and rigid shape.
Plant cells have an additional layer on the outer side of the cell membrane. This is called as the cell wall, that provides a frame work for support and stability.
The cell wall is formed from various compounds, the main one being cellulose. Cellulose helps to maintain the shape of the plant cell. This allows the plant to remain rigid and upright even if it grows to great heights. Each cell is interconnected with its neighbouring cells through openings called Plasmodesmata.
Cell wall

| Specialized cell | Structure | Function |
| Epithelial cells – they are
mostly flat and columnar in shape |
 |
They cover the surface of the body for protection |
| Muscle cells – they are long and spindle shaped |  |
They can contract and relax allowing the cell for movement. |
| Nerve cells – the body of nervous cell is branched with an elongated nerve fiber. |  |
Nerve cells are specialized to carry and conduct messages that coordinate the functions of the body. |
| Red blood cells – Round, biconcave and disc shaped |  |
Red blood cells carry oxygen and collect carbon dioxide from various part of the body. |
Cytoplasm – I am the “Area of Movement”:
When you look at the temporary mounts of an onion peel, you can see a large region of each cell an enclosed by the cell membrane. This region takes up very little stain. It is called the cytoplasm.
The cytoplasm includes all living parts of the cell with in the cell membrane, excluding the nucleus. The cytoplasm is made up of the cytosol and cell organelles. The cytosol is a watery, jelly like medium made up of 70% – 90% water and usually colourless.
Cell organelles and structures present in a cell are endoplasmic reticulum, vacuole, ribosome, golgi body, lysosome, mitochondria, centriole, chloroplast, surrounded by plasma membrane and cell wall.
Protoplasm vs. Cytoplasm:
In particular, the material inside and outside the nuclear membrane is known as Protoplasm. The fluid inside the nucleus is known as the nuclear fluid or nucleoplasm and outside the nucleus is called as cytoplasm.
Inside the cytoplasm
Mitochondria – “Power house of the Cell”.
Do you remember learning about the food as the energy source for the body? Just as wood is burnt to release the stored potential energy to make a fire to heat some water. The food that you ate to be broken down in order to release the energy which can be used by your body to function. Mitochondria are responsible to do this function.
Very active cells have more mitochondria than cells that are less active. Which type of cell, do you think, will have more mitochondria, a muscle cells or a bone cell?
Mitochondrian is an oval or rod shaped double membrane bounded organelle. Aerobic respiratory reactions take place with in the mitochondrion to release energy. So it is known as “the Power House” of the cell. The energy produced within the mitochondrion is used for all the metabolic activities of the cell.

Chloroplast- “Food Producers”.
Do you notice the green organelles present in plant cells and absent in animal cells. Chloroplasts are the only cell organelles that can produce food from the sun energy. Only plants with chloroplast are able to do photosynthesis because they contain the very important green pigment, chlorophyll. Chlorophyll can absorb radiant energy from the Sun and convert it to the chemical energy which can be used by the plants and animals. Animal cells lack chloroplasts and are unable to do photosynthesis.

Golgi Complex- I need a break
Membrane bounded sacs are stacked on top of the other with associated secretory vesicles are collectively known as golgi complex. Functions of golgi complex are the production of secretory substances, packaging and secretion. This is the secret behind the change in the colour and taste of fruits

Lysosome- “Suicidal Bag”.
Everything I touch, I destroy
You will find organelles called as lysosomes, which are very small to view using a light microscope. They are the main digestive compartments of the cell. They lyse a cell, hence they are called “suicidal bag”.

Centrioles
They are generally found close to the nucleus and are made up of tube-like structures. Centrioles or centrosomes are present only in animal cells and absent in plant cells. It helps in the separation of chromosomes during cell division.

Endoplasmic reticulum – You guys, be quiet, I have so much work to do:
It is an inter membranous network made up of flat or tubular sacs within the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic reticulum is of two types. They are rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum.

Endoplasmic reticulum
Rough endoplasmic reticulum are rough due to the ribosomes attached to the membrane. which helps in the synthesis of protein.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum. It is a network of tubular sacs without ribosomes on the membrane. They play a role in the synthesis of lipids, steroids and also transport them within the cell.
Nucleus – Everyone do what I say. Acting like the “Brain” of the cell
- Plant and animal cells have a nucleus inside the cytoplasm. It is surrounded by a nuclear envelope. One or two nucleolus and the chromatin body are present inside the nucleus. During cell division, the chromatin body is organised into a chromosome. Storage of genetic material and transfers heredity characters from generation to generation are the functions of chromosome.
Functions of Nucleus
- In controls all the processes and chemical reactions that take place inside the cell.
- Inheritance of character from one generation to another.

POINTS TO REMEMBER
- Cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms.
- Cells are microscopic and can be seen only under a microscope.
- Cell membranes are selectively permeable, which means they only allow certain substances to pass in and out of the cell.
- Plant cells have a cell wall around the cell membrane that is rigid and provides support and protection to the cell content.
- The Cytoplasm includes the organelles and the cytosol. The Cytosol is the jellylike medium, in which many chemical reactions take cell. Everything inside the cell membrane, except the nucleus, is considered to be the cytoplasm.
- Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration, which releases the energy from the food.
- Plants have chloroplasts with chlorophyll pigments to produce food by photosynthesis.
- Stem cells are cells that have the ability to divide and develop into many different types of the cell.
- A group of different tissues makes up an organ.
- Organs working together in groups form a systems or organ systems.
- Organ systems make up an organism, such as a human.
Do You Know?
Stem Cells:
Stem cells are quite amazing as they can divide and multiply while at the same time with their ability to develop into any other type of cell. Embryonic stem cells are very special as they can become absolutely any type of cell in the body, for example, blood cell, nerve cell, muscle cell or gland cell. So they are utilized by the Scientist and Medicos, to cure and prevent some diseases like Spinal cord injury.

Various range of these plastids impart different colours to various parts of plant. Chromoplast impart colour to flower and fruits. As fruits ripen, chloroplasts change to chromoplasts. Starch is converted to sugar.
Red blood cells:
Red blood cells do not contain a nucleus. Without a nucleus, these cells die quickly; about two million red blood cells die every second! Luckily, the body produces new red blood cells every day.