Atomic Structure Online Test 8th Science Lesson 12 Questions in English
Atomic Structure Online Test 8th Science Lesson 12 Questions in English
Atomic Structure Online Test 8th Science Lesson 12 Questions in English
Quiz-summary
0 of 70 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
Information
Atomic Structure Online Test 8th Science Lesson 12 Questions in English
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 70 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 70
1. Question
1. Totally how many elements have been identified worldwide?
Correct
Explanation
Every substance in our surrounding is made up of unique elements. There are 118 elements identified worldwide so far.
Incorrect
Explanation
Every substance in our surrounding is made up of unique elements. There are 118 elements identified worldwide so far.
-
Question 2 of 70
2. Question
2. Which among the following is not the elements found in the nature?
Correct
Explanation
Copper, Iron, Gold, Titanium, Germanium and Silver are some of the elements found in the nature. Elements like Technetium, Promethium, Neptunium and Plutonium are synthesised in the laboratories.
Incorrect
Explanation
Copper, Iron, Gold, Titanium, Germanium and Silver are some of the elements found in the nature. Elements like Technetium, Promethium, Neptunium and Plutonium are synthesised in the laboratories.
-
Question 3 of 70
3. Question
3. How many elements occur in the nature out of 118 elements?
Correct
Explanation
Out of these 118 elements, 92 elements occur in the nature and the remaining elements are synthesised in the laboratories.
Incorrect
Explanation
Out of these 118 elements, 92 elements occur in the nature and the remaining elements are synthesised in the laboratories.
-
Question 4 of 70
4. Question
4. Each element is made up of similar, minute particles called ____________
Correct
Explanation
Each element is made up of similar, minute particles called atoms. For example, the element gold is made up of similar atoms which determine its characteristics. The word atom is derived from the Greek word atomas. Tomas means smallest divisible particle and atomas means smallest indivisible particle
Incorrect
Explanation
Each element is made up of similar, minute particles called atoms. For example, the element gold is made up of similar atoms which determine its characteristics. The word atom is derived from the Greek word atomas. Tomas means smallest divisible particle and atomas means smallest indivisible particle
-
Question 5 of 70
5. Question
5. Who among the following Tamil poet has mentioned about atoms in his/her poem while describing Thirukkural?
Correct
Explanation
Our Tamil poet Avvaiyar has mentioned about atoms in her poem while describing Thirukkural (அணுவைத் துளைத்து ஏழ் கடலைப்புகட்டிக் குறுகத் தரித்த குறள்).
Incorrect
Explanation
Our Tamil poet Avvaiyar has mentioned about atoms in her poem while describing Thirukkural (அணுவைத் துளைத்து ஏழ் கடலைப்புகட்டிக் குறுகத் தரித்த குறள்).
-
Question 6 of 70
6. Question
6. Which ancient Greek philosopher have spoken about atoms?
Correct
Explanation
Ancient Greek philosophers like Democritus have spoken about atoms.
Incorrect
Explanation
Ancient Greek philosophers like Democritus have spoken about atoms.
-
Question 7 of 70
7. Question
7. The first scientific theory about atom was given by whom?
Correct
Explanation
The first scientific theory about atom was given by John Dalton. Followed by him, J.J. Thomson and Rutherford have given their theory about atom.
Incorrect
Explanation
The first scientific theory about atom was given by John Dalton. Followed by him, J.J. Thomson and Rutherford have given their theory about atom.
-
Question 8 of 70
8. Question
8. In which year John Dalton proposed a model of atom known as Dalton’s atomic theory?
Correct
Explanation
John Dalton provided a basic theory about the nature of matter. He proposed a model of atom known as Dalton’s atomic theory in 1808 based on his experiments.
Incorrect
Explanation
John Dalton provided a basic theory about the nature of matter. He proposed a model of atom known as Dalton’s atomic theory in 1808 based on his experiments.
-
Question 9 of 70
9. Question
9. Which among the following is not the postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory?
1) All the matters are made up of extremely small particles called atoms (Greek philosopher Democritus used the same name for the smallest indivisible particles). Atoms of the same element are identical in all respects (size, shape, mass and properties).
2) Atoms of different elements have same sizes and masses but possess different properties. Atoms can be created not be destroyed. i.e., atom is indestructible.
3) Atoms of different elements may combine with each other in a fixed simple ratio to form molecules or compounds. An atom is the smallest particle of matter that takes part in a chemical reaction.
Correct
Explanation
Atoms of different elements have different sizes and masses and possess different properties. Atoms can neither be created nor be destroyed. i.e., atom is indestructible.
Incorrect
Explanation
Atoms of different elements have different sizes and masses and possess different properties. Atoms can neither be created nor be destroyed. i.e., atom is indestructible.
-
Question 10 of 70
10. Question
10. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding Dalton’s atomic theory?
Correct
Explanation
Dalton’s theory explains most of the properties of gases and liquids. Atom is no longer considered as the smallest indivisible particle.
Incorrect
Explanation
Dalton’s theory explains most of the properties of gases and liquids. Atom is no longer considered as the smallest indivisible particle.
-
Question 11 of 70
11. Question
11. If atoms have the same element but have different masses it is known as ______
Correct
Explanation
If atoms have the same element but have different masses it is known as Isotopes.
Incorrect
Explanation
If atoms have the same element but have different masses it is known as Isotopes.
-
Question 12 of 70
12. Question
12. If atoms have the different elements but have same masses it is known as_________
Correct
Explanation
If atoms have the different elements but have same masses it is known as Isobars.
Incorrect
Explanation
If atoms have the different elements but have same masses it is known as Isobars.
-
Question 13 of 70
13. Question
13. In 1878, who conducting an experiment using a discharge tube, found certain visible rays travelling between two metal electrodes?
Correct
Explanation
In 1878, Sir William Crookes, while conducting an experiment using a discharge tube, found certain visible rays travelling between two metal electrodes.
Incorrect
Explanation
In 1878, Sir William Crookes, while conducting an experiment using a discharge tube, found certain visible rays travelling between two metal electrodes.
-
Question 14 of 70
14. Question
14. Crookes rays are also known as ______
Correct
Explanation
The Crookes rays are also known as Cathode rays. The discharge tube used in the experiment is now referred as Crookes tube or more popularly as Cathode Ray Tube (CRT).
Incorrect
Explanation
The Crookes rays are also known as Cathode rays. The discharge tube used in the experiment is now referred as Crookes tube or more popularly as Cathode Ray Tube (CRT).
-
Question 15 of 70
15. Question
15. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Cathode ray tube
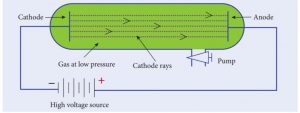
1) Cathode Ray Tube is a long glass tube filled with gas and sealed at both the ends. It consists of two metal plates (which act as electrodes) connected with high voltage. The electrode which is connected to the positive terminal of the battery is called the cathode (positive electrode).
2) The electrode connected to the negative terminal is called the anode (negative electrode). There is a side tube which is connected to a pump. The pump is used to lower the pressure inside the discharge tube.
Correct
Explanation
The electrode which is connected to the negative terminal of the battery is called the cathode (negative electrode). The electrode connected to the positive terminal is called the anode (positive electrode). There is a side tube which is connected to a pump. The pump is used to lower the pressure inside the discharge tube.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation
The electrode which is connected to the negative terminal of the battery is called the cathode (negative electrode). The electrode connected to the positive terminal is called the anode (positive electrode). There is a side tube which is connected to a pump. The pump is used to lower the pressure inside the discharge tube.

-
Question 16 of 70
16. Question
16. Electricity, when passes through air, removes the electrons from the gaseous atoms and produces ions. This is called _____
Correct
Explanation
Electricity, when passes through air, removes the electrons from the gaseous atoms and produces ions. This is called electrical discharge.
Incorrect
Explanation
Electricity, when passes through air, removes the electrons from the gaseous atoms and produces ions. This is called electrical discharge.
-
Question 17 of 70
17. Question
17. Which among the following statement is correct
Correct
Explanation
The fact that air is a poor conductor of electricity is a blessing in disguise for us. Imagine what would happen if air had been a good conductor of electricity. All of us would have got electrocuted, when a minor spark was produced by accident.
Incorrect
Explanation
The fact that air is a poor conductor of electricity is a blessing in disguise for us. Imagine what would happen if air had been a good conductor of electricity. All of us would have got electrocuted, when a minor spark was produced by accident.
-
Question 18 of 70
18. Question
18. Which among the following statement is correct regarding discovery of electron
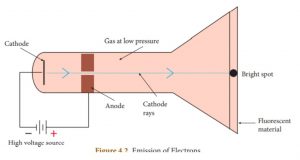
1) When a high electric voltage of 10,000 volts or more is applied to the electrode of a discharge tube containing air or any gas at atmospheric pressure, no electricity flows through the air.
2) However, when the high voltage of 10,000 volts is applied to the electrodes of discharge tube containing air or any gas at a very low pressure of about 0.001 mm of mercury, a greenish glow is observed on the walls of the discharge tube behind anode. This, observations clearly show some invisible ray coming from the cathode. Hence, these rays are called cathode rays. Later, they were named as electrons.
Correct
Explanation
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation

-
Question 19 of 70
19. Question
19. In television tube cathode rays are deflected by ____________
Correct
Explanation
In television tube cathode rays are deflected by magnetic fields. A beam of cathode rays is directed toward a coated screen on the front of the tube, where by varying the magnet field generated by electromagnetic coils, the beam traces a luminescent image
Incorrect
Explanation
In television tube cathode rays are deflected by magnetic fields. A beam of cathode rays is directed toward a coated screen on the front of the tube, where by varying the magnet field generated by electromagnetic coils, the beam traces a luminescent image
-
Question 20 of 70
20. Question
20. Which among the following is not the property of cathode rays?
Correct
Explanation
The nature of the cathode rays does not depend on the nature of the gas filled inside the tube or the
cathode usedIncorrect
Explanation
The nature of the cathode rays does not depend on the nature of the gas filled inside the tube or the
cathode used -
Question 21 of 70
21. Question
21. When invisible radiation falls on materials like zinc sulphide, they emit a visible light (or glow). These materials are _______
Correct
Explanation
When invisible radiation falls on materials like zinc sulphide, they emit a visible light (or glow). These materials are called fluorescent materials.
Incorrect
Explanation
When invisible radiation falls on materials like zinc sulphide, they emit a visible light (or glow). These materials are called fluorescent materials.
-
Question 22 of 70
22. Question
22. The presence of positively charged particles in the atom has been precisely predicted by whom?
Correct
Explanation
The presence of positively charged particles in the atom has been precisely predicted by Goldstein based on the conception that the atom being electrically neutral in nature, should necessarily possess positively charged particles to balance the negatively charged electrons.
Incorrect
Explanation
The presence of positively charged particles in the atom has been precisely predicted by Goldstein based on the conception that the atom being electrically neutral in nature, should necessarily possess positively charged particles to balance the negatively charged electrons.
-
Question 23 of 70
23. Question
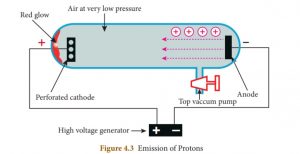
23. Goldstein repeated the cathode ray experiment by using a perforated cathode. On applying a high voltage under low pressure, he observed which colour on the wall behind the cathode?
Correct
Explanation
Goldstein repeated the cathode ray experiment by using a perforated cathode. On applying a high voltage under low pressure, he observed a faint red glow on the wall behind the cathode. Since these rays originated from the anode, they were called anode ray.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Explanation
Goldstein repeated the cathode ray experiment by using a perforated cathode. On applying a high voltage under low pressure, he observed a faint red glow on the wall behind the cathode. Since these rays originated from the anode, they were called anode ray.

-
Question 24 of 70
24. Question
24. Anode rays are also called as _______
Correct
Explanation
Anode rays are also called as canal rays or positive rays. Anode rays were found as a stream of positively charged particles.
Incorrect
Explanation
Anode rays are also called as canal rays or positive rays. Anode rays were found as a stream of positively charged particles.
-
Question 25 of 70
25. Question
25. Which among the following statement is correct regarding properties of anode rays
Correct
Explanation
The mass of the particle is the same as the atomic mass of the gas taken inside the discharge tube.
Incorrect
Explanation
The mass of the particle is the same as the atomic mass of the gas taken inside the discharge tube.
-
Question 26 of 70
26. Question
26. The proton can be defined as _______
Correct
Explanation
When hydrogen gas was taken in a discharge tube, the positively charged particles obtained from the hydrogen gas were called protons. Each of these protons are produced when one electron is removed from one hydrogen atom. Thus, a proton can be defined as a hydrogen ion (H+ ).
Incorrect
Explanation
When hydrogen gas was taken in a discharge tube, the positively charged particles obtained from the hydrogen gas were called protons. Each of these protons are produced when one electron is removed from one hydrogen atom. Thus, a proton can be defined as a hydrogen ion (H+ ).
-
Question 27 of 70
27. Question
27. Who discovered another fundamental particle, called neutron in 1932?
Correct
Explanation
At the time of J.J. Thomson, only two fundamental particles (proton and electron) were known. In the year 1932, James Chadwick discovered another fundamental particle, called neutron. But, the proper position of these particles in an atom was not clear till Rutherford described the structure of atom.
Incorrect
Explanation
At the time of J.J. Thomson, only two fundamental particles (proton and electron) were known. In the year 1932, James Chadwick discovered another fundamental particle, called neutron. But, the proper position of these particles in an atom was not clear till Rutherford described the structure of atom.
-
Question 28 of 70
28. Question
 Correct
Correct
Explanation
The mass of proton is 1.6 × 10–24 grams. Its relative charge is +1.
Incorrect
Explanation
The mass of proton is 1.6 × 10–24 grams. Its relative charge is +1.
-
Question 29 of 70
29. Question
29. Which English scientist, proposed the famous atom model in the year 1904, just after the discovery of electrons?
Correct
Explanation
J.J. Thomson, an English scientist, proposed the famous atom model in the year 1904, just after the discovery of electrons.
Incorrect
Explanation
J.J. Thomson, an English scientist, proposed the famous atom model in the year 1904, just after the discovery of electrons.
-
Question 30 of 70
30. Question
30. Thomson proposed that atom resembles which shape that having a radius of the order of 10-10 m?
Correct
Explanation
Thomson proposed that the shape of an atom resembles a sphere having radius of the order of 10– 10 m.
Incorrect
Explanation
Thomson proposed that the shape of an atom resembles a sphere having radius of the order of 10– 10 m.
-
Question 31 of 70
31. Question
31. Thomson’s atom model was also called as ________
Correct
Explanation
The positively charged particles are uniformly distributed with electrons arranged in such a manner that the atom is electrically neutral. Thomson’s atom model was also called as the plum pudding model or the watermelon model. The embedded electrons resembled the seed of watermelon while the watermelon’s red mass represented the positive charge distribution. The plum pudding atomic theory assumed that the mass of an atom is uniformly distributed all over the atom.
Incorrect
Explanation
The positively charged particles are uniformly distributed with electrons arranged in such a manner that the atom is electrically neutral. Thomson’s atom model was also called as the plum pudding model or the watermelon model. The embedded electrons resembled the seed of watermelon while the watermelon’s red mass represented the positive charge distribution. The plum pudding atomic theory assumed that the mass of an atom is uniformly distributed all over the atom.
-
Question 32 of 70
32. Question
32. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding limitation of Thomson’s atom model?
1) Thomson’s model failed to explain how the positively charged sphere is shielded from the negatively charged electrons without getting neutralised.
2) This theory explains only about the protons and electrons and failed to explain the presence of neutral particle neutron.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 33 of 70
33. Question
33. Who among the following said that an atom consists of subatomic particles namely, proton, electron and neutrons?
Correct
Explanation
In order to understand valency of elements clearly, we need to learn a little about Rutherford’s atom model here. According to Rutherford, an atom consists of subatomic particles namely, proton, electron and neutrons.
Incorrect
Explanation
In order to understand valency of elements clearly, we need to learn a little about Rutherford’s atom model here. According to Rutherford, an atom consists of subatomic particles namely, proton, electron and neutrons.
-
Question 34 of 70
34. Question
34. Protons and neutrons are found at the centre of an atom, called ________
Correct
Explanation
Protons and neutrons are found at the centre of an atom, called nucleus. Electrons are revolving around the nucleus in a circular path, called orbits or shells.
Incorrect
Explanation
Protons and neutrons are found at the centre of an atom, called nucleus. Electrons are revolving around the nucleus in a circular path, called orbits or shells.
-
Question 35 of 70
35. Question
35. The electrons revolving in the outermost orbit are called _________
Correct
Explanation
An atom has a number of orbits and each orbit has electrons. The electrons revolving in the outermost orbits are called valence electrons.
Incorrect
Explanation
An atom has a number of orbits and each orbit has electrons. The electrons revolving in the outermost orbits are called valence electrons.
-
Question 36 of 70
36. Question
36. The arrangement of electrons in the orbits is known as ________
Correct
Explanation
The arrangement of electrons in the orbits is known as electronic configuration. Atoms of all the elements will tend to have a stable electronic configuration, that is, they will tend to have either two electrons (known as duplet) or eight electrons (known as octet) in their outermost orbit.
Incorrect
Explanation
The arrangement of electrons in the orbits is known as electronic configuration. Atoms of all the elements will tend to have a stable electronic configuration, that is, they will tend to have either two electrons (known as duplet) or eight electrons (known as octet) in their outermost orbit.
-
Question 37 of 70
37. Question
37. Which is defined as the number of electrons lost, gained or shared by an atom in a chemical combination so that it becomes chemically inert?
Correct
Explanation
When molecules are formed, atoms combine together in a fixed proportion because each atom has different combining capacity. This combining capacity of an atom is called valency. Valency is defined as the number of electrons lost, gained or shared by an atom in a chemical combination so that it becomes chemically inert.
Incorrect
Explanation
When molecules are formed, atoms combine together in a fixed proportion because each atom has different combining capacity. This combining capacity of an atom is called valency. Valency is defined as the number of electrons lost, gained or shared by an atom in a chemical combination so that it becomes chemically inert.
-
Question 38 of 70
38. Question
38. Which among the following atom has one electron in its outermost orbit and in order to have stability it loses one electron and becomes positively charged?
Correct
Explanation
Helium has two electrons in the outermost orbit and so it is chemically inert. Similarly, neon is chemically inert because, it has eight electrons in the outermost orbit. sodium atom (Atomic number: 11) has one electron in its outermost orbit and in order to have stability it loses one electron and becomes positively charged.
Incorrect
Explanation
Helium has two electrons in the outermost orbit and so it is chemically inert. Similarly, neon is chemically inert because, it has eight electrons in the outermost orbit. sodium atom (Atomic number: 11) has one electron in its outermost orbit and in order to have stability it loses one electron and becomes positively charged.
-
Question 39 of 70
39. Question
39. Which among the following statement is correct
1) The valence electrons in an atom readily participate in a chemical reaction and so the chemical properties of an element are determined by these electrons. Atoms of all metals will have 1 to 3 electrons in their outermost orbit. By losing these electrons they will have stable electronic configuration. So, they lose them to other atoms in a chemical reaction and
become positively charged.2) All metals will have 4 to 7 electrons in the outermost orbit of their atoms. In order to attain stable electronic configuration, they need few electrons. They accept these electrons from same atoms in a chemical reaction and become negatively charged. These atoms which accept electrons are said to have negative valency.
Correct
Explanation
All non-metals will have 4 to 7 electrons in the outermost orbit of their atoms. In order to attain stable electronic configuration, they need few electrons. They accept these electrons from other atoms in a chemical reaction and become negatively charged. These atoms which accept electrons are said to have negative valency.
Incorrect
Explanation
All non-metals will have 4 to 7 electrons in the outermost orbit of their atoms. In order to attain stable electronic configuration, they need few electrons. They accept these electrons from other atoms in a chemical reaction and become negatively charged. These atoms which accept electrons are said to have negative valency.
-
Question 40 of 70
40. Question
40. Chlorine atom has how many electrons in its outermost orbit?
Correct
Explanation
Chlorine atom (Atomic number: 17) has seven electrons in its outermost orbit. By gaining one electron it attains stable electronic configuration. Thus, chlorine has negative valency.
Incorrect
Explanation
Chlorine atom (Atomic number: 17) has seven electrons in its outermost orbit. By gaining one electron it attains stable electronic configuration. Thus, chlorine has negative valency.
-
Question 41 of 70
41. Question
41. Which among the following statement is correct
1) Since hydrogen atom loses one electron in its outermost orbit, its valency is taken as one and it is selected as the standard. Valency of the other elements are expressed in terms of hydrogen. Thus, valency of an element can also be defined as the number of hydrogen atoms which combine with one atom of it.
2) In hydrogen chloride molecule, one hydrogen atom combines with one chlorine atom. Thus, the valency of chlorine is one. Similarly, in water molecule, two hydrogen atoms combine with one oxygen atom. So, valency of oxygen is two.
3) Since some of the elements do not combine with hydrogen, the valency of the element is also defined in terms of other elements like chlorine or oxygen. This is because almost all the elements combine with chlorine and oxygen.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 42 of 70
42. Question
42. What is the mass of Neutron?
Correct
Explanation
Neutron is a neutral particle, that is, it carries no charge. It has mass equal to that of a proton, that is 1.6 × 10^–24 grams.
Incorrect
Explanation
Neutron is a neutral particle, that is, it carries no charge. It has mass equal to that of a proton, that is 1.6 × 10^–24 grams.
-
Question 43 of 70
43. Question
43. Which among the following statement is correct
1) Since valency of chlorine is one, the number of chlorine atoms with which one atom of an element can combine is called valency. In sodium chloride (NaCl) molecule, one chlorine atom combines with one sodium atom. So, the valency of sodium is one. same in magnesium chloride (MgCl2) valency of magnesium is ono because it combines with one chlorine atoms.
2) In another way, valency can be defined as double the number of oxygen atoms with which one atom of an element can combine because valency of oxygen is two. For example, in magnesium oxide (MgO) valency of magnesium is two.
Correct
Explanation
Since valency of chlorine is one, the number of chlorine atoms with which one atom of an element can combine is called valency. In sodium chloride (NaCl) molecule, one chlorine atom combines with one sodium atom. So, the valency of sodium is one. But, in magnesium chloride (MgCl2) valency of magnesium is two because it combines with two chlorine atoms.
Incorrect
Explanation
Since valency of chlorine is one, the number of chlorine atoms with which one atom of an element can combine is called valency. In sodium chloride (NaCl) molecule, one chlorine atom combines with one sodium atom. So, the valency of sodium is one. But, in magnesium chloride (MgCl2) valency of magnesium is two because it combines with two chlorine atoms.
-
Question 44 of 70
44. Question
44. Which among the following is not the element with variable valency?
Correct
Explanation
Copper, mercury, tin and iron are elements with variable valency.
Incorrect
Explanation
Copper, mercury, tin and iron are elements with variable valency.
-
Question 45 of 70
45. Question
45. Which among the following statement is correct
1) Atoms of some elements combine with atoms of other elements and form more than one product. Thus, they are said to have different combining capacity. These atoms have more than one valency. Some cations exhibit more than one valency. For example, copper combines with oxygen and forms two products namely cuprous oxide (Cu2O) and cupric oxide (Cu O).
2) In Cu2O, valency of copper is one and in CuO valency of copper is two. For lower valency a suffix –ous is attached at the end of the name of the metal. For higher valency a suffix –ic is attached at the end of the name of the metal. Sometimes Roman numeral such as I, II, III, IV etc. indicated in parenthesis followed by the name of the metal can also be used.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 46 of 70
46. Question
46. What is the mass of electron?
Correct
Explanation
The mass of Electron (e) is 9.1 × 10^–28 grams. Its relative charge is –1.
Incorrect
Explanation
The mass of Electron (e) is 9.1 × 10^–28 grams. Its relative charge is –1.
-
Question 47 of 70
47. Question
47. In an atom, the number of protons is equal to what?
Correct
Explanation
In an atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons and so the atom is electrically neutral. But, during chemical reactions unstable atoms try to attain stable electronic configuration (duplet or octet) either by gaining or losing one or more electrons.
Incorrect
Explanation
In an atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons and so the atom is electrically neutral. But, during chemical reactions unstable atoms try to attain stable electronic configuration (duplet or octet) either by gaining or losing one or more electrons.
-
Question 48 of 70
48. Question
48. The atom which carry positive or negative charges are called _____
Correct
Explanation
When an atom gains an electron, it has a more number of electrons and thus it carries negative charge. At the same time when an atom loses an electron it has more number of protons and thus it carries positive charge. These atoms which carry positive or negative charges are called ions.
Incorrect
Explanation
When an atom gains an electron, it has a more number of electrons and thus it carries negative charge. At the same time when an atom loses an electron it has more number of protons and thus it carries positive charge. These atoms which carry positive or negative charges are called ions.
-
Question 49 of 70
49. Question
49. When an atom loses an electron, what sign is shown in the superscript?
Correct
Explanation
The number of electrons gained or lost by an atom is shown as a superscript to the right of its symbol. When an atom loses an electron, ‘+’ sign is shown in the superscript and ‘–’ sign is shown if an electron is gained by an atom. Sometimes, two or more atoms of different elements collectively loss or gain electrons to acquire positive or negative charge. Thus, we can say, an atom or a group of atoms when they either loss or gain electrons, get converted into ions or radicals.
Incorrect
Explanation
The number of electrons gained or lost by an atom is shown as a superscript to the right of its symbol. When an atom loses an electron, ‘+’ sign is shown in the superscript and ‘–’ sign is shown if an electron is gained by an atom. Sometimes, two or more atoms of different elements collectively loss or gain electrons to acquire positive or negative charge. Thus, we can say, an atom or a group of atoms when they either loss or gain electrons, get converted into ions or radicals.
-
Question 50 of 70
50. Question
50. Ions are classified into how many types?
Correct
Explanation
Ions are classified into two types. They are: cations and anions.
Incorrect
Explanation
Ions are classified into two types. They are: cations and anions.
-
Question 51 of 70
51. Question
51. Which among the following statement is correct
1) If an atom loses one or more electrons during a chemical reaction, it will have more number of negative charge on it. These are called cations (or) negative radicals. Sodium atom loses one electron to attain stability and it becomes cation. Sodium ion is represented as Na+
2) If an atom gains one or more electrons during a chemical reaction, it will have more number of negative charge on it. These are called anions or negative radicals. Chlorine atom attains stable electronic configuration by gaining an electron. Thus, it becomes anion. Chlorine ion is represented as Cl–
3) During a chemical reaction, an atom may gain or lose more than one electron. An ion or radical is classified as monovalent, divalent, trivalent or tetravalent when the number of charges over it is 1, 2, 3 or 4 respectively. Based on the charges carried by the ions, they will have different valences.
Correct
Explanation
If an atom loses one or more electrons during a chemical reaction, it will have more number of positive charge on it. These are called cations (or) positive radicals. Sodium atom loses one electron to attain stability and it becomes cation. Sodium ion is represented as Na+.
Incorrect
Explanation
If an atom loses one or more electrons during a chemical reaction, it will have more number of positive charge on it. These are called cations (or) positive radicals. Sodium atom loses one electron to attain stability and it becomes cation. Sodium ion is represented as Na+.
-
Question 52 of 70
52. Question
 Correct
Correct
 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 53 of 70
53. Question
53. Which among the following steps followed to write down the chemical formula of a substance is incorrect?
1) Write down the symbols of elements/ ions side by side so that the positive radical is on the right and the negative radical is on the left-hand side.
2) Write the valencies of the two radicals above their symbols to the right in superscript (Signs ‘+’ and ‘-’ of the ions are omitted).
3) Reduce the valency to simplest ratio if needed. Otherwise interchange the valencies of the elements/ions. Write these numbers as subscripts. However, ‘1’ appearing on the superscript of the symbol is omitted.
Correct
 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 54 of 70
54. Question
54. Which is a substance formed out of more than one element joined together by chemical bond?
Correct
Explanation
A chemical compound is a substance formed out of more than one element joined together by chemical bond. Such compounds have properties that are unique from that of the elements that formed them.
Incorrect
Explanation
A chemical compound is a substance formed out of more than one element joined together by chemical bond. Such compounds have properties that are unique from that of the elements that formed them.
-
Question 55 of 70
55. Question


 Correct
Correct
Explanation
In naming a compound containing a metal and a non-metal, the name of the metal is written first and the name of the non-metal is written next after adding the suffix-ide to its name. Examples: NaCl – Sodium chloride Ag Br – Silver bromide.
Incorrect
Explanation
In naming a compound containing a metal and a non-metal, the name of the metal is written first and the name of the non-metal is written next after adding the suffix-ide to its name. Examples: NaCl – Sodium chloride Ag Br – Silver bromide.
-
Question 56 of 70
56. Question
56. Every chemical equation has two components, what are they?
Correct
Explanation
A chemical equation is a short hand representation of a chemical reaction with the help of chemical symbols and formulae. Every chemical equation has two components: reactants and products. Reactants are the substances that take part in a chemical reaction and the products are the substances that are formed in a chemical reaction. Before writing the balanced equation of a chemical reaction, skeletal equation is written.
Incorrect
Explanation
A chemical equation is a short hand representation of a chemical reaction with the help of chemical symbols and formulae. Every chemical equation has two components: reactants and products. Reactants are the substances that take part in a chemical reaction and the products are the substances that are formed in a chemical reaction. Before writing the balanced equation of a chemical reaction, skeletal equation is written.
-
Question 57 of 70
57. Question

 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 58 of 70
58. Question
58. According to which law the total mass of all the atoms forming the reactants should be equal to that of all the atoms forming the products?
Correct
Explanation
According to law of conservation of mass, the total mass of all the atoms forming the reactants should be equal to that of all the atoms forming the products. This law will hold good only when the number of atoms of all types of elements on both sides is equal. A balanced chemical equation is one in which the total number of atoms of any element on the reactant side is equal to the total number of atoms of that element on the product side.
Incorrect
Explanation
According to law of conservation of mass, the total mass of all the atoms forming the reactants should be equal to that of all the atoms forming the products. This law will hold good only when the number of atoms of all types of elements on both sides is equal. A balanced chemical equation is one in which the total number of atoms of any element on the reactant side is equal to the total number of atoms of that element on the product side.
-
Question 59 of 70
59. Question
59. Which among the following is the methods of balancing a chemical equation?
Correct
Explanation
There are many methods of balancing a chemical equation. Trial and error method (direct inspection), fractional method and odd number-even number method are some of them.
Incorrect
Explanation
There are many methods of balancing a chemical equation. Trial and error method (direct inspection), fractional method and odd number-even number method are some of them.
-
Question 60 of 70
60. Question
60. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding balancing a chemical equation?
1)Initially the number of times an element occurs on both sides of the skeleton equation should be counted. An element which occurs least number of times in reactant and product side must be balanced first. Then, elements occurring two times, elements occurring three times and so on in an increasing order must be balanced.
2) When two or more elements occur same number of times, the non-metallic element is balanced first in preference metallic element. If more than one metal or nonmetal is present then a metal or non-metal with higher mass number (refer periodic table to find the mass number) is balanced first.
3) The number of molecules of reactants and products are written as coefficient. The formula should not be changed to make the elements equal. Fractional method of balancing must be employed only for molecule of an element (O2, H2, O3, P4,.) not for compound (H2O, NH3,.)
Correct
Explanation
When two or more elements occur same number of times, the metallic element is balanced first in preference to non-metallic element. If more than one metal or nonmetal is present then a metal or non-metal with higher atomic mass (refer periodic table to find the atomic mass) is balanced first.
Incorrect
Explanation
When two or more elements occur same number of times, the metallic element is balanced first in preference to non-metallic element. If more than one metal or nonmetal is present then a metal or non-metal with higher atomic mass (refer periodic table to find the atomic mass) is balanced first.
-
Question 61 of 70
61. Question
 Correct
Correct


 Incorrect
Incorrect



-
Question 62 of 70
62. Question
62. Which among the following information are given by balanced chemical equation?
Correct
Explanation
A balanced chemical equation gives us both qualitative and quantitative information.
Incorrect
Explanation
A balanced chemical equation gives us both qualitative and quantitative information.
-
Question 63 of 70
63. Question
63. Which among the following is not the qualitative information?
Correct
Explanation
A balanced chemical equation gives us qualitative information’s such as the names, symbols and formulae of the reactant molecules taking part in the reaction and those of the product molecules formed in the reaction. We also can get quantitative information like the number of molecules/ atoms of the reactants and products that are taking part in the reaction.
Incorrect
Explanation
A balanced chemical equation gives us qualitative information’s such as the names, symbols and formulae of the reactant molecules taking part in the reaction and those of the product molecules formed in the reaction. We also can get quantitative information like the number of molecules/ atoms of the reactants and products that are taking part in the reaction.
-
Question 64 of 70
64. Question
64. Which among the following is not the limitation of chemical equation?
Correct
Explanation
The limitation of chemical equation are i) Physical state of the reactants and the products. ii) Heat changes (heat liberated or heat absorbed) accompanying the chemical reaction. iii) Conditions such as temperature, pressure, catalyst etc., under which the reaction takes place. iv) Concentration (dilute or concentrated) of the reactants and products. V) Speed of the reaction.
Incorrect
Explanation
The limitation of chemical equation are i) Physical state of the reactants and the products. ii) Heat changes (heat liberated or heat absorbed) accompanying the chemical reaction. iii) Conditions such as temperature, pressure, catalyst etc., under which the reaction takes place. iv) Concentration (dilute or concentrated) of the reactants and products. V) Speed of the reaction.
-
Question 65 of 70
65. Question
65. Which among the following is not the ‘Laws of chemical combinations’?
Correct
Explanation
By studying quantitative measurements of many reactions, it was observed that the reactions taking place between various substances are governed by certain laws. They are called as the ‘Laws of chemical combinations. They are given below. 1. Law of conservation of mass 2. Law of constant proportion 3. Law of multiple proportions 4. Gay Loussac’s law of gaseous volumes.
Incorrect
Explanation
By studying quantitative measurements of many reactions, it was observed that the reactions taking place between various substances are governed by certain laws. They are called as the ‘Laws of chemical combinations. They are given below. 1. Law of conservation of mass 2. Law of constant proportion 3. Law of multiple proportions 4. Gay Loussac’s law of gaseous volumes.
-
Question 66 of 70
66. Question
66. The law of conservation of mass which relates the mass of the reactants and products during the chemical change was stated by which French chemist in 1774?
Correct
Explanation
The law of conservation of mass which relates the mass of the reactants and products during the chemical change was stated by a French chemist Lavoisier in 1774. It states that during any chemical change, the total mass of the products is equal to the total mass of the reactants.
Incorrect
Explanation
The law of conservation of mass which relates the mass of the reactants and products during the chemical change was stated by a French chemist Lavoisier in 1774. It states that during any chemical change, the total mass of the products is equal to the total mass of the reactants.
-
Question 67 of 70
67. Question
67. Law of conservation of mass is also known as _____
Correct
Explanation
The law of conservation of mass means that mass can neither be created nor be destroyed during any chemical reaction. This law is also known as Law of indestructibility of mass.
Incorrect
Explanation
The law of conservation of mass means that mass can neither be created nor be destroyed during any chemical reaction. This law is also known as Law of indestructibility of mass.
-
Question 68 of 70
68. Question
68. Which among the following is the process of formation of Ammonia from the reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen?
Correct

 Incorrect
Incorrect


-
Question 69 of 70
69. Question
69. Who among the following proposed law of constant proportions in 1779?
Correct
Explanation
Law of constant proportions was proposed by the scientist Joseph Proust in 1779. He states that in a pure chemical compound the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass.
Incorrect
Explanation
Law of constant proportions was proposed by the scientist Joseph Proust in 1779. He states that in a pure chemical compound the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass.
-
Question 70 of 70
70. Question
70. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Law of constant proportions?
1) Joseph Proust observed all the compounds with two or more elements and noticed that each of such compounds had the same elements in same proportions, irrespective of where the compound came from or who prepared it.
2)For example, water obtained from different sources like rain, well, sea, and river will always consist of the same two elements hydrogen and oxygen, in the ratio 1:8 by mass.
3) Similarly, the mode of preparation of compounds may be different but their composition will never change. It will be in dynamic ratio. Hence, this law is also known as ‘Law of dynamic proportions.
Correct
Explanation
Similarly, the mode of preparation of compounds may be different but their composition will never change. It will be in a fixed ratio. Hence, this law is also known as ‘Law of definite proportions.
Incorrect
Explanation
Similarly, the mode of preparation of compounds may be different but their composition will never change. It will be in a fixed ratio. Hence, this law is also known as ‘Law of definite proportions.
Leaderboard: Atomic Structure Online Test 8th Science Lesson 12 Questions in English
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||