Animals In Daily Life Notes 7th Science Lesson 16 Notes in English
7th Science Lesson 16 Notes in English
16] Animals In Daily Life

Introduction:
Animals are closely associated with human beings in their daily life. They are the greatest gift of nature. They are of great economic importance to our nation. Animals contribute many things for our use, as food, clothing and transportation. Let us learn the importance of animals and how to protect and maintain them.
Animal Products used as food:
Milk:
Milk is white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for infant mammals. We use milk in our daily life for the following:
- Milk is the daily essential product which is obtained from animals like cows, buffaloes goats and camels.
- Milk is necessary in our daily diet to prepare tea, coffee, ice creams, chocolates, sweets and other related products.
- Highly recommended nutritive food containing protein and calcium are made from milk like, Paneer, Cheese, Cream, Butter, Ghee and curd.
Curd Ghee
Eggs:
Eggs are laid by female birds of many different species to produce their young ones like hen, duck, turkey and ostrich. We use these in our daily life for the following:
- They are used in our daily diet to get energy and good health.
- It is highly nutritious and rich in protein.
- Eggs have 6 grams of high-quality protein. A protein packed breakfast helps to sustain mental and physical energy throughout the day. Consuming egg daily is good for any age people.
Eggs
Egg omlet
Meat:
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Most often it is used to describe skeletal muscle and fat that is found with it. Some people eat the flesh of animals such as chicken, sheep, rabbit, pig, goat, camel, buffalo (beef), fish, crab, prawn, lobster and many more.
- Animal meat is considered as the part of diet by most of the people.
- Meat consumption is considered essential for its nutritive values. Especially chicken breeding is done in large scale in the form of poultry farming for economic purpose.
Meat Chicken
Poultry Farming:
Poultry farming is the process of raising domesticated birds such as chicken, duck, turkey and geese for the purpose of getting meat and egg for food. Poultries are reared in large numbers and chickens being the most common one. Chickens are broadly of two types.
- Layers (egg laying chickens).
- Broilers (one’s that are reared for meat)
Poultry farming requires safe and sufficient space (wired gages) for the birds. Plenty of water, proper ventilation and regular feed that are rich in proteins, fats and vitamins. Poultry feed is comprised of maize, wheat, millet and rice bran in mashed form and ground nut cakes.
Diseases:
Poultry birds suffer from various diseases caused by some microbes. It is important to keep their shelters clean and get the birds vaccinated against common diseases. Some of the common diseases of poultry birds are the following.
Salmonellosis (diarrhoea) – Caused by bacteria
Ranikhat disease, (Fowl pox) – Caused by virus
Aspergilleses – Caused by fungus
Poultry Farm
Animal products used as clothing:
Animal hair has a great demand. The hair from goat and sheep is used for manufacturing woollen clothes, shawls and blankets, mufflers and socks. Similarly horse hair is used as bristles in small painting brushes. Even fur of animals including the skin is used to make warm and modern style clothes.
Animal Fibres:
Some fabric fibres such as cotton, jute, silk are called natural fibres. Cotton and jute are examples of plant fibres. Wool and silk fibres are examples of animal fibres. Wool is obtained from the fleece of sheep or goat. It is also obtained from the hair of rabbit, yak and camel. Silk fibre is obtained from the cocoon of silkworm.
Wool:
What type of clothes are being used by people of snow capped region?
Why such kind of clothing is preferred by them?
Wool is the fibre derived from the fur of animals of the Caprinae family principally sheep. The hair of other mammals like goat, yak, alpaca and rabbit may also be called wool. Mostly, wool is produced from the outer coat of sheep. The processing of wool involves five major steps. They are as follows Shearing, Grading (or) Sorting, Washing (or) Scouting, Carding and Spinning.
Sheep
Shearing
Washing
Carding
Spinning
Shearing:
The flesh of the sheep is removed from its body. This is called shearing.
Grading (or) Sorting:
The fleece from the same sheep may be different from different parts of the body. It is sorted out into separate piles of similar nature. This is known as Grading (or) Sorting.
Washing (or) Scouting:
The sheared skin is washed thoroughly with soap (or) detergents to remove dirt, dust and grease.
Carding:
The dried wool is carefully removed. These fibres then passed through the rollers which are covered with fine sheet of thin wire teeth. This process arranges the wool into a flat sheet called a web.
Spinning:
The web is drawn into narrow strand and then passed through spinning machines. The spinning machines twist the strands into yarn. The yarn is wound to form balls of wool. This yarn is either weaved into
fabric (or) retained for knitting.
Characteristic features of wool:
- It is resistant to heat, water, wear and tear.
- It absorbs moisture.
- Wool insulates against cold. So wool is a good insulator.
- It does not wrinkle easily.
Uses of wool:
Wool is a multifunctional fibre with a range of diameters that makes it suitable for clothing, household fabrics and technical textiles. Two third of wool is used in the manufacture of garments including sweaters, dresses, coats and active sportswear. Blended with other natural (or) synthetic fibres wool used as adds drape and crease resistance blankets, anti-static and noise absorbing carpets.
Silk:
Have you ever attended marriage functions? What type of dresses the bride and bridegroom wear? What is it made up of?
Silk is the secretions of the silk moth. Silk is obtained from the cocoon of silk worms, which feed on the mulberry leaves. Silk worms live for a very short time, only about two months. During this period they pass through four stages of development. They are eggs, caterpillars, cocoon and adult moth. These stages are called
as life cycle of a silk worm.
The cultivation and production of silk is known as Sericulture. An adult female silk moth lays about 500 eggs. The eggs are then kept in cold storage for six weeks. The eggs are placed in the incubator. After about ten
days, the eggs hatch out and the larvae spend the next 35 days eating mulberry leaves.
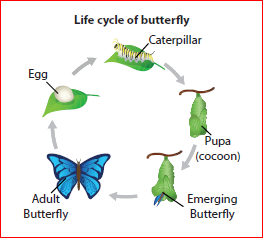

The silk worms spend about five days producing silk and spinning its cocoon of a single long thread. The cocoons are boiled to make it easier to unwind the silk and kill the pupae inside. If the silk moths were allowed to hatch, the long silk fibres will get turned by the hatching of moth. Cocoons are unwind and then the individual silk filament is reeled together to form a thread large enough for weaving. The silk thread is cleaned, dyed, woven into fabric.
Characteristic features of Silk:
- It is very soft , comfortable and versatile
- It can be easily dyed.
- It is the strongest natural fibre.
- It has a poor resistance to sunlight exposure.
Uses of Silk:
Silk has natural beauty and elegance. It gives comfort in warm weather and warmth during colder months. It is used in the manufacture of classical and high fashion clothes, modern dresses particularly silk sarees and the elegant of beautiful dresses. It is also used in household for making wall hangings, curtains, rugs and carpets. It is also being used in the manufacture of surgical threads for sutures.
Hazards in Silk and Wool Industry:
Hazard is any industry has the potential to cause injury, ill health or damage to human being and their property or the environment.
Hazards in Silk Industry:
Generally, the workers in silk industry affected with arthritis is they stand for a long time reeling the silk into yarn. They also develop back pain and visionary problem and skin injuries. Some time they may suffer from respiratory problem like asthma and bronchitis due to poor ventilated area of their work.
Similarly, hazards in wool industry the workers are exposed to various chemicals and detergents which causes allergies of the skin. They also get infected to anthrax bacterium which leads to fatal dead disease called the sorters disease.
Anthrax is caused by Bacillus anthracis by handling contaminated animal hair and contact with the live stock during hair processing. The symptoms are fever, cough and shortness of breath, similar to a typical pneumonia. Sometimes it may leads to nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea.
Treatment:
- Pencillin or Ciprofloxacin is given as the best medicine for treatment of anthrax.
- The spread of the disease is controlled by vaccination of animals and by burning or burial of infected animal’s carcases.
- It is the duty of the employer to take care of the industrial workers by providing hygienic and well ventilated work place.
Sericulture and Ahimsa silk ( Peace silk):
Sericulture or silk farming is the cultivation of silk worm to produce silk. It is the rearing of silk worms to obtain silk.
Ahimsa silk:
It is also known as Peace silk. In 1992, Kusuma Rajaiah, a Government officer from Andhra Pradesh state of India proposed ahimsa way of silk production for the making silks without killing the silkworm. It involves a humane method specifically letting the worms to hatch and then using the vacant cocoons.
Traditional silk manufacturing methods involve boiling the cocoons of the silk worms and then sorting out the threads, which is used later in silk production. It has been supported by many people who are interested in the welfare of animals.
Animal protection and maintenance:
Protecting animals is like protecting our own children or parent. They are living things similar to human beings. As elite, most intelligent and responsible human being on the planet, it is our duty to protect all the living organisms on earth. The human tendency and conscience towards the animals should be considerate to protect and safe guard the animals, hence as human it becomes a great responsibility and obligatory to protect the animals.
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change has released four New Gazette Notifications under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act 1960 to regulate dog breeders, animal marketers, aquarium and pet fish owners. This progress has come about as a joint effort by animal protection groups. With the protection of animals we actually protect ourselves and protect the environment. So we have to love and protect the animals and treat them as our family members.
Do you know?
Where from honey comes, or how it is produced? Have you seen a beehive where many bees are seen buzzing about? Bees collect nectar (sweet juices) from flowers, convert it into honey and store in their honey comb.
- Honey is a sweet liquid produced by honey bees from the nectar of flowers. It is extracted from beehives by us.
- Raw organic wild honey is extracted from selected hives by tribal honey hunters, who collect it from jungles.
- Honey has more medicinal values and highly nutritious food.
Beehive
Honey oozing out
The worker bees collect the nectar from the flowers. They nourish the young ones and repair the bee hive and also protect it.
India is the world’s second largest silk producing country. Kancheepuram, Thirubhuvanam and Arani are famous places for silk production in Tamil Nadu.
Study of breeding of animals and their maintenance is called Animal Husbandary.