Atmosphere 9th Social Science Lesson 21 Questions in English
9th Social Science Lesson 21 Questions in English
21] Atmosphere
1. Assertion (A): The Air blanket that surrounds the earth is called the Atmosphere.
Reasoning(R): Air is essential for the survival of all forms of life.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A
c) A is True but R is False
d) Both A and R is False
Explanation
Earth is a unique planet where life is found. The air is essential for the survival of all forms of life. The blanket of air that surrounds the Earth is called the atmosphere. It is held close to the earth by gravitational attraction.
2. What is the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere?
a) 53%
b) 1%
c) 21%
d) 78%
Explanation
Atmosphere is a mixture of gases, water vapor and dust particles in different proportions. Nitrogen (78%) and Oxygen (21%) are permanent gases of the atmosphere.
3. Which occupies the lowest percentage in the atmosphere?
a) Argon
b) Hydrogen
c) Ozone
d) Neon
Explanation
The remaining one percentage is occupied by Argon (0.93%), Carbon-dioxide,(0.03%), Neon (0.0018%), Helium (0.0005%), Ozone (0.00006%) and Hydrogen (0.00005%).
4. What is the percentage of water vapor present in the atmosphere?
a) 5%
b) 10%
c) 0.4%
d) 2.5%
Explanation
Water vapor (0 – 0.4%) is also found in the atmosphere which plays an important role in predicting weather phenomenon.
5. Which of the solid particles are not included in the atmosphere?
a) Salt particles
b) Smoke
c) Volcanic ashes
d) Soil
Explanation
The solid particle present in the atmosphere includes dust particles, salt particles, pollen grains, smoke, soot, volcanic ashes etc.
6. Who discovered Nitrogen in the atmosphere?
a) Nikola Tesla
b) Daniel Rutherford
c) Galileo Galilee
d) Ada Lovelace
Explanation
In 1772 CE Daniel Rutherford discovered Nitrogen in atmosphere.
7. When did Joseph priestly discover oxygen in the atmosphere?
a) 1774
b) 1872
c) 1763
d) 1823
Explanation
In 1774 Joseph priestly discovered oxygen in atmosphere.
8. By which of this process CO2 warms the atmosphere?
a) Convection and Insulation
b) Absorption and Radiation
c) Insulation and Radiation
d) Conduction and Convection
Explanation
Oxygen is most important for living organisms. CO2 absorbs heat and keeps the atmosphere warm by insulation and radiation.
9. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the atmosphere.
i) Nitrogen is chemically active and it acts as a diluent.
ii) Ozone protects the earth from radiation.
iii) The solid particles act as nuclei in the atmosphere.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Nitrogen acts as a diluent and is chemically inactive. Ozone helps in protecting the earth from radiation. The solid particles in the atmosphere acts as nuclei on which water vapor condense to form precipitation.
10. The atmosphere is thick near the _______ and ______ out until it merges with space.
a) Troposphere, Thin
b) Earth surface, Thin
c) Sun, Thick
d) Moon, Thins
Explanation
The atmosphere is thick near the earth surface and thins out until it eventually merges with space.
11. How many atmospheric layers are classified?
a) 7
b) 6
c) 5
d) 3
Explanation
The five atmospheric layers are: Troposphere, stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere and Exosphere
12. What is the meaning of the word tropos?
a) Radiate
b) Turn/ Change
c) Reflect
d) Absorb
Explanation
The lowest layer of the atmosphere is the troposphere. The Greek word ‘tropos’ means ‘turns’ or change.
13. Choose the correct statements.
i) The Troposphere layer extends up to 5 km at the equator.
ii) Temperature in troposphere decreases with increase in height.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The troposphere layer extends up to 8 km at the poles and up to 18 km at the Equator. The temperature decreases with increasing height.
14. What is the significance of the troposphere layer?
a) Weather making layer
b) Radio Communication layer
c) Ionizing layer
d) Ozone layer
Explanation
Almost all weather phenomenon’s take place in this troposphere layer. Hence it is called weather making layer.
15. Name the upper limit of the troposphere layer.
a) Mesopause
b) Stratopause
c) Tropopause
d) Ozonosphere
Explanation
The upper limit of the troposphere is called as Tropopause.
16. Which of this layer extends to height of 50km above earth surface?
a) Troposphere
b) Homosphere
c) Ionosphere
d) Stratosphere
Explanation
Stratosphere lies above the troposphere. It extends to a height of about 50km above earth surface.
17. Which of these layers are also called as Ozonosphere?
a) Stratosphere
b) Mesosphere
c) Homosphere
d) Troposphere
Explanation
The Stratosphere layer is a concentration of ozone molecules; it is also referred as ozonosphere.
18. Choose the correct statements.
i) The stratosphere is flying zone region for the large jet planes.
ii) The temperature decreases with increase in height in the stratosphere layer.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The temperature increases with increase in height in the stratosphere layer. Large jet planes normally fly here. The upper limit of the stratosphere is called as Stratopause.
19. Which of this layer exists between 50km and 80 km?
a) Mesosphere
b) Stratosphere
c) Ionosphere
d) Troposphere
Explanation
Mesosphere extends between 50km and 80km. The temperature increases with increasing height.
20. What is the significance of the mesosphere layer?
i) Radio waves transmitted from earth are reflected in this layer.
ii) The Meteors are burnt in this region.
iii) Mesopause is the upper most limit of this layer.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Radio waves transmitted from earth are reflected back to earth from the mesosphere layer. Most of the meteors nearing the earth get burned here. The upper most limit of the mesosphere is the Mesopause.
21. Which layer exists above the mesosphere region?
a) Thermosphere
b) Ionosphere
c) Stratopause
d) Mesopause
Explanation
Thermosphere exists above the mesosphere. It extends to about 600 km.
22. Why the lower thermosphere is called as Homosphere?
a) Same type of molecules
b) Composition of gases is more or less uniform.
c) Only oxygen exists in this layer.
d) All the above
Explanation
The composition of gases in the lower thermosphere is more or less uniform; hence it is called “Homosphere”.
23. Which of the following is correct regarding Heterosphere?
a) Lower portion of thermosphere.
b) Temperature decreases with increase in height.
c) Uneven composition of gas exists.
d) Mid-region of Homosphere.
Explanation
The upper portion of the thermosphere has uneven composition of gases and hence it is referred as “Heterosphere”. Here the temperature increases with increasing height
24. Which of this thermosphere region contains ions and free electrons?
a) Ionosphere
b) Heterosphere
c) Homosphere
d) Stratopause
Explanation
Ionosphere is a layer of the thermosphere that contains Ions and free electrons.
25. Assertion (A): Mesosphere lies beyond exosphere and it extends to 64,000km above the earth’s surface.
Reasoning(R): Magnetosphere is the earth’s magnetic belt.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Magnetosphere lies beyond the exosphere. It is the earth’s magnetic belt where proton and electrons, coming out from the sun are trapped by the earth. The magnetic field extends to around 64,000 km above the Earth.
26. What is the upper most layer of the atmosphere?
a) Heterosphere
b) Ionosphere
c) Troposphere
d) Exosphere
Explanation
The uppermost layer of the atmosphere is called exosphere. This layer is extremely rarefied with gases and gradually merges with the outer space. This zone is characterized by aurora Australis and aurora borealis.
27. What is the term used for the multicolored fireworks in earths polar sky?
a) Cosmic Lights
b) Sparkles
c) Auroras
d) None of the above
Explanation
Auroras are cosmic glowing lights produced by a stream of electrons discharged from the Sun’s surface due to magnetic storms that are seen as unique multicolored fireworks hanging in the polar sky during midnight.
28. Assertion (A): Every day behavior of the atmosphere is called as weather.
Reasoning(R): Weather and Climate are the terms related to the condition of atmosphere.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
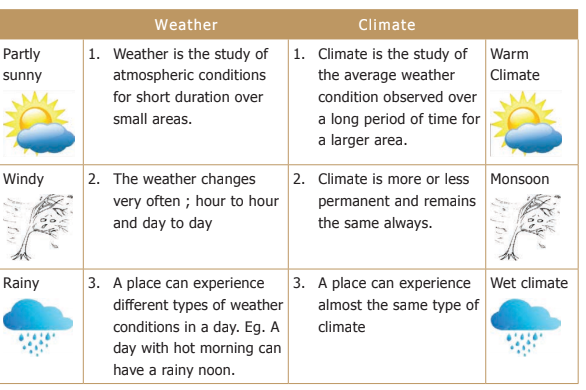
Weather and climate are the terms that are related to the atmospheric conditions. Weather denotes the way the atmosphere behaves every day and climate reveals the average of weather conditions over relatively long periods of time.
29. Which of this factor does not influence the weather and climate?
a) Cloud Cover
b) Cosmic glow
c) Natural vegetation
d) Ocean Currents
Explanation
There are many factors that influence weather and climate: Distance from the equator, Altitude, Nearness to the sea, Nature of the prevailing winds, Mountain barrier, Cloud cover, Ocean currents and Natural vegetation
30. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Weather is the study of atmospheric conditions for short duration of small areas.
ii) Climate is more or less permanent and remains same always.
iii) Rainy area denotes the climate of a region.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
31. Assertion (A): The study of the weather is called as Meteorology.
Reasoning(R): Climatology is the study of the climate conditions.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
32. Choose the correct statements.
i) The Sun rays fall vertically and heats up the earths equator.
ii) The regions near the equator are too hot because of the vertical sun rays.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The sun’s rays fall vertically on the equator. The rays are inclined on the regions away from the equator and near the poles due to the spherical shape of the earth. The vertical rays heat up the earth more than the inclined rays. Thus, the places near the equator are warmer than the places which are far away from the equator.
33. Which of these refers to the height above the sea level?
a) Base
b) Latitude
c) Altitude
d) Longitude
Explanation
Altitude refers to the height above sea level. The temperature decreases at the rate of 1° C for every 165 mt of height.
34. Which is called as the normal lapse rate?
a) 5°C increase for every 165 mt of height
b) 1°C decrease for every 165 mt of height
c) 10°C increase for every 150 mt of height
d) 1°C decrease for every 155 mt of height
Explanation
The Normal lapse rate is the temperature decrease at the rate of 1° C for every 165 mt of height. So places at the higher altitude have a lower temperature.
35. Which of these influence the climate of a place?
a) Nearness to the sea.
b) Depth of the sea.
c) Winds from the sea.
d) Both a and c
Explanation
The climate of a place varies according to its nearness to the sea. Places near the coast experience equable climate due to the influence of the winds from the sea.
36. Which of these places have a continental type of climate?
a) Near to the sea.
b) Located in land.
c) Near to the Polar Regions.
d) All the above
Explanation
Places located in the land, far from the sea, does not experience the moderating influence of the sea, such places experience a continental type of climate.
37. Assertion (A): The Wind blowing from the ocean to land in afternoon is called as sea breeze.
Reasoning(R): The land masses get heated and dry more rapidly than the oceans.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
During the day, the land masses get heated more rapidly than the oceans. Heated air ascends and this causes low pressure on the adjoining ocean. Therefore, the wind blows from ocean to land in the afternoon. This is called sea breeze.
38. What is the significance of the sea breeze?
a) Increases the rainfall of the land masses in winter season.
b) Increase the temperature of the land masses in summer season.
c) Reduces the temperature of the coastal region in summer season.
d) Increases the rainfall of the coastal region in winter season.
Explanation
Sea breeze helps in reducing the temperature of the coastal region especially during the summer season.
39. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The land cools more rapidly than the ocean in night times.
ii) The cool air from the land ascends and forms low pressure.
iii) The wind flow from land to sea at night times is called as land breeze.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
During the night, the land cools more rapidly than the ocean. Cool air sinks and forms high pressure. The wind blows from land to sea during the night, this is called land breeze.
40. Choose the correct statements.
i) The winds change the climate of a place based on the origin of blow.
ii) Wind blowing from a warm region makes the place warm.
iii) The on-shore winds cause rainfall and cool the place.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The winds change the climate of a place based on, from where they blow. When wind blows from a warm region, it makes the place warm and cold, when blows from a colder region. The on-shore winds cause rainfall making the place cool whereas the off-shore winds bring dry weather.
41. Assertion (A): The Location of mountain influence the climate of a country or a region.
Reasoning(R): The Mountains prevents the entry of cold winds or escape of monsoon winds in a country.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The location of the mountain influences the climate of a place. The mountain chains act as natural barrier for the wind. Sometimes they prevent the entry of cold winds into the country or the escape of monsoon winds, thus having a great influence over the climate.
42. Which region of a mountain receives heavy rainfall?
a) Leeward side
b) Peak of mountain
c) Windward side
d) Foothills
Explanation
The windward is the side of a mountain which faces the prevailing wind. It receives heavy rainfall.
43. The less rainfall region of a mountain is the ______ side as it has _____.
a) Leeward, sheltered from wind
b) Foothills, low wind
c) Windward, Low temperature
d) Mountain peak, low pressure
Explanation
The leeward side of the mountain is the side sheltered from the wind. It receives very less rainfall.
44. Assertion (A): Cloudy sky results in low temperature.
Reasoning(R): Heat radiated from sun is reflected by the clouds.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Clouds reflect a large amount of radiation from the sun. This prevents the entry of heat to the earth’s surface. So, in areas generally of cloudless sky like the deserts, temperature is very high. On the other hand under cloudy sky, the temperature is low.
45. Which factor increases the temperature of the coastal areas?
a) Climate condition
b) Direction of wind
c) Warm ocean current
d) None of the above
Explanation
The warm ocean currents raise the temperature of the nearby coastal areas, while the cold current lower the temperature of a place.
46. Which of these areas have lower range of temperature?
a) Forest
b) Coastal
c) Plateau
d) Plain surface
Explanation
The trees release water vapor into the air and make it cool. Thus forest areas have lower range of temperature throughout the year in contrast to no forested areas.
47. Which of these factors does not decide climate and weather condition?
a) Temperature
b) Clouds
c) Earth’s rotation
d) Humidity
Explanation
Elements of climate and weather depends on, Temperature, Pressure, Wind, Cloud, Precipitation and Humidity.
48. Choose the correct statements.
i) Sun is the chief source of energy for the earth.
ii) Temperature is the measure of warmth of an object.
iii) Thermometer measures the temperature in terms of Celsius and Fahrenheit.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Temperature is a measure of the warmth of an object expressed in terms of Celsius or Fahrenheit, measured with thermometer. Sun is the chief source of energy for the Earth.
49. What is the significance of the atmosphere?
a) Acts as an insulator
b) Maintains the temperature of earth
c) Prevents extreme temperature during day and night
d) All the above
Explanation
The atmosphere acts as an insulator and maintains the temperature of the earth. Without atmosphere, the earth would experience great extremes of temperatures during day and night.
50. Which of these are not responsible for atmospheric heat?
a) Ionization
b) Conduction
c) Convection
d) Advection
Explanation
Some of the processes that are responsible for atmospheric heat are radiation, Conduction, Convection and Advection.
51. Define Insolation.
a) Heat waves from atmosphere
b) Radiation from sun
c) Heat from sun of short waves
d) Temperature variation between earth and sun
Explanation
The amount of heat received from the sun in the form of short waves is called Insolation or Incoming Solar Radiation.
52. What is the term used for the outgoing heat from earth to space?
a) Re-radiation
b) Terrestrial radiation
c) Solar radiation
d) Both a and b
Explanation
The outgoing heat from the earth to space in the form of long waves is called terrestrial radiation. This is also called as re-radiation
53. What is Albedo?
a) Fraction between radiation and incoming solar radiation
b) Fraction between solar energy reflected from earth to space without heating earth surface
c) Fraction between Heat and temperature
d) None of the above
Explanation
Albedo is the fraction of solar energy reflected from the earth back into space without reaching or heating the earth surface.
54. Heat budget of earth is the balance between _____ and _____.
a) Total Radiation, Temperature of earth
b) Radiation, Convection
c) Re-radiation, Insolation
d) Insolation, Radiation
Explanation
There is a balance between insolation and radiation. This balance is termed as a heat budget of the earth.
55. Isotherms are ____ lines connecting points having equal_____.
a) Real, pressure
b) Imaginary, temperature
c) Temporary, climate
d) Permanent, radiation
Explanation
Isotherms are imaginary lines drawn on maps, connecting points that have equal temperatures.
56. What is the average global surface temperature?
a) 273°F
b) 35°C
c) 213°F
d) 13°C
Explanation
Temperature varies from place to place, season to season and continent to continent. The average global surface temperature is about 13 °C.
57. Match
A. Advection i) Contact
B. Convection ii) Horizontal movement
C. Conduction iii) Air circulation
a) iii, i, ii
b) ii, i, iii
c) i, iii, ii
d) ii, iii, i
Explanation
Conduction is the transfer of heat from hot body to a cold body through contact. Convection is transfer of heat by movement or circulation of air in a mass. Advection is the transfer of heat through the horizontal movement of air.
58. How many heat zones are classified based on insolation?
a) 3
b) 2
c) 4
d) 7
Explanation
Based on the amount of insolation received from the sun and the heat, Earth is classified into three heat zones namely torrid zone, temperate zone and Frigid Zone.
59. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding Torrid Zone.
i) Located between tropic of cancer and tropic of Capricorn.
ii) Have vertical sun rays and hot throughout the year.
iii) About 75% of earth surface is Torrid Zone.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Torrid Zone: This largest thermal zone covers almost 50% of the earth’s surface. It is located between the Tropic of Cancer (23½°N) and Tropic of Capricorn (23½°S). Torrid Zone experiences vertical sun rays almost throughout the year and is hot.
60. In which of this region the sun rays never fall vertically?
a) Temperate Zone
b) Torrid Zone
c) Equator
d) Frigid Zone
Explanation
Temperate Zones: The Temperate Zone stretches out between Tropic of Cancer (23½°N) and Arctic Circle (66½°N) in the northern hemisphere and between Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S) and Antarctic Circle (66½° S) in the southern hemisphere. The sun’s rays never fall vertical in this region.
61. Choose the correct statements regarding Frigid zones.
i) The sun ray’s fall slantingly in these zones.
ii) The artic and Antarctic circles lie in frigid zones.
iii) Frigid zones are the coldest regions in the world which is completely frozen.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The Frigid Zone is found between Arctic Circle (66½°N) and North Pole (90° N) in the northern hemisphere and stretches out between Antarctic Circle (66½° S ) and South Pole (90°S) in the southern hemisphere. The sun’s rays fall slanting in this zone. These are the coldest regions of the world. The surface remains permanently frozen under thick snow.
62. What is the unit of atmospheric pressure?
a) Microbar
b) Millibar
c) Pascal
d) Newton meter
Explanation
The atmospheric pressure is the weight exerted by air on a particular area of the earth surface. It is measured with a mercury barometer and the unit of measurement is millibar (mb).
63. Which of these denotes the equal atmospheric pressure to sea level?
a) Isobar
b) Isomers
c) Isotherm
d) None of the above
Explanation
An isobar is an imaginary line drawn through places having equal atmospheric pressure reduced to sea level.
64. Assertion (A): The Atmospheric pressure varies vertically on the surface of earth.
Reasoning(R): The distribution of atmospheric pressure is not uniform on earth surface.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The distribution of atmospheric pressure on the surface of the earth is not uniform. It varies both vertically and horizontally.
65. With reference to _____ the air pressure varies.
a) Altitude
b) Temperature
c) Sun
d) Earth rotation
Explanation
Air pressure decreases with altitude. The air molecules become scattered and more widely spaced at higher altitudes. The air pressure decreases by 34 millibars per 300 metres increase in height.
66. What are the factors influence the atmospheric pressure distribution in the world?
a) Air temperature
b) Earth’s rotation
c) Water vapor
d) All the above
Explanation
The horizontal distribution of atmospheric pressure in the world is not uniform. It varies from time to time and place to place due to (i) air temperature (ii) the earth’s rotation (iii) presence of water vapor.
67. Which of these is not the pressure belt of Earth?
a) Sub tropical high
b) Equatorial low
c) Sub polar high
d) Polar high
Explanation
The pressure belts of the world are: Equatorial low, Sub tropical highs, Sub polar lows, Polar highs.
68. State the significance of the Doldrums?
a) Absence of surface winds
b) High pressure belt
c) Heated waves
d) Planetary winds
Explanation
The Equatorial Low Pressure Belt: This belt extends from equator to 5° N and 5° S latitudes. At the equator, the earth gets heated by the vertical sun rays and in turn heats the air in contact with it. The heated air expands and rises upwards resulting in a low pressure belt. This belt is called doldrums due to virtual absence of surface winds.
69. In which of this region the converging winds and rising air encircling near the equator?
a) Horse Latitude
b) Doldrums
c) ITCZ
d) All the above
Explanation
The Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is the belt of converging winds and rising air encircling Earth near the Equator.
70. Which of these occur in the doldrums region?
a) Calm winds
b) Light unpredictable winds
c) Sudden cyclones
d) All the above
Explanation
Doldrums (the zone of calm) lies in the equatorial region with calms, light unpredictable winds and sudden cyclones.
71. What is the location of the sub-tropical high pressure belts?
a) Tropics to about 35° latitudes in both the hemispheres
b) Equator to about 65° latitudes in southern hemisphere
c) About 55° latitudes in both the hemispheres
d) Tropics to about 85° latitudes in northern hemisphere
Explanation
The sub-tropical high pressure belts extend from the tropics to about 35° latitudes in both the hemispheres. The air that rises in the equatorial region, becomes cold and heavy, and starts to descend in the Sub Tropical regions. This result in sub-tropical high pressure belts referred as the Horse latitude.
72. Which is called as the Horse latitude in olden days?
a) Tropical low pressure belts
b) Sub tropical high pressure belts
c) Polar High pressure belts
d) Sub polar low pressure belts
Explanation
HORSE LATITUDE: In olden days vessels with cargo of horses passing through sub-tropical high pressure belts found difficulty in sailing under calm conditions. With little water and food left for the humans, sailors used to throw the horses in to the sea in order to make the vessels lighter. Henceforth these belts or latitudes are also called ‘horse latitudes’.
73. Choose the correct statements.
i) The Sub polar low pressure belt extends between 45°N and the Arctic circle in the northern hemisphere.
ii) The low pressure air moves to the sub-tropical and Polar Regions to free from air pressure.
iii) The rotation of the earth makes the air to flow through various pressure regions.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The Sub-polar Low Pressure Belts: The sub-polar low pressure belts extend between 45°N and the Arctic Circle in the northern hemisphere and between 45°S and the Antarctic Circle in the southern hemisphere. The air present in this layer moves to the sub-tropical high pressure belt and polar high pressure belt making it free from air pressure forming the sub polar low pressure belt. This is made possible by the rotation of the earth.
74. Which of this earth region has the high pressure air belt?
a) Sub-tropical
b) Equator
c) Tropical
d) Polar
Explanation
The Polar High Pressure Belts: Sun rays are always slanting at poles resulting in low temperatures. Because of low temperature, air compresses and its density increases. Hence, high pressure is found here. Winds from these belts blow towards sub-polar low pressure belts.
75. Assertion (A): The Horizontal movement of air along the earth surface is called as Wind.
Reasoning(R): The Air Current is the vertical movement of air.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The horizontal movement of air along the surface of the earth is called the “Wind’ while the vertical movement of air is a called an “Air Current”.
76. On what basis a wind is named?
a) Pressure
b) Humidity
c) Direction
d) Time period
Explanation
The winds always blow from a high pressure area to a low pressure area. Wind is mostly named after the direction from which it blows. For example, the wind blowing from the east is known as the easterly wind.
77. The wind speed is recorded by______ and wind vane measures the _______.
a) Anemometer, Direction of the wind
b) Barometer, Pressure of the wind
c) Hygrometer, Humidity of the wind
d) None of the above
Explanation
An “anemometer” records wind speed while a “wind vane” measures the direction of the wind. The unit of measurement is kilometer per hour or knots.
78. How many major types of winds are classified?
a) 5
b) 3
c) 4
d) 7
Explanation
Winds are generally classified into the following four major types: Planetary winds, Periodic winds, Variable wind and Local wind.
79. What are the other names for the planetary winds?
a) Permanent winds
b) Prevailing winds
c) Seasonal winds
d) Both a and b
Explanation
Planetary winds: The winds which constantly blow in the same direction throughout the year are called the Planetary winds. They are also called as permanent winds or the prevailing winds. These winds include Trade winds, Westerlies and Polar Easterlies.
80. Choose the correct statements regarding the Trade winds.
i) These winds blow from the Subtropical high pressure belt to the equatorial low pressure belt in both hemispheres.
ii) They have a constant direction and regularity force throughout the year.
iii) These winds cause heavy rainfall to the East coast continents.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Trade Winds: Trade winds blow from the subtropical high pressure belt to the Equatorial low pressure belt in both the hemispheres. They blow with great regularity, force and in a constant direction throughout the year. These winds were very helpful to traders who depended on the winds while sailing in the seas. And so, they are named as Trade winds. As they travel over vast oceans, they collect more moisture and bring heavy rainfall to the East Coast of the continents of the tropics. As they move westwards, they become dry and do not give rainfall.
81. Assertion (A): Westerlies are the temporary winds blowing from high pressure to low pressure belts.
Reasoning (R): They blow from South East in Southern hemisphere to North West in the Northern hemisphere.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Westerlies: Westerlies are the permanent winds that blow from the tropical high pressure belt to the sub polar low pressure belt in both the hemispheres. They blow from South West to North East in the northern hemisphere and North West to South East in the southern hemisphere. The velocity of Westerlies become so vigorous and fast to be called Roaring Forties at 400,Furious Fifties at 500 and Screaming Sixties at 600 latitudes.
82. Choose the correct statements regarding Polar easterlies.
i) These are cold and dry polar winds blowing from high pressure belt to low pressure belt.
ii) It is a strong wind blowing from South East direction in the Southern Hemisphere.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Polar Easterlies: Polar easterlies are cold and dry polar winds that blow from the polar high pressure belt to the sub polar low pressure belt. These are weak winds blowing from North East direction in the Northern Hemisphere and South East direction in the Southern Hemisphere.
83. Which of these causes the periodic winds?
a) Differential heating of land and ocean.
b) Weak winds from North East direction
c) Dry polar winds
d) Pressure belts
Explanation
Periodic winds: The periodic winds are the seasonal winds that change their direction periodically. These winds are caused by the differential heating of land and ocean.
84. Define the Monsoon
a) Wind blowing from Polar Regions
b) Deflection of winds by earth’s rotation
c) Seasonal winds change direction periodically
d) Winds reverse with the change of seasons
Explanation
Winds which reverse their direction with the change of seasons are called monsoons. Tropical Monsoon winds of Indian subcontinent are a best example.
85. Name the effect caused by the effect of earth’s rotation causing wind deflection?
a) Newton’s Effect
b) Ferrell’s Force
c) Coriolis Effect
d) Centrifugal Force
Explanation
The rotation of the Earth causes deflection of winds from their original path, called the “Coriolis effect.
86. Who propounded the Ferrel’s law and use the term Coriolis force?
a) C.G. Coriolis
b) William Ferrel
c) Isaac Newton
d) Madam Curie
Explanation
Winds are deflected to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere which is known as “Ferrel’s law”. This was profounded by William Ferrel. He used “Coriolis force” named after G.G Coriolis (1792-1843) for proving Ferrel’s Law.
87. Name the disturbances in the local weather?
a) Trade winds
b) Planetary winds
c) Variable winds
d) Periodic winds
Explanation
Variable winds: The disturbance and the changes in the local weather cause variations in the prevailing winds. These winds are known as the variable winds. Variable winds usually end up with the development of cyclones, anticyclones and storms.
88. What is the origin of the word Cyclone?
a) Greek
b) Latin
c) Persia
d) Sanskrit
Explanation
Cyclones: The term cyclone is a Greek word meaning “coil of a snake”.
89. Assertion (A): The cyclonic winds in the northern hemisphere move in anticlockwise direction.
Reasoning(R): The Earth’s rotation influences the direction of the cyclonic winds.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Cyclones are centers of low pressure where, winds from the surrounding high pressure area converge towards the center in a spiral form. Due to the rotation of the earth, the cyclonic winds in the northern hemisphere move in anti-clock wise direction, where as they move in clockwise direction in the southern hemisphere.
90. How many types of cyclones are classified based on the region?
a) 4
b) 3
c) 5
d) 8
Explanation
Cyclones can be classified into Tropical cyclones, Temperate cyclones and Extra tropical cyclones.
91. Which of these cyclones occur in the tropical convergence zone(ITCZ)?
a) Extra Tropical cyclones
b) Temperate cyclones
c) Tropical cyclones
d) All the above
Explanation
Tropical cyclones: Tropical cyclones develop in the Inter tropical convergence zone [ITCZ]. They are formed due to the differential heating of land and sea.
92. Match the name of tropical cyclones and their regions.
A. Atlantic i) Willy Willy
B. Philippines ii) Hurricanes
C. Australia iii) Cyclones
D. Indian Ocean iv) Baguios
a) ii, iv, i, iii
b) iii, i, ii, iv
c) iv, iii, i, ii
d) iii, iv, ii, i
Explanation
Tropical cyclones are known as ‘cyclones’ in Indian ocean, ‘typhoons’ in the western pacific ocean, ‘hurricanes’ in the Atlantic and eastern Pacific ocean, ‘Baguios’ in Philippines and ‘willy willy’ in Australia. Tropical cyclones often cause heavy loss of life and property on the coasts and become weak after reaching the landmasses.
93. When did a worst devastating super cyclone hit Odisha?
a) 2012
b) 2007
c) 1999
d) 1965
Explanation
Super Cyclone: A violent cyclone that hit Odisha on Friday, 29 October 1999, was one of the most devastating and strong storm to hit the Indian coast. Winds of up to 260 kph raged for over 36 hours. The winds caused a seven-meter tidal wave that swept more than 20 km inland and brought massive destruction and death to a number of coastal districts in the state of Odisha. It is estimated that more than 10 million people in 12 coastal belt districts were affected by the cyclone.
94. What is the latitude points region of the temperate cyclones?
a) 85°S and 65°NW
b) 35°S and 65°N
c) 55°S and 5°NE
d) 20°SE and 25°N
Explanation
Temperate cyclones are formed along a front where hot and cold air masses meet in mid-latitudes between 35°S and 65°N.
95. In which of these regions the temperate cyclones occur commonly?
a) North Atlantic ocean
b) North West Europe
c) Mediterranean Basin
d) All the above
Explanation
Temperate cyclones do not become weak like the tropical cyclones on reaching the land. Temperate cyclone commonly occurs over the North Atlantic Ocean, North West Europe, Mediterranean basin.
96. Which of these are the Mediterranean temperate cyclones extends in India?
a) Eastern disturbances
b) Planetary winds
c) Western disturbances
d) Seasonal changes
Explanation
Mediterranean basin’s temperate cyclones extend up to Russia and India in winter. In India it is as called western disturbances.
97. What is the term used for the boundary separates the warm and cool air masses?
a) Pressure belts
b) Front
c) Boundary
d) Isomer
Explanation
A front is the boundary separating warm and cold air masses. One type of air mass is usually denser than the other, with different temperatures and humidity. This meeting of air mass causes rain, snow, cold days, hot days, and windy days.
98. Which of these statements is not true regarding the Extra tropical cyclones?
a) These occur in latitudes between 30° and 60° in the southern hemisphere only.
b) They collect energy from the pressure differences found in higher latitudes.
c) It is also termed as Mid-latitude cyclones.
d) These produce mild showers only.
Explanation
Extra tropical cyclones occur in the latitudes between 30° and 60° in both the hemispheres. They are also called as mid-latitude cyclones. They collect energy from temperature differences which are found in higher latitudes. Extra tropical cyclones produce mild showers to heavy gales, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes.
99. When a formula was agreed for naming cyclones in the Indian Ocean region?
a) 2003
b) 2001
c) 2000
d) 2004
Explanation
Deliberations for naming cyclones in the Indian Ocean region began in 2000 and a formula was agreed upon in 2004.
100. How many countries are involved in assigning name for the cyclonic storms in the Indian ocean region?
a) 7
b) 10
c) 8
d) 9
Explanation
Eight countries in the Indian Ocean region Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Srilanka, and Thailand contributed a set of names which our assigned sequentially whenever a cyclonic storm develops.
101. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding Anticyclones.
i) Anticyclones are the opposite of cyclones.
ii) A low pressure region is surrounded by high pressure on all sides.
iii) These are often accompanied by cold and heat waves.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Anticyclones are the opposite of cyclones. Here an area of high pressure region is found in the center surrounded by low pressure on all sides. The wind from the high pressure region move outwards to the low pressure regions in a spiral form. Anticyclones are often accompanied by cold and heat waves.
102. Assertion (A): Local winds names are created in a particular locality for the whole season.
Reasoning(R): The effects of the local winds can be experienced all over the world.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Local winds are the winds that blow only in a particular locality for a short period of time. The effect of these local winds is experienced only in that particular area.
103. Match the local names of the winds with places.
A. Loo i) Italy
B. Bora ii) Africa
C. Sirocco iii) France
D. Mistral iv) India
a) iv, iii, ii, i
b) i, iii, ii, iv
c) iv, i, ii, iii
d) ii, iv, i, iii
Explanation
They are mostly seasonal and have local names like, Foehn (Alps-Europe), Sirocco (North coast of Africa), Chinook (Rockies-North America), Loo (Thar Desert- India), Mistral (Mediterranean sea in France), Bora (Mediterranean sea in Italy).
104. Which is the principal source of atmospheric moisture?
a) Sea water evaporate
b) Wind from the mountain slopes
c) Coastal winds
d) All the above
Explanation
Large amount of water evaporates each day from the surface of the sea. This is the principal source of atmospheric moisture.
105. Which of these is true regarding the formation of clouds?
a) Pure water vapor without any impurities
b) Visible mass of water vapor above ground level
c) Warm air circulation
d) Cool air formation
Explanation
Cool moisture laden air, gets collected around particles like dust, salt content from the sea, smoke etc., and forms clouds. Sometimes, mixing of warmer and cooler air also produces clouds. A visible mass of condensed water vapor floating in the air above the ground level is called a cloud.
106. In which of these layers clouds are not located?
a) Troposphere
b) Ionosphere
c) Mesosphere
d) Stratosphere
Explanation
The three layers of atmosphere such as troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere are specific locations of clouds.
107. How many types of clouds are classified based on their height?
a) 5
b) 4
c) 3
d) 2
Explanation
According to their height, clouds are classified into the following types: High clouds (6-20km Height), Middle clouds (2.5km-6km Height), Low clouds (ground surface to 25 km height). These major types of clouds are further divided into different types on the basis of shape and structure
108. Which of these clouds are dry and does not provide rainfall?
a) Cirrus
b) Stratus
c) Nimbostratus
d) Cumulus
Explanation
Cirrus: Detached clouds in the form of white delicate fibrous silky filaments formed at the high sky (8000 meters to 12000 meters) are called Cirrus clouds. These clouds are dry and do not give rainfall.
109. Assertion (A): The White patched layer like clouds composed of ice crystals are called as Cirro-cumulus.
Reasoning(R): Cirro-stratus denotes the milky whitish clouds of tiny ice crystals.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Cirro-cumulus: White patched, sheet or layer like clouds composed of ice crystals. Cirro-stratus: Smooth milky transparent whitish clouds composed of tiny ice crystals.
110. State the term used for the colorful cirrus clouds during the sunset?
a) Mare’s Tails
b) Fire Rainbows
c) Light pillars
d) Sundog
Explanation
During sunset cirrus clouds look colorful hence they are called as “Mare’s Tails”.
111. Match the middle clouds with their characteristics.
A. Frozen water droplets i) Nimbo Stratus
B. Dark Coloured ii) Alto-Cumulus
C. Parallel cloud bands iii) Alto-Stratus
a) ii, iii, i
b) ii, i, iii
c) iii, i, ii
d) i, iii, ii
Explanation
Middle clouds
Alto-stratus: Thin sheets of grey or blue Coloured clouds in uniform appearance consisting of frozen water droplets
Alto-cumulus: clouds fitted closely together in parallel bands, called as ‘Sheep clouds’ or wool pack clouds.
Nimbo stratus: These are clouds of dark color very close to the ground surface associated with rain, snow or sleet.
112. Which of this sphere contains all clouds in the atmosphere?
a) Stratosphere
b) Ionosphere
c) Homosphere
d) Troposphere
Explanation
The only sphere which contains all clouds in the atmosphere is troposphere.
113. Identify the Incorrect Match.
A. Cumulus i) Fair weather
B. Strato-cumulus ii) Dome shaped
C. Stratus iii) Dense
D. Cumulo-nimbus iv) Tornadoes
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) iv only
Explanation
Low clouds Strato-cumulus:- Grey or whitish layer of non-fibrous low clouds found in rounded patches at an height of 2500 to 3000 metres, associated with fair or clear weather
Stratus:- Dense, low lying fog-like clouds associated with rain or snow
Cumulus:- Dome-shaped with a flat base often resembling a cauliflower, associated with fair weather
Cumulo-nimbus:- Fluffy thick towering thunderstorm cloud capable of producing heavy rain, snow, hailstorm or tornadoes
114. Define Precipitation
a) Fall of condensed water vapor in various forms.
b) Saturated water droplets
c) Occurs after the dew point
d) All the above
Explanation
Falling down of condensed water vapor in different forms is called Precipitation. When the dew point is reached in the cloud water droplets become saturated and start to fall. Hence, they fall on the earth as Precipitation.
115. Which of these factors influence the forms of precipitation?
a) Temperature
b) Ocean current
c) Sunlight
d) Earth’s rotation
Explanation
The climatic conditions/ factors influencing the forms of precipitation mainly are: Temperature, Altitude, Cloud type, Atmospheric conditions and Precipitation process.
116. Which of these is not a form of precipitation?
a) Sleet
b) Rain
c) Hail
d) Frost
Explanation
The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, hail etc.
117. Which of these statements are not correct regarding drizzle?
a) Un-uniform droplets of water.
b) Diameter is less than 0.5mm
c) Combination of fog reduces visibility.
d) Mostly occur from low clouds.
Explanation
Falling of numerous uniform minute droplets of water with diameter of less than 0.5mm is called a drizzle from low clouds. Sometimes drizzles are combined with fog and hence reduce visibility.
118. What is the diameter of a rain drop?
a) Above 2cm
b) Below 10m
c) Above 5mm
d) Below 1mm
Explanation
Rain is the most widespread and important form of precipitation in places having temperature above the freezing point. It occurs only when there is abundant moisture in the air. The diameter of a rain drop is more than 5mm.
119. Which of this precipitation is a mixture of snow and rain?
a) Sleet
b) Hails
c) Drizzle
d) Dew
Explanation
Sleet refers to a precipitation in the form of pellets made up of transparent and translucent ice. This precipitation is a mixture of snow and rain.
120. Choose the correct statements regarding Snow.
i) Snow is formed below the freezing point.
ii) The opaque and semi opaque precipitation of ice crystals are called as snow.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Snow is formed when condensation occurs below freezing point. It is the precipitation of opaque and semi opaque ice crystals. When these ice crystals collide and stick together, it becomes snowflakes.
121. Which of these fall from the sky in a rainstorm or thunderstorm?
a) Ice fleet
b) Snow
c) Hails
d) Drizzle
Explanation
Hails are chunks of ice (greater than 2cm in diameter) falling from the sky, during a rainstorm or thunderstorm.
122. Assertion (A): Hailstones are destructive and dreaded form of solid precipitation.
Reasoning(R): Agricultural crops and human lives are destroyed by the hailstones.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Hailstones are a form of solid precipitation where small pieces of ice fall downwards. These are destructive and dreaded forms of solid precipitation because they destroy agricultural crops and human lives.
123. Which of this weather phenomenon destroy the plants and human life?
a) Snow
b) Hailstorm
c) Rain
d) Drizzle
Explanation
Any thunderstorm which is associated with fall of hail stones is known as hailstorm. Hailstorm is one of the most feared weather phenomenon because it has the potential to destroy plant, trees, crops, animals and human life.
124. Which is the most predominant form of precipitation?
a) Snow
b) Cyclone
c) Rainfall
d) Ice pellets
Explanation
Rainfall is the most predominant type of Precipitation. Moisture laden air masses raise upwards, forms clouds and bring rainfall.
125. How many types of rainfall are categorized based on the mechanism?
a) 5
b) 3
c) 4
d) 7
Explanation
Based on the mechanisms of raising the air, there are three types of rainfall. Convectional rainfall, Frontal or cyclonic rainfall and Orographic rainfall.
126. Which of this air currents results in the convectional rainfall?
a) Summer Monsoon current
b) Winter Monsoon current
c) Convectional air current
d) Ocean current
Explanation
Earth surface is intensely heated through solar radiation during the day time. When the air near the earth surface is heated, it rises and expands. This heating results is the formation of convectional air currents. Thus the ascending moist air cools, condenses and results in convectional rainfall.
127. Assertion (A): The Convectional rainfall regularly occurs in the equatorial regions.
Reasoning(R): The tropical, sub-tropical and temperate regions experience convectional rainfall in summer months.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Convectional rainfall occurs regularly in the equatorial region in the evenings. It is also experienced in tropical, sub-tropical and temperate regions in the summer months and on warmer days.
128. Where will the cyclonic rainfall occur?
a) Equator
b) Polar region
c) Tropical region
d) Sub-tropical region
Explanation
Cyclonic precipitation occurs during cyclones when air masses are made to converge and move upward so that adiabatic cooling occurs. Cyclonic rainfall occurs in tropical as well as temperate regions.
129. Which of this rainfall occurs on the boundary between warm and cold air masses?
a) Cyclonic rainfall
b) Frontal rainfall
c) Relief rainfall
d) Orographic rainfall
Explanation
When warm and cold air masses converge, condensation and precipitation takes place on the boundary between warm and cold air masses called as Frontal rainfall.
130. Which of these is not true regarding the Orographic rainfall?
a) It is also called as relief rainfall.
b) Mountain barriers force the moisture along the slope.
c) The cooling air form clouds and rain.
d) Air is forced to rise against coastal plains.
Explanation
Orographic rainfall, also called relief rainfall, is caused when air is forced to rise against a high mountain. The mountain barriers lying across the direction of air flow, force the moisture laden air rise along the mountain slope. This results in the cooling of the air, which leads to the formation of clouds and rain. This rainfall is called Orographic rainfall.
131. Assertion (A): The Windward region of the mountain receives heavy rainfall.
Reasoning(R): Rain shadow region is the leeward side of the mountain which receives less rainfall.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The side of the mountain facing the wind is called the windward side and receives heavy rainfall. It is called the rain fed region. The other side of the mountain that does not face the wind is called the leeward side and receives less rainfall becomes rain shadow region.
132. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Humidity affects the weather condition of the atmosphere.
ii) Humidity of the air is high when it has large quantities of water vapor.
iii) The ratio between the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere and it can hold is called relative humidity.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Humidity is an important aspect of the atmosphere because it affects both weather and climate. The amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere is referred to as humidity. Humidity of the atmosphere is high when it has large quantities of water vapor. The amount of water vapor in the atmosphere is called absolute humidity. The ratio between the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere and the amount of water vapor it can hold is relative humidity
133. Assertion (A): Relative humidity decreases when air gets heated and increases if the air gets cold.
Reasoning(R): Cool air can hold more water vapor than hot air.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Hot air can hold more water vapor then cold air. Relative humidity increases when air gets cold and decreases when air gets heated up.
134. Which is known as the wettest place of India?
a) Patna
b) Jaisalmer
c) Mawsynram
d) Shillong
Explanation
Mawsynram is the wettest place of India as it is located in the windward side of the Purvachal hills.
135. Assertion (A): Shillong, Mumbai and Pune are some of the places are the high rainfall areas in India.
Reasoning(R): The places situated in the leeward side receive less rainfall.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Shillong lies on the leeward side and thus receives less rainfall. This is the same, in the case of Mumbai and Pune.
136. Assertion (A): The Relative Humidity is expressed in percentage.
Reasoning(R): The Absolute humidity is expressed in terms of water vapor per cubic meter of air.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Absolute humidity is expressed in terms of grams of water vapor present per cubic meter of air. Relative humidity is expressed in percentage.
137. Which of these conditions are related to the dew point?
a) Relative humidity of air is 100%
b) Saturated air
c) Temperature of saturated air
d) All the above
Explanation
When the relative humidity of the air is 100%, the air is said to be saturated. Saturated air will not absorb any more water vapor. The temperature at which air gets saturated is called dew point.
138. Which of this is used to measure the humidity of the atmosphere?
a) Manometer
b) Hygrometer
c) Altimeter
d) Barometer
Explanation
Humidity of the atmosphere is measured by the wet and dry bulb thermometer also called the Hygrometer.
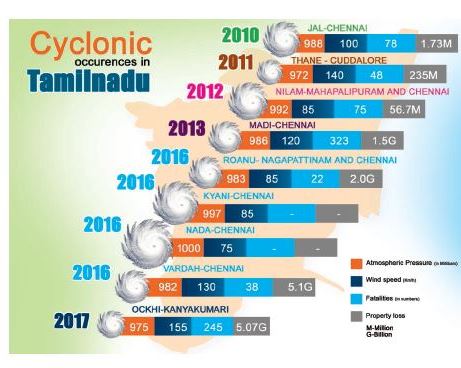
139. Which of the cyclones had a relatively high atmospheric pressure in recent years?
a) Nilam
b) Nada
c) Thane
d) Madi
Explanation
140. Name the recent cyclone formed in the Indian Ocean?
a) Fani
b) Bulbul
c) Vayu
d) Hikaa
Explanation
The Cyclone Fani emerged from the Indian Ocean and caused huge damage in Odisha, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and East India in the year 2020.