9th Std Science Lesson Wise Questions in English – Part 1
9th Science Lesson 2 Questions in English
2] Motion
1. Choose the correct statements.
i) The change in position of an object is defined as Motion.
ii) Immovable objects are also moving due to the rotation of Earth.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Motion is the change in the position of an object with respect to its surrounding. Everything in the universe is in motion. Even though an object seems to be not moving, actually it is moving because the Earth is moving around the Sun.
2. Which of these values are not used to describe motion?
a) Acceleration
b) Time
c) Mass
d) Speed
Explanation
Motion is described in terms of distance, speed, acceleration and time.
3. In which of this position the object has a zero velocity?
a) Rest
b) Motion
c) Swing
d) Linear
Explanation
In physics the objects which do not change their position are said to be at rest, while those which change their position are said to be in motion.
4. Assertion (A): Motion is a relative phenomenon with respect to the viewer.
Reasoning(R): Trees would appear to move backwards for a person travelling in the train.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True and R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Motion is a relative phenomenon. This means that an object appearing to be in motion to one person can appear to be at rest as viewed by another person. For example, trees on road side would appear to move backward for a person travelling in a car while the same tree would appear to be at rest for a person standing on the road side.
5. Identify the Incorrect Match
A. Oscillatory Motion i) Single to and fro movement
B. Linear Motion ii) Along a straight line
C. Circular Motion iii) Along a circular path
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
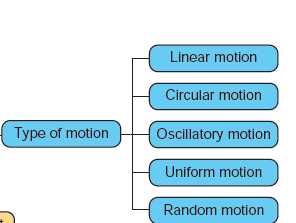
Linear motion: Motion along a straight line.
Circular motion: Motion along a circular path.
Oscillatory motion: Repetitive to and fro motion of an object at regular interval of time.
6. Which of this motion is depicted in bird fly?
a) Oscillatory Motion
b) Random Motion
c) Linear Motion
d) Circular Motion
Explanation
Random motion: Motion of the object which does not fall in any of the categories is called as random motion. It is a type of motion that is unpredictable. In this type of motion the object moves in any direction, and the direction continually changes.
7. What is the type of motion for a flight covering a distance of 300km every one hour?
a) Uniform Motion
b) Accelerated Motion
c) Non-Uniform Motion
d) Non- Linear Motion
Explanation
Consider a car which covers 60 km in the first hour, 60 km in the second hour, and another 60 km in the third hour and so on. The car covers equal distance at equal interval of time. We can say that the motion of the car is uniform.
8. Assertion (A): Uniform Motion of an object is defined as covering equal distance in equal interval of time.
Reasoning(R): The Time interval for a uniform motion must be equal to the distance covered.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True and R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
An object is said to be in uniform motion if it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time howsoever big or small these time intervals may be.
9. Which of this example denotes a Non-uniform motion?
a) Movement of fan
b) An object thrown into air
c) Earth moving round the sun
d) A vibrating spring in a sewing machine
Explanation
Non-uniform motion: Now, consider a bus starting from one stop. It proceeds slowly when it passes through crowded area of the road. Suppose, it manages to travel merely 100 m in 5 minutes due to heavy traffic and is able to travel about 2 km in 5 minutes when the road is clear. Hence, the motion of the bus is non-uniform i.e. it travels unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
10. Define a non-uniform motion?
a) Equal distances in equal intervals of time
b) Unequal distances in equal intervals of time
c) Equal distances in unequal intervals of time
d) Unequal distances in unequal intervals of time
Explanation
An object is said to be in non-uniform motion if it covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
11. What is the length of the line AB in the given picture?
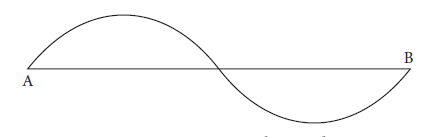
a) Displacement
b) Speed
c) Acceleration
d) Velocity
Explanation
An object moving from the point A moves along the path given in the Figure and reaches the point B. The total length of the path travelled by the body from A to B is called distance travelled by the body. The length of the straight line AB is called displacement of the body.
12. Which of these denotes the total length of the path travelled by an object?
a) Force
b) Momentum
c) Distance
d) Velocity
Explanation
An object moving from one point moves along the path given and reaches another point. The total length of the path travelled by the body from start to end point is called distance travelled by the object.
13. Choose the correct statements regarding Distance.
i) The actual length of the path travelled by moving body.
ii) The measurement is meter in the SI system.
iii) It is a scalar quantity.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Distance: The actual length of the path travelled by a moving body irrespective of the direction is called the distance travelled by the body. It is measured in meter in SI system. It is a scalar quantity having magnitude only.
14. Assertion (A): The change in position of a moving body in a particular direction is defined as Displacement.
Reasoning (R): The Displacement is a vector quantity measured in terms of meter in SI system.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True and R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Displacement: It is defined as the change in position of a moving body in a particular direction. It is a vector quantity having both magnitude and direction. It is also measured in meter in SI system.
15. Choose the correct statements.
a) Speed shows how fast an object is moving.
b) Velocity is measured in meter.
c) Speed is a vector quantity.
d) Velocity measures the direction of a moving object.
Explanation
Speed is the quantity which shows how fast the body is moving but velocity is the quantity which shows the speed as well as the direction of the moving body.
16. Which of these quantity measures the rate of change of distance travelled by an object in unit time?
a) Displacement
b) Acceleration
c) Speed
d)Velocity
Explanation
Speed is the rate of change of distance or the distance travelled in unit time.
17. How long would it take to travel a distance of 70 miles if a person is travelling at 30 miles per hour?
a) 2 hours 20 minutes
b) 2 hours 20 seconds
c) 1 hour 50 minutes
d) 1 hour 20 minutes
Explanation
Speed = Distance travelled / Time taken
Distance is 70 miles, Speed is 30mph
Time = 70/30
Time = 70/30 = 2.33
2.33 x 60 = 140 minutes = 2 hours and 20 minutes
18. What is the SI unit of speed?
a) ms1
b) ms-1
c) ms-2
d) ms2
Explanation
Speed is a scalar quantity. The SI unit of speed is ms-1.
19. What is the average speed of an object moving 50 m in 30 s, 30 m in next 20 s and 20 m in another 15 s?
a) 1.54 ms-1
b) 15.4 ms1
c) 1.54 ms-2
d) 154 ms-1
Explanation
Total distance travelled by the object = 50 m + 30 m + 20 m = 100 m
Total time taken = 30s + 20s + 15s = 65 s
Average speed = Total distance travelled / Total time taken
s = 1.54 ms-1
Therefore, the average speed of the object is 1.54ms-1
20. Which of this graph denotes the Uniform accelerated motion of an object?
a) 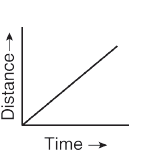
b) 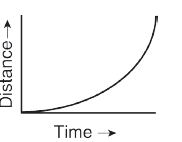
c) 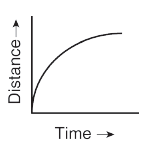
d) 
Explanation
For an accelerated motion, the distance-time graph is not a straight line. For a uniform acceleration, the graph is a parabola. The figure b) shows the graph for a uniformly accelerated motion. For non-uniform acceleration, the graph has irregular shape.
21. Choose the correct statements regarding Velocity.
i) Velocity is the rate of change of displacement.
ii) It is a scalar quantity.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement. It is the displacement in unit time. It is a vector quantity.
22. Which of these quantities have a SI unit of ms-1?
a) Velocity
b) Acceleration
c) Displacement
d) Speed
Explanation
The SI unit of velocity is ms-1.
23. What is the formula to calculate the velocity of an object in a particular direction?
a) Speed / Time
b) Distance / Direction
c) Displacement / Time
d) Speed / Displacement
Explanation
Velocity = Displacement / Time taken
24. Which of these are not true regarding the concept of Acceleration?
a) Rate of change of speed
b) Rate of change of velocity
c) Vector quantity
d) SI unit is ms-2
Explanation
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity or it is the change of velocity in unit time. It is a vector quantity. The SI unit of acceleration is ms-2.
25. Define acceleration in terms of velocity and time.
a) Change in velocity * Time
b) Time / Final velocity
c) Change in velocity / Time
d) Final velocity – Initial velocity
Explanation
Acceleration = Change in velocity/Time = (Final velocity – Initial velocity)/Time
a = (v–u)/t
26. The value of acceleration is positive for a moving object if,
i) Moving object reverses its direction with time.
ii) Initial velocity is greater than Final velocity.
iii) Velocity value increases with time.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Consider a situation in which a body moves in a straight line without reversing its direction. From the above equation if v > u, i.e. if final velocity is greater than initial velocity, the velocity increases with time and the value of acceleration is positive.
27. State the condition for the negative acceleration for a moving object?
a) Initial velocity is less than final velocity.
b) Final velocity is less than initial velocity.
c) Both velocities are negative.
d) None of the above
Explanation
If v < u, i.e. if final velocity is less than initial velocity, the velocity decreases with time and the value of acceleration is negative. It is called negative acceleration.
28. What are the other names of negative acceleration?
a) Retardation
b) Deceleration
c) Acceleration
d) Both a and b
Explanation
Negative acceleration is called retardation or deceleration. If the acceleration has a value of –2 ms2, we say that tdeceleration is 2 ms-2.
29. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the Uniform motion distance-time graph.
i) It is a straight line graph.
ii) Velocity is obtained from the slope of the line.
iii) Steeper the slope speed is increased.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
In the distance – time graph for a Uniform motion it is a straight line. It shows that the speed is constant. The parameter speed is referred as the slope of the line. Speed = Distance covered / Time taken = Slope of the straight line = BC/AC. Steeper the slope (in other words the larger value) the greater is the speed.
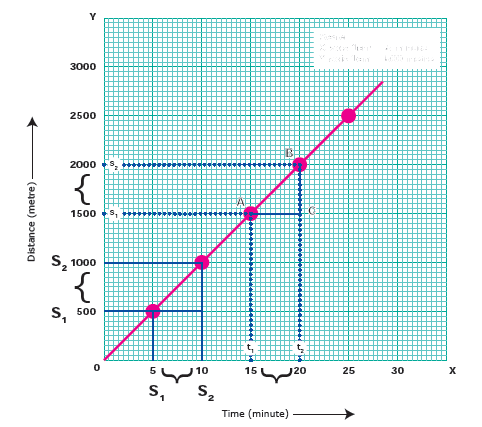
30. Which of this quantity is changed by the change in the slope of the line for a uniform motion in the Distance- Time graph?
a) Velocity
b) Acceleration
c) Speed
d) None of the above
Explanation
The slope of the line on the distance – time graph becomes steeper and steeper as the speed increases.
31. The distance and time varies ____ for a non-uniform motion.
a) Linearly
b) Elliptically
c) Non-Linear
d) Tangentially
Explanation
This Distance-time graph shows non–linear variation of the distance travelled by the object with time. Thus, the graph represents motion with non-uniform speed for a Non-uniform motion.
32. In which of these conditions the velocity-time graph will have a straight line?
a) Increased speed
b) Uniform velocity
c) Uniform Motion
d) Steeper slope
Explanation
The variation in velocity of an object with time can be represented by velocity – time graph. In the graph, time is represented along the X – axis and the velocity is represented along the Y – axis. If the object moves at uniform velocity, a straight line parallel to X-axis is obtained.
33. Which of this quantity is inferred by the shaded portion of the velocity- time graph?
a) Velocity variation
b) Acceleration
c) Speed
d) Displacement
Explanation
The area under the velocity – time graph is equal to the magnitude of the displacement. So, the distance (displacement), S covered by the object in a time interval of t can be expressed as,
S = AC × CD
S = Area of the rectangle ABCD (shaded portion in the graph)
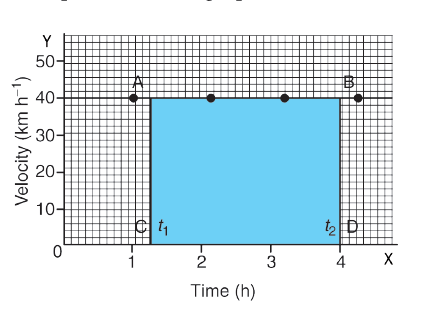
34. A velocity-time graph of an object shows,
i) Changes in velocity in equal interval of time.
ii) Displacement or the distance covered by an object.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The nature of the graph shows that the velocity changes by equal amounts in equal intervals of time. Thus, for all uniformly accelerated motion, the velocity – time graph is a straight line.
35. Which of these quantity changes the velocity in the velocity- time graph?
a) Acceleration
b) Speed
c) Distance
d) All the above
Explanation
The magnitude of the velocity of the object is changing due to acceleration. The distance, S travelled by the object will be given by the area under the velocity – time graph.
36. Which of these motion is described from the below velocity- time graph?
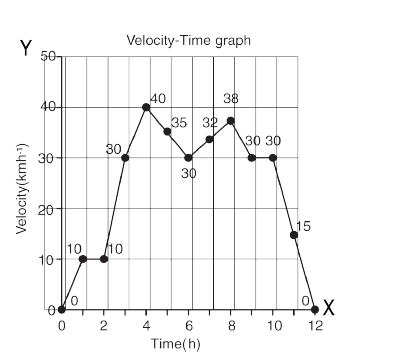
a) Uniform motion
b) Non-uniform motion
c) Circular motion
d) Non- circular motion
Explanation
In the case of non-uniformly accelerated motion, distance – time graph and velocity – time graphs can have any shape.
37. Which of this value is measured by a speedometer in an automobile?
a) Maximum Speed
b) Instantaneous Speed
c) Acceleration
d) Minimum Speed
Explanation
The speedometer of an automobile measures the instantaneous speed of the automobile.
38. Choose the correct statements.
i) The average velocity is equal to the instantaneous velocity for a uniformly moving object.
ii) Instantaneous velocity is also called as instantaneous speed or velocity.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
In a uniform motion in one dimension, the average velocity is equal to instantaneous velocity. Instantaneous velocity is also called velocity or instantaneous speed or simply speed.
39. Which of these quantities are discussed by Newton’s equation for moving objects?
a) Velocity
b) Acceleration
c) Time
d) All the above
Explanation
Newton studied the motion of an object and gave a set of three equations. These equations relate displacement, velocity, acceleration and time of an object under motion.
40. Which of this equation does not related to Newton’s study?
a) v = u + at
b) v – u = at2
c) s = u t + ½ a t2
d) v2 = u2 + 2 as
Explanation
An object in motion with initial velocity, u attains a final velocity, v in time, t due to acceleration a and reaches a distance s. Three equations can be written for this motion.
v = u + at
s = ut + ½ a t2
v2 = u2 + 2as
41. Which of these quantities are related by the first equation of motion?
a) Initial velocity, Final velocity, Time
b) Time, Acceleration, Distance
c) Displacement, Speed, Time
d) Initial velocity, Final velocity, Acceleration, Time
Explanation
First equation of motion: By definition, Acceleration = Change in velocity / Time = (Final velocity – Initial velocity)/Time
v = u + at This is the first equation of motion.
42. A Trolley slides down an inclined plane at an acceleration of 2 m s-2 after 3s find the velocity of the trolley?
a) 4 m/ s2
b) 6 m / s
c) 60 m / s2
d) 0. 6 m / s
Explanation
Initially trolley at rest position so u = 0, Given a = 2 m /s2 and t = 3s
From Newton’s first law of motion v = u + at
v = 6 m/ s
43. Which of this quantity is derived from the Newton’s second equation of motion?
a) Speed
b) Distance
c) Average velocity
d) Maximum Acceleration
Explanation
Second equation of motion s = u t + ½ at2
44. State the newton’s third equation motion.
a) v2 + u2 = 2 as
b) v = g t
c) v2 = u2 + 2 as
d) u + v = as
Explanation
The distance covered by the object during time, t is given by the area of the trapezium.
Then, s = Area of trapezium
= ½ × Sum of length of parallel side × Distance between parallel sides
s = ½ × (u + v) × t
Since, a= (v – u) / t or t = (v – u)/a
s = ½ × (v + u) × (v – u)/a
2as = v2 – u 2
v2 = u2 + 2 as
45. Which of this value is replaced by the gravity value g for a free falling body?
a) u
b) a
c) v
d) h
Explanation
The equation of motion for a freely falling body can be obtained by replacing ‘a’ in equations with g, the acceleration due to gravity. For a freely falling body which is initially at rest, u = 0. Thus we get the following equations. v = gt, s = ½ gt2, v2 = 2gh
46. If an object thrown vertically upwards in space,
a) The highest point has zero velocity.
b) Max velocity at the lowest point
c) Minimum acceleration due to gravity.
d) Maximum velocity at highest point.
Explanation
When a body is thrown vertically upwards in space, at the highest point, the body has zero velocity but it has acceleration due to the gravity.
47. What is the value of acceleration when the object falls from space towards earth?
a) a = 0
b) a = -g
c) a = +g
d) a = ∞
Explanation
When we throw an object vertically upwards, it moves against the acceleration due to gravity. Hence, ‘a’ is taken to be –g and when moving downwards ‘a’ is taken as +g.
48. Which is not a characteristic of a Uniform Circular motion?
a) Objects move in a circular path
b) Velocity and direction of movement are equal.
c) Variation in speed.
d) No tangential acceleration
Explanation
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion. The velocity vector is tangent to the trajectory at each point and its direction is the same as the direction of the motion. This means that the motion has normal acceleration. In non-uniform circular motion an object is moving in a circular path with a varying speed. Since the speed is changing, there is tangential acceleration in addition to normal acceleration.
49. What changes the velocity of an object in a circular path of accelerated motion?
a) Constant motion
b) Change in speed
c) Change in direction
d) Constant speed
Explanation
When an object is moving with a constant speed along a circular path, the velocity changes due to the change in direction. Hence, it is an accelerated motion.
50. Which of these are not examples of accelerated motion?
a) Revolution of the earth around sun
b) Rotation of earth on its own axis
c) Second hand movement of a clock
d) Revolution of moon around the earth
Explanation
For example, revolution of earth around the sun, revolution of moon around the earth and the tip of the second’s hand of a clock are all accelerated motions.
51. What is the value of speed of an object with circular path radius r and time T?
a) (2 * r) / T
b) π * r * T
c) (2 * π* r ) / T
d) T / (2 * π * r)
Explanation
If an object, moving along a circular path of radius, r takes time, T to come back to its starting position then the speed V is given by, Speed = Circumference/Time taken; V = 2 π r/T
52. Assertion (A): Motion of an object with constant speed and continuous change of direction in circular path is an accelerated motion.
Reasoning(R): An object is accelerated if the velocity changes in magnitude and direction.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True and R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
A body is said to be accelerated, if the velocity of the body changes either in magnitude or in direction. So, the motion of a stone in circular path with constant speed and continuous change of direction is an accelerated motion.
53. Choose the correct statements.
i) The acceleration acting along the string of an object moving in a circular path is Centripetal Acceleration.
ii) The centripetal acceleration is directed towards the center of the circular path.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
In the case of an object tied to string moving in a circular path with const speed and continuous change of direction there must be an acceleration acting along the string directed inwards, which makes the stone to move in circular path. This acceleration is known as centripetal acceleration and the force is known as centripetal force. Since the centripetal acceleration is directed radially towards the center of the circle the centripetal force must act on the object radially towards the center.
54. Find the velocity of an object along a circular path of radius r and centripetal acceleration a?
a) v= 2a / r
b) v= ar / 2
c) v = 4r / 2
d) v = ar * 2
Explanation
Let us consider an object of mass m, moving along a circular path of radius r, with a velocity, v. Its centripetal acceleration is given by a = v2 /r
55. What is the magnitude value of the Centripetal force?
a) m v / 2 r
b) m v 2 / r
c) 2 mv / r
d) r m / 2 v
Explanation
The magnitude of centripetal force is given by, F = Mass × Centripetal acceleration
F = mv 2 / r
56. Find the mass of an object with acceleration 5ms-2 and the net force acting is 250N.
a) 50
b) 10
c) 0.5
d) 500
Explanation
Net force acting upon an object, F = m a ; m = F / a ; m = 250 / 5 = 50
57. Which of these forces could not act as a centripetal force?
a) Gravitational Force
b) Frictional Force
c) Electrostatic Force
d) Centrifugal Force
Explanation
Any force like gravitational force, frictional force, magnetic force, electrostatic force may act as a centripetal force.
58. Assertion (A): Force acting away from the center of the circular path is called as Centrifugal force.
Reasoning(R): The direction of centrifugal and centripetal force is always same.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True and R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
A pulling force that acts away from the center is called as centrifugal force. Force acting on a body away from the center of circular path is called centrifugal force. Thus, centrifugal force acts in a direction which is opposite to the direction of centripetal force.
59. Which of this force is applied in the dryer mechanism of a washing machine?
a) Centrifugal Force
b) Gravitational Force
c) Centripetal Force
d) Frictional Force
Explanation
Its magnitude is same as that of centripetal force. The dryer in a washing machine is an example for the application of centrifugal force.
60. Which of these is not classified as a motion type?
a) Circular
b) Trapezoidal
c) Oscillatory
d) Random
Explanation
9th Science Lesson 3 Questions in English
3] Fluids
1. A small iron nail sinks in water, whereas a huge ship of heavy mass floats on sea water. Astronauts have to wear a special suit while traveling in space. All these have a common reason called _____
- Density
- Pressure
- Friction
- Heat
Explanation
A small iron nail sinks in water, whereas a huge ship of heavy mass floats on sea water. Astronauts have to wear a special suit while traveling in space. All these have a common reason called ‘pressure’.
2. Which among the following statement is correct
- If the pressure increases in a liquid, based on its inherent properties, it experiences tension and ultimately deforms or breaks. In the case of gases, it causes them to flow rather than to deform.
- Although liquids and gases share some common characteristics, they have many distinctive characteristics on their own. It is easy to compress a gas whereas liquids are incompressible. Learning of all these facts helps us to understand pressure better.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
If the pressure increases in a solid, based on its inherent properties, it experiences tension and ultimately deforms or breaks. In the case of fluids, it causes them to flow rather than to deform.
3. Which among the following statement is correct
- When you stand on loose sand, the force is acting on an area equal to the area of your feet. When you lie down, the same force acts on an area of your whole body, which is larger than the area of your feet. Thus, the force acting parallel to the surface is called thrust.
- Therefore, the effect of thrust, depends on the area on which it acts. The effect of thrust on sand is larger while standing than while lying.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
When you stand on loose sand, the force is acting on an area equal to the area of your feet. When you lie down, the same force acts on an area of your whole body, which is larger than the area of your feet. Thus, the force acting perpendicular to the surface is called thrust.
4. Which among the following equation defines pressure
- Areas of contact / Thrust
- Area of contact / Weight of Particle
- Thrust / Area of contact
- Friction / Area of contact
Explanation
The force per unit area acting on an object concerned is called pressure. Thus, we can say thrust on a unit area is pressure. Pressure = Thrust / Area of contact.
5. In SI units, the unit of thrust is ____
- Newton
- Pascal
- Watt
- Joule
Explanation
In SI units, the unit of thrust is newton (denoted as N).
6. Which among the following is the unit of Pressure?
- N-2m-1
- Nm-1
- N-2m
- Nm-2
Explanation
The unit of pressure is newton per square metre or newton metre–2 (denoted as Nm-2).
7. In the honour of the great French scientist, 1 Nm-2 = what?
- 1 Nm-2 = 1 W
- 1 Nm-2 = 1 pa
- 1 Nm-2 = 1 Joule
- 1 Nm-2 = 1 Farad
Explanation
In the honour of the great French scientist, Blaise Pascal, 1 newton per square metre is called as 1 pascal denoted as Pa. 1 Pa = 1 N m-2.
8. Which among the following is called as fluids?
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gases
- Both liquid and gases
Explanation
All the flowing substances, both liquids and gases are called fluids. Like solids, fluids also have weight and therefore exert pressure. When filled in a container, the pressure of the fluid is exerted in all directions and at all points of the fluid. Since the molecules of a fluid are in constant, rapid motion, particles are likely to move equally in any direction.
9. Which among the following equation calculate pressure in fluid?
- F/A
- Pa/A
- N/A
- A/Pa
Explanation
Pressure in fluids is calculated as shown below. Fluid Pressure = Total force exerted by the fluid / Area over which the force is exerted = F / A.
10. The force exerted due to the pressure of a liquid on a body submerged in it and on the walls of the container is always what to the surface?
- Parallel
- Semi parallel
- Perpendicular
- Both parallel and perpendicular
Explanation
The force exerted due to the pressure of a liquid on a body submerged in it and on the walls of the container is always perpendicular to the surface.
11. Pressure exerted by a liquid at a point is determined by what?
- Depth
- Density of the liquid
- Acceleration due to gravity
- All the above
Explanation
Pressure exerted by a liquid at a point is determined by, (i) depth (h) (ii) density of the liquid (ρ) (iii) acceleration due to gravity (g).
12. A man whose mass is 90 kg stands on his feet on a floor. The total area of contact of his two feet with the floor is 0.036 m2 (Take, g = 10 ms-2). How much is the pressure exerted by him on the floor?
- 15000 N
- 15000 Pa
- 25000 N
- 25000 Pa
Explanation
The weight of the man (thrust),
F = mg = 90Kg * 10ms-2 = 900 N
Pressure, p = F/A = 900N / 0.036 m2 = 25000 Pa
13. A tall beaker is filled with liquid so that it forms a liquid column. The area of cross section at the bottom is A. The density of the liquid is ρ. The height of the liquid column is h. In other words, the depth of the water from the top-level surface is ‘h. what is pressure due to liquid column?
- P = hρAg
- P = hρg
- P = hA / ρg
- P = 1 / hρg
Explanation
We know that, thrust at the bottom of the column (F) = weight of the liquid.
Therefore, F = mg (1)
We can get the mass of the liquid by multiplying the volume of the liquid and its density. Mass, m = ρV (2)
Volume of the liquid column, V = Area of cross section (A) × Height (h) = Ah (3)
Substituting (3) in (2)
Mass, m = ρAh (4)
Substituting (4) in (1)
Force = mg = ρAhg
Pressure, P = Thrust (F) / Area (A) = mg / A = ρ(Ah)g / A = ρhg
∴ Pressure due to a liquid column, P = hρg.
14. Earth is surrounded by a layer of air up to certain height (nearly 300 km) and this layer of air around the earth is called ____
- Crust
- Galaxy
- Atmosphere
- Debris
Explanation
Earth is surrounded by a layer of air up to certain height (nearly 300 km) and this layer of air around the earth is called atmosphere of the earth. Since air occupies space and has weight, it also exerts pressure. This pressure is called atmospheric pressure.
15. Which among the following statement is true
- Air gets thinner with decrease in altitude
- Air gets heavier as we go above the sea level
- Air gets thinner with increase in altitude
- All the above
Explanation
The air gets ‘thinner’ with increasing altitude. Hence, the atmospheric pressure decreases as we go up in mountains. On the other hand, air gets heavier as we go down below sea level like mines.
16. The atmospheric pressure we normally refer is _____
- The air pressure at stratospheric level
- The air pressure at ground level
- The air pressure at sea level
- The air pressure at mountain level
Explanation
The atmospheric pressure we normally refer is the air pressure at sea level.
17. What is the pressure of sea level at which human lung is adapted to breath?
- 93.7 K Pa
- 101.3 K Pa
- 104.8K Pa
- 98.2K Pa
Explanation
Human lung is well adapted to breathe at a pressure of sea level (101.3 k Pa). As the pressure falls at greater altitudes, mountain climbers need special breathing equipments with oxygen cylinders. Similar special equipment’s are used by people who work in mines where the pressure is greater than that of sea level.
18. The instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure is called ____
- Anemometer
- Tachometer
- Galvanometer
- Barometer
Explanation
The instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure is called barometer.
19. A mercury barometer, first designed by which Italian physicist?
- Pascal
- Galileo
- Enrico Fermi
- Torricelli
Explanation
A mercury barometer, first designed by an Italian Physicist Torricelli, consists of a long glass tube (closed at one end, open at the other) filled with mercury and turned upside down into a container of mercury. This is done by closing the open end of the mercury filled tube with the thumb and then opening it after immersing it in to a trough of mercury.
20. Which among the following statement is correct
- The barometer works by balancing the mercury in the glass tube against the outside air pressure. If the air pressure increases, it pushes more of the mercury up into the tub and if the air pressure decreases, more of the mercury drains from the tube.
- As there is no air trapped in the space between mercury and the closed end, there is vacuum in that space. Vacuum cannot exert any pressure. So, the level of mercury in the tube provides a precise measure of air pressure which is called atmospheric pressure. This type of instrument can be used in a lab or weather station.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
21. On a typical day at sea level, the height of the mercury column is ____
- 720 mm
- 760 mm
- 780 mm
- 820 mm
Explanation
On a typical day at sea level, the height of the mercury column is 760 mm.
22. Let us calculate the pressure due to the mercury column of 760 mm which is equal to the atmospheric pressure. The density of mercury is 13600 kg m-3?
- P = 2.134 × 105 Pa
- P = 1.013 × 105 Pa
- P = 0.714 × 105 Pa
- P = 3.182 × 105 Pa
Explanation
Pressure, P = hρg
= (760 3 10–3m) 3 (13600 kgm-3) 3 (9.8 ms-2)
= 1.013 × 105 Pa.
23. What is the other unit of one atmospheric pressure?
- Joule
- Watt
- Bar
- Farad
Explanation
Pressure P = 1.013 × 105 Pa is called one atmospheric pressure (atm). There is also another unit called (bar) that is also used to express such high values of pressure.
1 atm = 1.013 × 105 Pa.
1 bar = 1 × 105 Pa.
Hence, 1 atm = 1.013 bar.
Expressing the value in kilopascal gives 101.3 k Pa. This means that, on each 1 m2 of surface, the force acting is 1.013 k N.
24. Calculate the pressure exerted by a column of water of height 0.85 m (density of water, ρw = 1000 kg m-3) and kerosene of same height (density of kerosene, ρk = 800 kg m-3)
- Pressure due to water = 8500 Pa and pressure due to kerosene = 6800 Pa
- Pressure due to water = 7200 Pa and pressure due to kerosene = 6800 Pa
- Pressure due to water = 8500 Pa and pressure due to kerosene = 5600 Pa
- Pressure due to water = 7200 Pa and pressure due to kerosene = 5600 Pa
Explanation
Pressure due to water = hρwg
= 0.85 m × 1000 kg m-3 × 10 m s-2 = 8500 Pa.
Pressure due to kerosene = hρkg
= 0.85 m × 800 kg m-3 × 10 ms-2 = 6800 Pa.
25. For pressures higher than atmospheric pressure, absolute pressure = ?
- Atmospheric pressure – Gauge pressure
- Gauge pressure – Atmospheric pressure
- Atmospheric Pressure + Gauge Pressure
- Gauge pressure / Atmospheric pressure
Explanation
The absolute pressure is zero-referenced against a perfect vacuum and gauge pressure is zero referenced against atmospheric pressure.
For pressures higher than atmospheric pressure, absolute pressure = atmospheric pressure + gauge pressure
For pressures lower than atmospheric pressure, absolute pressure = atmospheric pressure – gauge pressure.
26. In petrol bunks, the tyre pressure of vehicles is measured in a unit called ____
- Pa
- Psi
- Pv
- Pnm
Explanation
In petrol bunks, the tyre pressure of vehicles is measured in a unit called psi. It stands for pascal per inch, an old system of unit for measuring pressure.
27. which among the following Law is the basis for the Hydraulic pressure?
- Pascal’s Law
- Hooke’s Law
- Graham’s Law
- Kepler’s Law
Explanation
Pascal’s law became the basis for one of the important machines ever developed, the hydraulic press. It consists of two cylinders of different cross-sectional areas.
28. Pascal’s law states that the external pressure applied on an incompressible liquid is transmitted how?
- Transmitted perpendicular to the liquid surface
- Transmitted parallel to the liquid surface
- Transmitted along the edges of liquid
- Transmitted equally throughout the liquid
Explanation
Pascal’s principle is named after Blaise Pascal (1623-1662), a French mathematician and physicist. The law states that the external pressure applied on an incompressible liquid is transmitted uniformly throughout the liquid. Pascal’s law can be demonstrated with the help of a glass vessel having holes all over its surface. Fill it with water. Push the piston. The water rushes out of the holes in the vessel with the same pressure.
29. In Hydraulic press, the force F2 that acts on the larger piston is greater than the force F1 acting on the smaller piston. Hydraulic systems working in this way are known as ____
- Flow force
- Force dynamic
- Force multipliers
- Force extensions
Explanation
The force F2 that acts on the larger piston is greater than the force F1 acting on the smaller piston. Hydraulic systems working in this way are known as force multipliers.
Pressure on piston of small area ‘a’ is given by, P = F1 / A1 (1)
Applying Pascal’s law, the pressure on large piston of area A will be the same as that on small piston. Therefore, P = F2 / A2 (2)
Comparing equations (1) and (2), we get F1 / A1 = F2 / A2. or F2 = F1 × (A2 / A1).
Since, the ratio A2 / A1 is greater than 1, the force F2 that acts on the larger piston is greater than the force F1.
30. A hydraulic system is used to lift a 2000 kg vehicle in an auto garage. If the vehicle sits on a piston of area 0.5 m2, and a force is applied to a piston of area 0.03 m2, what is the minimum force that must be applied to lift the vehicle?
- F2 = 1038 N
- F2 = 1176 N
- F2 = 1236 N
- F2 = 1383 N
Explanation
Given: Area covered by the vehicle on the piston A1 = 0.5 m2
Weight of the vehicle, F1 = 2000 kg × 9.8 m s-2
Area on which force F2 is applied, A2 = 0.03 m2
Solution:
P1 = P2 ; F1 / A1 = F2 /A2 and F2 = (F1 / A1) × A2 ;
F2 = (2000 × 9.8) 0.03 0.5 = 1176 N
31. Which among the following is the mass per unit volume of a given substance?
- The surface tension of a substance
- The force of a substance
- The Temperature of a substance
- The density of a substance
Explanation
Let us assume that the mass of the flask be 80 g. So, the mass of the flask filled with water is 330 g and the mass of flask filled with kerosene is 280 g. Mass of water only is 250 g and kerosene only is 200 g. Mass per unit volume of water is 250/250 cm3. This is 1g/cm3. Mass per unit volume of kerosene is 200 g/250 cm3. This is 0.8 g/cm3. The result 1 g/cm3 and 0.8 gcm3 are the densities of water and kerosene respectively. Therefore, the density of a substance is the mass per unit volume of a given substance.
32. The SI unit of density is ____
- N / m2
- Kgm3
- Kg / m3
- Nm2
Explanation
The SI unit of density is kilogram per meter cubic (kg/m3) also gram per centimetre cubic (g/cm3).
33. The symbol for density is ____
- ρ
- J
- w
- c
Explanation
The symbol for density is rho (ρ).
34. At what temperature density of the water is 1g/cm3?
- 20 C
- 40 C
- 80 C
- 100 C
Explanation
We can compare the densities of two substances by finding their masses. But, generally density of a substance is compared with the density of water at 4 °C because density of water at that temperature is 1g/cm3.
35. Density of any other substance with respect to the density of water at 4 °C is called ____
- Absolute density
- Co-Operative density
- Relative density
- All the above
Explanation
Density of any other substance with respect to the density of water at 4 °C is called the relative density. Thus, relative density of a substance is defined as ratio of density of the substance to density of water at 4 °C.
Mathematically, relative density (R.D), = Density of the substance / Density of water at 4 °C.
36. Which among the following equation defines Density?
- Mass / Volume
- Volume / Mass
- Mass / Temperature
- Temperature / Mass
Explanation
Density = Mass / Volume
∴ Relative density = (Mass of the substance/Volume of the substance) \ (Mass of water/Volume of water)
Since the volume of the substance is equal to the volume of water,
Relative density = Mass of certain volume of substance / Mass of equal volume of water (at 4°C)
37. Which among the following is used to measure relative density?
- Lactometer
- Pycnometer
- Barometer
- Hydrometer
Explanation
Relative density can be measured using Pycnometer also called density bottle. It consists of ground glass stopper with a fine hole through it. The function of the hole in a stopper is that, when the bottle is filled and the stopper is inserted, the excess liquid rises through the hole and runs down outside the bottle. By this way the bottle will always contain the same volume of whatever the liquid is filled in, provided the temperature remains constant. Thus, the density of a given volume of a substance to the density of equal volume of referenced substance is called relative density or specific gravity of the given substance.
38. You have a block of a mystery material, 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 3.5 cm thick. Its mass is 1155 grams. What is its density?
- Density = 0.3 g cm-3
- Density = 1.8 g cm-3
- Density = 2.5 g cm-3
- Density = 3.2 g cm-3
Explanation
Density = Mass / Volume
= 1155g / (12 cm × 11 cm × 3.5 cm) = 1155 g / 462 cm3
= 2.5 g cm-3
The mystery material is denser than the water. So, it sinks.
If the density of a substance is less than the density of the liquid it will float.
39. A direct-reading instrument used for measuring the density or relative density of the liquid is called ____
- Hydrometer
- Pycnometer
- Barometer
- Saccharometer
Explanation
A direct-reading instrument used for measuring the density or relative density of the liquid is called hydrometer. Hydrometer is based on the principle of flotation, i.e., the weight of the liquid displaced by the immersed portion of the hydrometer is equal to the weight of the hydrometer.
40. Which among the following is incorrect about Hydrometer?
- Hydrometer consists of a cylindrical stem having a spherical bulb at its lower end and a narrow tube at its upper end. The lower spherical bulb is partially filled with lead shots or mercury. This helps hydrometer to float or stand vertically in liquids. The narrow tube has markings so that relative density of a liquid can be read directly.
- The liquid to be tested is poured into the glass jar. The hydrometer is gently lowered in to the liquid until it floats freely. The reading against the level of liquid touching the tube gives the relative density of the liquid.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
41. Which among the following instrument is used for measuring the density of sugar in a liquid?
- Barometer
- Lactometer
- Saccharometer
- Tachometer
Explanation
Hydrometers may be calibrated for different uses such saccharometer for measuring the density of sugar in a liquid and alcoholometer for measuring higher levels of alcohol in spirits.
42. Which among the following instrument is used to check the purity of milk?
- Tachometer
- Lactometer
- Alcoholometer
- Barometer
Explanation
One form of hydrometer is a lactometer, an instrument used to check the purity of milk. The lactometer works on the principle of gravity of milk.
43. The lactometer consists of a long-graduated test tube with a cylindrical bulb with the graduation ranging from what to what?
- 15 at top to 45 at bottom
- 20 at top to 50 at bottom
- 45 at top to 15 at bottom
- 50 at top to 20 at bottom
Explanation
The lactometer consists of a long-graduated test tube with a cylindrical bulb with the graduation ranging from 15 at the top to 45 at the bottom. The test tube is filled with air. This air chamber causes the instrument to float. The spherical bulb is filled with mercury to cause the lactometer to sink up to the proper level and to float in an upright position in the milk.
44. The correct lactometer reading is obtained only at the temperature of what?
- 930 F
- 820 F
- 700 F
- 600 F
Explanation
Inside the lactometer there may be a thermometer extending from the bulb up into the upper part of the test tube where the scale is located. The correct lactometer reading is obtained only at the temperature of 60 °F. A lactometer measures the cream content of milk. More the cream, lower the lactometer floats in the milk. The average reading of normal milk is 32.
45. Where the pressure is more in Liquid?
- Top
- Bottom
- Centre
- Uniformly distributed
Explanation
We already saw that a body experiences an upward force due to the fluid surrounding, when it is partially or fully immersed in to it. We also know that pressure is more at the bottom and less at the top of the liquid.
46. The pressure difference causes a force on the object and pushes it upward. This force is called ________
- Inertia force
- Joule force
- Buoyant force
- Magnitude force
Explanation
The pressure difference causes a force on the object and pushes it upward. This force is called buoyant force and the phenomenon is called buoyancy.
47. Which among the following factor is known as positively buoyant?
- If the object weighs more than the amount of water it has displaced
- If the object weighs less than the amount of water it has displaced
- If the object weighs equal to the amount of water it has displaced
- None of the above
Explanation
Most buoyant objects are those with a relatively high volume and low density. If the object weighs less than the amount of water it has displaced (density is less), buoyant force will be more and it will float (such object is known as positively buoyant). But, if the object weighs more than the amount of water it has displaced (density is more), buoyant force is less and the object will sink (such object is known as negatively buoyant).
48. Which among the following is an experiment that demonstrates the principle of buoyancy?
- Galileo’s experiment
- Millikan’s driver
- Eratosthenes driver
- Cartesian driver
Explanation
Cartesian diver is an experiment that demonstrates the principle of buoyancy. It is a pen cap with clay. The Cartesian diver contains just enough liquid that it barely floats in a bath of the liquid; its remaining volume is filled with air. When pressing the bath, the additional water enters the diver, thus increasing the average density of the diver, and thus it sinks.
49. Archimedes principle is the consequence of what?
- Newton law
- Joules law
- Pascal law
- Schrodinger law
Explanation
Archimedes principle is the consequence of Pascal’s law. According to legend, Archimedes devised the principle of the ‘hydrostatic balance’ after he noticed his own apparent loss in weight while sitting in his bath. Archimedes principle states that ‘a body immersed in a fluid experiences a vertical upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces’.
50. When a body is partially or completely immersed in a fluid at rest, it experiences what?
- Upthrust which is equal to the weight of the fluid displayed by it
- Upthrust which is less to the weight of the fluid displaced by it
- Upthrust which is more to the weight of the fluid displaced by it
- Down thrust which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it
Explanation
When a body is partially or completely immersed in a fluid at rest, it experiences an upthrust which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it. Due to the upthrust acting on the body, it apparently loses a part of its weight and the apparent loss of weight is equal to the upthrust.
51. Which among the following equation gives apparent weight of an object in Archimedes principle?
- True weight of an object in air – Upthrust
- Upthrust – True weight of an object in air
- True weight of an object in air + Upthrust
- True weight of an object in air / Upthrust
Explanation
Thus, for a body either partially or completely immersed in a fluid,
Upthrust = Weight of the fluid displaced = Apparent loss of weight of the body
Apparent weight of an object = True weight of an object in air – Upthrust (weight of water displaced).
52. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding law of floatation?
- The weight of a floating body in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body.
- The centre of gravity of the floating body and the centre of buoyancy are in the same horizontal line.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The centre of gravity of the floating body and the centre of buoyancy are in the same vertical line. The point through which the force of buoyancy is supposed to act is known as centre of buoyancy.
53. Which among the following statement is correct
- Salt water provides more buoyant force than fresh water, because, buoyant force depends as much on the density of fluids as on the volume displaced.
- Flotation therapy uses water that contains Epsom salts rich in sodium. As a floater relaxes, he or she is absorbing this sodium through the skin.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Flotation therapy uses water that contains Epsom salts rich in magnesium. As a floater relaxes, he or she is absorbing this magnesium through the skin. Magnesium helps the body to process insulin, which lowers a person’s risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes.
54. A mercury barometer in a physics laboratory shows a 732 mm vertical column of mercury. Calculate the atmospheric pressure in pascal. [Given density of mercury, ρ = 1.36 × 104 kg m-3, g = 9.8 m s-2]?
- P = 7.63 × 104 Pa
- P = 8.19 × 104 Pa
- P = 9.76 × 104 Pa
- P = 6.82 × 104 Pa
Explanation
Atmospheric pressure in the laboratory,
P = hρg = 732 × 10-3 × 1.36 × 104 × 9.8
= 9.76 × 104 Pa (or) 0.976 × 105 Pa
9th Science Lesson 4 Questions in English
4] Electric Charge And Electric Current
1. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Atoms have particles like electrons, protons and neutrons.
- Neutrons has both positive and negative charge
- An electric current consists of moving electric charges.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Like mass and length, electric charge also is a fundamental property of all matter. We know that matter is made up of atoms and molecules. Atoms have particles like electrons, protons and neutrons. By nature, electrons and protons have negative and positive charge respectively and neutrons do not have charge. An electric current consists of moving electric charges. Electricity is an important source of energy in the modern times.
2. Which of the following are present in a nucleus of an atom?
- Electron
- Neutron
- Proton
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Inside each atom there is a nucleus with positively charged protons and chargeless neutrons and negatively charged electrons orbiting the nucleus. Usually there are as many electrons as there are protons and the atoms themselves are neutral.
3. Assertion (A): An electron is removed from the atom is called a positive ion.
Reason (R): If an electron is removed from the atom, the atom becomes positively charged
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
If an electron is removed from the atom, the atom becomes positively charged. Then it is called a positive ion. If an electron is added in excess to an atom then the atom is negatively charged and it is called negative ion.
4. When the comb is rubbed against hair which of the following acquires negative charge?
- Hair
- Comb
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
When you rub a plastic comb on your dry hair, the comb obtains power to attract small pieces of paper, is it not? When you rub the comb vigorously, electrons from your hair leave and accumulate on the edge of the comb. Your hair is now positively charged as it has lost electrons and the comb is negatively charged as it has gained electrons.
5. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Electric charge is measured in coulomb and the symbol for the same is C
- The charge of an electron (represented as e) is the fundamental unit with a charge equal to 1.6 × 10^19 C.
- Any charge (q) has to be an integral multiple (n) of this fundamental unit of electron charge (e).
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Electric charge is measured in coulomb and the symbol for the same is C. The charge of an electron is numerically a very tiny value. The charge of an electron (represented as e) is the fundamental unit with a charge equal to 1.6 × 10^–19 C. This indicates that any charge (q) has to be an integral multiple (n) of this fundamental unit of electron charge (e). q = ne. Here, n is a whole number.
6. How many electrons will be there in one coulomb of charge?
- 1.6 x 10^-19
- 6.25 x 10^18
- 6.25 x 10^20
- 6.25 x 10^28
Explanation

7. Electrostatic forces between two-point charges obey____
- Newton’s third law
- Newton’s second law
- Newton’s first law
- Coulomb’s law
Explanation
Electrostatic forces between two-point charges obey Newton’s third law. The force on one charge is the action and on the other is reaction and vice versa.
8. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Electric charge is additive in nature
- Practically, we have µC (micro coulomb), nC (nano coulomb) and pC (pico coulomb) as units of electric charge.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Practically, we have µC (micro coulomb), nC (nano coulomb) and pC (pico coulomb) as units of electric charge. 1 µC = 10-6 C, 1nC=10-9 and 1pC = 10-12C Electric charge is additive in nature. The total electric charge of a system is the algebraic sum of all the charges located in the system. For example, let us say that a system has two charges +5C and –2C. Then the total or net charge on the system is, (+5C) + (–2C) = +3C.
9. Assertion(A): Two charges are not in contact they experience electric force
Reason(R): Electric force can be experienced even when the charges are not in contact.
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
Among electric charges, there are two types of electric force (F): one is attractive and the other is repulsive. The like charges repel and unlike charges attract. The force existing between the charges is called as ‘electric force’. These forces can be experienced even when the charges are not in contact.
10. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The region in which a charge experiences electric force forms the ‘electric field’ around the charge
- The direction of the electric field is the direction of the force that would act on a small positive charge
- The electric lines of force are straight or curved paths along which a unit positive charge tends to move in the electric field.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The region in which a charge experiences electric force forms the ‘electric field’ around the charge. Often electric field (E) is represented by lines and arrowheads indicating the direction of the electric filed. The direction of the electric field is the direction of the force that would act on a small positive charge. Therefore, the lines representing the electric field are called ‘electric lines of force’. The electric lines of force are straight or curved paths along which a unit positive charge tends to move in the electric field. Electric lines of force are imaginary lines.
11. For an isolated negative charge electric lines of force are radially__________
- Outwards
- Inwards
- Around it
- None
Explanation
The strength of an electric field is represented by how close the field lines are to one another. For an isolated positive charge, the electric lines of force are radially outwards and for an isolated negative charge they are radially inwards.
12. ______at a point is a measure of force acting on a unit positive charge placed at that point.
- Electric wave
- Electric charge
- Electric field
- All the above
Explanation
Electric field at a point is a measure of force acting on a unit positive charge placed at that point. A positive charge will experience force in the direction of electric field and a negative charge will experience in the opposite direction of electric field.
13. _____ is a measure of the work done on unit positive charge to bring it to that point against all
electrical forces
- Electric charge
- Electric current
- Electric potential
- Electric field
Explanation
Though there is an electric force (either attractive or repulsive) existing among the charges, they are still kept together. We now know that in the region of electric charge there is an electric field. Other charges experience force in this field and vice versa. There is a work done on the charges to keep them together. This results in a quantity called ‘electric potential’. Electric potential is a measure of the work done on unit positive charge to bring it to that point against all electrical forces.
14. Which of the following statement is correct?
- When the charged object is provided with a conducting path, electrons start to flow through the path from lower potential to higher potential region
- Potential difference is produced by a cell or battery.
- Electric current is formed by moving electrons.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
When the charged object is provided with a conducting path, electrons start to flow through the path from higher potential to lower potential region. Normally, the potential difference is produced by a cell or battery. When the electrons move, we say that an electric current is produced. That is, an electric current is formed by moving electrons.
15. Assertion(A): In electrical circuits the positive terminal is represented by a long line and negative terminal as a short line
Reason(R): The movement of the positive charge is called as ‘conventional current’
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
Before the discovery of the electrons, scientists believed that an electric current consisted of moving positive charges. Although we know this is wrong, the idea is still widely held, as the discovery of the flow of electrons did not affect the basic understanding of the electric current. The movement of the positive charge is called as ‘conventional current’. The flow of electrons is termed as ‘electron current’. In electrical circuits the positive terminal is represented by a long line and negative terminal as a short line. Battery is the combination of more than one cell.
16. Which of the following is/are unit of current?
- A
- V
- Cs^-1
- 1 alone
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
If q is the quantity of charge passing through a cross section of a wire in time t, quantity of current (I) is represented as, I = q/t The standard SI unit for current is ampere with the symbol A. Current of 1 ampere means that there is one coulomb (1C) of charge passing through a cross section of a wire every one second (1 s). 1 ampere = 1 coulomb / 1 second (or) 1 A = 1 C / 1 s = 1Cs^-1.
17. _____ is an instrument used to measure the strength of the electric current
- Ammeter
- Voltmeter
- Galvanometer
- All the above
Explanation
Current is the rate at which charges flow past a point on a circuit. Ammeter is an instrument used to measure the strength of the electric current in an electric circuit.
18. Ammeter should be connected________ in a circuit
- Parallel
- Series
- Anywhere
- Near to battery/cell only
Explanation
The ammeter is connected in series in a circuit where the current is to be found. The current flows through the positive (+) red terminal of ammeter and leaves from the negative (–) black terminal.
19. If, 25 C of charge is determined to pass through a wire of any cross section in 50 s, what is the
measure of current?
- 1 A
- 0.5 A
- 5 A
- 50 A
Explanation
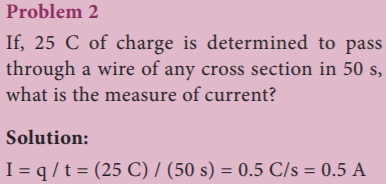
20. The current flowing through a lamp is 0.2A. If the lamp is switched on for one hour, what is the
total electric charge that passes through the lamp?
- 72 C
- 720 C
- 7.2 C
- 0.72 C
Explanation

21. Which of the following energy can be converted from electric energy?
- Light
- Heat
- Mechanical
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
One does not just let the circuit connect one terminal of a cell to another. Often we connect, say a bulb or a small fan or any other electrical device in an electric circuit and use the electric current to drive them. This is how a certain amount of electrical energy provided by the cell or any other source of electrical energy is converted into other form of energy like light, heat, mechanical and so on.
22. What is the SI unit of e.m.f?
- V/s
- V
- V/m
- qs
Explanation
For each coulomb of charge passing through the light bulb (or any appliances) the amount of electrical energy converted to other forms of energy depends on the potential difference across the electrical device or any electrical component in the circuit. The potential difference is represented by the symbol V.
V = W/q
where, W is the work done, i.e., the amount of electrical energy converted into other forms of energy measured in joule and q is amount of charge measured in coulomb. The SI unit for both e.m.f and potential difference is the same i.e., volt (V).
23. A charge of 2 x 10^4 C flows through an electric heater. The amount of electrical energy
converted into thermal energy is 5 3 10^6 J. What is the potential difference?
- 220 V
- 250 V
- 440 V
- 330 V
Explanation

24. In a circuit Voltmeter should be connected in___
- Parallel
- Series
- Anywhere
- Near to battery/cell only
Explanation
Voltmeter is an instrument used to measure the potential difference. To measure the potential difference across a component in a circuit, the voltmeter must be connected in parallel to it. Note the positive (+) red terminal of the voltmeter is connected to the positive side of circuit and the negative (–) black terminal is connected to the negative side of the circuit across a component
25. Which of the following has negligible resistance to electric current flow?
- Copper
- Aluminium
- Nichrome
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The Resistance (R) is the measure of opposition offered by the component to the flow of electric current through it. Different electrical components offer different electrical resistance. Metals like copper, aluminium etc., have very much negligible resistance. That is why they are called good conductors. On the other hand, materials like nichrome, tin oxide etc., offer high resistance to the electric current. We also have a category of materials called insulators; they do not conduct electric current at all (glass, polymer, rubber and paper). All these materials are needed in electrical circuits to have usefulness and safety in electrical circuits.
26. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The SI unit of resistance is ohm with the symbol (Ω).
- The resistors can be fixed or variable
- One ohm is the resistance of a component when the potential difference of one volt applied across the component drives a current of one ampere through it
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The SI unit of resistance is ohm with the symbol (Ω). One ohm is the resistance of a component when the potential difference of one volt applied across the component drives a current of one ampere through it. We can also control the amount of flow of current in a circuit with the help of resistance. Such components used for providing resistance are called as ‘resistors’. The resistors can be fixed or variable. Fixed resistors have fixed value of resistance, while the variable resistors like rheostats can be used to obtain desired value of resistance.
27. Assertion(A): As both e.m.f and potential difference are measured in volt, they may appear the Same
Reason(R): e.m.f refers to the voltage developed across the terminals of an electrical source and potential difference refers to the voltage developed between any two points (even across electrical devices) in an electric circuit
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
As both e.m.f and potential difference are measured in volt, they may appear the same. But they are not. The e.m.f refers to the voltage developed across the terminals of an electrical source when it does not produce current in the circuit. Potential difference refers to the voltage developed between any two points (even across electrical devices) in an electric circuit when there is current in the circuit.
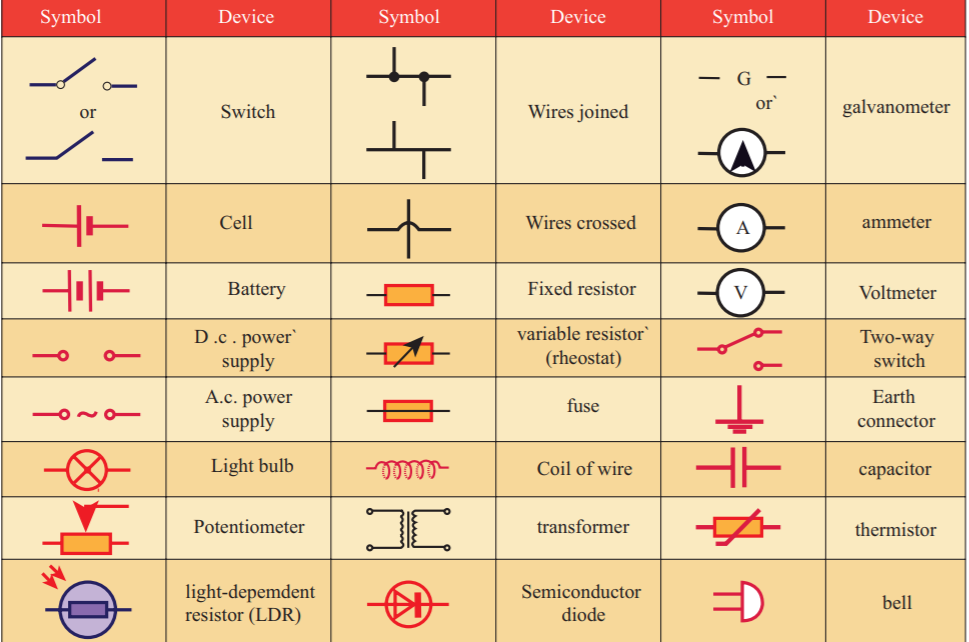
28. Match the following:
 1. Earth connector
1. Earth connector 2. Bell
2. Bell 3. LDR
3. LDR 4. Light Bulb
4. Light Bulb- 2, 1, 3, 4
- 1, 2, 4, 3
- 3, 4, 2, 1
- 3, 2, 4, 1
Explanation
29. Which of the following statement about series network is correct?
- In a series circuit the components are connected one after another in a single loop
- From the above we can know that the current I all along the series circuit remain same
- In a series circuit the current in each point of the circuit is same
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
In a series circuit the components are connected one after another in a single loop. In a series circuit there is only one pathway through which the electric charge flow. From the above we can know that the current I all along the series circuit remain same. That is in a series circuit the current in each point of the circuit is same.
30. How many minimum loops are required for parallel circuit?
- 1
- 3
- 4
- 2
Explanation
In parallel circuits, the components are connected to the e.m.f source in two or more loops. In a parallel circuit there is more than one path for the electric charge to flow. In a parallel circuit the sum of the individual current in each of the parallel branches is equal to the main current flowing into or out of the parallel branches. Also, in a parallel circuit the potential difference across separate parallel branches are same.
31. Which of the following are effects of electric current?
- Heating effect
- Chemical effect
- Magnetic effect
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
When current flows in a circuit it exhibits various effects. The main effects are heating, chemical and magnetic effects.
32. Which of the following statement is correct?
- When the flow of current is ‘resisted’ generally heat is produced
- Work has to be done to overcome the resistance which is converted in to heat energy.
- This conversion of electrical energy into heating energy is called ‘Joule heating’
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
When the flow of current is ‘resisted’ generally heat is produced. This is because the electrons while moving in the wire or resistor suffer resistance. Work has to be done to overcome the resistance which is converted in to heat energy. This conversion of electrical energy into heating energy is called ‘Joule heating’ as this effect was extensively studied by the scientist Joule. This forms the principle of all electric heating appliances like iron box, water heater, toaster etc. Even connecting wires offer a small resistance to the flow of current. That is why almost all electrical appliances including the connecting wires are warm when used in an electric circuit.
33. The process of conduction of electric current through solutions is called__________
- Electron transfer
- Electrolysis
- Electrolyte
- All the above
Explanation
So far, we have come across the cases in which only the electrons can conduct electricity. But, here when current passes through electrolyte like copper sulphate solution, both the electron and the positive copper ion conduct electricity. The process of conduction of electric current through solutions is called ‘electrolysis’
34. The positive terminal inserted in to the solution is called_______
- Cathode
- Anode
- Anion
- Cation
Explanation
The positive terminal inserted in to the solution is called ‘anode’ and the negative terminal ‘cathode’. In the above experiment, copper wire is anode and carbon rod is cathode.
35. Extremely weak electric current is produced in the human body are called________
- Synaptic signal
- Asynaptic signal
- Electrode signal
- None
Explanation
Extremely weak electric current is produced in the human body by the movement of charged particles. These are called synaptic signals. These signals are produced by electro-chemical process. They travel between brain and the organs through nervous system.
36. A wire or a conductor carrying current develops a magnetic field___ to the direction of the flow of current.
- Parallel
- Perpendicular
- Adjacent
- All the above
Explanation
A wire or a conductor carrying current develops a magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of the flow of current. This is called magnetic effect of current. The discovery of the scientist Oersted and the ‘right hand thumb rule’ are detailed in the chapter on Magnetism and Electromagnetism. Direction of current is shown by the right-hand thumb and the direction of magnetic field is shown by other fingers of the same right hand.
37. Which of the following statement is correct?
- There are two distinct types of electric currents that we encounter in our everyday life: direct current (dc) and alternating current (ac).
- Electrons move from negative terminal of the battery to positive of the battery
- Some other sources of dc are solar cells, thermocouples etc
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
There are two distinct types of electric currents that we encounter in our everyday life: direct current (dc) and alternating current (ac). We know current in electrical circuits is due to the motion of positive charge from higher potential to lower potential or electron from lower to higher electrical potential. Electrons move from negative terminal of the battery to positive of the battery. Battery is used to maintain a potential difference between the two ends of the wire. Battery is one of the sources for dc current. The dc is due to the unidirectional flow of electric charges. Some other sources of dc are solar cells, thermocouples etc.
38. Which of the following works on DC?
- Cell phones
- Radio
- Electric vehicles
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Many electronic circuits use dc. Some examples of devices which work on dc are cell phones, radio, electric keyboard, electric vehicles etc.
39. Which of the following statement is correct?
- If the direction of the current in a resistor or in any other element changes its direction alternately, the current is called an alternating current
- The alternating current varies sinusoidally with time.
- Frequency is the number of complete cycle of variation, gone through by the ac in one second
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
If the direction of the current in a resistor or in any other element changes its direction alternately, the current is called an alternating current. The alternating current varies sinusoidally with time. This variation is characterised by a term called as frequency. Frequency is the number of complete cycle of variation, gone through by the ac in one second. In ac, the electrons do not flow in one direction because the potential of the terminals vary between high and low alternately. Thus, the electrons move to and fro in the wire carrying alternating current.
40. The device used to convert ac to dc is called______
- DC convertor
- Rectifier
- Invertor
- Adaptor
Explanation
Domestic supply is in the form of ac. When we want to use an electrical device in dc, then we have to use a device to convert ac to dc. The device used to convert ac to dc is called rectifier. Colloquially it is called with several names like battery eliminator, dc adaptor and so on. The device used to convert dc into ac is called inverter.
41. What does the symbol represent?
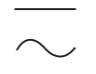
- AC
- DC
- AC or DC
- None
Explanation
42. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The voltage of ac can be varied easily using a device called transformer.
- The ac can produce electromagnetic induction which is useful in several ways.
- The dc can be easily converted into ac and generating dc is easier than ac.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The voltage of ac can be varied easily using a device called transformer. The ac can be carried over long distances using step up transformers. The loss of energy while distributing current in the form of ac is negligible. Direct current cannot be transmitted as such. The ac can be easily converted into dc and generating ac is easier than dc. The ac can produce electromagnetic induction which is useful in several ways.
43. Which of the following can be done only using dc?
- Electroplating
- electro refining
- electrotyping
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Electroplating, electro refining and electrotyping can be done only using dc. Electricity can be stored only in the form of dc.
44. What is the frequency of ac used for domestic purpose in USA?
- 50 Hz
- 60 Hz
- 30 Hz
- 55 Hz
Explanation
In India, the voltage and frequency of ac used for domestic purpose is 220 V and 50 Hz respectively where as in United States of America it is 110 V and 60 Hz respectively.
45. What is the Resistance of a dry human body?
- 1,00,000 ohm
- 1,000 ohm
- 100 ohm
- 10,000 ohm
Explanation
Resistance of a dry human body is about 1,00,000 ohm. Because of the presence of water in our body the resistance is reduced to few hundred ohm. Thus, a normal human body is a good conductor of electricity. Hence, precautions are required while doing electrical work.
9th Science Lesson 5 Questions in English
5] Magnetism and Electromagnetism
1. Which among the following was the strongest natural magnet?
- Limestone
- Metaquartzite
- Sandstone
- Lodestone
Explanation
Natural magnets exist in the nature. These kinds of magnets can be found in rocks and sandy deposits in various parts of the world. The strongest natural magnet is lodestone magnetite. The magnetic property in the natural magnets is permanent. It never gets destroyed.
2. What was the purpose of the magnet used by the captain of the ship effectively?
- To identify weather
- To identify the distance from land
- To identify the direction
- All the above
Explanation
Captains of the ships effectively used the magnets to identify the direction of the ship in the sea. There are two kinds of magnets that we can see around us: Natural magnet and Artificial magnet. Natural magnet lodestones were used to make compasses in the olden days. Artificial magnets are made by us. The magnets available in the shops are basically artificial magnets.
3. What is the unit of magnetic field?
- Newton
- Joule
- Tesla
- Weber
Explanation
The magnetic field is the region around the magnet where its magnetic influence can be felt. It is denoted by B and its unit is Tesla.
4. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which shields which layer from the solar wind?
- Mantle layer
- Crust layer
- Exo layer
- Ozone layer
Explanation
Magnetic field can penetrate through all kinds of materials, not just air. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which shields the earth’s ozone layer from the solar wind and it is important for navigation also.
5. Which among the following statement is correct about magnetic field lines?
- They start at north pole and end at south pole
- They start at south pole and end at north pole
- They start at both north and south pole
- None of the above
Explanation
A magnetic field line is defined as a curve drawn in the magnetic field in such a way that the tangent to the curve at any point gives the direction of the magnetic field. They start at north pole and ends at south pole. The magnetic field at a point is tangential to the magnetic field lines.
6. The number of magnetic field lines passing through a given area is know as ____
- Magnetic impulse
- Magnetic pulse
- Magnetic loop
- Magnetic flux
Explanation
Magnetic flux is the number of magnetic field lines passing through a given area.
7. The number of magnetic field lines crossing unit area kept normal to the direction of field lines is called ___
- Magnetic flux inventor
- Magnetic flux density
- Magnetic flux frustrates
- Magnet flux impulse
Explanation
The number of magnetic field lines crossing unit area kept normal to the direction of field lines is called magnetic flux density.
8. Which among the following is the unit of Magnetic flux?
- Newton
- Joule
- Tesla
- Weber
Explanation
Magnetic flux is denoted by ϕ and its unit is weber (Wb).
9. Which among the following animals can return to their birth place many decades after they were born by perceiving variations in magnetic parameters of Earth such as magnetic field intensity and remember them?
- Sheep
- Bison
- Turtle
- Shark
Explanation
Some sea turtles (loggerhead sea turtle) return to their birth beach many decades after they were born, to nest and lay eggs. In a research, it is suggested that the turtles can perceive variations in magnetic parameters of Earth such as magnetic field intensity and remember them. This memory is what helps them in returning to their homeland.
10. Which among the following is the unit of magnetic flux density?
- Wb/m2
- Wb/m3
- Wb/m
- Wb m
Explanation
Magnetic flux density unit is Wb/m2.
11. Which among the following is not the Properties of magnetic lines of force?
- Magnetic lines of force are closed, continuous curves, extending through the body of the magnet.
- Magnetic lines of force never intersect.
- They will be maximum at the equator than at the poles.
- The tangent drawn at any point on the curved line gives the direction of magnetic field.
Explanation
Magnetic lines of force start from the North Pole and end at the South Pole. They will be maximum at the poles than at the equator.
12. Who among the following in 1820 discovered that electric current create magnetic field while demonstrating electrical circuits in the class?
- Andre Marie Ampere
- Hans Christian Oersted
- James Clerk Maxwell
- Michael Faraday
Explanation
It was on 21st April 1820, Hans Christian Oersted, a Danish Physicist was giving a lecture. He was demonstrating electrical circuits in that class. He had to often switch on and off the circuit during the lecture. Accidentally, he noticed the needle of the magnetic compass that was on the table. It deflected whenever he switched on and the current was flowing through the wire. The compass needle moved only slightly, so that the audience didn’t even notice. But it was clear to Oersted that something significant was happening. He conducted many experiments to find out a startling effect, the magnetic effect of current.
13. Which among the following statement is correct
- Oersted aligned a wire XY such that they were exactly along the North-South direction. He kept one magnetic compass above the wire at A and another under the wire at B. When the circuit was open and no current was flowing through it, the needle of both the compass was pointing to north.
- Once the circuit was closed and electric current was flowing, the needle at A pointed to east and the needle at B to the west. This showed that current carrying conductor produces magnetic field around it.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
14. The direction of the magnetic lines around a current carrying conductor can be easily understood using which rule?
- Faraday rule
- Right hand thumb rule
- Sea rule
- Kirchhoff rule
Explanation
The direction of the magnetic lines around a current carrying conductor can be easily understood using the right-hand thumb rule.
15. The magnetic field is always what to the direction of current?
- Parallel
- Perpendicular
- Both parallel and perpendicular
- None
Explanation
Hold the wire with four fingers of your right hand with thumbs-up position. If the direction of the current is towards the thumb then the magnetic lines curl in the same direction as your other four fingers. This shows that the magnetic field is always perpendicular to the direction of current.
16. Which among the following the strength of the magnetic field at a point due to current carrying wire doesn’t depend on?
- The current in the wire
- Distance of the point from the wire
- Surrounding temperature in the environment
- The magnetic nature of the wire
Explanation
The strength of the magnetic field at a point due to current carrying wire depends on: (i) the current in the wire, (ii) distance of the point from the wire, (iii) the orientation of the point from the wire and (iv) the magnetic nature of the medium. The magnetic field lines are stronger near the current carrying wire and it diminishes as you go away from it. This is represented by drawing magnetic field lines closer together near the wire and farther away from the wire.
17. Who found that a charge moving in a magnetic field, in a direction other than the direction of magnetic field, experiences a force?
- H.A. Lorentz
- Max Plank
- H.K. Onnes
- Pieter Zeeman
Explanation
H.A. Lorentz found that a charge moving in a magnetic field, in a direction other than the direction of magnetic field, experiences a force. It is called the magnetic Lorentz force.
18. Which among the following statement is correct
- Charge in motion constitutes a current, a conductor carrying moving charges, placed in magnetic field other than the direction of magnetic field, will also experience a force and can produce motion in the conductor.
- The current carrying wire has a magnetic field parallel to the wire (by looking at the deflection of the compass needle in the vicinity of a current carrying conductor). The deflection of the needle implies that the current carrying conductor exerts a force on the compass needle.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The current carrying wire has a magnetic field perpendicular to the wire (by looking at the deflection of the compass needle in the vicinity of a current carrying conductor). The deflection of the needle implies that the current carrying conductor exerts a force on the compass needle.
19. In 1812, who discovered that a current carrying conductor also gets deflected when it is placed in a magnetic field?
- Georg Ohm
- J.J. Thomson
- Nikola Tesla
- Michael Faraday
Explanation
In 1821, Michael Faraday discovered that a current carrying conductor also gets deflected when it is placed in a magnetic field. The magnetic field of the permanent magnet and the magnetic field produced by the current carrying conductor interact and produce a force on the conductor.
20. If a current, I is flowing through a conductor of length, L kept perpendicular to the magnetic field B, then the force F experienced by it is given by which equation?
- F= I L / B
- F=I / L B
- F=I L / B
- F=I L B
Explanation
If a current, I is flowing through a conductor of length, L kept perpendicular to the magnetic field B, then the force F experienced by it is given by the equation, F = I L B. The above equation indicates that the force is proportional to current through the conductor, length of the conductor and the magnetic field in which the current carrying conductor is kept.
21. When the conductor is parallel to the magnetic field, the force will be _____
- Maximum
- Minimum
- Zero
- Can’t define
Explanation
The angle of inclination between the current and magnetic field also affects the magnetic force. When the conductor is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the force will be maximum (=BIL). When it is parallel to the magnetic field, the force will be zero.
22. The Force is always what quantity?
- Radar
- Vector
- Scalar
- Both scalar and vector
Explanation
The force is always a vector quantity. A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction. It means we should know the direction in which the force would act. The direction is often found using what is known as Fleming’s Left-hand Rule.
23. In Fleming’s Left-hand rule while stretching the three fingers of left hand in perpendicular manner with each other, if the direction of the current is denoted by the middle finger of the left hand, what does the second finger denotes?
- Direction of the force
- Direction of the magnetic field
- Direction of the conductor
- Direction of the thrust
Explanation
Fleming’s Left-hand Rule states that while stretching the three fingers of left hand in perpendicular manner with each other, if the direction of the current is denoted by the middle finger of the left hand and the second finger is for direction of the magnetic field, then the thumb of the left hand denotes the direction of the force or movement of the conductor.
24. A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2×10–3 T. Find the force on the conductor?
- F = 5 × 10 N
- F = 5 × 103 N
- F = 5 × 10-3 N
- F = 5 × 10-1 N
Explanation
Force on the conductor = ILB
= 5 × 50 × 10-2 × 2 ×10-3
= 5 × 10-3 N
25. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- We have seen that a current carrying conductor has a magnetic field around it. If we place another conductor carrying current parallel to the first one, the second conductor will experience a force due to the magnetic field of the first conductor.
- The first conductor will experience a force due to the magnetic field of the second conductor. These two forces will be equal in direction and opposite in magnitude. Using Fleming’s left-hand rule, we can find that the direction of the force on each wire would be same when the current in both of them are flowing in the different direction, i.e., the wires would experience an attractive force
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The first conductor will experience a force due to the magnetic field of the second conductor. These two forces will be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Using Fleming’s left-hand rule, we can find that the direction of the force on each wire would be towards each other when the current in both of them are flowing in the same direction, i.e., the wires would experience an attractive force.
26. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- Before 18th century people thought that magnetism and electricity were separate subjects of study. After Oersted’s experiment the electricity and magnetism were united and became a single subject called ‘Electromagnetism’.
- When there is current, the magnetic field is produced and the current carrying conductor behaves like a magnet. You may now wonder how was it possible for a lodestone to behave like a magnet when there was no current passing through it. Only in the twentieth century, we understood that the magnetic property arises due to the motion of neutrons in the lodestone.
- In the circuit the electrons flow from positive of the battery to negative of the battery and constitutes current. As a result, it produces magnetic field. In natural magnets and artificial magnets that we buy in shops, the neutron move around the nucleus constitutes current which leads to magnetic property.
- Only 1
- Only 3
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
Explanation
When there is current, the magnetic field is produced and the current carrying conductor behaves like a magnet. You may now wonder how was it possible for a lodestone to behave like a magnet when there was no current passing through it. Only in the twentieth century, we understood that the magnetic property arises due to the motion of electrons in the lodestone.
In the circuit the electrons flow from negative of the battery to positive of the battery and constitutes current. As a result, it produces magnetic field. In natural magnets and artificial magnets that we buy in shops, the electrons move around the nucleus constitutes current which leads to magnetic property.
27. An electric motor is a device which converts electrical energy into what?
- Chemical energy
- Sound energy
- Mechanical energy
- Heat energy
Explanation
An electric motor is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric motors are crucial in modern life. They are used in water pump, fan, washing machine, juicer, mixer, grinder etc. when electric current is passed through a conductor placed normally in a magnetic field, a force is acting on the conductor and this force makes the conductor to move.
28. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Electric motor?
- A simple coil is placed inside two poles of a magnet. Now look at the current carrying conductor segment AB. The direction of the current is towards B, whereas in the conductor segment CD the direction is opposite. As the current is flowing in opposite directions in the segments AB and CD, the direction of the motion of the segments would be in opposite directions according to Fleming’s left-hand rule.
- If the current flow is along the line ABCD, then the coil will rotate in clockwise direction first and then in anticlockwise direction. If we want to make the coil rotate in any one direction, say clockwise, then the direction of the current should be along ABCD in the first half of the rotation and along DCBA in the second half of the rotation. To change the direction of the current, a small device called split ring commutator is used.
- When the gap in the split ring commutator is aligned with terminals X and Y, there is no flow of current in the coil. But, as the coil is moving, it continues to move forward bringing one of the split ring commutators in contact with the carbon brushes X and Y. The reversing of the current is repeated at each half rotation, giving rise to a continuous rotation of the coil.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
29. Which among the following doesn’t increase the speed of rotation of coil?
- Increasing the strength of current in the coil
- Increasing the size of the magnet
- Increasing the number of turns in the coil.
- Increasing the area of the coil
Explanation
The speed of rotation of coil can be increased by: i. increasing the strength of current in the coil. ii. increasing the number of turns in the coil. iii. increasing the area of the coil and iv. increasing the strength of the magnetic field.
30. Who in 1831, explained the possibility of producing an e.m.f across the conductor when the magnetic flux linked with the conductor is changed.?
- Andre Marie Ampere
- Hans Christian Oersted
- Michael Faraday
- James Clerk Maxwell
Explanation
When it was shown by Oersted that magnetic field is produced around a conductor carrying current, the reverse effect was also attempted. In 1831, Michael Faraday explained the possibility of producing an e.m.f across the conductor when the magnetic flux linked with the conductor is changed.
31. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Faraday’s experiment 2?
- The greater the number of turns, the higher is the voltage generated
- The greater the number of turns, the lower is the voltage generated
- The greater the number of turns, there is no change in the voltage generated
- The greater the number of turns, the voltage will become null
Explanation
In the Faraday’s experiment, current (or voltage) is generated by the movement of the magnet in and out of the coil. The greater the number of turns, the higher is the voltage generated.
32. Which among the following statement is correct regarding faraday’s experiment
- In experiment 1, two coils were wound on a soft iron ring (separated from each other). The coil on the left is connected to a battery and a switch K. A galvanometer is attached to the coil on the right. When the switch is put ‘on’, at that instant, there is a deflection in the galvanometer. Likewise, when the switch is put ‘off’, again there is a deflection – but in the opposite direction. This proves the generation of current.
- In experiment 3, the magnet is stationary, but the coil is moved in and out of the magnetic field (indicated by the magnetic lines of force). Here also, current is induced. All these observations made Faraday to conclude that whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with a closed circuit an emf is produced and the amount of emf induced varies inversely as the rate at which the flux changes.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
All these observations made Faraday to conclude that whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with a closed circuit an emf is produced and the amount of emf induced varies directly as the rate at which the flux changes.
33. The change in the magnetic flux linked with a closed circuit an emf is produced and the amount of emf induced varies directly as the rate at which the flux changes. This emf is known as ____
- Flux emf
- Coiled emf
- Induced emf
- All the above
Explanation
The change in the magnetic flux linked with a closed circuit an emf is produced and the amount of emf induced varies directly as the rate at which the flux changes. This emf is known as induced emf.
34. The phenomenon of producing an induced emf due to change in the magnetic flux linked with a closed circuit is known as _____
- Flux inductor
- Magnetic flux
- Electromagnetic induction
- Electromagnetic flux
Explanation
The phenomenon of producing an induced emf due to change in the magnetic flux linked with a closed circuit is known as electromagnetic induction.
35. A current carrying conductor of certain length, kept perpendicular to the magnetic field experiences a force F. What will be the force if the current is increased four times, length is halved and magnetic field is tripled?
- F = 2F
- F = 6F
- F = 12F
- F = 24F
Explanation
F = I L B = (4I) × (L/2) × (3 B) = 6 F
Therefore, the force increases six times.
36. The direction of the induced current was given by which law?
- Faraday’s law
- Joule’s law
- Lenz’s law
- Stefan’s law
Explanation
The direction of the induced current was given by Lenz’s law, which states that the induced current in the coil flows in such a direction as to oppose the change that causes it. The direction of induced current can also be given by another rule called Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
37. Which among the following was the main discovery of Michel Faraday?
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Diamagnetism
- Electrolysis
- All the above
Explanation
Michael Faraday (22nd Sep,1791–25th Aug, 1867) was a British Scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis.
38. In Fleming’s Right Hand Rule, if the fore finger indicates the direction of magnetic field and the thumb indicates the direction of motion of the conductor what does middle finger indicate?
- Direction of induced current
- Direction of magnetic flux
- Direction of force
- Direction of magnetic rays
Explanation
In Fleming’s Right Hand Rule, if the fore finger indicates the direction of magnetic field and the thumb indicates the direction of motion of the conductor, then the middle finger will indicate the direction of induced current.
39. Fleming’s Right hand rule is also called _____
- Generator rule
- Motor rule
- Flux rule
- Magnetic rule
Explanation
Fleming’s Right hand rule is also called ‘generator rule’.
40. In an alternating current (AC) generator, there is a rotating rectangular coil ABCD called what placed between the two poles of a permanent magnet?
- Horseshoe
- Slip ring
- Armature
- Coil
Explanation
An alternating current (AC) generator, consists of a rotating rectangular coil ABCD called armature placed between the two poles of a permanent magnet.
41. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Electric generator.
- An alternating current (AC) generator, consists of a rotating rectangular coil ABCD called armature placed between the two poles of a permanent magnet. The two ends of this coil are connected to two slip rings S1 and S2. The inner sides of these rings are insulated. Two conducting stationary brushes B1 and B2 are kept separately on the rings S1 and S2 respectively.
- The two rings S1 and S2 are externally attached to an axle. The axle may be mechanically rotated from outside to rotate the coil outside the magnetic field. Outer ends of the two brushes are connected to the internal circuit. When the coil is rotated, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes. This change in magnetic flux will lead to generation of induced current.
- The direction of the induced current, as given by Fleming’s Right Hand Rule, is along ABCD in the coil and in the outer circuit it flows from B2 to B1. During the second half of rotation, the direction of current is along DCBA in the coil and in the outer circuit it flows from B1 to B2. As the rotation of the coil continues, the induced current in the external circuit is changing its direction for every half a rotation of the coil.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
The two rings S1 and S2 are internally attached to an axle. The axle may be mechanically rotated from outside to rotate the coil inside the magnetic field. Outer ends of the two brushes are connected to the external circuit. ed with the coil changes. This change in magnetic flux will lead to generation of induced current.
42. To get a direct current (DC), which type commutator must be used?
- Full ring
- Split ring
- Coiled full ring
- Both full and split ring
Explanation
To get a direct current (DC), a split ring type commutator must be used. With this arrangement, one brush is at all times in contact with the arm moving up in the field while the other is in contact with the arm moving down. Thus, a unidirectional current is produced. The generator is thus called a DC generator.
43. Which is a device used for converting low voltage into high voltage and high voltage into low voltage?
- Motor
- Generator
- Transformer
- Invertor
Explanation
Transformer is a device used for converting low voltage into high voltage and high voltage into low voltage. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
44. In Transformer the alternating current flowing through the primary coil induces magnetic field in what?
- Copper ring
- Iron ring
- Gold ring
- Aluminium
Explanation
Transformer consists of primary and secondary coil insulated from each other. The alternating current flowing through the primary coil induces magnetic field in the iron ring. The magnetic field of the iron ring induces a varying emf in the secondary coil.
45. Which among the following statement is correct
- The transformer used to change a low alternating voltage to a high alternating voltage is called a step-up transformer. i.e., Vs > Vp. In a step-up transformer, the number of turns in the primary coil is more than the number of turns in the secondary coil (Ns < Np).
- The transformer used to change a high alternating voltage to a low alternating voltage is called a step-down transformer (Vs < Vp). In a step-down transformer, the number of turns in the primary coils are less than the number of turns in the secondary coil (Ns > Np).
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The transformer used to change a low alternating voltage to a high alternating voltage is called a step-up transformer. i.e., Vs > Vp. In a step-up transformer, the number of turns in the secondary coil is more than the number of turns in the primary coil (Ns > Np).
The transformer used to change a high alternating voltage to a low alternating voltage is called a step-down transformer (Vs < Vp). In a step-down transformer, the number of turns in the secondary coils are less than the number of turns in the primary coil (Ns < Np).
46. Which among the following gives the correct formula for Transfrmer?
- Es / E p = Ns / N p
- Es E p = Ns N p
- Es / E p = Np / N s
- None of the above
Explanation
The formulae pertaining to the transformers are given in the following equations
Es / E p = Ns / N p or
Number of primary turns Np/ Number of secondary turns Ns = Primary voltage Vp/ Secondary voltage Vs
Number of secondary turns Ns/ Number of primary turns Np = Primary current Ip/ Secondary current Is
47. A transformer cannot be used with the which current?
- Alternative current
- Reverse current
- Direct current
- None of the above
Explanation
A transformer cannot be used with the direct current (DC) source because, current in the primary coil is constant (ie. DC). Then there will be no change in the number of magnetic field lines linked with the secondary coil and hence no emf will be induced in the secondary coil.
48. The primary coil of a transformer has 800 turns and the secondary coil has 8 turns. It is connected to a 220 V ac supply. What will be the output voltage?
- 2.2 volt
- 32 volts
- 1.1 volt
- 16 volts
Explanation
In a transformer, Es / E p = Ns / Np
Es = (Ns / Np) × E p
= 8/800 × 220 = 220/100 = 2.2 volt
49. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- Inside the speaker, an electromagnet is placed in front of a permanent magnet. The permanent magnet is fixed firmly in position whereas the electromagnet is mobile. As pulses of electricity pass through the coil of the electromagnet, the direction of its magnetic field is rapidly changed.
- This means that it is in turn attracted to and repelled from the permanent magnet vibrating back and forth. The electromagnet is attached to a cone made of a flexible material such as paper or plastic which amplifies these vibrations, pumping sound waves into the surrounding air towards our ears.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
50. Which is a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields?
- Magnetic projection
- Magnetic levitation
- Magnetic convection
- Magnetic rejection
Explanation
Magnetic levitation (Maglev) is a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields. In maglev trains two sets of magnets are used, one set to repel and push the train up off the track, then another set to move the floating train ahead at great speed without friction. In this technology, there is no moving part.
51. Which among the following electromagnetic is used?
- MRI
- X-ray
- Scanners
- All the above
Explanation
Nowadays electromagnetic fields play a key role in advanced medical equipment’s such as hyperthermia treatments for cancer, implants and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Many of the medical equipment’s such as scanners, x-ray equipment’s and other equipment’s also use the principle of electromagnetism for their functioning.
52. The space surrounding a bar magnet in which its influence in the form of magnetic force can be detected, is called ____
- Magnetic field
- Magnetic flux
- Magnetic current
- Magnetic coil
Explanation
The space surrounding a bar magnet in which its influence in the form of magnetic force can be detected, is called magnetic field.
9th Science Lesson 6 Questions in English
6] Light
1. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Light is a form of energy which travels as electromagnetic waves
- The branch of physics that deals with the properties and applications of light is called optics
- Telescopes, binoculars, cameras and projectors works on the principles of light.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Light is a form of energy which travels as electromagnetic waves. The branch of physics that deals with the properties and applications of light is called optics. In our day to day life we use number of optical instruments. Microscopes are inevitable in science laboratories. Telescopes, binoculars, cameras and projectors are used in educational, scientific and entertainment fields.
2. Assertion(A): Light falling on any polished surface such as a mirror, is reflected
Reason(R): Refraction of light on polished surfaces does not follow any law
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
Light falling on any polished surface such as a mirror, is reflected. This reflection of light on polished surfaces follows certain laws and you have studied about them in your lower classes.
3. Which of the following statement about figure is correct?
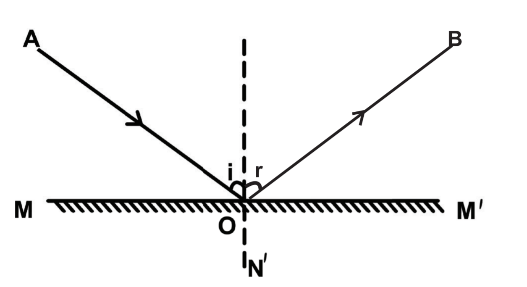
- The ray AO is called incident ray
- The ray OB is called refracted ray
- The line ON is called normal.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Consider a plane mirror MM′ as shown in Figure. Let AO be the light ray incident on the plane mirror at O. The ray AO is called incident ray. The plane mirror reflects the incident ray along OB. The ray OB is called reflected ray. Draw a line ON at O perpendicular to MM′. This line ON is called normal.
4. Which of the following statement about Laws of reflection is correct?
- The incident ray and the normal at the point of incidence alone lie in the same plane.
- The angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Laws of reflection are given as:
* The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same
plane.
* The angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
5. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Mirrors do not actually reverse left and right and they do not reverse up and down also
- What actually mirrors do is reverse inside out
- The word lateral comes from the Latin word latus which means side. Lateral inversion means sidewise inversion.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The word lateral comes from the Latin word latus which means side. Lateral inversion means sidewise inversion. It is the apparent inversion of left and right that occurs in a plane mirror. Mirrors do not actually reverse left and right and they do not reverse up and down also. What actually mirrors do is reverse inside out.
6. If the light rays coming from an object actually meet, after reflection, the image formed will be___
- Real
- Virtual
- Inverted
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
If the light rays coming from an object actually meet, after reflection, the image formed will be a real image and it is always inverted. A real image can be produced on a screen. When the light rays coming from an object do not actually meet, but appear to meet when produced backwards, that image will be virtual image. The virtual image is always erect and cannot be caught on a screen.
7. To see our entire image in mirror the mirror should be at-least _________
- Half of your height
- 1/3rd of your height
- 1/4th of your height
- Twice your height
Explanation
To see your entire body in a mirror, the mirror should be atleast half of your height.
Height of the mirror= Your height/2.
8. The most commonly used type of curved mirror is______
- Oval mirror
- Spherical mirror
- Square mirror
- Parabolic mirror
Explanation
We studied about laws of reflection. These laws are applicable to all types of reflecting surfaces including curved surfaces. In your earlier classes, you have studied that there are many types of curved mirrors, such as spherical and parabolic mirrors. The most commonly used type of curved mirror is spherical mirror.
9. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- In curved mirrors, the reflecting surface can be considered to form a part of the surface of a sphere.
- In some spherical mirrors the reflecting surface is curved inwards, that is, it faces towards the centre of the sphere. They are called convex mirrors.
- In some other mirrors, the reflecting surface is curved outward. They are called concave mirror.
- 1 alone
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
Explanation
In curved mirrors, the reflecting surface can be considered to form a part of the surface of a sphere. Such mirrors whose reflecting surfaces are spherical are called spherical mirrors. In some spherical mirrors the reflecting surface is curved inwards, that is, it faces towards the centre of the sphere. They are called concave mirrors. In some other mirrors, the reflecting surface is curved outward. They are called convex mirror.
10. The parallel rays of sun light could be focused at a point using________
- Concave mirror
- Convex mirror
- Convex lens
- None
Explanation
The parallel rays of sun light could be focused at a point using a concave mirror. Now let us place a lighted candle and a white screen in front of the concave mirror. Adjust the position of the screen. Move the screen front and back. Note the size of the image and its shape. You can see a small and inverted image.
11. Which of the following statement is correct?
- behaviour of the concave mirror is much more complicated than the plane mirror.
- behaviour of the concave mirror is same as that of plane mirror.
- behaviour of the concave mirror is same as that of convex mirror.
- 1, 2
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 3
Explanation
As you bring the object closer to the mirror the image becomes bigger. Try to locate the image when you bring the candle very close to the mirror. An erect magnified image of the candle is seen. In some positions of the object an image is obtained on the screen. However, at some positions of the object no image is obtained. It is clear that the behaviour of the concave mirror is much more complicated than the plane mirror.
12. Which of the following statement is correct?
- In the case of plane mirror, we used only two rays to understand how to get full image of a person
- For understanding the nature of image formed by a spherical mirror we need to look at four specific rules
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
With the use of geometrical techniques, we can simplify and understand the behaviour of the image formed by a concave mirror. In the case of plane mirror, we used only two rays to understand how to get full image of a person. But, for understanding the nature of image formed by a spherical mirror we need to look at four specific rules.
13. Which of the following statement is correct?
- A ray passing through the centre of curvature is reflected back along its own path
- A ray passing through the focus gets reflected and travels perpendicular to the principal axis
- A ray incident at the pole of the mirror gets reflected along a path such that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
To find the position and nature of the image formed by a spherical mirror, we need to know the following rules.
Rule 1: A ray passing through the centre of curvature is reflected back along its own path
Rule 2: A ray parallel to the principal axis passes through or appears to be coming from the principal focus (in case of convex mirror) after reflection
Rule 3: A ray passing through the focus gets reflected and travels parallel to the principal axis
Rule 4: A ray incident at the pole of the mirror gets reflected along a path such that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
14. What is the nature of the image when the object is far away (at infinity)?
- Real
- Virtual
- Inverted
- Highly diminished
- 1, 2, 3
- 1, 2, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- 1, 3, 4
Explanation
When the object is far away (at infinity), the rays of light reaching the concave mirror are parallel to each other.
Position of the Image: The image is formed at the principal focus F.
Nature of the Image: It is real, inverted and highly diminished in size
15. When the object is beyond the centre of curvature, what will be the position of image?
- Image is formed at the principal focus F
- The image is at the centre of curvature itself
- The image is beyond centre of curvature
- Image is formed between principal focus F and centre of curvature C
Explanation
When the object is beyond the centre of curvature. Position of the image: Between the principal focus F and centre of curvature C. Nature of the image: Real, inverted and smaller than object.
16. Match the following
- object is in between the focus F and the pole P 1. Image is beyond C
- object is at the principal focus F 2. Image is at C
- object is in between the centre of curvature and principal focus 3. No image
- object is at the centre of curvature 4. image is behind the
mirror
- 1, 3, 2, 4
- 3, 1, 2, 4
- 4, 3, 1, 2
- 4, 3, 2, 1
Explanation
1. When the object is at the centre of curvature.
Position of the image: The image is at the centre of curvature itself.
Nature of the image: It is real, inverted and same size as the object.
2. When the object is in between the centre of curvature C and principal focus F.
Position of the image: The image is beyond C
Nature of the image: Image is real, inverted and magnified.
3. When the object is at the principal focus F.
Nature of the image: No image can be captured on the screen nor any virtual image can be seen.
4. When the object is in between the focus F and the pole P.
Position of the image: The image is behind the mirror.
Nature of the image: It is virtual, erect and magnified
17. Which of the following statement about cartesian sign convention is correct?
- The object is always placed on the left side of the mirror
- All distances are measured from the pole of the mirror
- Distances measured in the direction of incident light are taken as positive and those measured in the opposite direction are taken as negative
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
We follow a set of sign conventions called the cartesian sign convention to measure distances in ray diagram. In this convention, the pole (P) of the mirror is taken as the origin. The principal axis is taken as the X-axis of the coordinate system.
* The object is always placed on the left side of the mirror.
* All distances are measured from the pole of the mirror.
* Distances measured in the direction of incident light are taken as positive and those measured in the opposite direction is taken as negative.
* All distances measured perpendicular to and above the principal axis are considered to be positive.
* All distances measured perpendicular to and below the principal axis are considered to be negative.
18. According to sign convention, the sign of the height of virtual image for convex mirror formed
will be_____
- Positive
- Negative
- No Virtual image
- None
Explanation
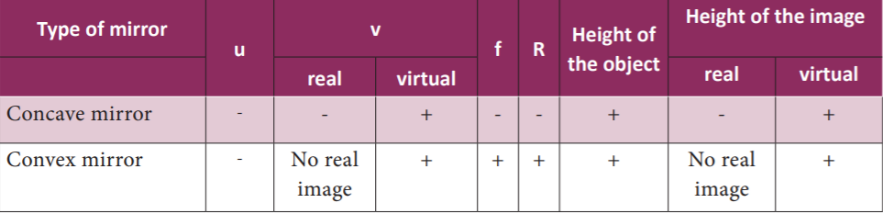
19. According to mirror equation, what is 1/f?
- u/v
- v/u
- 1/u + 1/v
- 1/u – 1/v
Explanation
The expression relating the distance of the object (u), distance of the image (v) and the focal length (f) of a spherical mirror is called the mirror equation. It is given as:
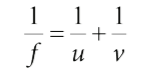
20. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Magnification can be defined as the ratio of the height of the image (hi) to the height of the object (ho).
- A negative sign in the value of magnification indicates that the image is virtual
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Magnification produced by a spherical mirror gives how many times the image of an object is magnified with respect to the object size. It can be defined as the ratio of the height of the image (hi) to the height of the object (ho). A negative sign in the value of magnification indicates that the image is real. A positive sign in the value of magnification indicates that the image is virtual.
21. In which of the following Concave mirrors are used?
- Dentist’s head mirror
- Make-up mirror
- head lights in vehicles
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
In dentist’s head mirror, a parallel beam of light is made to fall on the concave mirror. This mirror focuses the light beam on a small area of the body (such as teeth, throat etc.). When a makeup mirror is held near the face, an upright and magnified image is seen. Here, our face will be seen magnified (concave mirror is used). Concave mirrors are also used as reflectors in torches, head lights in vehicles and search lights to get powerful beams of light. Large concave mirrors are used in solar heater.
22. Which of the following is correct about image formed by Concave mirror?
- Enlarged
- Diminished
- Inverted
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Stellar objects are at an infinite distance. Therefore, the image formed by a concave mirror would be diminished, and inverted. Yet, astronomical telescopes use concave mirrors.
23. Assertion (A): Convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors in vehicles.
Reason (R): When the vehicles are moving away from the driver, then image size decreases.
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
Convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors in vehicles. It always forms a virtual, erect, small-sized image of the object. As the vehicles approach the driver from behind, the size of the image increases. When the vehicles are moving away from the driver, then image size decreases.
24. Which of the following mirror is used in acute bends of narrow roads?
- Concave mirror
- Convex mirror
- Plane mirror
- None
Explanation
Convex mirrors are installed on public roads as traffic safety device. They are used in acute bends of narrow roads such as hairpin bends in mountain passes where direct view of oncoming vehicles is restricted. It is also used in blind spots in shops.
25. A car is fitted with a convex mirror of focal length 20 cm. Another car is 6 m away from the first
car. Find the position of the second car as seen in the mirror of the first?
- 19.35 cm
- 19.35 m
- 6.45 cm
- 5.16 cm
Explanation

26. Who first estimated the speed of light by observing one of the twelve moons of the planet Jupiter?
- Armand Fizeau
- Galileo Galilee
- Ole Roemer
- Landsteiner
Explanation
In early seventeenth century, the Italian scientist Galileo Galilee (1564‒1642) tried to measure the speed of light. In 1665, the Danish astronomer Ole Roemer first estimated the speed of light by observing one of the twelve moons of the planet Jupiter. He estimated the speed of light to be about 220,000 km per second. In 1849, the first land-based estimate was made by Armand Fizeau. Today the speed of light in vacuum is known to be almost exactly 300,000 km per second.
27. Assertion (A): Light rays get deviated from their original path while entering from one transparent medium to another medium of different optical density.
Reason (R): This deviation (change in direction) in the path of light is due to the change in velocity of light in the different medium.
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
The bending of light rays when they pass obliquely from one medium to another medium is called refraction of light. Light rays get deviated from their original path while entering from one transparent medium to another medium of different optical density. This deviation (change in direction) in the path of light is due to the change in velocity of light in the different medium.
28. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Velocity of light is less in a rarer medium
- Velocity of light is more in a denser medium
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The velocity of light depends on the nature of the medium in which it travels. Velocity of light is more in a rarer medium (low optical density) than in a denser medium (high optical density).
29. Match the following:
- Ray of light travels from optically rarer 1. Goes without any deviation
medium to optically denser medium
- Ray of light travels from an optically denser 2. Bends away from the normal
medium to an optically rarer medium
- Ray of light incident normally on a 3. Bends towards the normal
denser medium
- 2, 1, 3
- 3, 2, 1
- 2, 1, 3
- 1, 3, 2
Explanation
When a ray of light travels from optically rarer medium to optically denser medium, it bends towards the normal. When a ray of light travels from an optically denser medium to an optically rarer medium it bends away from the normal. A ray of light incident normally on a denser medium, goes without any deviation.
30. What is the unit of refractive index?
- Lumen
- Candela
- Parsec
- No unit
Explanation
The refractive index has no unit as it is the ratio of two similar quantities. The refractive index of a medium is also defined in terms of speed of light in different media.
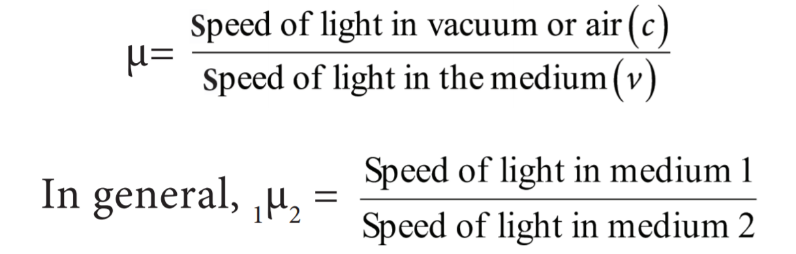
31. Which of the following statement about snell’s law is correct?
- The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant for a light of given colour.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Laws of refraction, also known as Snell’s law of refraction are given below as:
- The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant for a light of given colour and for the given pair of media.
32. The speed of light in air is 3 × 108 m/s and in glass it is 2 × 108 m/s. What is the refractive
index of glass?
- 0.108
- 1.9
- 1.5
- 1.8
Explanation
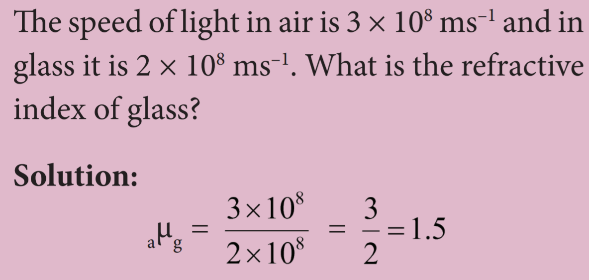
33. Light travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium. The angles of incidence and refraction are respectively 45° and 30°. Calculate the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium?
- 1
- 1.732
- 1.414
- 0.5
Explanation

34. Which of the following statement is correct?
- When light travels from denser medium into a rarer medium, it gets refracted away from the normal
- The angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is 90º is called the critical angle.
- When the angle of incidence exceeds the value of critical angle, the refracted ray is not possible.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
When light travels from denser medium into a rarer medium, it gets refracted away from the normal. While the angle of incidence in the denser medium increases the angle of refraction also increases and it reaches a maximum value of r = 90º for a particular value. This angle of incidence is called critical angle. The angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is 90º is called the critical angle. At this angle, the refracted ray grazes the surface of separation between the two media. When the angle of incidence exceeds the value of critical angle, the refracted ray is not possible. Since r > 90º the ray is totally reflected back to the same medium. This is called as total internal reflection.
35. Which of the following are the conditions required for Total internal reflection to take place?
- Light must travel from denser medium to rarer medium
- Light must be intense.
- The angle of incidence inside the denser medium must be greater than that of the critical angle
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
In order to achieve Total Internal Reflection following conditions must be met:
- Light must travel from denser medium to rarer medium. (Example: From water to air).
- The angle of incidence inside the denser medium must be greater than that of the critical angle
36. Which of the following are the effects of Total Internal Reflection?
- Spectacular brilliance of diamonds
- Twinkling of stars
- Mirage
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Mirage is an effect of Total Internal Reflection. On hot summer days, patch of water may be on the road. This is an illusion. In summer, the air near the ground becomes hotter than the air at higher levels. Hotter air is less dense, and has smaller refractive index than the cooler air. Thus, a ray of light bends away from the normal and undergoes total internal reflection. Total internal reflection is the main cause for the spectacular brilliance of diamonds and twinkling of stars.
37. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Optical fibres are bundles of high-quality composite glass/quartz fibres
- The refractive index of the material of the cladding is higher than that of the core
- When a signal in the form of light is directed at one end of the fibre at a suitable angle, it undergoes repeated total internal reflection along the length of the fibre and finally comes out at the other end.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Optical fibres are bundles of high-quality composite glass/quartz fibres. Each fibre consists of a core and cladding. The refractive index of the material of the core is higher than that of the cladding. Optical fibres work on the phenomenon of total internal reflection. When a signal in the form of light is directed at one end of the fibre at a suitable angle, it undergoes repeated total internal reflection along the length of the fibre and finally comes out at the other end.
38. Which of the following are the uses of Optical fibres?
- Transmitting Audio
- Transmitting Video
- Perform surgery
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Optical fibres are extensively used for transmitting audio and video signals through long distances. Moreover, due to their flexible nature, optical fibres enable physicians to look and work inside the body through tiny incisions without having to perform surgery.
39. _______ is regarded as the Father of Fibre Optics.
- Einstein
- Newton
- Armstrong
- Narinder Kapany
Explanation
Optical fibres are bundles of high-quality composite glass/quartz fibres. An Indian-born physicist Narinder Kapany is regarded as the Father of Fibre Optics.
40. Match the following
- Pole 1. diameter of the circular rim of the mirror
- Radius of curvature 2. midpoint of the spherical mirror
- Aperture 3. radius of the hollow sphere of which the spherical mirror
forms a part
- Principal axis 4. normal to the centre of the mirror
- 2, 1, 4, 3
- 2, 1, 3, 4
- 2, 3, 1, 4
- 1, 4, 2, 3
Explanation

9th Science Lesson 7 Questions in English
7] Heat
1. Which of the following are the sources of heat?
- Sun
- Combustion
- Friction
- 1, 2
- 2, 3
- 1, 2, 3
- 1, 3
Explanation
Sources of heat
- Sun
- Combustion (Burning)
- Friction
- Electricity
2. Which of the following statement is correct?
- We cannot generate heat by rubbing two surfaces of some substances.
- In the past people used to rub two stones together to light fire.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
We can generate heat by rubbing two surfaces of some substances. In the past people used to rub two stones together to light fire.
3. Which of the following is correct?
- When electric current flows through a conductor, heat energy is produced.
- The water heater, iron box, electric kettle etc., work on the principle of electromagnetic induction
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
When electric current flows through a conductor, heat energy is produced. The water heater, iron box, electric kettle etc., work on this principle.
4. Which of the following is the property of heat?
- Heat is not a matter.
- It does occupy space
- It has no weight
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- 1, 2, 3
- 1, 2
Explanation
Heat is not a matter. It doesn’t occupy space. It has no weight. Like light, sound and electricity, heat is a form of energy.
5. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Molecules in objects are constantly vibrating or moving inside objects.
- When we heat the object this vibration and movement of molecules increases and temperature of the object also increases.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Molecules in objects are constantly vibrating or moving inside objects. We cannot see that movement with our naked eye. When we heat the object this vibration and movement of molecules increases and temperature of the object also increases.
6. Which of the following is the unit of heat?
- Joule
- Calorie
- Farad
- 1, 2
- 1, 2, 3
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
Explanation
Heat is the total kinetic energy of constituent particles of objects. SI Unit of Heat is joule. The unit calorie is also used.
7. What is the SI unit of heat?
- Joule
- Calorie
- Kelvin
- Fahrenheit
Explanation
Heat is the total kinetic energy of constituent particles of objects. SI Unit of Heat is joule. The unit calorie is also used.
8. Heat is the total_____ energy of constituent particles of objects.
- Mechanical
- Kinetic
- Potential
- All the above
Explanation
Heat is the total kinetic energy of constituent particles of objects. SI Unit of Heat is joule. The unit calorie is also used.
9.______ are used to measure temperature accurately and quantitatively
- Barometer
- Thermometer
- Dynamometer
- Ammeter
Explanation
Measuring temperature by touching is not correct. Thermometers are used to measure temperature accurately and quantitatively.
10. The measurement of warmness or coldness of a substance is known as its______
- Heat
- Coldness
- Temperature
- All the above
Explanation
The measurement of warmness or coldness of a substance is known as its Temperature. SI unit of temperature is kelvin. Celsius and Fahrenheit are the other units used. Celsius is called as Centigrade as well.
11. What is the SI unit of Temperature?
- Fahrenheit
- Celsius
- Kelvin
- Centigrade
Explanation
SI unit of temperature is kelvin. Celsius and Fahrenheit are the other units used. Celsius is called as Centigrade as well.
12. Which of the following are the units of temperature?
- Fahrenheit
- Celsius
- Kelvin
- 1, 2
- 1, 2, 3
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
Explanation
SI unit of temperature is kelvin. Celsius and Fahrenheit are the other units used. Celsius is called as Centigrade as well.
13. Which of the following statement is correct?
- SI unit of temperature is Fahrenheit
- Temperature determines the direction of flow of heat when two bodies are not in contact.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
SI unit of temperature is kelvin. Celsius and Fahrenheit are the other units used. Celsius is called as Centigrade as well. It determines the direction of flow of heat when two bodies are placed in contact.
14. Water boils at____ o C.
- 0
- 100
- 30
- 45
Explanation
Normally, the room temperature of water is approximately 30o C. When we heat water, its temperature raises and it boils at 100oC. If we cool the water, it freezes at 0o C.
15. At what temperature freezes?
- 20o C
- 30oC
- 0o C
- 100o C
Explanation
Normally, the room temperature of water is approximately 30o C. When we heat water, its temperature raises and it boils at 100o C. If we cool the water, it freezes at 0o C.
16. Our normal body temperature is______
- 37o C
- 30o C
- 108o C
- 102o C
Explanation
The minus sign (–) is used when the temperature falls below the freezing point of water, which is 0o C. If water becomes ice at 0o C, you can imagine how cold – 89o C would be. Our normal body temperature is 37o C. Our body feels cool if the air temperature is around 15 to 20 degree Celsius.
17. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The minus sign (–) is used when the temperature falls below the freezing point of water, which is 0o C.
- The thermometer should not touch the vessel in which the water is being heated. Otherwise the thermometer will be broken at high temperature.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The thermometer should not touch the vessel in which the water is being heated. Otherwise the thermometer will be broken at high temperature. The minus sign (–) is used when the temperature falls below the freezing point of water, which is 0o C. If water becomes ice at 0o C, you can imagine how cold – 89o C would be. Our normal body temperature is 37o C. Our body feels cool if the air temperature is around 15 to 20 degree Celsius.
18. Our body feels cool if the air temperature is around____ degree Celsius.
- 15 to 20
- 15 to 25
- 5 to 15
- 10 to 17
Explanation
The minus sign (–) is used when the temperature falls below the freezing point of water, which is 0o C. If water becomes ice at 0o C, you can imagine how cold – 89o C would be. Our normal body temperature is 37o C. Our body feels cool if the air temperature is around 15 to 20 degree Celsius.
19. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Heat and temperature are the same thing
- Heat measures the total Kinetic Energy of the molecules in the substance.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Heat and temperature are not the same thing, they in fact mean two different things. Heat measures the total Kinetic Energy of the molecules in the substance.
20. ________ is related to how fast the atoms or molecules move or vibrate within the substance
- Temperature
- Heat
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
Temperature is related to how fast the atoms or molecules move or vibrate within the substance.
21.______ measures the average kinetic energy of molecules.
- Heat
- Temperature
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
Temperature measures the average kinetic energy of molecules. Heat measures the total Kinetic Energy of the molecules in the substance.
22. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Heat not only depends on the temperature of the substance but also depends on how many molecules are there in the object
- Temperature is related to how fast the atoms or molecules move or vibrate within the substance.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Temperature is related to how fast the atoms or molecules move or vibrate within the substance. Heat not only depends on the temperature of the substance but also depends on how many molecules are there in the object.
23. Total heat is measured by_____
- Kelvin
- Centigrade
- Calorie
- None
Explanation
Total heat is measured by calorie, the amount of heat needed to raise one gram of water by one degree centigrade.
24. Water ‘flows’ when there is a difference in the______ in different places
- ‘levels’ of water
- Temperature
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
Water ‘flows’ when there is a difference in the ‘levels’ of water in different places. It does not matter if there is more water in one place or another.
25. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Water ‘flows’ when there is a difference in the ‘levels’ of water in different places. It does not matter if there is more water in one place or another.
- Water from a puddle can flow into a reservoir or the other way around.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Water ‘flows’ when there is a difference in the ‘levels’ of water in different places. It does not matter if there is more water in one place or another. Water from a puddle can fl ow into a reservoir or the other way around.
26. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The ‘temperature’ of an object is like the water level – it determines the direction in which ‘heat’ will flow.
- Heat energy flows from higher temperature to lower temperature.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The ‘temperature’ of an object is like the water level – it determines the direction in which ‘heat’ will flow. Heat energy flows from higher temperature to lower temperature.
27. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Two objects are said to be in thermal contact if they can exchange heat energy. T
- Thermal equilibrium exists when two objects in thermal contact no longer affect each other’s temperature.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Two objects are said to be in thermal contact if they can exchange heat energy. Thermal equilibrium exists when two objects in thermal contact no longer affect each other’s temperature.
28. Most substances____ when heated
- Expand
- Contract
- First expand then contract
- None
Explanation
Most substances expand when heated and contract when cooled. The change in length / area or volume (due to contraction / expansion) is directly related to temperature change.
29. Substance_____ when Cooled
- Expand
- Contract
- First expand then Contract
- None
Explanation
Most substances expand when heated and contract when cooled. The change in length / area or volume (due to contraction / expansion) is directly related to temperature change.
30. Which of the following is directly related to temperature change?
- change in length
- change in area
- change in volume
- 1, 2
- 1, 2, 3
- 2, 3
- None
Explanation
Most substances expand when heated and contract when cooled. The change in length / area or volume (due to contraction / expansion) is directly related to temperature change.
31. The expansion of a substance on heating is called, the thermal____ of that substance.
- Thermal expansion
- Thermal contraction
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
The expansion of a substance on heating is called, the thermal expansion of that substance.
32. When solid is heated it expands in______
- All directions
- Opposite to the heating side
- On the side of heating
- None
Explanation
A solid has a definite shape, so when a solid is heated, it expands in all directions i.e., in length, area and volume, all increase on heating.
33. The expansion in length is called_____ expansion
- Linear
- Rectilinear
- Cubical
- Vertical
Explanation
The expansion in length is called linear expansion and the expansion in volume is called cubical expansion.
34. The expansion in volume is called____ expansion.
- Linear
- Cubical
- Vertical
- None
Explanation
The expansion in length is called linear expansion and the expansion in volume is called cubical expansion.
35. Why is a small gap left between two lengths of railway lines?
- To avoid expansion of track during summer
- To avoid contraction of track during summer
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
A small gap is left between two lengths of the railway line to avoid the track resentment due to the heat expansion of metal.
36. The diameter of the iron ring is___ that of the wooden wheel.
- Slightly less than
- Slightly greater than
- Equal
- None
Explanation
The diameter of the iron ring is slightly less than that of the wooden wheel. Therefore, it cannot be easily slipped on from the rim of wooden wheel.
37.Which of the following statement is correct?
- The iron ring is, therefore, first heated to a higher temperature so that it expands in size and the hot ring is then easily slipped over to the rim of the wooden wheel.
- Cold water is now poured on the iron ring so that it contracts in size and holds the wooden wheel tightly
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The iron ring is, therefore, fi rst heated to a higher temperature so that it expands in size and the hot ring is then easily slipped over to the rim of the wooden wheel. Cold water is now poured on the iron ring so that it contracts in size and holds the wooden wheel tightly.
38. Rivets are used to join____ steel plates together.
- 2
- 4
- 5
- 3
Explanation
Rivets are used to join two steel plates together. Hot rivet is driven through the hole in the plates. One end of the rivet is hammered to form a new rivet head. When cooled, the rivet will contract and hold the two plates tightly together.
39. Which of the following is correct about Rivetting?
- Hot rivet is driven through the hole in the plates.
- One end of the rivet is hammered to form a new rivet head. When cooled, the rivet will contract and hold the two plates tightly together.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Rivets are used to join two steel plates together. Hot rivet is driven through the hole in the plates. One end of the rivet is hammered to form a new rivet head. When cooled, the rivet will contract and hold the two plates tightly together.
40. Glass is a______conductor of heat.
- Good
- Poor
- Initially good then bad
- None
Explanation
Glass is a poor conductor of heat. When hot liquid is poured into the tumbler, the inner surface of the tumbler becomes hot and expands while the outer surface remains at the room temperature and does not expand. Due to this unequal expansion, the tumbler cracks.
41. When hot liquid is poured into the tumbler, the inner surface of the tumbler becomes hot and_____
- Contract
- Expand
- First expand then contract
- None
Explanation
Glass is a poor conductor of heat. When hot liquid is poured into the tumbler, the inner surface of the tumbler becomes hot and expands while the outer surface remains at the room temperature and does not expand. Due to this unequal expansion, the tumbler cracks.
42. Which of the following is incorrect?
- When hot liquid is poured into the tumbler, the inner surface of the tumbler becomes hot and expands while the outer surface remains at the room temperature and does not expand
- Due to this unequal expansion, the tumbler cracks.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Glass is a poor conductor of heat. When hot liquid is poured into the tumbler, the inner surface of the tumbler becomes hot and expands while the outer surface remains at the room temperature and does not expand. Due to this unequal expansion, the tumbler cracks.
43. On cold days Electric wires between electric posts_____
- Sag
- Contract
- Expand
- None
Explanation
Electric wires between electric posts contract on cold days and sag in summers. To solve this problem, we leave wires slack so that they are free to change length
44. In Summer the Electric wires between electric posts_____
- Sag
- Contract
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
Electric wires between electric posts contract on cold days and sag in summers. To solve this problem, we leave wires slack so that they are free to change length.
45. Glassware used in kitchen and laboratory are generally made up of_______
- Borosilicate glass
- pyrex glass
- Carbo-Silicate
- Either a or b
Explanation
Glassware used in kitchen and laboratory are generally made up of Borosilicate glass (pyrex glass). The reason is that the Borosilicate glass do not expand much on being heated and therefore they do not crack.
46. Which of the following do not expand much on being heated?
- Borosilicate glass
- Normal glass
- pyrex glass
- Either a or c
Explanation
Glassware used in kitchen and laboratory are generally made up of Borosilicate glass (pyrex glass). The reason is that the Borosilicate glass do not expand much on being heated and therefore they do not crack.
47.______calorie heat energy is needed to raise the temperature of the water from 30o C to 31o C.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Explanation
One calorie heat energy is needed to raise the temperature of the water from 30o C to 31o C.
48. Total Kinetic Energy of molecules: Heat :: Average Kinetic Energy : __________
- Temperature
- Kinetic Energy
- Potential Energy
- Heat
Explanation
Temperature measures the average kinetic energy of molecules. Heat measures the total Kinetic Energy of the molecules in the substance.
9th Science Lesson 8 Questions in English
8] Sound
1. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding sound?
- Sound is a form of energy which produces sensation of hearing in our ears
- All sounds are produced by vibrations of substances
- Human ear can hear all range of frequency of sound
- The vibrations travel as disturbances in a medium and reach our ears as sound
Explanation
Human ear can hear only a particular range of frequency of sound that too with a certain range of energy. We are not able to hear sound clearly if it is below certain intensity. The quality of sound also differs from one another.
2. Which among the following medium does sound wave propagate?
- Air
- Steel
- Water
- All the above
Explanation
Sound needs a material medium like air, water, steel etc., for its propagation. It cannot travel through vacuum.
3. Which among the following experiment demonstrate Sound needs a medium for propagation?
- Light – sound experiment
- Bell – jar experiment
- Wave – light experiment
- All the above
Explanation
An electric bell and an airtight glass jar are taken. The electric bell is suspended inside the airtight jar. The jar is connected to a vacuum pump. If the bell is made to ring, we will be able to hear the sound of the bell. Now, when the jar is evacuated with the vacuum pump, the air in the jar is pumped out gradually and the sound becomes feebler and feebler. We will not hear any sound, if the air is fully removed.
4. Which among the following statement is correct
- Sound moves from the point of generation to the ear of the listener through a medium. When an object vibrates, it sets the particles of the medium around to vibrate. But the vibrating particles do not travel all the way from the vibrating object to the ear.
- A particle of the medium in contact with the vibrating object is displaced from its equilibrium position. It then exerts a force on an adjacent particle. As a result of which the adjacent particle gets displaced from its position of rest. After displacing the adjacent particle, the first particle comes back to its original position.
- This process continues in the medium till the sound reaches our ears. It is to be noted that both the disturbance created by a source of sound and the particles of the medium travels through the medium. All the particles of the medium carry themselves with a small to and fro motion called vibration which enables the disturbance to be carried forward.
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
Explanation
This process continues in the medium till the sound reaches our ears. It is to be noted that only the disturbance created by a source of sound travels through the medium not the particles of the medium. All the particles of the medium restrict themselves with only a small to and fro motion called vibration which enables the disturbance to be carried forward.
5. The sound disturbance which is carried forward in a medium is called _________
- Particle
- Alpha
- Wave
- Pitch
Explanation
The sound disturbance which is carried forward in a medium is called Wave.
6. The waves that propagates with compressions and rarefactions are _______
- Longitudinal wave
- Latitudinal wave
- Both longitudinal wave
- Isolated wave
Explanation
The waves that propagates with compressions and rarefactions are called longitudinal waves. In longitudinal waves the particles of the medium move to and fro along the direction of propagation of the wave.
7. Which among the following are the regions of low pressure where particles are spread apart?
- Rarefaction
- Compression
- Convection
- Conjunction
Explanation
Sound also is a longitudinal wave. Sound can travel only when there are particles which can be compressed and rarefied. Compressions are the regions where particles are crowded together. Rarefactions are the regions of low pressure where particles are spread apart. A sound wave is an example of a longitudinal mechanical wave.
8. Which among the following characteristic does not describe a sound wave?
- Time period
- Wavelength
- Amplitude
- Temperature
Explanation
A sound wave can be described completely by five characteristics namely amplitude, frequency, time period, wavelength and velocity or speed.
9. The SI unit of velocity of sound is ________
- m s
- m s-1
- m s-2
- m s2
Explanation
The SI unit of velocity of sound is m s-1.
10. Which among the following is the SI unit of time period?
- m/s
- s
- m s
- m s2
Explanation
The time required to produce one complete vibration (wave or cycle) is called time period of the wave. It is denoted as T. The SI unit of time period is second (s). Frequency and time period are reciprocal to each other (T = 1 / n).
11. The distance travelled by the sound wave in one second is called ____
- Wavelength
- Time Period
- Velocity
- Frequency
Explanation
The distance travelled by the sound wave in one second is called velocity of the sound.
12. The minimum distance in which a sound wave repeats itself is called its _____
- Amplitude
- Wavelength
- Frequency
- Speed
Explanation
The minimum distance in which a sound wave repeats itself is called its wavelength. In a sound wave, the distance between the centres of two consecutive compressions or two consecutive rarefactions is also called wavelength.
13. The SI unit of wavelength is _____
- m
- m s
- m s-1
- s
Explanation
The wavelength is usually denoted as λ (Greek letter, lambda). The SI unit of wavelength is metre (m).
14. The number of vibrations (complete waves or cycles) produced in one second is called ___
- Amplitude
- Frequency
- Module
- Speed
Explanation
The number of vibrations (complete waves or cycles) produced in one second is called frequency of the wave. It is denoted as n.
15. The SI unit of frequency is ____
- Hertz
- Joule
- Newton
- Pascal
Explanation
The SI unit of frequency is s-1 (or) hertz (Hz).
16. The maximum displacement of the particles of the medium from their original undisturbed positions, when a wave passes through the medium is called _____
- Wavelength
- Frequency
- Amplitude
- Speed
Explanation
The maximum displacement of the particles of the medium from their original undisturbed positions, when a wave passes through the medium is called amplitude of the wave. If the vibration of a particle has large amplitude, the sound will be loud and if the vibration has small amplitude, the sound will be soft.
17. The SI unit of Amplitude is ______
- m
- s
- s-1
- m-1
Explanation
Amplitude is denoted as A. Its SI unit is meter (m).
18. What is the frequency up to which human ear can hear?
- 10 Hz to 10,000 Hz
- 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
- 10Hz to 20,000 Hz
- 15Hz to 25,000 Hz
Explanation
Human ear can hear sound of frequency from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Sound with frequency less than 20 Hz is called infrasonic sound. Sound with frequency greater than 20,000 Hz is called ultrasonic sound. Human beings cannot hear infrasonic and ultrasonic sounds.
19. What are the factors that can distinguish sound from one another in terms of the how many factors?
- Loudness
- Pitch
- Timber
- All the above
Explanation
Sounds can be distinguished from one another in terms of the following three different factors. 1. Loudness 2. Pitch 3. Timbre (or quality).
20. Which is one of the characteristics of sound by which we can distinguish whether a sound is shrill or base?
- Loudness
- Intensity
- Pitch
- Timbre
Explanation
Pitch is one of the characteristics of sound by which we can distinguish whether a sound is shrill or base. High pitch sound is shrill and low pitch sound is flat. Two music sounds produced by the same instrument with same amplitude, will differ when their vibrations are of different frequencies.
21. A sound of single frequency is called ____
- Tone
- Note
- Chorus
- All the above
Explanation
Timbre is the characteristic which distinguishes two sounds of same loudness and pitch emitted by two different instruments. A sound of single frequency is called a tone and a collection of tones is called a note. Timbre is then a general term for the distinguishable characteristics of a tone.
22. Which among the following statement is correct?
- Loudness is a quantity by virtue of which a sound can be distinguished from another one, both having the same frequency. Loudness or softness of sound depends on the amplitude of the wave.
- If we strike a table lightly, we hear a soft sound because we produce a sound wave of less amplitude. If we hit the table hard, we hear a louder sound. Loud sound can travel a longer distance as loudness is associated with higher energy. A sound wave spreads out from its source. As it moves away from the source its amplitude decreases and thus its loudness decreases
- The loudness of a sound depends on the intensity of sound wave. Intensity is defined as the amount of energy crossing per unit area per unit time parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
The loudness of a sound depends on the intensity of sound wave. Intensity is defined as the amount of energy crossing per unit area per unit time perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
23. Which among the following equation defines speed of sound?
- Distance × Time
- Distance / Time
- Time / Distance
- None of the above
Explanation
The speed of sound is defined as the distance travelled by a sound wave per unit time as it propagates through an elastic medium.
Speed (v) = Distance / Time.
24. If the distance travelled by one wave is taken as one wavelength (λ), and the time taken for this propagation is one time period (T), then speed is ___
- v = T / λ
- v = λ / T
- v = T λ
- v = 1 / λ T
Explanation
If the distance traveled by one wave is taken as one wavelength (λ), and the time taken for this propagation is one time period (T), then
Speed (v) = One wavelength (λ) / One time period (T) (or) v = λ / T
As, T = 1 n, the speed (v) of sound is also written as, v = n λ.
25. A sound wave has a frequency of 2 kHz and wavelength of 15 cm. How much time will it take to travel 1.5 km?
- t = 10 s
- t = 5 s
- t = 20 s
- t = 15 s
Explanation
Speed, v = n λ
Here, n = 2 kHz = 2000Hz
λ = 15 cm = 0.15 m
v = 0.15 × 2000 = 300 m s-1
Time (t) = Distance (d) / Velocity (v)
t = 1500 300 = 5 s
The sound will take 5 s to travel a distance of 1.5 km.
26. Which among the following statement is correct
- Sound travels with a speed which is much less than the speed of light
- Sound travels with a speed which is much more than the speed of light
- Both sound and light travel at the same speed
- None of the above
Explanation
Sound propagates through a medium at a finite speed. The sound of thunder is heard a little later than the flash of light is seen. So, we can make out that sound travels with a speed which is much less than the speed of light. The speed of sound depends on the properties of the medium through which it travels.
27. Which among the following statement is correct
- The speed of sound is less in gaseous medium compared to solid medium.
- The speed of sound is more in gaseous medium compared to solid medium.
- In any medium the speed of sound increases if we decrease the temperature of the medium.
- In any medium the speed of sound increases if we increase the temperature of the medium.
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- Both 1 and 4
- Both 2 and 4
Explanation
The speed of sound is less in gaseous medium compared to solid medium. In any medium the speed of sound increases if we increase the temperature of the medium. For example, the speed of sound in air is 330 ms-1 at 0 °C and 340 ms-1 at 25 °C. The speed of sound at a particular temperature.
28. When the speed of any object exceeds the speed of sound in air (330 ms-1) it is said to be travelling at what?
- Sonic speed
- Supersonic speed
- Mega sonic
- Sonic mass
Explanation
When the speed of any object exceeds the speed of sound in air (330 ms-1) it is said to be travelling at supersonic speed. Bullets, jet, aircrafts etc., can travel at supersonic speeds.
29. When an object travels at a speed higher than that of sound in air, it produces shock waves. The air pressure variations associated with this type of shock waves produce a very sharp and loud sound called ________
- Sonic mass
- Sonic velocity
- Sonic crust
- Sonic boom
Explanation
When an object travels at a speed higher than that of sound in air, it produces shock waves. These shock waves carry a large amount of energy. The air pressure variations associated with this type of shock waves produce a very sharp and loud sound called the ‘sonic boom’. The shock waves produced by an aircraft have energy to shatter glass and even damage buildings.
30. Which among the following factor the intensity of sound heard at a place doesn’t depend on?
- Amplitude of the source
- Surface area of the source
- Density of the medium
- Temperature of the source
Explanation
The intensity of sound heard at a place depends on the following five factors. I) Amplitude of the source. ii) Distance of the observer from the source. iii) Surface area of the source. iv) Density of the medium and v) Frequency of the source.
31. Which among the following statement is correct
- Sound travels about 5 times faster in water than in air. Since the speed of sound in sea water is very large (being about 1530ms-1 which is more than 5500km/h-1), two whales in the sea which are even hundreds of kilometres away can talk to each other very easily through the sea water.
- Sound bounces off a surface of solid or a liquid medium like a rubber ball that bounces off from a wall. An obstacle of large size which may be polished or rough is needed for the reflection of sound waves.
- The laws of reflection are: • The angle in which the sound is incident is greater to the angle in which it is reflected. • Direction of incident sound, the reflected sound and the normal are in the perpendicular plane to each other.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
The laws of reflection are: • The angle in which the sound is incident is equal to the angle in which it is reflected. • Direction of incident sound, the reflected sound and the normal are in the same plane.
32. Which among the following statement is correct
- Megaphones, loud speakers, horns, musical instruments such as nathaswaram, shehnai and trumpets are all designed to send sound in a particular direction without spreading it in all directions. In these instruments, a tube followed by a conical opening reflects sound successively to guide most of the sound waves from the source in the forward direction towards the audience.
- Stethoscope is a medical instrument used for listening to sounds produced in the body. In stethoscopes, these sounds reach doctor’s ears by multiple reflections that happen in the connecting tube.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
33. The sensation of sound persists in our brain for about how many seconds?
- 0.05 s
- 0.1 s
- 1.5 s
- 0.5 s
Explanation
When we shout or clap near a suitable reflecting surface such as a tall building or a mountain, we will hear the same sound again a little later. This sound which we hear is called an echo. The sensation of sound persists in our brain for about 0.1 s. Hence, to hear a distinct echo the time interval between the original sound and the reflected sound must be at least 0.1s.
34. Let us consider the speed of sound to be 340 ms-1 at 25° C. The sound must go to the obstacle and return to the ear of the listener on reflection after 0.1s. The total distance covered by the sound from the point of generation to the reflecting surface and back should be at least what distance?
- 34 m
- 340 m
- 0.34 m
- 3.4 m
Explanation
The total distance covered by the sound from the point of generation to the reflecting surface and back should be at least 340 ms-1 × 0.1 s = 34 m.
Thus, for hearing distinct echoes, the minimum distance of the obstacle from the source of sound must be half of this distance i.e. 17 m. This distance will change with the temperature of air. Echoes may be heard more than once due to successive or multiple reflections. The roaring of thunder is due to the successive reflections of the sound from a number of reflecting surfaces, such as the clouds at different heights and the land.
35. What is the wavelength of a sound wave in air at 20° C with a frequency of 22 MHz?
- 12.13 µm
- 15.64 µm
- 17.27 µm
- 18.26 µm
Explanation
λ = v/n
Here, v = 344 ms-1.
n = 22 MHz = 22 × 106 Hz
λ = 344/22 × 106 = 15.64 × 10-6 m = 15.64 µm.
36. The repeated reflection that results in this persistence of sound is called ____
- Vibration
- Conjunction
- Reverberation
- Bi junction
Explanation
A sound created in a big hall will persist by repeated reflection from the walls until it is reduced to a value where it is no longer audible. The repeated reflection that results in this persistence of sound is called reverberation.
37. Which among the following sound absorbing material used to reduce reverberation in roof and walls?
- Compressed fibreboard
- Rough plaster
- Draperies
- All the above
Explanation
In an auditorium or big hall excessive reverberation is highly undesirable. To reduce reverberation, the roof and walls of the auditorium are generally covered with sound absorbing materials like compressed fibreboard, flannel cloths, rough plaster and draperies. The seat materials are also selected on the basis of their sound absorbing properties.
38. Which branch of the physics takes the aspects of sound in to account while designing auditoria, opera halls, theatres etc?
- Optics
- Acoustic
- Relativity
- All the above
Explanation
There is a separate branch in physics called acoustics which takes the aspects of sound in to account while designing auditoria, opera halls, theatres etc.
39. Which among the following animals doesn’t use echolocation to identify and locate objects?
- Rats
- Hyena
- Bats
- Dolphins
Explanation
Animals, such as bats, dolphins, rats, whales and oil birds, use echolocation, an ultrasound technique that uses echoes to identify and locate objects. Echolocation allows bats to navigate through dark caves and find insects for food. Dolphins and whales emit a rapid series of underwater clicks in ultrasonic frequencies to locate their prey and navigate through water.
40. A man fires a gun and hears its echo after 5 s. The man then moves 310 m towards the hill and fires his gun again. If he hears the echo after 3 s, calculate the speed of sound?
- 155 ms-1
- 310 ms-1
- 620 ms-1
- 775 ms-1
Explanation
Distance (d) = velocity (v) × time (t)
Distance travelled by sound when gun fires first time, 2d = v × 5 —— (1)
Distance travelled by sound when gun fires second time, 2d – 620 = v × 3 ——– (2)
Rewriting equation (2) as,
2d = (v × 3) + 620 ——- (3)
Equating (1) and (3), 5v = 3v + 620
2v = 620
Velocity of sound, v = 310 ms-1
41. Ultrasonic sound is the term used for sound waves with frequencies greater than what?
- 10,000 Hz
- 15,000 Hz
- 20,000 Hz
- 25,000 Hz
Explanation
Ultrasonic sound is the term used for sound waves with frequencies greater than 20,000Hz. These waves cannot be heard by the human ear, but the audible frequency range for other animals includes ultrasound frequencies. For example, dogs can hear ultrasonic sound. Ultrasonic whistles are used in cars to alert deer to oncoming traffic so that they will not leap across the road in front of cars.
42. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- An important use of ultrasound is in examining inner parts of the body. The ultrasonic waves allow different tissues such as organs and bones to be ‘seen’ or distinguished by bouncing of ultrasonic waves by the objects examined.
- The waves are detected, analysed and stored in a computer. A sonogram is an image obtained by the use of reflected ultrasonic waves. It is used as a medical diagnostic tool. Ultrasonic sound is having application in marine surveying also.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The waves are detected, analysed and stored in a computer. An echogram is an image obtained by the use of reflected ultrasonic waves. It is used as a medical diagnostic tool. Ultrasonic sound is having application in marine surveying also.
43. Which among the following statement is correct
- Ultrasounds can be used in cleaning technology. Minute foreign particles can be removed from objects placed in a liquid bath through which ultrasound is passed. Ultrasounds can also be used to detect cracks and flaws in metal blocks.
- Ultrasonic waves are made to reflect from various parts of the heart and form the image of the heart. This technique is called ‘sonogram’. Ultrasound may be employed to break small ‘stones’ formed in the kidney into fine grains. These grains later get flushed out with urine.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Ultrasonic waves are made to reflect from various parts of the heart and form the image of the heart. This technique is called ‘echo cardiography’. Ultrasound may be employed to break small ‘stones’ formed in the kidney into fine grains. These grains later get flushed out with urine.
44. Which is a device that uses ultrasonic waves to measure the distance, direction and speed of underwater objects?
- Quadrat
- Megger
- Sonar
- Load cell
Explanation
SONAR stands for Sound Navigation and Ranging. Sonar is a device that uses ultrasonic waves to measure the distance, direction and speed of underwater objects.
45. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- Sonar consists of a transmitter and a detector and is installed at the bottom of boats and ships. The transmitter produces and transmits ultrasonic waves. These waves travel through water and after striking the object on the seabed, get reflected back and are sensed by the detector.
- The detector converts the ultrasonic waves into electrical signals which are appropriately interpreted. The distance of the object that reflected the sound wave can be calculated by knowing the speed of sound in water and the time interval between transmission and reception of the ultrasound.
- Let the time interval between transmission and reception of ultrasound signal be ‘t’. Then, the speed of sound through sea water is v /t = 2d. This method is called echo-ranging. Sonar technique is used to determine the depth of the sea and to locate underwater hills, valleys, submarine, icebergs etc.
- Only 2
- Only 3
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
Explanation
Let the time interval between transmission and reception of ultrasound signal be ‘t’. Then, the speed of sound through sea water is 2d /t = v. This method is called echo-ranging. Sonar technique is used to determine the depth of the sea and to locate underwater hills, valleys, submarine, icebergs etc.
46. A ship sends out ultrasound that returns from the seabed and is detected after 3.42 s. If the speed of ultrasound through sea water is 1531ms-1, what is the distance of the seabed from the ship?
- 10476 m
- 5236 m
- 2618 m
- 1309 m
Explanation
We know, distance = speed × time
2d = speed of ultrasound × time
2d = 1531 × 3.42
∴ d = 5236 / 2 = 2618 m
Thus, the distance of the seabed from the ship is 2618 m or 2.618 km.
47. Which among the following statement is correct
- The electrocardiogram (ECG) is one of the simplest and oldest cardiac investigations available. It can provide a wealth of useful information and remains an essential part of the assessment of cardiac patients. In ECG, the sound variation produced by heart is converted into chemical signals.
- Thus, an ECG is simply a representation of the chemical activity of the heart muscle as it changes with time. Usually it is printed on paper for easy analysis. The sum of this chemical activity, when amplified and recorded for just a few seconds is known as an ECG.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is one of the simplest and oldest cardiac investigations available. It can provide a wealth of useful information and remains an essential part of the assessment of cardiac patients. Thus, an ECG is simply a representation of the electrical activity of the heart muscle as it changes with time. Usually it is printed on paper for easy analysis. The sum of this electrical activity, when amplified and recorded for just a few seconds is known as an ECG.
48. The outer ear is called ________
- Pinna
- Tympanic
- Cochlea
- Jaw
Explanation
The outer ear is called ‘pinna’. It collects the sound from the surroundings. The collected sound passes through the auditory canal.
49. Ear allows us to convert pressure variations in air with audible frequencies into what signals that travel to the brain via the auditory nerve?
- Chemical signal
- Electric signal
- Mechanical signal
- None of the above
Explanation
We are able to hear with the help of an extremely sensitive device called the ear. It allows us to convert pressure variations in air with audible frequencies into electric signals that travel to the brain via the auditory nerve.
50. Which among the following is located at the end of the ear?
- Helix
- Earlobe
- Eardrum
- All the above
Explanation
At the end of the ear is eardrum or tympanic membrane. When a compression of the medium reaches the eardrum the pressure on the outside of the membrane increases and forces the eardrum inward. Similarly, the eardrum moves outward when a rarefaction reaches it. In this way the eardrum vibrates.
51. Which among the following is not the bone in the middle ear which amplifies the vibration?
- Hammer
- Phalange
- Anvil
- Stirrup
Explanation
The vibrations are amplified several times by three bones (the hammer, anvil and stirrup) in the middle ear. The middle ear transmits the amplified pressure variations received from the sound wave to the inner ear.
52. In the inner ear, the pressure variations are turned into electrical signals by what?
- Helix
- Earlobe
- Cochlea
- Phalange
Explanation
In the inner ear, the pressure variations are turned into electrical signals by the cochlea. These electrical signals are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve and the brain interrupts them as sound.