9th Std Science Lesson Wise Questions in English – Part 2
9th Science Lesson 9 Questions in English
9] Universe
1. Which Greek astronomer in 2nd century held geocentric model i.e., Earth is the centre of all the objects in the space?
- Ptolemy
- Euclid
- Copernicus
- Kepler
Explanation
In the earlier days, before the invention of astronomical instruments, people thought that Earth is the centre of all the objects in the space. This was known as the geocentric model, held by Greek astronomer Ptolemy (2nd Century), Indian astronomer Aryabhata (5th Century) and many astronomers around the world.
2. Which polish astronomer proposed the heliocentric model (helios = Sun), with Sun at the centre of the solar system?
- Eratosthenes
- Euclid
- Copernicus
- Kepler
Explanation
Later Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus proposed the heliocentric model (helios = Sun), with Sun at the centre of the solar system.
3. Where telescope was invented in 1608, created a revolution in astronomy?
- German
- Japan
- Netherland
- America
Explanation
Invention of the telescope in the Netherlands, in 1608, created a revolution in astronomy.
4. Which among the following statement is correct
- The basic constituent of the universe is luminous matter i.e., galaxies which are really the collection of billions of stars. The universe contains everything that exists including the Earth, planets, stars, space, and galaxies. This includes all matter, energy and even time.
- No one knows how big the universe is. It could be infinitely large. Scientists, however, measure the size of the universe by what they can see. This is called the ‘observable universe’.
- One of the interesting things about the universe is that it is currently expanding. It is growing larger and larger all the time. Not only is it growing larger, but the edge of the universe is expanding at a faster and faster rate. However, most of the universe what we think of is empty space.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
5. All the atoms together only make up around what percent of the universe?
- 4%
- 8%
- 12%
- 18%
Explanation
All the atoms together only make up around four percent of the universe.
6. The majority of the universe consists of something scientists call _____
- Light matter and light energy
- Dark matter and dark energy
- Grey matter and grey energy
- None of the above
Explanation
The majority of the universe consists of something scientists call dark matter and dark energy.
7. Scientists think that the universe began with the start of a massive explosion called ____
- Creation theory
- Steady state
- Big Bang
- Extra dimensional holography
Explanation
Scientists think that the universe began with the start of a massive explosion called the Big Bang.
8. About how many years ago, an explosion occurred and all the matter were ejected in all directions in the form of galaxies?
- 14.1 million years ago
- 13.7 billion years ago
- 15.3 trillion years ago
- 18.3 million years ago
Explanation
According to Big Bang theory, all the matter in the universe was concentrated in a single point of hot dense matter. About 13.7 billion years ago, an explosion occurred and all the matter were ejected in all directions in the form of galaxies.
9. Nearly all of the matter in the universe that we understand is made of what that created in the Big Bang.?
- Nitrogen and oxygen
- Carbon and nitrogen
- Oxygen and helium
- Hydrogen and helium
Explanation
Nearly all of the matter in the universe that we understand is made of hydrogen and helium, the simplest elements, created in the Big Bang.
10. The oxygen, the carbon, calcium, and iron, and silicon are formed in the cores of what?
- Dark matter
- Star
- Earth
- Black hole
Explanation
The oxygen, the carbon, calcium, and iron, and silicon are formed in the cores of stars. The gravity that holds these stars together generally keeps these elements deep inside their interiors. When these stars explode, these fundamental building blocks of planetary systems are liberated throughout the universe.
11. Which is a massive collection of gas, dust, and billions of stars and their solar systems?
- Black hole
- Sun
- Galaxy
- Warm hole
Explanation
Immediately after the Big Bang, clouds of gases began to compress under gravity to form the building blocks of galaxies. A galaxy is a massive collection of gas, dust, and billions of stars and their solar systems.
12. Which among the following statement is correct
- Scientists believe that there are one million (106) galaxies in the observable universe. Galaxies are also in different shapes. Depending on their appearance, galaxies are classified as spiral, elliptical, or circular.
- Galaxies occur alone or in pairs, but they are more often parts of groups, clusters, and super clusters. Galaxies in such groups often interact and even merge together. Our Sun and all the planets in the solar system are in the Milky Way galaxy.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Scientists believe that there are one hundred billion (1011) galaxies in the observable universe. Galaxies are also in different shapes. Depending on their appearance, galaxies are classified as spiral, elliptical, or irregular.
13. Which is our closest neighbouring galaxy?
- Andromeda
- Antenna
- Cigar
- Circinus
Explanation
There are many galaxies besides our Milky Way. Andromeda galaxy is our closest neighbouring galaxy. The Milky Way galaxy is spiral in shape. It is called Milky Way because it appears as a milky band of light in the sky. It is made up of approximately 100 billion stars and its diameter is 1,00,000 light years.
14. Our solar system is how many light years away from the centre of our galaxy?
- 250 light years
- 25000 light years
- 2500 light years
- 25 million light years
Explanation
Our solar system is 25,000 light years away from the centre of our galaxy.
15. How many years does it takes the Sun goes around the centre of the galaxy?
- 25000 years
- 25 million years
- 250 million years
- 2500 million years
Explanation
Just as the Earth goes around the Sun, the Sun goes around the centre of the galaxy and it takes 250 million years to do that.
16. Stars are built by which among the following gases?
- Nitrogen gases
- Sulphur gases
- Carbon gases
- Hydrogen gases
Explanation
Stars are the fundamental building blocks of galaxies. Stars were formed when the galaxies were formed during the Big Bang. Stars produce heat, light, ultraviolet rays, x-rays, and other forms of radiation. They are largely composed of gas and plasma (a superheated state of matter). Stars are built by hydrogen gases.
17. In star, Hydrogen atoms fuse together to form which atoms and in the process they produce large amount of heat?
- Oxygen atoms
- Helium atoms
- Nitrogen atoms
- All the above
Explanation
Hydrogen atoms fuse together to form helium atoms and in the process they produce large amount of heat. In a dark night we can see nearly 3,000 stars with the naked eye. We don’t know how many stars exist. Our universe contains more than 100 billion galaxies, and each of those galaxies may have more than 100 billion stars.
18. The distance of Andromeda, our nearest galaxy is approximately what?
- 2.5 million light year
- 25 million light year
- 250 million light year
- 2500 million light year
Explanation
The distance of Andromeda, our nearest galaxy is approximately 2.5 million light-years. If we move at the speed of the Earth (30 km/s), it would take us 25 billion years to reach it.
19. What colour does hot stars appears?
- Red
- Orange
- Green
- Blue
Explanation
Though the stars appear to be alone, most of the stars exist as pairs. The brightness of a star depends on their intensity and the distance from the Earth. Stars also appear to be in different colours depending on their temperature. Hot stars are white or blue, whereas cooler stars are orange or red in colour. They also occur in many sizes.
20. A group of stars forms an imaginary outline or meaningful pattern on the space, this group of stars is called ________
- Capricornus
- Constellations
- Missoula
- Kalispell
Explanation
A group of stars forms an imaginary outline or meaningful pattern on the space. They represent an animal, mythological person or creature, a god, or an object. This group of stars is called constellations. People in different cultures and countries adopted their own sets of constellation outlines.
21. How many formally accepted constellations are there?
- 22
- 44
- 68
- 88
Explanation
There are 88 formally accepted constellations. Aries, Gemini, Leo, Orion, Scorpius and Cassiopeia are some of the constellations.
22. Which force between sun and celestial bodies keep them revolving around it?
- Frictional force
- Gravitational force
- Tension force
- Thermal force
Explanation
Sun and the celestial bodies which revolve around it form the solar system. It consists of large number of bodies such as planets, comets, asteroids and meteors. The gravitational force of attraction between the Sun and these objects keep them revolving around it.
23. How many quarters of the Sun has hydrogen gas?
- Two
- Three
- Four
- One
Explanation
The Sun is a medium sized star, a very fiery spinning ball of hot gases. Three quarters of the Sun has hydrogen gas and one quarter has helium gas. It is over a million times as big as the Earth.
24. Hydrogen atoms combine together to form helium under enormous pressure. This process, called ______
- Nuclear fusion
- Nuclear fission
- Nuclear convention
- Both nuclear fission and fusion
Explanation
Hydrogen atoms combine or fuse together to form helium under enormous pressure. This process, called nuclear fusion releases enormous amount of energy as light and heat. It is this energy which makes Sun shine and provide heat.
25. Sun is believed to be more than how many years old?
- 4.6 billion
- 7.8 billion
- 9.3 billion
- 14.8 billion
Explanation
Sun is situated at the centre of the solar system. The strong gravitational fields cause other solar matter, mainly planets, asteroids, comets, meteoroids and other debris, to orbit around it. Sun is believed to be more than 4.6 billion years old.
26. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- At the time of the Big Bang, helium gas condensed to form huge clouds, which later concentrated and formed the numerous galaxies. Some of the helium gas was left free and started floating around in our galaxy. With time, due to some changes, this free-floating helium gas concentrated and paved way for the formation of the Sun and solar system.
- Gradually, the Sun and the solar system turned into a slowly spinning molecular cloud, composed of hydrogen and helium along with dust. The cloud started to undergo the process of compression, as a result of its own gravity. Its excessive and high-speed spinning ultimately resulted in its flattening into a giant disc.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
At the time of the Big Bang, hydrogen gas condensed to form huge clouds, which later concentrated and formed the numerous galaxies. Some of the hydrogen gas was left free and started floating around in our galaxy. With time, due to some changes, this free-floating hydrogen gas concentrated and paved way for the formation of the Sun and solar system.
27. A planet revolves around the Sun along a definite curved path which is called _____
- Sphere
- Milky way
- Orbit
- Satellite
Explanation
A planet revolves around the Sun along a definite curved path which is called an orbit. It is elliptical. The time taken by a planet to complete one revolution is called its period of revolution. Besides revolving around the Sun, a planet also rotates on its own axis like a top.
28. Which among the following statement is correct
- The time taken by a planet to complete one rotation is called its period of axis. The period of rotation of the Earth is 23 hours and 56 minutes and so the length of a day on Earth is taken as 24 hours. The planets are spaced unevenly
- The first four planets are relatively close together and close to the Sun. They form the inner solar system. Farther from the Sun is the outer solar system, where the planets are much more spread out. Thus, the distance between Saturn and Uranus is much greater (about 20 times) than the distance between the Earth and the Mars.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The time taken by a planet to complete one rotation is called its period of rotation. The period of rotation of the Earth is 23 hours and 56 minutes and so the length of a day on Earth is taken as 24 hours.
29. Which among the following planet doesn’t come under inner planets of solar system?
- Venus
- Earth
- Jupiter
- Mars
Explanation
The four planets grouped together in the inner solar system are Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. They are called inner planets. They have a surface of solid rock crust and so are called terrestrial or rocky planets. Their insides, surfaces and atmospheres are formed in a similar way and form similar pattern. Our planet, Earth can be taken as a model of the other three planets.
30. The outer planets are also called as ____
- Rocky planets
- Gaseous planets
- Silver planets
- Cold planets
Explanation
The four large planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune spread out in the outer solar system and slowly orbit the Sun are called outer planets. They are made of hydrogen, helium and other gases in huge amounts and have very dense atmosphere. They are known as gas giants and are called gaseous planets. The four outer planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune have rings whereas the four inner planets do not have any rings.
31. The gaseous planet have rings which is actually tiny pieces of rock covered with what?
- Lava
- Dark matter
- Fire
- Ice
Explanation
The gaseous planet has rings which actually tiny pieces of rock covered with ice.
32. Which is a rocky planet nearest to the Sun?
- Mercury
- Venus
- Mars
- Pluto
Explanation
Mercury is a rocky planet nearest to the Sun. It is very hot during day but very cold at night. Mercury can be easily observed thorough telescope than naked eye since it is very faint and small. It always appears in the eastern horizon or western horizon of the sky.
33. Which among the following is known as red planet?
- Venus
- Jupiter
- Mars
- Saturn
Explanation
The first planet outside the orbit of the Earth is Mars. It appears slightly reddish and therefore it is also called the red planet. It has two small natural satellites (Deimos and Phobos).
34. Which among the following planet has the longest summers and winters each lasting 42 years?
- Jupiter
- Uranus
- Mars
- Saturn
Explanation
Uranus is a cold gas giant and it can be seen only with the help of large telescope. It has a greatly tilted axis of rotation. As a result, in its orbital motion it appears to roll on its side. Due to its peculiar tilt, it has the longest summers and winters each lasting 42 years.
35. Which among the following planet is the hottest planet in our solar system?
- Mercury
- Venus
- Saturn
- Mars
Explanation
Venus is a special planet from the Sun, almost the same size as the Earth. It is the hottest planet in our solar system. After our moon, it is the brightest heavenly body in our night sky.
36. Which is called as Giant planet?
- Jupiter
- Uranus
- Saturn
- Earth
Explanation
Jupiter is called as Giant planet. It is the largest of all planets (about 11 times larger and 318 times heavier than Earth).
37. Which planet spins in the opposite direction to all other planets in solar system?
- Saturn
- Uranus
- Venus
- Mars
Explanation
Venus spins in the opposite direction to all other planets. So, unlike Earth, the Sun rises in the west and sets in the east here. Venus can be seen clearly through naked eye. It always appears in the horizon of eastern or western sky.
38. Which among the following planet appear as greenish star?
- Mars
- Uranus
- Saturn
- Neptune
Explanation
Neptune spins in the opposite direction to all other planets. So, unlike Earth, the Sun rises in the west and sets in the east here. Venus can be seen clearly through naked eye. It always appears in the horizon of eastern or western sky.
39. From space, the Earth appears which colour due to the reflection of light from water and land mass on its surface?
- Reddish blue
- Bluish green
- Reddish green
- Brownish blue
Explanation
The Earth where we live is the only planet in the solar system which supports life. Due to its right distance from the Sun it has the right temperature, the presence of water and suitable atmosphere and a blanket of ozone. All these have made continuation of life possible on the Earth. From space, the Earth appears bluish green due to the reflection of light from water and land mass on its surface.
40. Which is the largest moon of our solar system?
- Triton
- Ganymede
- Titan
- Nagato
Explanation
Jupiter has 3 rings and 65 moons. Its moon Ganymede is the largest moon of our solar system.
41. Which is the second biggest and a giant gas planet in the outer solar system?
- Neptune
- Pluto
- Saturn
- Jupiter
Explanation
Saturn Known for its bright shiny rings, Saturn appears yellowish in colour. It is the second biggest and a giant gas planet in the outer solar system.
42. Which is the only moon in the solar system that moves in the opposite direction to the direction in which its planet spins?
- Triton
- Deimos
- Titan
- Nagato
Explanation
Neptune has 13 moons – Triton being the largest. Triton is the only moon in the solar system that moves in the opposite direction to the direction in which its planet spins.
43. Which is the only moon in the solar system with clouds?
- Phobos
- Deimos
- Titan
- Nagato
Explanation
Saturn has at least 60 moons are present – the largest being Titan. Titan is the only moon in the solar system with clouds. Having least density of all (30 times less than Earth), this planet is so light.
44. A broad belt containing about half a million pieces of rocks occupied between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter that were left over when the planets were formed is called as ____
- Comets
- Asteroids
- Satellites
- All the above
Explanation
There is a large gap in between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. This gap is occupied by a broad belt containing about half a million pieces of rocks that were left over when the planets were formed and now revolve around the Sun. These are called asteroids.
45. Which among the following are lumps of dust and ice that revolve around the Sun in highly elliptical orbits?
- Comets
- Meteorites
- Satellites
- Meteors
Explanation
Comets are lumps of dust and ice that revolve around the Sun in highly elliptical orbits. Their period of revolution is very long. When approaching the Sun, a comet vaporizes and forms a head and tail. Some of the biggest comets ever seen had tails 160 million (16 crores) km long. This is more than the distance between the Earth and the Sun.
46. A body moving in an orbit around a planet is called _____
- Meteors
- Meteorites
- Satellite
- Comets
Explanation
A body moving in an orbit around a planet is called satellite. In order to distinguish them from the man-made satellites (called as artificial satellites), they are called as natural satellites or moons. Satellite of the Earth is called Moon (other satellites are written as moon). We can see the Earth’s satellite Moon, because it reflects the light of the Sun.
47. Which among the following statement is correct
- Meteorites are small piece of rocks scattered throughout the solar system. Traveling with high speed, these small pieces come closer to the Earth’s atmosphere and are attracted by the gravitational force of Earth.
- Most of them are burnt up by the heat generated due to friction in the Earth’s atmosphere. They are called meteors. Some of the bigger meteorites may not be burnt completely and they fall on the surface of Earth. These are called meteors.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Meteors are small piece of rocks scattered throughout the solar system. Traveling with high speed, these small pieces come closer to the Earth’s atmosphere and are attracted by the gravitational force of Earth. Most of them are burnt up by the heat generated due to friction in the Earth’s atmosphere. They are called meteors. Some of the bigger meteors may not be burnt completely and they fall on the surface of Earth. These are called meteorites.
48. Which among the following planet doesn’t have natural satellite?
- Mars
- Venus
- Jupiter
- Neptune
Explanation
Satellite moves around the planets due to gravity, and the centripetal force. Among the planets in the solar system all the planets have moons except Mercury and Venus.
49. The time taken by the sun to complete one revolution around the Milky Way is called as ____
- Century year
- Cosmic year
- Solar year
- Inferno year
Explanation
The Sun travelling at a speed of 250 km per second (9 lakh km/h) takes about 225 million years to complete one revolution around the Milky Way. This period is called a cosmic year.
50. Match the following planets with its corresponding moons
- Saturn – 1. Phobos
- Jupiter – 2. Titan
- Mars – 3. Triton
- Neptune – 4. Ganymede
- 2 – 4 – 1 – 3
- 3 – 4 – 2 – 1
- 4 – 1 – 2 – 3
- 1 – 3 – 2 – 4
Explanation
Mars has two small natural satellites (Deimos and Phobos). Jupiter has 3 rings and 65 moons. Its moon Ganymede is the largest moon of our solar system. At least 60 moons are present in Saturn – the largest being Titan. Neptune has 13 moons – Triton being the largest.
51. Which among the following was the first artificial satellite launched in 1956?
- Skylab
- Rohini
- Orion
- Sputnik
Explanation
We saw that there are natural satellites moving around the planets. There will be gravitational force between the planet and satellites. Nowadays many artificial satellites are launched into the Earth’s orbit. The first artificial satellite Sputnik was launched in 1956.
52. Which was the first Indian artificial satellite launched on April 19, 1975?
- Rohini
- Kalpana-1
- Aryabhata
- SARAL
Explanation
India launched its first satellite Aryabhata on April 19, 1975. Artificial satellites are made to revolve in an orbit at a height of few hundred kilometres. At this altitude, the friction due to air is negligible. The satellite is carried by a rocket to the desired height and released horizontally with a high velocity, so that it remains moving in a nearly circular orbit.
53. The horizontal velocity that has to be imparted to a satellite at the determined height so that it makes a circular orbit around the planet is called ____
- Orbital velocity
- Horizontal velocity
- Circular velocity
- Asteroid velocity
Explanation
The horizontal velocity that has to be imparted to a satellite at the determined height so that it makes a circular orbit around the planet is called orbital velocity.
54. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- The orbital velocity of the satellite depends on its altitude above Earth. Nearer the object to the Earth, the faster is the required orbital velocity. At an altitude of 200 kilometres, the required orbital velocity is little more than 27,400 kph. That orbital speed and distance permit the satellite to make one revolution in 24 hours.
- Since Earth also rotates once in 24 hours, a satellite stays in a fixed position relative to a point on Earth’s surface. Because the satellite stays over the same spot all the time, this kind of orbit is called ‘stationary orbit’.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Since Earth also rotates once in 24 hours, a satellite stays in a fixed position relative to a point on Earth’s surface. Because the satellite stays over the same spot all the time, this kind of orbit is called ‘geostationary’.
55. Which among the following formula can be used to calculate orbital velocity?
- v = √ ((R+h)/GM)
- v = √ (GM/(R+h))
- v = (R+h)/GM
- v = GM/(R+h)
Explanation
V = √ (GM/(R+h))
G = Gravitational constant (6.673 × 10–11 Nm2 kg-2)
M = Mass of the Earth (5.972 × 1024 kg)
R = Radius of the Earth (6371 km)
h = Height of the satellite from the surface of the Earth.
56. Which is the condition in which people or objects appear to be weightless?
- Microgravity
- Macrogravity
- Nano gravity
- Neo gravity
Explanation
Microgravity is the condition in which people or objects appear to be weightless. The effects of microgravity can be seen when astronauts and objects float in space. Micro- means very small, so microgravity refers to the condition where gravity ‘seems’ to be very small.
57. Can you calculate the orbital velocity of a satellite orbiting at an altitude of 500 km?
- v = 5818 ms-1
- v = 6813 ms-1
- v = 7613 ms-1
- v = 9724 ms-1
Explanation
G = 6.673 × 10-11 SI units; M = 5.972 × 1024 kg; R = 6371000 m; h = 500000 m
V = √ (GM/(R+h))
= √ ((6.67 × 10-11 × 5.972 × 1024) / (6371000+500000))
= 7613 ms-1 or 7.613 kms-1
58. Time taken by a satellite to complete one revolution round the Earth is called ____
- Satellite period
- Time period
- Earth period
- All the above
Explanation
Time taken by a satellite to complete one revolution round the Earth is called time period.
Time period, T = Distance covered / Orbital velocity
T = 2πr / v Substituting the value of v, we get
T = 2π (R + h) / √GM (R + h).
59. What is the name of the one star which appears to us stationary in its position?
- Equator star
- Oceanic star
- Yellow star
- Pole star
Explanation
All stars appear to us as moving from east to west, where as there is one star which appears to us stationary in its position. It has been named as Pole star. The pole star appears to us as fixed in space at the same place in the sky in the north direction because it lies on the axis of rotation of the Earth which itself is fixed and does not change its position in space. It may be noted that the pole star is not visible from the southern hemisphere.
60. At an orbital height of 500 km, find the orbital period of the satellite.
- T = 75 min
- T = 84 min
- T = 95 min
- T = 101 min
Explanation
h = 500 × 103 m, R = 6371 × 103 m, v = 7616 × 103 kms-1.
T = 2π (R + h) / v = 2 × (22/7) × {(6371+500) / 7616}
= 5. 6677 × 103 s = 5667 s
Thus, T = 95 min
61. In the early 1600s, who among the following proposed three laws of planetary motion?
- Kepler
- Newton
- Copernicus
- Aristotle
Explanation
In the early 1600s, Johannes Kepler proposed three laws of planetary motion. Kepler was able to summarize the carefully collected data of his mentor, Tycho Brahe with three statements that described the motion of planets in a Sun-cantered solar system. Kepler’s efforts to explain the underlying reasons for such motions are no longer accepted; nonetheless, the actual laws themselves are still considered an accurate description of the motion of any planet and any satellite.
62. Which among the following is not the Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion?
- All planets revolve around the Sun in elliptical orbits with Sun at one of their foci.
- The line connecting the planet and the Sun covers equal areas in equal intervals of time.
- The planets rotes itself while revolving around the sun in a fixed axis around it
- The square of time period of revolution of a planet around the Sun is directly proportional to the cube of the distance between sun and the planets.
Explanation
First Law – The Law of Ellipses: All planets revolve around the Sun in elliptical orbits with Sun at one of their foci.
Second Law – The Law of Equal Areas: The line connecting the planet and the Sun covers equal areas in equal intervals of time
Third Law – The Law of Harmonies: The square of time period of revolution of a planet around the Sun is directly proportional to the cube of the distance between sun and the planets.
63. Which is a large spacecraft which can house astronauts?
- Planetary station
- Star ship
- International Cloud station
- International space station
Explanation
ISS is a large spacecraft which can house astronauts. It goes around in low Earth orbit at approximately 400 km distance. It is also a science laboratory. It’s very first part was placed in orbit in 1998 and its core construction was completed by 2011. It is the largest man-made object in space which can also be seen from the Earth through the naked eye.
64. In which year the first human crew went to the ISS?
- 2000
- 2004
- 2008
- 2010
Explanation
The first human crew went to the ISS in 2000. Ever since that, it has never been unoccupied by humans. At any given instant, at least six humans will be present in the ISS. According to the current plan, ISS will be operated until 2024, with a possible extension until 2028. After that, it could be deorbited, or recycled for future space stations.
65. Which among the following statement is correct
- Using the technology developed for the ISS, areas having water scarcity can gain access to advanced water filtration and purification systems. The water recovery system (WRS) and the oxygen generation system (OGS) developed for the NASA have already saved a village in Mexico from being deserted due to lack of clean water.
- The Eye Tracking Device, built for a microgravity experiment, has proved ideal to be used in many laser surgeries. Also, eye tracking technology is helping disabled people with limited movement and speech. For example, a kid who has severe disability in body movements can use his eye-movements alone and do routine tasks and lead an independent life.
- Robotic arms developed for research in the ISS are providing significant help to the surgeons in removing inoperable tumours (e.g., brain tumours) and taking biopsies with great accuracies. Its inventors say that the robot could take biopsies with remarkable precision and consistency.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Using the technology developed for the ISS, areas having water scarcity can gain access to advanced water filtration and purification systems. The water recovery system (WRS) and the oxygen generation system (OGS) developed for the ISS have already saved a village in Iraq from being deserted due to lack of clean water.
66. Which among the following country is matched incorrectly with its space organisation?
- USA – NASA
- China – CSA
- Japan – JAXA
- ESA – Europe
Explanation
NASA (USA), Roskosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan) and CSA (Canada).
67. Which among the following country is not the member 16 countries provides, maintains and operates the ISS?
- Brazil
- Italy
- India
- Denmark
Explanation
As great as the ISS’ scientific achievements are, no less in accomplishment is the international co-operation which resulted in the construction of the ISS. An international collaboration of five different space agencies of 16 countries provides, maintains and operates the ISS. They are: NASA (USA), Roskosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan) and CSA (Canada). Belgium, Brazil, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Holland, Norway, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the UK are also part of the consortium.
68. Which among the following is the value of 1 light year?
- 9.4607 × 1010 km
- 9.4607 × 1012 km
- 8.1836 × 1010 km
- 8.1836 × 1012 km
Explanation
The observable universe is around 93 billion light years (1 light year = the distance that light travels in one year, which is 9.4607 × 1012 km) across.
9th Science Lesson 10 Questions in English
10] Matter Around Us
1. Which among the following is not the matter?
- Clouds
- Stones
- Plants
- Sunlight
Explanation
Matter is everything around us. The air we breathe, the food we eat, the pen we write, clouds, stones, plants, animals, a drop of water or a grain of sand everything is matter. Samples of any of these materials have two properties in common. They have mass and they occupy space. Not all things that we see or feel are matter. For example, sunlight, sound, force and energy neither occupy space nor have any mass. They are not matter.
2. Matters can be broadly classified into how many types on the basis of chemical composition?
- Two
- Three
- Five
- Four
Explanation
Broadly speaking, matter has been classified into pure substances and mixtures. From the point of view of chemistry, pure substances are those which contain only one kind of particles whereas impure substances (mixtures) contain more than one kind of particles. The two types of pure substance are elements and compounds. Two types are impure substance are homogeneous and heterogeneous.
3. The substance that cannot be broken into simpler substances is called ____
- Elements
- Compounds
- Core
- Filament
Explanation
The substance that cannot be broken into simpler substances is called elements. All l substances on earth are made up of certain simple substances called elements. Plants, cats, apples, rocks, cars and even our bodies contain elements. Thus, elements are the building block of all materials.
4. Which among the following is not the elements?
- Copper
- Oxygen
- Salt
- Hydrogen
Explanation
The examples of elements are copper, oxygen, hydrogen. The examples of compounds are water, sugar, salt, etc.
5. Which among the following is not the heterogenous mixture?
- Sand + Sugar
- Water + Alcohol
- Water + Oil
- None of the above
Explanation
Homogeneous mixture examples are sugar + H2 O, water + alcohol. Heterogenous mixture examples are sand + sugar, water + oil.
6. In the modern periodic table how many elements are known to us?
- 102
- 110
- 118
- 135
Explanation
In the modern periodic table, there are 118 elements known to us.
7. Out of 118 elements, how many of which are naturally occurring elements?
- 81
- 86
- 92
- 102
Explanation
Out of 118 elements, 92 of which are naturally occurring while the remaining 26 have been artificially created. But from these 118 elements, crores of compounds are formed some naturally occurring and some artificial.
8. Who among the following used the name element for any substance that cannot be broken down further, into a simpler substance?
- Robert Boyle
- Antoine Lavoisier
- John Dalton
- Robert Hooke
Explanation
Robert Boyle used the name element for any substance that cannot be broken down further, into a simpler substance. This definition can be extended to include the fact that each element is made up of only one kind of atom. Eg., aluminium is an element which is made up of only aluminium atoms. It is not possible to obtain a simpler substance chemically from the aluminium atoms. You can only make more complicated substances from it, such as aluminium oxide, aluminium nitrate and aluminium sulphate.
9. The smallest unit of an element which may or may not have an independent existence, but always takes part in a chemical reaction is called ____
- Molecule
- Ion
- Mole
- Atom
Explanation
The smallest unit of an element which may or may not have an independent existence, but always takes part in a chemical reaction is called atom.
10. The smallest unit of a pure substance, which always exists independently and can retain physical and chemical properties of that substance is called ____
- Molecule
- Ion
- Atom
- Element
Explanation
The smallest unit of a pure substance, which always exists independently and can retain physical and chemical properties of that substance is called a molecule. Examples; Hydrogen molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms (H2 ) Water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms (H2 ) and one oxygen atom (O).
11. Which among the following element is Metalloid?
- Copper
- Chromium
- Boron
- Neon
Explanation
All elements can be classified according to various properties. A simple way to do this is to classify them as metals, non-metals and metalloids. Examples of Metal are Copper, Chromium, Gold, Mercury. Example of Metalloid are Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic. Example of Non-metal are Carbon, Oxygen, Neon, Chlorine.
12. When two or more elements combine chemically to form a new substance, the new substance is called ____
- Atom
- Ion
- Compound
- None of the above
Explanation
When two or more elements combine chemically to form a new substance, the new substance is called a compound.
13. The cane sugar is not made up of which among the following element?
- Carbon
- Hydrogen
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
Explanation
The cane sugar is made up of three elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The chemical forumula of cane sugar is C12 H22 O11.
14. The Common salt, also known as _____
- Potassium chloride
- Sodium chloride
- Sulphate chloride
- Aluminium chloride
Explanation
A compound has properties that are different from those of the elements from which it is made. Common salt, also known as sodium chloride, is a compound. It is added to give taste to our food. It is a compound made up of a metal, sodium and a non-metal, chlorine.
15. Which among the following compounds is not used in fertilizers?
- Phosphorous
- Nitrogen
- Fluorine
- Potassium
Explanation
Compounds of phosphorous, nitrogen and potassium are used in fertilizers.
16. Which among the following compounds are of immense importance in the computer industry?
- Silicon
- Potassium
- Fluorine
- Chlorine
Explanation
Silicon compounds are of immense importance in the computer industry.
17. Which among the following compound are used in our toothpastes as they strengthen our teeth?
- Sulphate
- Potassium
- Fluorine
- Chlorine
Explanation
Compounds of fluorine are used in our toothpastes as they strengthen our teeth.
18. Which among the following is not the properties of element?
- Made up of only one kind of atom
- The smallest particle that retains all its properties is the molecule.
- Cannot be broken down into simpler substances
- All the above
Explanation
The property of elements is i) Made up of only one kind of atom, ii) The smallest particle that retains all its properties is an atom, and iii) Cannot be broken down into simpler substances.
The property of compound is i) Made up of more than one kind of atom, ii) The smallest particle that retains all its properties is the molecule and iii) Can be broken down into elements by chemical methods.
19. Which among the following is the mixture?
- Lemonade
- Alloy
- Tap water
- All the above
Explanation
A mixture is an impure substance. It contains two or more kinds of elements or compounds or both physically mixed together in any ratio. For, example, tap water is a mixture of water and some dissolved salts. Lemonade is a mixture of lemon juice, sugar and water. Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour and other gases. Alloys are mixtures of metals.
20. Liquefied Petroleum Gas contains mixture of what gases?
- Methane and propane
- Butane and Methane
- Butane and Propane
- Ethane and Butane
Explanation
Liquefied Petroleum Gas is highly inflammable hydrocarbon gas. It contains mixture of butane and propane gases. LPG, liquefied through pressurisation, is used for heating, cooking, auto fuel etc.
21. Match the following substance with its appearance colour
- Iron – 1. Black solid
- Sulphur – 2. Dark grey powder
- Iron + Sulphur (Mixture) – 3. Dirty yellow powder
- Iron sulphide – 4. Yellow powder
- 2 – 4 – 3 – 1
- 3 – 1 – 2 – 4
- 2 – 3 – 4 – 1
- 3 – 4 – 1 – 2
Explanation
Iron + sulphur ????(heat) ????Iron sulphide
The Iron sulphide formed has totally different properties to the mixture of iron and sulphur.
Iron (element) – Dark grey powder, Sulphur (element) – Yellow powder, Iron + Sulphur (Mixture) – Dirty yellow powder, Iron sulphide (compound) – Black solid.
22. Which among the following is not the components of blood?
- Platelets
- Cortex
- Plasma
- White blood corpuscles
Explanation
Blood is not a pure substance. It is a mixture of various components such as platelets, red and white blood corpuscles and plasma.
23. Which among the following is not the property of mixtures?
- It contains two or more substances
- The constituent may be present in any proportion.
- They do not show the properties of the constituent elements.
- The components may be separated easily by physical methods.
Explanation
Properties of Mixtures are i) It contains two or more substances, ii) The constituent may be present in any proportion. iii) They show the properties of their constituents. iv) The components may be separated easily by physical methods.
24. Which among the following statement is correct
- A mixture in which the components cannot be seen separately is called a homogeneous mixture. It has a uniform composition and every part of the mixture has the same properties. Tap water, milk, air, ice cream, sugar syrup, ink, steel, bronze and salt solution are homogeneous mixtures.
- A mixture in which the components can be seen separately is called a heterogeneous mixture. It does not have a uniform composition and properties. Soil, a mixture of iodine and common salt, a mixture of sugar and sand, a mixture of oil and water, a mixture of sulphur and iron filings and a mixture of milk and cereals are heterogeneous mixture.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
25. Which among the following is not the property of compound?
- It is a single substance
- The constituents are present in definite proportions.
- They do not show the properties of the constituent elements
- The components may be separated easily by physical methods.
Explanation
The properties of components are i) It is a single substance, ii) The constituents are present in definite proportions, iii) They do not show the properties of the constituent elements and iv) The constituents can only be separated by one or more chemical reactions.
26. Which among the following mixtures is not the heterogeneous mixture?
- Solid and solid
- Insoluble solid and liquid
- Soluble solid and liquid
- Two immiscible liquids
Explanation
Heterogeneous – Solid and solid, Insoluble solid and liquid, Two immiscible liquids.
Homogeneous – Soluble solid and liquid, Two miscible liquids, Solution of two or more solids in a liquid.
27. Which among the following methods of separation is not used for solid and solid mixtures?
- Handpicking
- Sieving
- Sublimation
- Centrifugation
Explanation
The Methods of separation used for solid and solid mixtures are Handpicking, sieving, winnowing, magnetic separation, sublimation.
28. Certain solid substances when heated change directly from solid to gaseous state without attaining liquid state. The vapours when cooled give back the solid substance. This process is known as _____
- Sublimation
- Sieving
- Winnowing
- Crystallisation
Explanation
Certain solid substances when heated change directly from solid to gaseous state without attaining liquid state. The vapours when cooled give back the solid substance. This process is known as sublimation. Examples: Iodine, camphor, ammonium chloride etc.,
29. Which among the following statement is correct regarding sublimation process?
- The powdered mixture of Ammonium chloride and sand is taken in a china dish and covered with a perforated asbestos sheet. An inverted funnel is placed over the asbestos sheet. The open end of the stem of the funnel is closed using cotton wool and the china dish is heated
- The non-volatile impurities pass through the holes in the asbestos sheet and condense on the inner sides of the funnel. The pure vapours of the volatile solid remain in the china dish.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The pure vapours of the volatile solid pass through the holes in the asbestos sheet and condense on the inner sides of the funnel. The non-volatile impurities remain in the china dish.
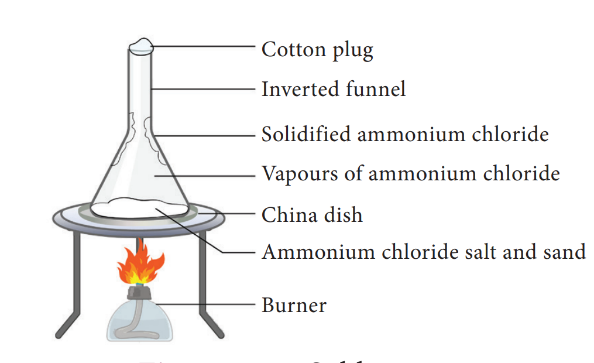
30. Moth balls, made of what are used to drive away moths and some other insects?
- Benzene
- Naphthalene
- Toluene
- Aniline
Explanation
The air fresheners are used in toilets. The solid slowly sublimes and releases the pleasant smell in the toilet over a certain period of time. Moth balls, made of naphthalene are used to drive away moths and some other insects. These also sublime over time.
31. Which among the following method of separation is used for Insoluble solid and liquid mixtures?
- Chromatography
- Solvent extraction
- Centrifugation
- Crystallisation
Explanation
The method of separations for Insoluble solid and liquid mixtures are Sedimentation and decantation, loading, filtration, centrifugation.
32. Which is the process by which fine insoluble solids from a solid- liquid mixture can be separated in a machine called a centrifuge.?
- Decantation
- Distillation
- Centrifugation
- Chromatography
Explanation
Centrifugation is the process by which fine insoluble solids from a solid- liquid mixture can be separated in a machine called a centrifuge. A centrifuge rotates at a very high speed. On being rotated by centrifugal force, the heavier solid particles move down and the lighter liquid remains at the top. In washing machines, this principle is used to squeeze out water from wet clothes. Centrifugation is also used in pathological laboratories to separate blood cells from a blood sample.
33. Which among the following is not the method of separation for soluble solid and liquid mixtures?
- Evaporation
- Chromatography
- Distillation
- Crystallisation
Explanation
The methods of separations for soluble solid and liquid mixtures are Evaporation, distillation, crystallisation.
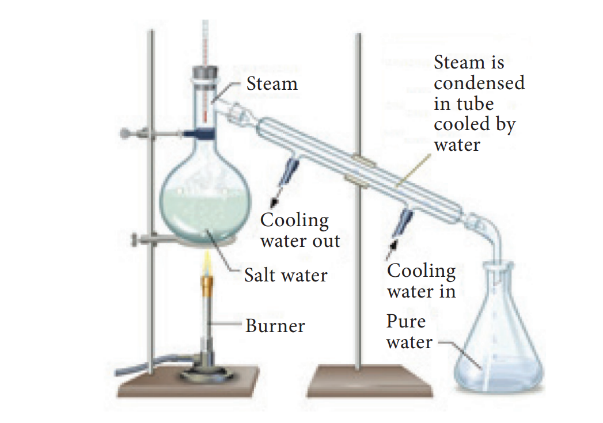
34. Which is a process of obtaining pure liquid from a solution that is actually a combination of evaporation and condensation?
- Crystallisation
- Distillation
- Decantation
- Loading
Explanation
Distillation is a process of obtaining pure liquid from a solution. It is actually a combination of evaporation and condensation i.e., Distillation = Evaporation + Condensation.
35. Which among the following statement is correct regarding distillation method?
- In this method, a solution is heated in order to vaporise the liquid. The vapours of the liquid on cooling, condense into pure liquid. For example, sea water in many countries is converted into drinking water by distillation. This method is also used to separate two liquids whose boiling points differ more than 25 K.
- A distillation flask is fixed with a water condenser. A thermometer is introduced into the distillation flask through a one-holed stopper. The bulb of the thermometer should be slightly below the side tube.
- The brackish water (sea water) to be distilled is taken in the distillation flask and heated for boiling. The pure water vapour passes through the inner tube of the condenser. The vapours on cooling condense into pure water (distillate) and are collected in a receiver. The salt is left behind in the flask as a residue.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
36. Which among the following is the main process in perfume development and it is also used to obtain dyes from various sources?
- Crystallisation
- Solvent extraction
- Fractional distraction
- All the above
Explanation
Solvent extraction is an old practice done for years. It is the main process in perfume development and it is also used to obtain dyes from various sources.
37. Which among the following method of separation is used for Two miscible liquids mixtures?
- Evaporation
- Crystallisation
- Fractional distillation
- Sieving
Explanation
The method of separation used for two miscible liquid mixtures are Fractional distillation.
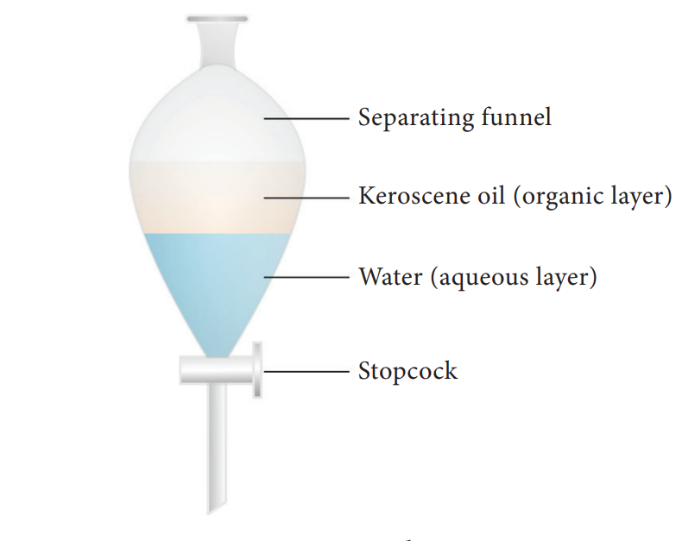
38. Which among the following method of separation is used to separate mixture of water and oil?
- Solvent extraction
- Crystallisation
- Chromatography
- Winnowing
Explanation
Two immiscible liquids can be separated by solvent extraction method. This method works on the principle of difference in solubility of two immiscible liquids in a suitable solvent. For example, mixture of water and oil can be separated using a separating funnel. Solvent extraction method is used in pharmaceutical and petroleum industries.
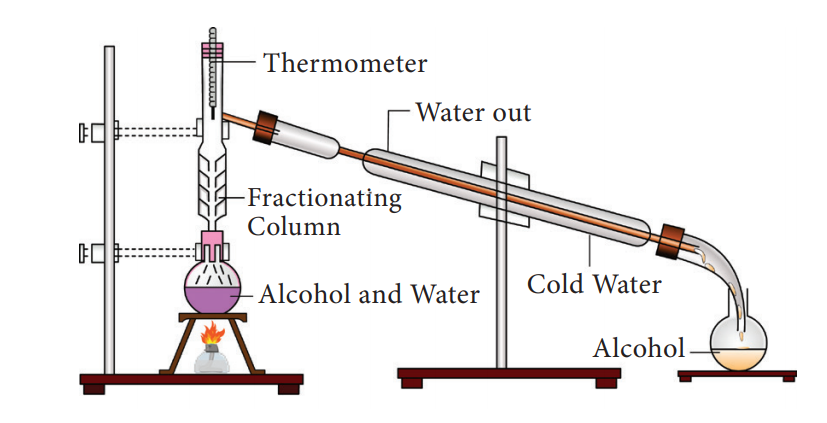
39. Which among the following method of separation is used in petrochemical industry to obtain different fractions of petroleum, to separate the different gases from air, to distil alcohols etc?
- Sieving
- Decantation
- Loading
- Fractional distillation
Explanation
To separate two or more miscible liquids which do not differ much in their boiling points (difference in boiling points is less than 25 K) fractional distillation is employed. Fractional distillation is used in petrochemical industry to obtain different fractions of petroleum, to separate the different gases from air, to distil alcohols etc.
40. Which is the process in which the particles of a substance are concentrated only at the surface of another substance?
- Absorption
- Conservation
- Accretion
- Adsorption
Explanation
Adsorption is the process in which the particles of a substance is concentrated only at the surface of another substance.
41. Which is a separation technique, which is used to separate different components of a mixture based on their different solubilities in the same solvent?
- Solvent extraction
- Crystallisation
- Chromatography
- Winnowing
Explanation
Chromatography is also a separation technique. It is used to separate different components of a mixture based on their different solubilities in the same solvent. There are several types of chromatography based on the above basic principles. The simplest type is paper chromatography.
42. Which is the process in which the substance is uniformly distributed throughout the bulk of another substance?
- Absorption
- Conservation
- Accretion
- Adsorption
Explanation
Absorption is the process in which the substance is uniformly distributed throughout the bulk of another substance.
For example, when a chalk stick is dipped in ink, the surface retains the colour of the ink due to adsorption of coloured molecules while the solvent of the ink goes deeper into the stick due to absorption. Hence, on breaking the chalk stick, it is found to be white from inside.
43. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding paper chromatography?
- Paper chromatography method is used to separate the different coloured dyes in a sample of ink. A spot of the ink (e.g. black ink) is put on to a piece of chromatography paper. This paper is then set in a suitable solvent.
- The black ink separates into its constituent dyes. As the solvent moves down the paper, the dyes are carried away from it and begin to separate. They separate because they have different solubility in the solvent and are adsorbed to different extents by the chromatography paper. The chromatogram shows that the black ink contains three dyes.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The black ink separates into its constituent dyes. As the solvent moves up the paper, the dyes are carried with it and begin to separate. They separate because they have different solubility in the solvent and are adsorbed to different extents by the chromatography paper. The chromatogram shows that the black ink contains three dyes.
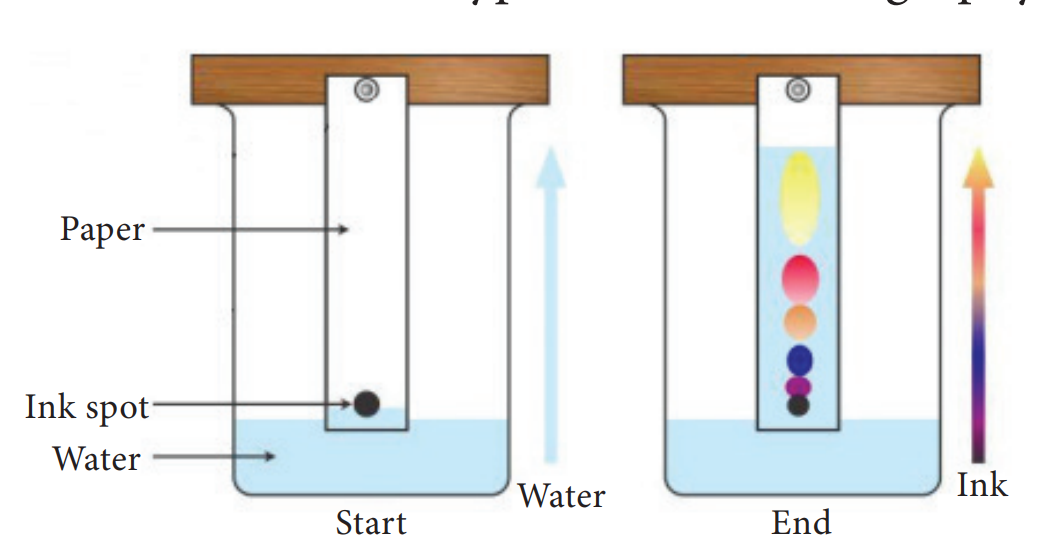
44. In a solution, the component present in lesser amount by weight is called _____
- Solute
- Solvent
- Adsorb
- Pollen
Explanation
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. In a solution, the component present in lesser amount by weight is called solute and the component present in larger amount by weight is called solvent.
In short, a solution can be represented as follows: solute + solvent solution.
45. Based on the particle size of the solute, the solutions are divided into how many types?
- Two
- Three
- Five
- Six
Explanation
Based on the particle size of the solute, the solutions are divided into three types. They are 1. True solution, 2. Colloidal solution and 3. Suspension solution.
46. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- We can see that in the case of sugar and water mixture we get a clear solution and the particles never settle down. This mixture is called as true solution. Particle size less than 107 cm
- In the case of wheat flour mixed with water we get a very turbid mixture and fine particles slowly settle down at the bottom after some time. This mixture is called colloidal solution. The particle size between 10-7 cm and 10-5 cm.
- In the case of starch and water we get a cloudy mixture. This mixture is called as suspension. The particle size greater than 10-5 cm.
- Only 1
- Only 3
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 2 and 3
Explanation
In the case of wheat flour mixed with water we get a very turbid mixture and fine particles slowly settle down at the bottom after some time. This mixture is called as suspension. The particle size greater than 10-5 cm.
In the case of starch and water we get a cloudy mixture. This mixture is called as colloidal solution. The particle size between 10-7 cm and 10-5 cm.
47. Which is a heterogeneous system consisting of the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium?
- True solution
- Colloidal solution
- Suspension
- All the above
Explanation
A colloidal solution is a heterogeneous system consisting of the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium. Dispersed phase or the dispersion medium can be a solid, or liquid or gas.
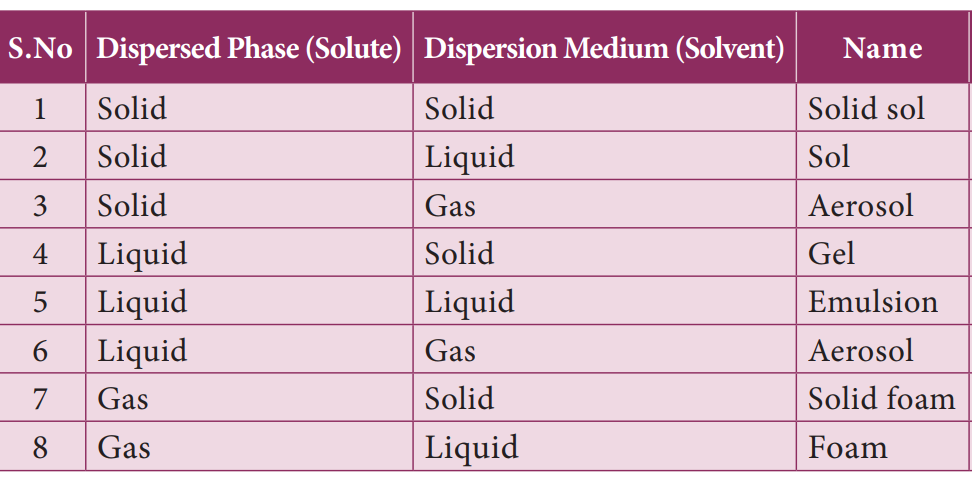
48. How many combinations of colloids solution possible based on physical state of dispersed phase and dispersion medium?
- Two
- Four
- Six
- Eight
Explanation
There are eight different combinations possible. The combination of gas in gas is not possible because gas in gas always forms a true solution.
49. The beam of light coming from headlights of vehicles is due to which effect?
- Bunsen effect
- Fourier effect
- Tyndall effect
- Pasteur effect
Explanation
The beam of light coming from headlights of vehicles is due to Tyndall effect. Blue colour of sky is also due to Tyndall effect.
50. Match the following colloids name with its correct dispersed phase (solute) and dispersion medium (solvent)
Dispersed phase and Dispersion medium Colloids name
- Solid Liquid – 1. Emulsion
- Solid Gas – 2. Sol
- Liquid Solid – 3. Foam
- Liquid Liquid – 4. Gel
- Gas Liquid – 5. Aerosol
- 3 – 1 – 4 – 5 – 2
- 2 – 5 – 4 – 1 – 3
- 4 – 1 – 5 – 3 – 2
- 5 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 1
Explanation
51. Who observed that when a strong beam of light is focused on a colloidal solution the path of the beam becomes visible?
- Needham
- Pasteur
- Tyndall
- Spencer
Explanation
Tyndall (1869) observed that when a strong beam of light is focused on a colloidal solution the path of the beam becomes visible. This phenomenon is known as Tyndall effect and the illuminated path is called Tyndall cone. This phenomenon is not observed in case of true solution.
52. When colloidal solutions are viewed under powerful microscope, it can be seen that colloidal particles are moving constantly and rapidly in zig-zag directions. This movement is known as ____
- Brownian movement
- Spencer movement
- Pasteur movement
- Galton movement
Explanation
When colloidal solutions are viewed under powerful microscope, it can be seen that colloidal particles are moving constantly and rapidly in zig-zag directions. The Brownian movement of colloidal particles is due to the unbalanced bombardment of the particles by the molecules of dispersion medium.
53. Which is a colloid of two or more immiscible liquids where one liquid is dispersed in another liquid?
- Emulsion
- Solvent
- Carbonate
- None of the above
Explanation
An emulsion is a colloid of two or more immiscible liquids where one liquid is dispersed in another liquid. This means one type of liquid particles get scattered in another liquid.
54. The word emulsion comes from which language?
- Greek
- French
- Latin
- Abram
Explanation
The word emulsion comes from the Latin word meaning “to-milk” (milk is one example of an emulsion of fat and water). Milk, butter, cream, egg yolk, paints, cough syrups, facial creams, pesticides etc. are some common examples of emulsions.
55. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- An emulsion is a special type of mixture made by combining two liquids that normally don’t mix. The process of turning a liquid mixture into an emulsion is called Accretion.
- The two liquids mixed can form different types of emulsions. For example, oil and water can form an oil in water emulsion (O/W-e.g. cream), where the oil droplets are dispersed in water, or they can form a water in oil emulsion (W/O-e.g. butter), with water dispersed in oil.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
An emulsion is a special type of mixture made by combining two liquids that normally don’t mix. The process of turning a liquid mixture into an emulsion is called emulsification.
56. Match the following colloids with its example
- Gel – 1. Aerated water
- Aerosol – 2. Smoke
- Foam – 3. Butter
- Emulsion – 4. Curd
- Sol – 5. Paint
- 2 – 1 – 5 – 3 – 4
- 5 – 2 – 1 – 4 – 3
- 3 – 5 – 1 – 2 – 4
- 4 – 2 – 1 – 3 – 5
Explanation

9th Science Lesson 11 Questions in English
11] Atomic Structure
1. Who among the following did gold foil experiment?
- J.J. Thomson
- Rutherford
- Neil’s Bohr
- Marie Curie
Explanation
In 1911, Lord Rutherford, a scientist from New Zealand, performed his famous experiment of bombarding a thin gold foil with very small positively charged particles called alpha (α) particles. He selected a gold foil because, he wanted as thin layer as possible and gold is the most malleable metal.
2. Which of the following were observed by Rutherford in his gold foil experiment?
- Most of the alpha particles passed straight through the foil.
- Some alpha particles were slightly deflected from their straight path
- Very few alpha particles completely bounced back.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Rutherford observed that:
1. Most of the alpha particles passed straight through the foil.
2. Some alpha particles were slightly deflected from their straight path.
3. Very few alpha particles completely bounced back.
Rutherford generalized these results of alpha particles scattering experiment and suggested a model of the atom that is known as Rutherford’s Atomic model.
3. Which of the following statement is correct about Rutherford’s Atomic model?
- The atom contains large empty space.
- A nucleus as a whole is electrically neutral
- The size of the nucleus of an atom is very small compared to the size of an atom.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
According to Rutherford’s Atomic model:
i. The atom contains large empty space.
ii. There is a positively charged mass at the centre of the atom, known as nucleus.
iii. The size of the nucleus of an atom is very small compared to the size of an atom.
iv. The electrons revolve around the nucleus in close circular paths called orbits.
v. An atom as a whole is electrically neutral, i.e., the number of protons and electrons in an atom are equal.
4. Who’s atomic structure is similar to the structure of the solar system?
- J.J. Thomson
- Rutherford
- Neil’s Bohr
- Marie Curie
Explanation
Rutherford’s model of the atom was somewhat like that of the solar system. Rutherford’s model of atomic structure is similar to the structure of the solar system. Just as in the solar system, the Sun is at the centre and the planets revolve around it, similarly in an atom the nucleus present at the centre and the electrons revolve around it in orbits or shells.
5. Assertion (A): Rutherford’s model failed to explain the stability of an atom.
Reason (R): According to Electromagnetic theory, a moving electron should accelerate and continuously lose energy. Due to the loss of energy, path of electron may reduce and finally, the electron should fall into the nucleus.
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
According to Electromagnetic theory, a moving electron should accelerate and continuously lose energy. Due to the loss of energy, path of electron may reduce and finally the electron should fall into the nucleus. If it happens so, atom becomes unstable. But atoms are stable. Thus, Rutherford’s model failed to explain the stability of an atom.
6. Who among the following explained the causes of the stability of the atom?
- J. J. Thomson
- Rutherford
- Neil’s Bohr
- James Chadwick
Explanation
In 1913, Neil’s Bohr, a Danish physicist, explained the causes of the stability of the atom in a different manner.
7. Which of the following are postulates of Bohr’s model of an atom?
- While revolving around the nucleus in an orbit, an electron neither loses nor gains energy
- An electron in a shell can move to a higher or lower energy shell by absorbing or releasing a fixed amount of energy
- The orbits or shells are represented by the letters K, L, M, N, … or the numbers, n= 1, 2, 3, …
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The main postulates of Bohr’s model of an atom are:
i. In atoms, the electrons revolve around the nucleus in stationary circular paths called orbits or shells or energy levels.
ii. While revolving around the nucleus in an orbit, an electron neither loses nor gains energy.
iii. An electron in a shell can move to a higher or lower energy shell by absorbing or releasing a fixed amount of energy.
iv. The orbits or shells are represented by the letters K, L, M, N, … or the numbers, n= 1, 2, 3, 4, ….
8. According to Bohr’s model of atom which orbit has least amount of energy?
- K
- L
- M
- N
Explanation
The orbit closest to the nucleus is the K shell. It has the least amount of energy and the electrons present in it are called K electrons, and so on with the successive shells and their electrons. These orbits are associated with fixed amount of energy, so Bohr called them as energy level or energy shells.
9. Which of the following element was/were able to be explained by Bohr’s model?
- Hydrogen
- He+
- Li2+
- All the above
Explanation
One main limitation was that Bohr’s model was applicable only to hydrogen and hydrogen like ions (example, He+, Li2+, Be3+, and so on). It could not be extended to multi electron nucleus.
10. Who invented neutrons?
- J. J. Thomson
- Rutherford
- Neil’s Bohr
- James Chadwick
Explanation
In 1932 James Chadwick observed when Beryllium was exposed to alpha particles, particles with about the same mass as protons were emitted. In 1920, Rutherford predicted the presence of another particle in the nucleus as neutral. James Chadwick, the inventor of neutron was student of Rutherford.
11. What was the superscript of Neutron?
- 0
- 2
- 1
- 3
Explanation
Beryllium + alpha ray ???? carbon + neutron
The resultant emitted particles which carried no electrical charges. They were called as neutrons. It is denoted by 0 n1. The superscript 1 represents its mass and subscript 0 represents its electric charge.
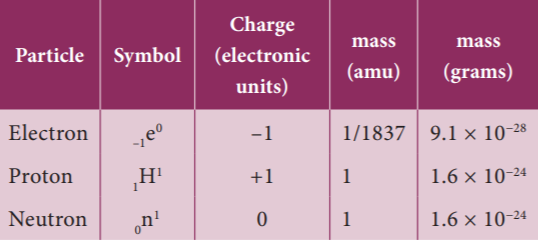
12. What was the mass of neutron?
- 1.676 × 10^−24 g
- 1.676 × 10^24 g
- 1.676 × 10^−14 g
- 1.676 × 10^14 g
Explanation
Properties of Neutrons
1. This particle was not found to be deflected by any magnetic or electric field, proving that it is electrically neutral.
2. Its mass is equal to 1.676 × 10−24 g (1 amu).
13. Which sub-atomic particles is of great importance in understanding the structure of an atom?
- Electrons
- Protons
- Positrons
- Neutrons
- 1, 2
- 1, 3, 4
- 1, 2, 4
- 2, 3, 4
Explanation
The atom is built up of a number of subatomic particles. The three sub-atomic particles of great importance in understanding the structure of an atom are electrons, protons and neutrons.
14. What is the mass of Proton?
- 1 amu
- 2 amu
- 1/18379 amu
- 1.5 amu
Explanation
15. Which of the following are collectively known as nucleons?
- Protons
- Electrons
- Neutrons
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
There are two structural parts of an atom, the nucleus and the empty space in which there are imaginary paths called orbits. Orbit is defined as the path, by which electrons revolve around the nucleus. The protons and neutrons [collectively called nucleons] are found in the nucleus of an atom.
16. Which of the following are particles discovered in the nucleus of an atom?
- Mesons
- Neutrino
- Antineutrino
- Positrons
- 1, 2, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- 1, 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Besides the fundamental particles like protons, electrons and neutrons some more particles are discovered in the nucleus of an atom. They include mesons, neutrino, antineutrino, positrons etc.
17. Which of the following decides which element it is?
- Electrons
- Protons
- Neutrons
- None
Explanation
Only hydrogen atoms have one proton in their nuclei. Only helium atoms have two protons. Indeed, only gold atoms have 79 protons. This shows that the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom decides which element it is.
18. Atomic Number is equal to_____
- Number of protons
- Number of neutrons
- Number of electrons
- 1 alone
- 1 or 3
- 2 or 3
- All the above
Explanation
Atomic number (Z) = Number of protons = Number of electrons
This is a very important number is known as the atomic number (proton number, given the symbol Z) of an atom.
19. Mass number is the sum of____
- Number of protons
- Number of neutrons
- Number of electrons
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2 alone
- All the above
Explanation
Protons alone do not make up all of the mass of an atom. The neutrons in the nucleus also contribute to the total mass. The mass of the electron can be regarded as so small that it can be ignored. As a proton and a neutron have the same mass, the mass of a particular atom depends on the total number of protons and neutrons present. This number is called the mass number (or nucleon number, given the symbol A) of an atom.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
20. What is the Atomic number of Nitrogen?
- 8
- 7
- 14
- 16
Explanation
For any element, the atomic numbers are shown as subscripts and mass number are shown as superscripts. For example, nitrogen is written as 14 N 7. Here 7 is its atomic number and 14 is its mass number.
21. In an atom, Z can be called as___________
- Mass number
- Atomic number
- Number of Neutrons
- None
Explanation
Z stands for Zahl, which means NUMBER in German. Z can be called Atomzahl or atomic number A is the symbol recommened in the ACS style guide instead of M (massenzahl in German).
22. Calculate the atomic number of an element whose mass number is 39 & number of neutrons is 20?
- 21
- 19
- 59
- 9
Explanation

23. Match the following
- N Shell 1. 32
- K Shell 2. 8
- M Shell 3. 18
- L Shell 4. 2
- 3, 1, 2, 4
- 2, 1, 4, 3
- 1, 4, 3, 2
- 1, 2, 4, 3
Explanation
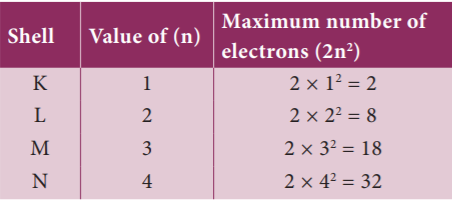
24. How many electrons are there in M shell of Aluminium?
- 8
- 18
- 3
- 2
Explanation

25. What is the forces between the protons and the neutrons in the nucleus?
- EM forces
- Yukawa forces
- Gravitational forces
- GM forces
Explanation
The forces between the protons and the neutrons in the nucleus are of special kind called Yukawa forces. This strong force is more powerful than gravity.
26. What is the electronic configuration of Oxygen?
- 2, 8
- 2, 6
- 2, 8, 18
- 2, 8, 6
Explanation
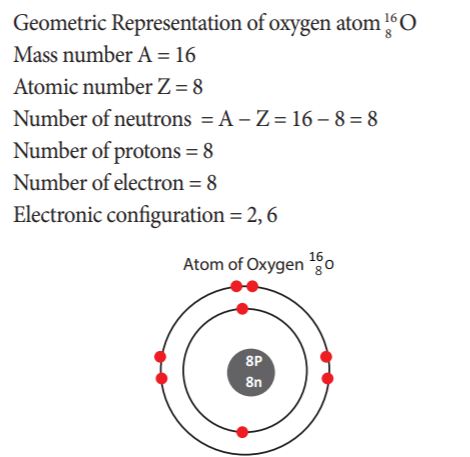
27. Size of an atom can be measured in_______
- Milli-meter
- Nano-meter
- Micro- meter
- Fermi-meter
Explanation
Atoms are so tiny their mass number cannot be expressed in grams but expressed in amu (atomic mass unit). New unit is U. Size of an atom can be measured in nano metre (1 nm = 10−9 m) Even though atom is an invisible tiny particle now-a-days atoms can be viewed through SEM that is Scanning Electron Microscope.
28. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The outermost shell of an atom is called valence shell
- The electrons present in the valence shell are known as valence electrons
- The chemical properties of elements are decided by these valence electrons
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The outermost shell of an atom is called valence shell and the electrons present in the valence shell are known as valence electrons. The chemical properties of elements are decided by these valence electrons, since they are the ones that take part in chemical reactions.
29. Assertion(A): The elements with same number of electrons in the valence shell show similar
Properties
Reason (R): Elements with 4 to 7 electrons in their valence shell are non-metals.
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
The elements with same number of electrons in the valence shell show similar properties and those with different number of valence electrons show different chemical properties. Elements, which have 1 or 2 or 3 valence electrons (except Hydrogen) are metals. Elements with 4 to 7 electrons in their valence shell are non-metals.
30. Assertion(A): Valency of the elements having valence electrons 1, 2, 3, 4 is 1, 2, 3, 4 respectively
Reason(R): Valency of an element is the combining capacity of the element with other elements and is equal to the number of electrons that take part in a chemical reaction
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
Valency of an element is the combining capacity of the element with other elements and is equal to the number of electrons that take part in a chemical reaction. Valency of the elements having valence electrons 1, 2, 3, 4 is 1, 2, 3, 4 respectively. Valency of an element with 5, 6 and 7 valence electrons is 3, 2 and 1 (8–valence electrons) respectively. Because 8 is the number of electrons required by an element to attain stable electronic configuration. Elements having completely filled outermost shell show Zero valency. For example: The electronic configuration of Neon is 2,8 (completely filled). So, valency is 0.
31. What is the valency of Magnesium?
- 2
- 7
- 0
- 1
Explanation
Electronic configuration of magnesium is 2, 8, 2. So valency is 2.
Electronic configuration of sulphur is 2, 8, 6. So valency is 2 i.e. (8 – 6).
32. Match the following:
- Phosphorus 1. Noble gas
- Neon 2. Non- metal
- Potassium 3. Metal
- 1, 3, 2
- 1, 2, 3
- 2, 1, 3
- 2, 3, 1
Explanation
33. Which of the following are Isotopes of Hydrogen?
- Protium
- Deuterium
- Tritium
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- 1, 3
- All the above
Explanation
In nature, a number of atoms of elements have been identified, which have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. For example, take the case of hydrogen atom, it has three atomic species as shown below:
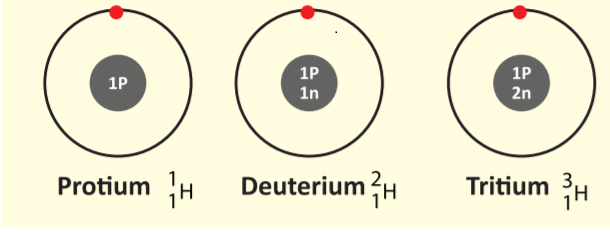
The atomic number of all the three isotopes is 1, but the mass number is 1, 2 and 3, respectively.
34. Which of the following is a radio-isotope?
- U-235
- Cobalt- 60
- Ar- 40
- Both a and b
Explanation
On the basis of these examples, isotopes are defined as the different atoms of the same element, having same atomic number but different mass numbers. There are two types of isotopes: stable and unstable. The isotopes which are unstable, as a result of the extra neutrons in their nuclei are radioactive and are called radioisotopes. For example, uranium-235, which is a source of nuclear reactors, and cobalt-60, which is used in radiotherapy treatment are both radioisotopes.
35. Which of the following are same in Isobars?
- Electrons
- Protons
- Neutrons
- Nucleons
Explanation
Let us consider two elements – calcium (atomic number 20), and argon (atomic number 18). They have different number of protons and electrons. But, the mass number of both these elements is 40. It follows that the total number of nucleons in both the atoms are the same. They are called isobars. Atoms of different elements with different atomic numbers, and same mass number are known as isobars.
36. Which of the following are same in case of isotones?
- Electrons
- Protons
- Neutrons
- Nucleons
Explanation
No of neutrons in boron = 11 – 5 = 6
No of neutrons in carbon = 12 – 6 = 6
The above pair of elements Boron and Carbon has the same number of neutrons but different number of protons and hence different atomic numbers. Atoms of different elements with different atomic numbers and different mass numbers, but with same number of neutrons are called isotones.
37. Who proposed Law of multiple proportions?
- Jeremias Ritcher
- John Dalton
- Gay Lussac
- Marie Curie
Explanation
Law of multiple proportions was proposed by John Dalton in 1804. It states that, “When two elements A and B combine together to form more than one compound, then different masses of A which separately combine with a fixed mass of B are in simple ratio”.
38. What is the ratio of masses of oxygen in CO and CO2?
- 1: 3
- 1: 4
- 1: 1
- 1: 2
Explanation
Carbon combines with oxygen to form two different oxides, carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2). The ratio of masses of oxygen in CO and CO2 for fixed mass of carbon is 1: 2.
39. What is the ratio of masses of Sulphur in SO2 and SO3?
- 1: 3
- 2: 3
- 3: 2
- 1: 1
Explanation
Let us take one more example, Sulphur combines with oxygen to form sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide. The ratio of masses of oxygen in SO2 and SO3 for fixed mass of Sulphur is 2:3. The ratio of masses of sulphur is 1: 1
40. Who proposed law of reciprocal proportions?
- Jeremias Ritcher
- John Dalton
- Gay Lussac
- Marie Curie
Explanation
The law of reciprocal proportions was proposed by Jeremias Ritcher in 1792. It states that, “If two different elements combine separately with the same weight of a third element, the ratio of the masses in which they do so are either same or a simple multiple of the mass ratio in which they combine among themselves.”
41. Match the following:
- Principal quantum number 1. m
- Azimuthal quantum number 2. l
- spin quantum number 3. s
- Magnetic quantum number 4. n
- 2, 1, 4, 3
- 1, 4, 2, 3
- 4, 2, 1, 3
- 3, 1, 2, 4
Explanation
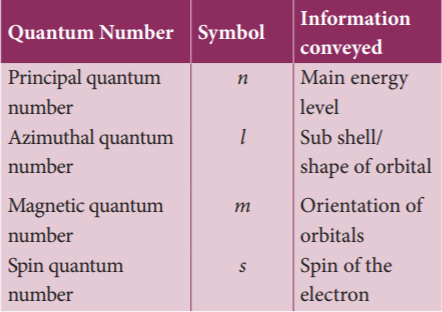
42. How many ways are there for defining the properties of an electron?
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 5
Explanation
we have four ways of defining the properties of an electron, i.e. four quantum numbers. Thus, the numbers which designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom are called quantum numbers.
43. Who proposed the Law of Combining Volumes?
- Jeremias Ritcher
- John Dalton
- Gay Lussac
- Marie Curie
Explanation
According to Gay Lussac’s Law, whenever gases react together, the volumes of the reacting gases bear a simple ratio, and the ratio is extended to the product when the product is also in gaseous state, provided all the volumes are measured under similar conditions of temperature and pressure.
9th Science Lesson 12 Questions in English
12] Periodic Classification Of Elements
1. As of now how many elements were discovered?
- 134
- 118
- 124
- 112
Explanation
We live in the world of substances with great diversity. Substances are formed by the combination of various elements. All the elements are unique in their nature and property. To categorize these elements according to their properties, scientists started to look for a way. In 1800, there were only 31 known elements. By 1865, their number became 63. Now 118 elements have been discovered.
2. Who arranged the elements into groups containing three elements each?
- Dobereiner
- John Newlands
- Dmitri Mendeleev
- Dmitrich
Explanation
In 1817, Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner, a German chemist, suggested a method of grouping elements based on their relative atomic masses. He arranged the elements into groups containing three elements each. He called these groups as ‘triads’ (tri – three).
3. Which of the following statement is correct about Dobereiner’s law of triads?
- when the three elements in a triad are arranged in the ascending order of their atomic masses their average will be three
- when the three elements in a triad are arranged in the ascending order of their atomic masses, their average will be 1
- when the three elements in a triad are arranged in the ascending order of their atomic masses, the atomic mass of the middle element is nearly the same as average of atomic masses of other two elements
- when the three elements in a triad are arranged in the ascending order of their atomic masses, the atomic mass of the first element is nearly the same as average of atomic masses of other two elements
Explanation
Dobereiner showed that when the three elements in a triad are arranged in the ascending order of their atomic masses, the atomic mass of the middle element is nearly the same as average of atomic masses of other two elements. This statement is called the Dobereiner’s law of triads.
4. Dobereiner’s law of triads was not applicable to_________
- Very high atomic mass
- Average atomic mass
- Very low atomic mass
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Limitations of Dobereiner’s law of triads:
- Dobereiner could identify only three triads from the elements known at that time and all elements could not be classified in the form of triads.
- The law was not applicable to elements having very low and very high atomic mass.
5. Which of the following statement is correct?
- John Newlands arranged 56 known elements in the increasing order of their atomic mass
- He observed that every eighth element had properties similar to those of the first element like the eighth note in an octave of music is similar to the first.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
In 1866, John Newlands arranged 56 known elements in the increasing order of their atomic mass. He observed that every eighth element had properties similar to those of the first element like the eighth note in an octave of music is similar to the first. This arrangement was known as ‘law of octaves’.
6. Which of the following are the limitations of Newlands’ Law of Octaves?
- Newlands’ table was restricted to only 56 elements and did not leave any room for new elements.
- The law of octaves was not valid for elements that had atomic masses higher than that of calcium
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Limitations of Newlands’ Law of Octaves:
- There are instances of two elements being fitted into the same slot, e.g. cobalt and nickel.
- Some elements, totally dissimilar in their properties, were fitted into the same group. (Arrangement of Co, Ni, Pd, Pt and Ir in the row of halogens)
- The law of octaves was not valid for elements that had atomic masses higher than that of calcium.
- Newlands’ table was restricted to only 56 elements and did not leave any room for new elements.
- Discovery of inert gases (Neon. Argon….) at later stage made the 9th element similar to the first one. Eg: Neon between Fluorine and Sodium.
7. Which of the following statement about Mendeleev’s Periodic Table is correct?
- Russian chemist, Dmitri Mendeleev observed that the elements of similar properties repeat at regular intervals when the elements are arranged in the order of their atomic masses
- He proposed the law of periodicity which states that “the physical and chemical properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their atomic masses”
- He arranged 76 elements known at that time according to his law of periodicity
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
In 1869, Russian chemist, Dmitri Mendeleev observed that the elements of similar properties repeat at regular intervals when the elements are arranged in the order of their atomic masses. Based on this, he proposed the law of periodicity which states that “the physical and chemical properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their atomic masses”. He arranged 56 elements known at that time according to his law of periodicity. This was best known as the short form of periodic table.
8. Which of the following is the last element in Newland’s table of octaves?
- Ca
- Au
- Th
- Bi
Explanation
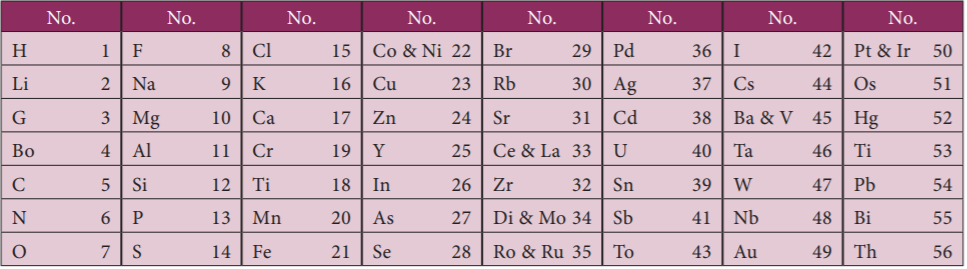
9. Which of the following statement about Mendeleev’s Periodic Table is correct?
- It has eight vertical columns called ‘groups’ and six horizontal rows called ‘period’.
- Columns were left vacant for elements which were not known at that time and their properties also were predicted.
- Mendeleev reassessed the atomic mass of beryllium as 9 and assigned beryllium a proper place.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Features of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table:
- It has eight vertical columns called ‘groups’ and seven horizontal rows called ‘period’
- Each group has two subgroups ‘A’ and ‘B’. All the elements appearing in a group were found to have similar properties.
- For the first time, elements were comprehensively classified in such a way that elements of similar properties were placed in the same group.
- It was noticed that certain elements could not be placed in their proper groups in this manner. The reason for this was wrongly determined atomic masses. Consequently, those wrong atomic masses were corrected. Eg: The atomic mass of beryllium was known to be 14. Mendeleev reassessed it as 9 and assigned beryllium a proper place
- Columns were left vacant for elements which were not known at that time and their properties also were predicted. This gave motivation to experiment in Chemistry
10. The discovery of which element proved Mendeleev correct?
- Silicon
- Germanium
- Copper
- Silver
Explanation
Mendeleev gave names Eka Aluminium and Eka Silicon to those elements which were to be placed below Aluminium and Silicon respectively in the periodic table and predicted their properties. The discovery of Germanium later on, during his life time, proved him correct.
11. Which of the following statement are limitations of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table is correct?
- No place for isotopes in the periodic table
- The increasing order of atomic mass was not strictly followed throughout
- No proper position could be given to the element hydrogen.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Limitations of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table:
- Elements with large difference in properties were included in the same group. Eg: Hard metals like copper (Cu) and silver (Ag) were included along with soft metals like sodium (Na) and potassium (K).
- No proper position could be given to the element hydrogen. Non-metallic hydrogen was placed along with metals like lithium (Li), sodium (Na) and potassium (K)
- The increasing order of atomic mass was not strictly followed throughout. Eg. Co & Ni, Te & I.
- No place for isotopes in the periodic table.
12. According to Mendeleev’s prediction what was the atomic mass of Germanium?
- 73
- 72
- 82
- 121
Explanation
13. Who proved that properties of elements depend on the atomic number and not on atomic mass?
- Mendeleev
- Henry Moseley
- Gay Lucas
- Lavoisier
Explanation
In 1913, the English Physicist Henry Moseley, through his X-ray diffraction experiments, proved that the properties of elements depend on the atomic number and not on the atomic mass.
14. Modern periodic table is the extension of the original_______ table.
- Newland’s table
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Dobereiner’s law of triads
- All the above
Explanation
The modern periodic table was prepared by arranging elements in the increasing order of their atomic number. This modern periodic table is the extension of the original Mendeleev’s periodic table and known as the long form of periodic table.
15. Which of the following statement is correct about modern periodic law?
- Atomic number of an element (Z) indicates the number of protons (positive charge) or the number of electrons (negative charge)
- The physical and chemical properties of elements depend not only on the number of protons but also on the number of electrons and their arrangement
- Based on the modern periodic law, the modern periodic table is derived
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Atomic number of an element (Z) indicates the number of protons (positive charge) or the number of electrons (negative charge). The physical and chemical properties of elements depend not only on the number of protons but also on the number of electrons and their arrangements (electronic configuration) in atoms. Hence, the modern periodic law can be stated as follows: “The chemical and physical properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their atomic numbers”. Based on the modern periodic law, the modern periodic table is derived.
16. Which of the following statement about modern periodic table is correct?
- All the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number.
- There are eight periods in the periodic table.
- There are 18 groups in the periodic table
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
- All the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number.
- The horizontal rows are called periods. There are seven periods in the periodic table.
- The elements are placed in periods based on the number of shells in their atoms.
- Vertical columns in the periodic table starting from top to bottom are called groups. There are 18 groups in the periodic table.
- Based on the physical and chemical properties of elements, they are grouped into various families.
17. Match the following:
- Group 14 1. Noble gases
- Group 2 2. Chalcogen Family
- Group 18 3. Carbon Family
- Group 16 4. Alkaline earth metals
- 2, 1, 3, 4
- 3, 4, 1, 2
- 4, 1, 2, 3
- 2, 1, 4, 3
Explanation
18. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Electrons in an atom are accommodated in shells around the nucleus
- Each shell consists of one or more subshells in which the electrons are distributed in certain manner
- Subshells are designated as s, p, d, and f
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
We know that the electrons in an atom are accommodated in shells around the nucleus. Each shell consists of one or more subshells in which the electrons are distributed in certain manner. These subshells are designated as s, p, d, and f. Based on the arrangement of electrons in subshells, the elements of periodic table are classified into four blocks namely s, p, d and f blocks.
19. What is the state of matter at STANDARD STATE (25 °C; 101 kPa)?
- Ne 1. Liquid
- Fe 2. Solid
- Hg 3. Synthetic
- TC 4. Gas
- 1, 3, 2, 4
- 1, 2, 4, 3
- 4, 2, 1, 3
- 4, 2, 3, 1
Explanation
20. Which of the following statement about s-Block Elements is correct?
- It includes group 1 (alkali metals) and group 2 (alkaline earth metals) elements.
- The elements of group 1 (except hydrogen) are metals
- They react with water to form solutions that change the colour of a litmus paper from blue to red.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
s-Block Elements includes group 1 (alkali metals) and group 2 (alkaline earth metals) elements. They are also called as representative elements. The elements of group 1 (except hydrogen) are metals. They react with water to form solutions that change the colour of a litmus paper from red to blue. These solutions are said to be highly alkaline or basic. Hence, they are called alkali metals. The elements of group 2 are also metals. They combine with oxygen to form oxides, formerly called ‘earths’, and these oxides produce alkaline solutions when they are dissolved in water. Hence, these elements are called alkaline earth metals.
21. Which group elements are included in p-Block Elements?
- 13 to 15
- 9 to 12
- 13 to 18
- 11 to 18
Explanation
p-Block Elements are in group 13 to 18 in the periodic table. They include boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine families in addition to noble gases (Except helium). They are also called as representative elements. The p-block is home to the biggest variety of elements and is the only block that contains all three types of elements: metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
22. Which block elements have their properties are intermediate to of s block and p block elements?
- f – block
- d – block
- e – block
- o – block
Explanation
d-Block Elements includes group 3 to group 12 elements. They are found in the centre of the periodic table. Their properties are intermediate to that of s block and p block elements and so they are called transition elements.
23. Which of the following statement about f – Block Elements is correct?
- It includes 14 elements after (Lanthanum) La (57), called Lanthanides and 14 elements after (Actinium) Ac (89), called Actinides
- They are also called as inner Transition elements
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
f – Block Elements includes 14 elements after (Lanthanum) La (57), called Lanthanides and 14 elements after (Actinium) Ac (89), called Actinides. They are placed at the bottom of the periodic table. They are also called as inner Transition elements.
24. Which of the following statement regarding Modern Periodic Table is correct?
- The table is based on a more fundamental property i.e., atomic mass
- Each group is an independent group and the idea of subgroups has been discarded.
- One position for all isotopes of an element is justified, since the isotopes have the same atomic number
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
- The table is based on a more fundamental property i.e., atomic number.
- It correlates the position of the element with its electronic configuration more clearly
- The completion of each period is more logical. In a period, as the atomic number increases, the energy shells are gradually filled up until an inert gas configuration is reached
- It is easy to remember and reproduce.
- Each group is an independent group and the idea of subgroups has been discarded.
- One position for all isotopes of an element is justified, since the isotopes have the same atomic number
- The position of the eighth group (in Mendeleev‘s table) is also justified in this table. All transition elem6ents have been brought in the middle as the properties of transition elements are intermediate between left portion and right portion elements of the periodic table.
25. In Modern Periodic Table, the non-metals are present in____ corner.
- Upper left corner
- Upper right corner
- Lower left corner
- Upper left corner
Explanation
The table completely separates metals from non-metals. The non-metals are present in upper right corners of the periodic table. The positions of certain elements which were earlier misfit (interchanged) in the Mendeleev’s periodic table are now justified because it is based on atomic number of the elements. Justification has been offered for placing lanthanides and actinides at the bottom of the periodic table.
26. Which of the following statement about hydrogen in the periodic table is correct?
- Hydrogen is the lightest, smallest and first element of the periodic table
- Its electronic configuration (1s2) is the simplest of all the elements.
- It behaves like alkali metals as well as chalcogens in its properties.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Hydrogen is the lightest, smallest and first element of the periodic table. Its electronic configuration (1s1) is the simplest of all the elements. It occupies a unique position in the periodic table. It behaves like alkali metals as well as halogens in its properties.
27. Maximum number of electrons in each sub shell 2s is_______
- 1
- 2
- 6
- 10
Explanation
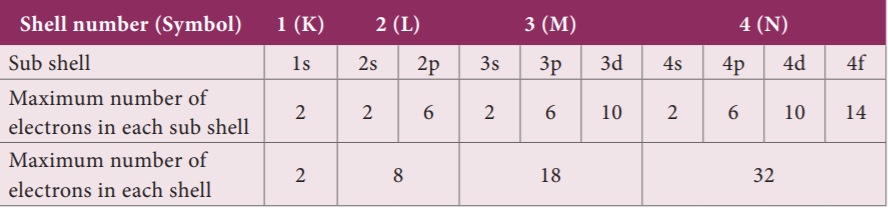
28. In the periodic table, Hydrogen is placed at the top of the_________
- Alkaline earth metals
- Alkali metals
- Non-metals
- Lanthanides
Explanation
In the periodic table, Hydrogen is placed at the top of the alkali metals.
- Hydrogen can lose its only one electron to form a hydrogen ion (H+) like alkali metals.
- It can also gain one electron to form the hydride ion (H-) like halogens.
- Alkali metals are solids while hydrogen is a gas
Hence the position of hydrogen in the modern periodic table is still under debate as the properties of hydrogen are unique.
29. Which group elements are called as inert gases?
- Group 9
- Group 18
- Group 19
- Group 15
Explanation
The elements Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon and Radon of group 18 in the periodic table are called as Noble gases or Rare gases. They are monoatomic gases and do not react with other substances easily, due to completely filled subshells. Hence, they are called as inert gases. They are found in very small quantities and hence they are called as rare gases.
30. Which of the following is not a property of metal?
- Shiny
- Hard
- Ductile
- Non-fusible
Explanation
Metals are typically hard, shiny, malleable (can be made as sheet), fusible and ductile (can be drawn into wire) with good electrical and thermal conductivity. Except mercury, most of the metals are solids at room temperature.
31. Match the following:
- Alkali metals 1. Al
- Alkaline earth metals 2. Radium
- p-block metals 3. Francium
- 3, 1, 2
- 3, 2, 1
- 2, 1, 3
- 1, 2, 3
Explanation
Metals occupy larger area in the periodic table and are categorized as:
(i) Alkali metals. e.g. Lithium to Francium (top to bottom)
(ii) Alkaline earth metals. e.g: Beryllium to Radium (top to bottom)
(iii) Transition Metals. Group 3 to 12
(iv) p-block metals. e.g: Al, Ga, In, Tl, Sn, Pb and Bi.
32. Which of the following are non-metals?
- C
- N
- P
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
A non-metal is an element that does not have the characters like hardness, shiny, malleable, suitable and ductile. In other words, a non-metal is an element that does not have the properties of metal. All non-metals are arranged in p-block only. E.g. C, N, O, P, S, Se, Halogen (F, Cl, Br and I) and inert gases (He to Rn).
33. Which of the following is a metalloid?
- Silver
- Arsenic
- Carbon
- Hydrogen
Explanation
Elements which have the properties of both metals and non-metals are called as metalloids. (eg) Boron, Arsenic.
34. Which of the following statement is correct?
- During 3500 BC(BCE), people used an alloy named ‘bronze’
- Rarely non-metals are also mixed with metals to produce alloys
- Alloy brass is made from copper and zinc.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
During 3500 BC(BCE), people used an alloy named ‘bronze’. The idea of making an alloy was quite old. The majority of the metallic substances used today are alloys. Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals and are formed by mixing molten metals thoroughly. Rarely nonmetals are also mixed with metals to produce alloys. It is generally found that alloying produces a metallic substance that has more useful properties than the original pure metals from which it is made. For example, the alloy brass is made from copper and zinc.
35. Metals mixed with which forms an amalgam?
- Zinc
- Tin
- Mercury
- Polonium
Explanation
- Alloys do not get corroded or get corroded to very less extent
- When metal is alloyed with mercury, it is called amalgam.
- They are harder and stronger than pure metals (Example: Gold is mixed with copper and it is harder than pure gold).
36. Solder is an alloy of______
- Mercury
- Tin
- Zinc
- Lead
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- 2, 4
Explanation
Some alloys have lower melting point than pure metals (Example: Solder is an alloy of lead and tin which has lower melting point than each of the metals). Alloys have less conductance than pure metals (Example: Copper is good conductor of heat and electricity whereas brass and bronze are not good conductors).
37. Which of the following is known as long form of periodic table?
- Mendeleev’s periodic table
- Modern periodic table
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newlands’ Law of Octaves
Explanation
The modern periodic table is the extension of the original Mendeleev’s periodic table and known as the long form of periodic table.
38. Arrange the Noble gas in correct order?
- He
- Rn
- Ar
- Kr
- 1, 4, 2, 3
- 1, 3, 2, 4
- 2, 1, 4, 3
- 1, 3, 4, 2
Explanation
39. Which of the following does not belong to Carbon family?
- Carbon
- Silicon
- Arsenic
- Tin
Explanation
Group 14 elements belong to Carbon family.
40. Uranium belongs to which of the following?
- Carbon family
- Lanthanide
- Actinide
- Halogen family
Explanation
9th Science Lesson 13 Questions in English
13] Chemical Bonding
1. Which of the following alone exists in independent state?
- Chalcogen
- Nobel gas
- Halogen
- All the above
Explanation
We already know that atoms are the building blocks of matter. Under normal conditions no atom exists as an independent (single) entity in nature, except noble gases.
2. Which of the following statement is correct?
- A group of atoms is found to exist together as one species called molecule
- There should be a force to keep the constituent atoms together as the thread holds the flowers together in a garland
- This attractive force which holds the atoms together is called a bond
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
A group of atoms is found to exist together as one species. Such a group of atoms is called molecule. Obviously, there should be a force to keep the constituent atoms together as the thread holds the flowers together in a garland. This attractive force which holds the atoms together is called a bond. A chemical bond may be defined as the force of attraction between the atoms that binds them together as a unit called molecule.
3. Who explained about why atoms combine to form molecules based on Noble gases?
- Kossel
- Karol
- Lewis
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Kossel and Lewis gave successful explained the concept of electronic configuration of noble gases about why atoms combine to form molecules. Atoms of noble gases have little or no tendency to combine with each other or with atoms of other elements. This means that these atoms must be having stable electronic configurations.
4. Match the following:
- Krypton 1. 2
- Neon 2. 2,8,18,18,8
- Helium 3. 2, 8
- Xenon 4. 2,8,18,8
- 3, 1, 4, 2
- 4, 3, 1, 2
- 4, 3, 2, 1
- 3, 4, 1, 2
Explanation
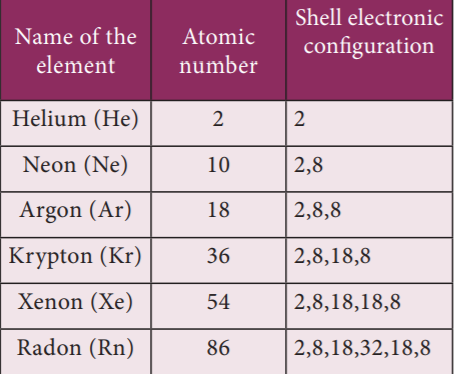
5. Which Noble gas doesn’t have eight electrons in their valence shell?
- Helium
- Neon
- Krypton
- Radon
Explanation
Except Helium, all other noble gases have eight electrons in their valence shell. Even helium has its valence shell completely filled and hence no more electrons can be added. The number of electrons lost from a metal atom is the valency of the metal and the number of electrons gained by a nonmetal is the valency of the non-metal.
6. Assertion(A): Noble gases do not form diatomic molecules and exist as monoatomic gaseous atoms
Reason(R): Because of their stable valence shell electronic configuration, the noble gas atoms
neither have any tendency to gain nor to lose electrons
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
Because of having stable valence shell electronic configuration, the noble gas atoms neither have any tendency to gain nor to lose electrons and hence their valency is zero. They are so inert that they even do not form diatomic molecules and exist as monoatomic gaseous atoms.
7. When did Kossel and Lewis proposed ‘Electronic theory of valence’ or Octet rule?
- 1920
- 1916
- 1909
- 1954
Explanation
Based on the noble gas electronic configuration, Kossel and Lewis proposed a theory in 1916 to explain chemical combination between atoms and this theory is known as ‘Electronic theory of valence’ or Octet rule.
8. Which of the following statement about Octet rule is correct?
- Atoms of all elements, other than inert gases, combine to form molecules because they have incomplete valence shell
- They tend to attain a stable electronic configuration similar to noble gases
- The tendency of atoms to have eight electrons in the valence shell is known as the ‘Octet rule’ or the ‘Rule of eight’
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
According to ‘Electronic theory of valence’ or Octet rule, atoms of all elements, other than inert gases, combine to form molecules because they have incomplete valence shell and tend to attain a stable electronic configuration similar to noble gases. Atoms can combine either by transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another or by sharing of valence electrons in order to achieve the stable outer shell of eight electrons. The tendency of atoms to have eight electrons in the valence shell is known as the ‘Octet rule’ or the ‘Rule of eight’.
9. What is the electronic configuration of Chlorine?
- 2,8,7
- 2,8
- 2,8,9
- 2,8,18
Explanation
Sodium with atomic number 11 will readily loose one electron to attain neon’s stable electronic configuration. Similarly, chlorine has electronic configuration 2,8,7. To get the nearest noble gas (i.e. argon) configuration, it needs one more electron. So, chlorine readily gains one electron from other atoms and obtains stable electronic configuration. Thus, elements tend to have stable valence shell (eight electrons) either by losing or gaining electrons.
10. Match the following atoms with their Valency:
- Boron 1. 1
- Nitrogen 2. 3
- Oxygen 3. 5
- Sodium 4. 6
- 1, 4, 2, 3
- 2, 1, 4, 3
- 2, 3, 4, 1
- 1, 3, 2, 4
Explanation
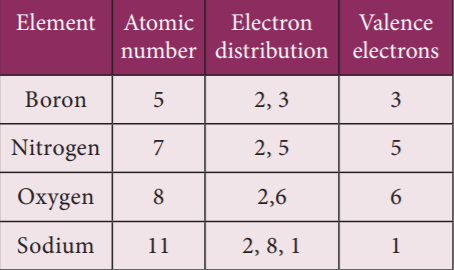
11. Which of the following statement is correct?
- When atoms combine to form compounds, their valence electrons involve in bonding
- The Lewis dot structure or electron dot symbol for an atom consists of the symbol of the element surrounded by dots representing the electrons of the valence shell of the atom
- The unpaired electron in the valence shell is represented by double dot
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
When atoms combine to form compounds, their valence electrons involve in bonding. Therefore, it is helpful to have a method to depict the valence electrons in the atoms. This can be done using Lewis dot symbol method. The Lewis dot structure or electron dot symbol for an atom consists of the symbol of the element surrounded by dots representing the electrons of the valence shell of the atom. The unpaired electron in the valence shell is represented by a single dot whereas the paired electrons are represented by a pair of dots.
12. Which of the following are used to differentiate the electrons of the different atoms in molecule?
- Circle
- Dot
- Crosses
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Symbols other than dots, like crosses or circles may be used to differentiate the electrons of the different atoms in the molecule.
13. Match the following:
- Hydrogen 1. 2,6
- Nitrogen 2. 2
- Helium 3. 1
- Oxygen 4. 2, 5
- 3, 1, 4, 2
- 2, 1, 4, 3
- 3, 4, 2, 1
- 4, 3, 1, 2
Explanation

14. Which of the following statement is correct?
- All the elements have different valence shell electronic configuration
- Depending on the type of bond, they show different characteristics or properties
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
All the elements have different valence shell electronic configuration. So, the way in which they combine to form compounds also differs. Hence, there are different types of chemical bonding possible between atoms which make the molecules. Depending on the type of bond, they show different characteristics or properties. Such types of bonding, that are considered to exist in molecules.
15. An ionic bond is a chemical bond formed by_______
- Electrostatic repulsion
- Electrostatic attraction
- Magnetic pulling
- None
Explanation
An ionic bond is a chemical bond formed by the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions. The bond is formed between two atoms when one or more electrons are transferred from the valence shell of one atom to the valence shell of the other atom.
16. The atom that loses electrons will form______
- Anion
- Cation
- Anode
- Cathode
Explanation
The atom that loses electrons will form a cation (positive ion) and the atom that gains electrons will form an anion (negative ion). These oppositely charged ions come closer to each other due to electrostatic force of attraction and thus form an ionic bond.
17. When the bond is between the ions, then it is called as______
- Covalent bond
- Electrovalent bond
- Electrostatic bond
- Ionic bond
Explanation
As the bond is between the ions, it is called Ionic bond and the attractive forces being electrostatic, the bond is also called Electrostatic bond. Since the valence concept has been explained in terms of electrons, it is also called as Electrovalent bond.
18. Ionic bond is formed between__________
- Metals
- Non-metals
- Noble gases
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Let us consider two atoms A and B. Let atom A has one electron in excess and atom B has one electron lesser than the stable octet electronic configuration. If atom A transfer one electron to atom B, then both the atoms will acquire stable octet electronic configuration. As the result of this electron transfer, atom A will become positive ion (cation) and atom B will become negative ion (anion). These oppositely charged ions are held together by electrostatic force of attraction which is called Ionic bond or Electrovalent bond. In general, ionic bond is formed between a metal and non-metal.
19. Which group elements form ionic compounds when they react with non-metals?
- Group 1
- Group 4
- Group 2
- Group 5
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- 2, 4
- 1, 3
Explanation
The compounds containing ionic bonds are called ionic compounds. Elements of Group 1 and 2 in periodic table, i.e. alkali and alkaline earth metals form ionic compounds when they react with non-metals. The number of electrons that an atom of an element loses or gains to form an electrovalent bond is called its Electro-valency.
20. What is the nearest stable electronic configuration (noble gas) of Sodium?
- Helium
- Neon
- Argon
- Krypton
Explanation
The atomic number of Sodium is 11 and its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 1. It has one electron excess to the nearest stable electronic configuration of a noble gas – Neon. So, sodium has a tendency to lose one electron from its outermost shell and acquire a stable electronic configuration forming sodium cation (Na+).
21. What is the nearest stable electronic configuration (noble gas) of Chlorine?
- Radon
- Neon
- Argon
- Krypton
Explanation
The atomic number of Chlorine is 17 and its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 7. It has one electron less to the nearest stable electronic configuration of a noble gas – Argon. So, Chlorine has a tendency to gain one electron to acquire a stable electronic configuration forming chloride anion (Cl−).
22. Which of the following are Weak Chemical bonding?
- Hydrogen bond
- Covalent bond
- Van der walls interaction
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
23. What is the atomic number of magnesium?
- 13
- 12
- 16
- 21
Explanation
The atomic number of magnesium is 12 and the electronic configuration is 2, 8, 2. It has two electron excess to the nearest stable electronic configuration of a noble gas – Neon. So, magnesium has a tendency to lose two electrons from its outermost shell and acquire a stable electronic configuration forming magnesium cation (Mg2+).
24. Ionic compounds are_____ at room temperature.
- Crystalline solids
- Liquid
- Gas
- None
Explanation
Ionic compounds are formed because of the strong electrostatic force between cations and anions which are arranged in a well-defined geometrical pattern. Thus, ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature.
25. Which of the following statement about ionic compound is correct?
- Ionic are tightly held together
- In molten state their aqueous solutions conduct electricity
- In solid state they cannot move freely, and they do not conduct electricity.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Ionic compounds are crystalline solids and so their ions are tightly held together. The ions, therefore, cannot move freely, and they do not conduct electricity in solid state. However, in molten state their aqueous solutions conduct electricity.
26. Which of the following statement about ionic compound is correct?
- High melting and Low boiling points
- High melting and boiling points
- Low melting and boiling points
- Low melting and High boiling point
Explanation
The strong electrostatic force between the cations and anions hold the ions tightly together, so very high energy is required to separate them. Hence ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
27. In Which of the following ionic compounds are insoluble?
- Benzene
- Carbon tetra chloride
- Water
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents like water. They are insoluble in non-polar solvents like benzene (C6 H6), carbon tetra chloride (CCl4). Ionic compounds have high density and they are quite hard because of the strong electrostatic force between the ions. But they are highly brittle. Ionic compounds undergo ionic reactions which are practically rapid and instantaneous
28. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Atoms can combine with each other by sharing the unpaired electrons in their outermost shell
- Covalent bond is formed because of the sharing of electrons which become common to both the atoms
- Covalent bond is also called as atomic bond.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Atoms can combine with each other by sharing the unpaired electrons in their outermost shell. Each of the two combining atoms contributes one electron to the electron pair which is needed for the bond formation and has equal claim on the shared electron pair. According to Lewis concept, when two atoms form a covalent bond between them, each of the atoms attains the stable electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas. Since the covalent bond is formed because of the sharing of electrons which become common to both the atoms, it is also called as atomic bond.
29. How many types of Covalent bond exists?
- 3
- 1
- 4
- 2
Explanation
Formation of Covalent bond:
Let us consider two atoms A and B. Let atom A has one valence electron and atom B has seven valence electrons. As these atoms approach nearer to each other, each atom contributes one electron and the resulting electron pair fills the outer shell of both the atoms. Thus, both the atoms acquire a completely filled valence shell electronic configuration which leads to stability. There are three types of Covalent bond.
30. Match the following:
- Double Covalent bond 1. Between Nitrogen atoms
- Single Covalent bond 2. Between Oxygen atoms
- Triple Covalent bond 3. Between Hydrogen atoms
- 2, 1, 3
- 3, 2, 1
- 2, 3, 1
- 1, 3, 2
Explanation

31. How many valence electrons does Chlorine atom have?
- 1
- 2
- 7
- 3
Explanation
Chlorine molecule is formed by two chlorine atoms. Each chlorine atom has seven valence electrons (2,8,7). These two atoms achieve a stable completely filled electronic configuration (octet) by sharing a pair of electrons.
32. Methane molecule is formed by the combination of_______
- One Carbon and three Hydrogen
- One Carbon and four Hydrogen
- Two Carbon and five Hydrogen
- One Caron and one Hydrogen
Explanation
Methane molecule is formed by the combination of one carbon and four hydrogen atoms. The carbon atom has four valence electrons (2, 4). These four electrons are shared with four atoms of hydrogen to achieve a stable electronic configuration (octet) by sharing a pair of electrons.
33. How many valence electrons does Oxygen atom have?
- 3
- 1
- 6
- 5
Explanation
Oxygen molecule is formed by two oxygen atoms. Each oxygen atom has six valence electrons (2, 6). These two atoms achieve a stable electronic configuration (octet) by sharing two pair of electrons. Hence a double bond is formed in between the two atoms.
34. What is the electronic configuration of Nitrogen?
- 2, 7
- 2, 5
- 2, 1
- 2
Explanation
Nitrogen molecule is formed by two nitrogen atoms. Each nitrogen atom has five valence electrons (2, 5). These two atoms achieve a stable completely filled electronic configuration (octet) by sharing three pair of electrons. Hence a triple bond is formed in between the two atoms.
35. What are the Physical state of Covalent bond compound?
- Gas
- Solid
- Liquid
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Depending on force of attraction between covalent molecule the bond may be weaker or stronger. Thus, covalent compounds exist in gaseous, liquid and solid form. Eg. Oxygen-gas; Water-liquid: Diamond-solid.
36. Assertion (A): Covalent compounds are Bad conductor of electricity
Reason (R): They do not contain charged particles
- Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) does not explain (A)
- Both (A) and (R) are wrong
- Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A)
- (A) is Correct and (R) is wrong
Explanation
Covalent compounds do not contain charged particles (ions), so they are bad conductors of electricity. Covalent compounds are neither hard nor brittle. But they are soft and waxy.
37. In which of the following Covalent bond compounds are insoluble?
- Benzene
- Carbon tetra chloride
- Water
- All the above
Explanation
Covalent compounds are readily soluble in non-polar solvents like benzene (C6 H6), carbon tetra chloride (CCl4). They are insoluble in polar solvents like water. Covalent compounds undergo molecular reactions in solutions and these reactions are slow
38. Which of the following compounds are Polar solvents?
- Water
- Acetone
- Acetic acid
- Ammonia
- 1, 2, 3
- 2, 3, 4
- 1, 3, 4
- All the above
Explanation
Polar solvents contain bonds between atoms with very different electronegativities, such as oxygen and hydrogen. Ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents. Ex: water, ethanol, acetic acid, ammonia.
39. Non polar solvents contain bonds between atoms with similar electro negativities, such as___
- Carbon
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Non polar solvents contain bonds between atoms with similar electro negativities, such as carbon and hydrogen. Covalent compounds are soluble in nonpolar solvents. Ex: acetone, benzene, toluene, turpentine.
40. Which of the following statement is correct?
- A metal combines with a nonmetal through ionic bond.
- A compound is said to be ionic when the charge of the cation and anion are completely separated.
- In 1923, Robert Frost found, through his X-Ray crystallographic studies, that some of the ionic compounds show covalent character.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
As we know, a metal combines with a nonmetal through ionic bond. The compounds so formed are called ionic compounds. A compound is said to be ionic when the charge of the cation and anion are completely separated. But in 1923, Kazimierz Fajans found, through his X-Ray crystallographic studies, that some of the ionic compounds show covalent character.
41. According to Fajan’s rule, when the size of the cation is small and that of anion is large, the bond
is of more_________
- Ionic
- Covalent
- Coordinate
- Hydrogen
Explanation
Fajan’s rules are formulated by considering the charge of the cation and the relative size of the cation and anion.
- When the size of the cation is small and that of anion is large, the bond is of more covalent character
- Greater the charge of the cation, greater will be the covalent character
42. Which of the following are features of Ionic bond?
- Low positive charge
- Large cation
- Small anion
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
43. In aluminium triiodide, the bond is_______
- Ionic
- Covalent
- Coordinate
- Hydrogen
Explanation
In sodium chloride, low positive charge (+1), a fairly large cation and relatively small anion make the charges to separate completely. So, it is ionic. In aluminium triiodide, higher is the positive charge (+3), larger is the anion and thus no complete charge separation. So, it is covalent.
44. Coordinate covalent bond is also known as________
- Atomic bond
- Dative bond
- Hydrogen bond
- Van der walls interaction
Explanation
In the formation of normal covalent bond each of the two bonded atoms contribute one electron to form the bond. However, in some compounds, the formation of a covalent bond between two atoms takes place by the sharing of two electrons, both of which comes from only one of the combining atoms. This bond is called Coordinate covalent bond or Dative bond.
45. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Mostly the lone pair of electrons from an atom in a molecule may be involved in the dative bonding
- The atom which provides the electron pair is called donor atom while the other atom which accepts the electron pair is called acceptor atom.
- The coordinate covalent bond is represented by an arrow (→) which points from the donor to the acceptor atom.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Mostly the lone pair of electrons from an atom in a molecule may be involved in the dative bonding. The atom which provides the electron pair is called donor atom while the other atom which accepts the electron pair is called acceptor atom. The coordinate covalent bond is represented by an arrow (→) which points from the donor to the acceptor atom.
46. Which of the following statement about coordinate covalent compound is correct?
- These compounds exist as gases, liquids or solids
- Coordinate compounds also do not contain charged particles (ions), so they are bad conductors of electricity
- They are soluble in polar solvents like water
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Characteristics of coordinate covalent compounds:
Physical state: These compounds exist as gases, liquids or solids.
Electrical conductivity: Like covalent compounds, coordinate compounds also do not contain charged particles (ions), so they are bad conductors of electricity.
Melting point: These compounds have melting and boiling points higher than those of purely covalent compounds but lower than those of purely ionic compounds.
Solubility: Insoluble in polar solvents like water but are soluble in non-polar solvents like benzene, CCl4, and toluene.
Reactions: Coordinate covalent compounds undergo molecular reactions which are slow.
47. Which of the following results in Oxidation?
- Addition of oxygen
- Addition of hydrogen
- Loss of electron
- Removal of hydrogen
- 1, 2, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- 1, 3, 4
- All the above
Explanation
The chemical reaction which involves addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen or loss of electrons is called oxidation.
48. What is the below reaction?
2 Na + H2 → 2 NaH
- Oxidation
- Reduction
- Redox
- None
Explanation
The chemical reaction which involves addition of hydrogen or removal of oxygen or gain of electrons is called reduction.
2 Na + H2 → 2 NaH (addition of hydrogen)
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2 O (removal of oxygen)
Fe3++ e− →Fe2+ (gain of electron)
49. 2 PbO + C → 2 Pb + CO2
What is the above reaction?
- Oxidation
- Reduction
- Redox
- None
Explanation
Generally, the oxidation and reduction occur in the same reaction (simultaneously). If one reactant gets oxidised, the other gets reduced. Such reactions are called oxidation-reduction reactions or Redox reactions.
2 PbO + C → 2 Pb + CO2
Zn + CuSO4 → Cu + ZnSO4
50. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Substances which have the ability to oxidise other substances are called oxidising agents
- These are also called as electron acceptors
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Substances which have the ability to oxidise other substances are called oxidising agents. These are also called as electron acceptors because they remove electrons from other substances. Example: H2 O2, MnO4 −, CrO3, Cr2 O7 2−
51. Which of the following are Reducing agents?
- H2 O
- NaBH4
- Platinum
- Palladium
- 1, 3, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- 1, 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Substances which have the ability to reduce other substances are called Reducing agents. These are also called as electron donors because they donate electrons to other substances. Example: NaBH4, LiAlH4 and metals like Palladium, Platinum.
52. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The oxidation reaction in food materials is called Rancidity
- The shining surface of metals tarnishes due to the formation of respective metal oxides on their surfaces. This is called corrosion.
- The freshly cut surfaces of vegetables and fruits turn brown after some time because of the oxidation of compounds present in them.
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- 1, 2
- All the above
Explanation
In nature, the oxygen present in atmospheric air oxidises many things, starting from metals to living tissues.
- The shining surface of metals tarnishes due to the formation of respective metal oxides on their surfaces. This is called corrosion
- The freshly cut surfaces of vegetables and fruits turn brown after some time because of the oxidation of compounds present in them
- The oxidation reaction in food materials that were left open for a long period is responsible for spoiling of food. This is called Rancidity
53. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Oxidation number is also called oxidation state
- The sum of oxidation numbers of all the atoms in the formula for a neutral compound is ZERO.
- Negative oxidation number in a compound of two unlike atoms is assigned to the more electronegative atom
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Oxidation number of an element is defined as the total number of electrons that an atom either gains or loses in order to form a chemical bond with another atom. Oxidation number is also called oxidation state. If the oxidation number is positive then it means that the atom loses electron, and if it is negative it means that the atom gains electrons. If it is zero then the atom neither gains nor loses electrons. The sum of oxidation numbers of all the atoms in the formula for a neutral compound is ZERO. The sum of oxidation numbers of an ion is the same as the charge on that ion. Negative oxidation number in a compound of two unlike atoms is assigned to the more electronegative atom.
54. Match the following:
- Oxidation number of Br in KBr 1. +1
- Oxidation number of Oxygen in most cases 2. – 1
- Oxidation number of H 3. – 2
- 3, 1, 2
- 2, 3, 1
- 2, 1, 3
- 3, 2, 1
Explanation
• Oxidation number of K and Br in KBr molecule is +1 and –1 respectively.
• Oxidation number of N in NH3 molecule is –3.
• Oxidation number of H is +1 (except hydrides).
• Oxidation number of Oxygen in most cases is –2.
55. What is the Oxidation Number of S in H2SO4?
- 4
- 6
- 1
- 3
Explanation
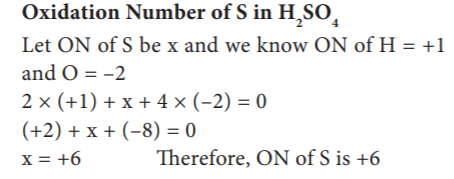
56. What is the Oxidation Number of H in H2O?
- 2
- 1
- 3
- -2
Explanation
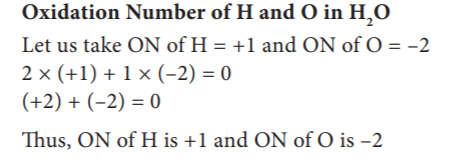
57. What is the Oxidation Number of Cr in K2 Cr2 O7?
- 7
- 12
- 6
- 3
Explanation
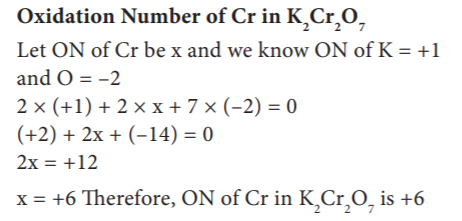
9th Science Lesson 14 Questions in English
14] Acids, Bases And Salts
1. Which are the chemical substances used in everyday life?
a) Acid
b) Salt
c) Base
d) All the above
Explanation
Soil, air, water, all the life forms and the materials that they use are all consist of chemicals. Out of such chemicals, acids, bases and salts are mostly used in everyday life.
2. Which of this acid is secreted in human stomach?
a) Nitric Acid
b) Sulphuric Acid
c) Hydrochloric Acid
d) Chloric Acid
Explanation
Our body metabolism is carried out by means of hydrochloric acid secreted in our stomach.
3. Assertion (A): Acids forms hydrogen ions in the aqueous solution.
Reasoning (R): Base compounds forms hydroxyl ions in the aqueous solution.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
An acid is a the compound which is capable of forming hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution whereas a base is a compound that forms hydroxyl ions (OH–) in solution.
4. Which of this chemical element is neutral?
a) Acid
b) Base
c) Salt
d) All the above
Explanation
When an acid and a base react with each other a neutral product is formed which is called salt.
5. What is the taste of an acid?
a) Bitter
b) Sour
c) Tasteless
d) None of the above
Explanation
A certain type of chemical compounds present in them gives sour taste. These are called acids. Substances with sour taste are called acids.
6. What is the root word of Acid?
a) Acidus
b) Acidi
c) Aidus
d) Aicidi
Explanation
The word ‘acid’ is derived from the Latin name “acidus”.
7. Match
A. Tea i) Oxalic acid
B. Vinegar ii) Tannic acid
C. Orange iii) Acetic acid
D. Tomato iv) Ascorbic acid
a) ii, iv, iii, i
b) i, iv, iii, ii
c) ii, iii, iv, i
d) i, ii, iv, iii
Explanation
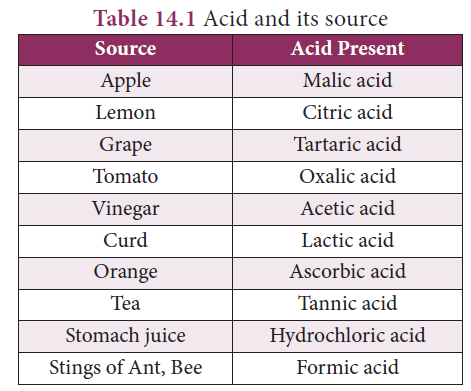
8. When Svante Arrhenius proposed a theory on acids and base?
a) 1889
b) 1725
c) 1761
d) 1884
Explanation
In 1884 a Swedish chemist Svante Arrhenius proposed a theory on acids and bases.
9. Arrhenius theory produces ____ or ____ ions in aqueous solution.
a) H+, HO
b) H-, H2
c) H+, H3O+
d) H-, H2O
Explanation
According to Arrhenius theory an acid is a substance which furnishes H+ ions or H3O+ ions in aqueous solution.
10. Which ion is separated from HCl molecule in the presence of water?
a) He2+
b) Cl
c) H+
d) N2
Explanation
Hydrogen ions in HCl are produced in the presence of water. The separation of H+ ion from HCl molecules cannot occur in the absence of water.
11. Which of these statements are not true?
a) Hydrogen ions exist in combined state with water.
b) Hydrogen ions can also exist alone.
c) Hydrogen ions is always H+ or H3O+.
d) All the above
Explanation
Hydrogen ions cannot exist alone but they exist in combined state with water molecules. Thus hydrogen ions must always be H+ (or) Hydronium (H3O+).
12. Assertion (A): The Hydrogen containing substances are classified as acids.
Reasoning (R): All the acids contain one or more hydrogen.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
All acids essentially contain one or more hydrogen. But all the hydrogen containing substances are not acids. For example, methane (CH4) and ammonia (NH3) also contain hydrogen. But they do not produce H+ ions in aqueous solution.
13. Which of these acids has three replaceable hydrogen ions?
a) Acetic acid
b) Phosphoric acid
c) Formic acid
d) Nitric acid
Explanation

14. Choose the correct statements.
i) Organic acids are present in plants and living things.
ii) Hydrochloric acid is an example of organic acid.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Based on their sources: Organic Acids: Acids present in plants and animals (living things) are organic acids. Example: HCOOH, CH3COOH
15. Which of these is the source of the Inorganic acid?
a) Plants
b) Sea water
c) Animals
d) Minerals
Explanation
Inorganic Acids: Acids prepared from rocks and minerals are inorganic acids or mineral acids. Example: HCl, HNO3, H2SO4
16. State the example of a monobasic acid?
a) H3PO4
b) H2SO4
c) HNO3
d) CH3COOH
Explanation
Monobasic Acid: Acid that contains only one replaceable hydrogen atom per molecule is called monobasic acid. It gives one hydrogen ion per molecule of the acid in solution. Example: HCl, HNO3
17. Choose the correct statements.
i) Basicity refers the number of replaceable hydrogen atoms in one molecule of an acid.
ii) The total number of hydrogen atoms in the molecular formula classifies the basicity.
iii) CH3COOH is a tribasic acid.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
For acids, we use the term basicity that refers to the number of replaceable hydrogen atoms present in one molecule of an acid. For example, acetic acid (CH3COOH) has four hydrogen atoms but only one can be replaced. Hence it is monobasic.
18. Assertion (A): Acid which gives two hydrogen ions per molecule of acid are called dibasic acid.
Reasoning (R): H3PO4 is an example for the dibasic acid.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Dibasic Acid: An acid which gives two hydrogen ions per molecule of the acid in solution. Example: H2SO4, H2CO3
Tribasic Acid: An acid which gives three hydrogen ions per molecule of the acid in solution. Example: H3PO4
19. Choose the correct statements.
i) Acids do not get ionized in water completely.
ii) A strong acid completely ionize in water.
iii) Weak acids do not ionize in water.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Acids get ionized in water (produce H+ ions) completely or partially. Based on the extent of ionization acids are classified as below.
Strong Acids: These are acids that ionize completely in water. Example: HCl
Weak Acids: These are acids that ionize partially in water. Example: CH3COOH.
20. Which of these causes the ionization?
a) Heat
b) Electrical discharge
c) Chemical reactions
d) All the above
Explanation
Ionization is the condition of being dissociated into ions by heat or radiation or chemical reactions or electrical discharge.
21. How many types of acids are classified based on the concentration?
a) 3
b) 2
c) 4
d) 5
Explanation
Concentrated Acid: It has relatively large amount of acid dissolved in a solvent. Dilute Acid: It has relatively smaller amount of acid dissolved in solvent.
22. Which of these are the properties of acids?
a) Turns red litmus to red.
b) Acid aqueous solutions conduct electricity
c) Bitter taste
d) Only source of acids are minerals.
Explanation
Properties of Acids: They have sour taste. Their aqueous solutions conduct electricity since they contain ions. Acids turn blue litmus red.
23. Which of these will react with acids and give hydrogen gas?
a) Salts
b) Water
c) Metals
d) Base
Explanation
Acids react with active metals to give hydrogen gas.
Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2 ↑
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 ↑
24. Which gas is resulted in the reaction of acids with metal carbonates?
a) Carbon dioxide
b) Methane
c) Oxygen
d) Nitrogen
Explanation
Acids react with metal carbonate and metal hydrogen carbonate to give carbon dioxide.
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2 ↑
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2 ↑
25. Which of these is not involved in a neutralization reaction?
a) Metallic oxides
b) Salt
c) Base
d) Gas
Explanation
Acids react with metallic oxides to give salt and water. CaO + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + H2O
Acids react with bases to give salt and water. HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
The reaction is known as neutralization reaction.
26. What are the end products of a neutralization reaction?
a) Gas, Salt
b) Salt, water
c) Water, Base
d) Base, Salt
Explanation
Acids react with bases to give salt and water. The reaction is known as neutralization reaction
27. Which acid is called as the King of chemicals?
a) Nitric acid
b) Hydrochloric acid
c) Sulphuric acid
d) Phosphoric acid
Explanation
Sulphuric acid is called King of Chemicals because it is used in the preparation of many other compounds. It is used in car batteries also.
28. Which of this acid is used as a food preservative?
a) Hydrochloric acid
b) Citric acid
c) Formic acid
d) Lactic acid
Explanation
Hydrochloric acid is used as a cleansing agent in toilets. Citric acid is used in the preparation of effervescent salts and as a food preservative.
29. Which of these are manufactured by Nitric Acid?
a) Fertilizers
b) Paints
c) Drugs
d) All the above
Explanation
Nitric acid is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, dyes, paints and drugs.
30. Which of these is not a usage of Oxalic acid?
a) Cleansing agent in toilets
b) Bleach for wood
c) Remove black stains
d) Clean iron and manganese deposits
Explanation
Oxalic acid is used to clean iron and manganese deposits from quartz crystals. It is also used as bleach for wood and removing black stains.
31. Which of this acid is used in aerated drinks?
a) Oxalic acid
b) Carbonic acid
c) Nitric acid
d) Hydrochloric acid
Explanation
Carbonic acid is used in aerated drinks. Tartaric acid is a constituent of baking powder.
32. Choose the correct statements.
i) Acids ionize in water which determines its properties.
ii) Acids partially ionize in organic solvents.
iii) HCl is dissolved in ethanol and produce H+ and Cl– ions.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Acids show their properties only when dissolved in water. In water, they ionize to form H+ ions which determine the properties of acids. They do not ionize in organic solvents. For example when HCl is dissolved in water it produces H+ ions and Cl– ions whereas in organic solvents like ethanol they do not ionize and remain as molecule.
33. Assertion (A): Aquaregia is a mixture of HCl and HNO3.
Reasoning (R): Gold and silver react with HCl and HNO3.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Metals like gold and silver are not reactive with either HCl or HNO3. But the mixture of these two acids can dissolve gold. This mixture is called Aquaregia.
34. State the properties of Aquaregia.
i) HCl and HNO3 mixture of molar ratio 3:1
ii) A yellow-orange fuming liquid.
iii) Highly corrosive can dissolve gold.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Aquaregia is a mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid prepared optimally in a molar ratio of 3:1. It is a yellow-orange fuming liquid. It is a highly corrosive liquid, able to attack gold and other substances.
35. What is the boiling point of the Aquaregia?
a) 108°C
b) 226°C
c) – 42°C
d) 231K
Explanation
Aquaregia
Chemical formula: 3 HCl + HNO3
Solubility in Water: Miscible in water
Melting point: – 42°C (- 44°F, 231K)
Boiling point: 108°C (226°F, 381K)
36. Which language is the origin for the word Aquaregia?
a) Rome
b) Latin
c) French
d) Persian
Explanation
The term Aquaregia is a Latin phrase meaning ‘King’s Water’. The name reflects the ability of aquaregia to dissolve the noble metals such as gold, platinum and palladium.
37. What are the uses of aquaregia?
a) Dissolve gold and platinum
b) Cleaning gold
c) Refining gold
d) All the above
Explanation
Uses of Aquaregia
1. It is used chiefly to dissolve metals such as gold and platinum.
2. It is used for cleaning and refining gold.
38. According to Arrhenius theory Bases,
i) Ionize in water to form hydroxyl ions.
ii) React with acids and result in salt and water.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
According to Arrhenius theory bases are substances that ionize in water to form hydroxyl ions (OH–). There are some metal oxides which give salt and water on reaction with acids. These are also called bases.
39. What is the name of water soluble base substances soluble?
a) Alkalis
b) Salts
c) Carbonates
d) Metals
Explanation
Bases that are soluble in water are called alkalis. A base reacts with an acid to give salt and water only. Base + Acid → Salt + Water
40. Which of these is not an alkali?
a) Copper Hydroxide
b) Sodium Hydroxide
c) Potassium Hydroxide
d) Calcium Hydroxide
Explanation
Sodium hydroxide ionizes in water to give hydroxyl ions and thus get dissolved in water. So it is an alkali. NaOH (aq) → Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
41. Assertion (A): All the bases are alkalis.
Reasoning (R): All alkalis are not bases.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
All alkalis are bases but not all bases are alkalis. For example: NaOH and KOH are alkalis whereas Al (OH)3 and Zn(OH)2 are bases.
42. How many number of hydroxyl ions are present in Calcium hydroxide?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 4
d) 3
Explanation
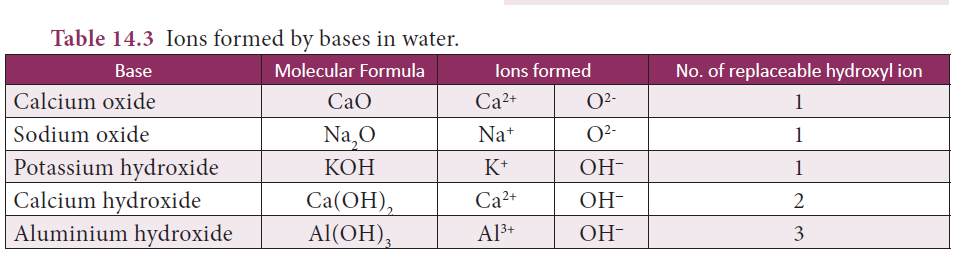
43. Identify the incorrect match.
A. Diacidic Base i) Magnesium Hydroxide
B. Monoacidic Base ii) Zinc Hydroxide
C. Triacidic Base iii) Aluminum Hydroxide
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Classification of Bases: Based on their Acidity
Monoacidic Base: It is a base that ionizes in water to give one hydroxide ion per molecule. Example: NaOH, KOH
Diacidic Base: It is a base that ionizes in water to give two hydroxide ions per molecule. Example: Ca(OH)2. Mg(OH)2
Triacidic Base: It is a base that ionizes in water to give three hydroxide ions per molecule. Example: Al(OH)3, Fe(OH)3
44. Which of the following is correct based on the concentration of alkalis.
a) Concentrated Alkali has high percentage of alkali in its aqueous solution.
b) Dilute Alkali is an aqueous solution.
c) Concentrated alkali exists as solid form of substances.
d) Dilute Alkali has low percentage of aqueous solution.
Explanation
Based on concentration
Concentrated Alkali: It is an alkali having a relatively high percentage of alkali in its aqueous solution. Dilute Alkali: It is an alkali having a relatively low percentage of alkali in its aqueous solution.
45. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Strong Bases ionize completely in the aqueous solution.
ii) Sodium Hydroxide is classified as weak base.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Based on Ionization
Strong Bases: These are bases which ionize completely in aqueous solution. Example: NaOH, KOH
Weak Bases: These are bases that ionize partially in aqueous solution. Example: NH4OH, Ca(OH)2
46. Acidity of a base means the number of replaceable ________ in _______of a base.
a) Hydrogen, ten molecules
b) Nitrogen, one molecule
c) Hydroxyl, one molecule
d) Oxygen, 100 molecules
Explanation
The term acidity is used for base which means the number of replaceable hydroxyl groups present in one molecule of a base.
47. Choose the correct statements regarding the properties of a base.
i) Red litmus is turned to blue.
ii) Bitter taste
iii) Aqueous solution is soapy
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Properties of Bases
a) They have bitter taste.
b) Their aqueous solutions have soapy touch.
c) They turn red litmus blue.
d) Their aqueous solutions conduct electricity.
48. What is the resultant gas of Base reacting with metal?
a) Nitrogen
b) Oxygen
c) Hydrogen
d) Ammonia
Explanation
Bases react with metals to form salt with the liberation of hydrogen gas.
Zn + 2 NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2↑
49. What is the nature of non-metallic oxides?
a) Acidic
b) Base
c) Neutral
d) All the above
Explanation
Bases react with non-metallic oxides to produce salt and water. Since this is similar to the reaction between a base and an acid we can conclude that nonmetallic oxides are acidic in nature. Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3+ H2O
50. Define a neutralization reaction.
a) Salt + Acid —-> Base
b) Acid + Base —-> Salt + water
c) Base + Acid —-> Salt
d) Salt + Base —-> Water
Explanation
Bases react with acids to form salt and water. KOH + HCl → KCl + H2O
The above reaction between a base and an acid is known as Neutralization reaction.
51. Which of these results in ammonium gas while heating with ammonium salts?
a) Base
b) Acid
c) Metal
d) All the above
Explanation
On heating with ammonium salts, bases give ammonia gas. NaOH + NH4Cl → NaCl + H2O + NH3↑
52. Which of these metals does not react with sodium hydroxide?
a) Copper
b) Chromium
c) Silver
d) All the above
Explanation
Few metals do not react with sodium hydroxide. Example: Cu, Ag, Cr
53. Match
A. Sodium Hydroxide i) Medicine
B. Ammonium Hydroxide ii) White washes
C. Calcium Hydroxide iii) Soap making
D. Magnesium Hydroxide iv) Cloth stain remover
a) iv, ii, iii, i
b) iii, iv, ii, i
c) ii, iii, i, iv
d) iii, i, ii, iv
Explanation
Uses of Bases
(i) Sodium hydroxide is used in the manufacture of soap.
(ii) Calcium hydroxide is used in white washing of building.
(iii) Magnesium hydroxide is used as a medicine for stomach disorder.
(iv) Ammonium hydroxide is used to remove grease stains from cloths.
54. Choose the correct statements.
i) An acid turns blue litmus paper into red.
ii) Phenolphthalein is colorless in acid medium.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Test with a litmus paper: An acid turns blue litmus paper into red. A base turns red litmus paper into blue. Test with an indicator Phenolphthalein: In acid medium, phenolphthalein is colorless. In basic medium, phenolphthalein is pink in color.
55. In which of the medium the Methyl orange is pink color?
a) Acid
b) Base
c) Neutral
d) All the above
Explanation
Test with an indicator Methyl orange: In acid medium, methyl orange is pink in color. In basic medium, methyl orange is yellow in color.
56. Match the color indicator of base.
A. Methyl Orange i) Pink
B. Phenolphthalein ii) Blue
C. Litmus iii) Yellow
a) ii, i, iii
b) i, iii, ii
c) iii, i, ii
d) ii, iii, i
Explanation

57. What does a pH scale measures?
a) Hydrogen ion concentration
b) Neutrality
c) Acidity
d) None of the above
Explanation
A scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution is called pH scale.
58. What does p denote in a pH scale?
a) Potenz
b) Product
c) Pole
d) Partial
Explanation
The ‘p’ in pH stands for ‘potenz’ in German meaning power.
59. What is the maximum scale of a pH scale?
a) 8
b) 7
c) 14
d) 10
Explanation
The pH scale is a set of numbers from 0 to 14 which is used to indicate whether a solution is acidic, basic or neutral.
60. What is the pH value of a neutral solution?
a) < 7
b) =7
c) > 7
d) 0
Explanation
Acids have pH less than 7, Bases have pH greater than 7 and a neutral solution has pH equal to 7.
61. Which of this salt is separated from the sea water?
a) Potassium Chloride
b) Sodium Carbonate
c) Sodium Chloride
d) Calcium Hydroxide
Explanation
When you say salt you may think of the common salt. Sea water contains many salts dissolved in it. Sodium chloride is separated from these salts.
62. Salts are,
i) It is a product of acid base reaction.
ii) It produces only positive ions in water.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Salts are the products of the reaction between acids and bases. Salts produce positive ions and negative ions when dissolved in water.
63. Which of this reaction produce a normal salt?
a) Neutralization
b) Double replacement
c) Ionization
d) Combustion
Explanation
Normal Salts: A normal salt is obtained by complete neutralization of an acid by a base.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
64. Assertion (A): Acid salt is obtained by adding calculated amount of base to a polybasic acid.
Reasoning (R): Metals partially replace hydrogen ions of an acid.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Acid Salts: It is derived from the partial replacement of hydrogen ions of an acid by a metal. When a calculated amount of a base is added to a polybasic acid, acid salt is obtained.
NaOH + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + H2O
65. Which of these ions are partially replaced to form a Basic salt?
a) Nitrogen
b) Hydroxide
c) Hydrogen
d) Chlorine
Explanation
Basic Salts: Basic salts are formed by the partial replacement of hydroxide ions of a diacidic or triacidic base with an acid radical. Pb(OH)2 + HCl → Pb(OH)Cl + H2O
66. Which of these are the characteristics of a Double salt?
a) Combination of saturated solution of two salts.
b) Salts are in equimolar ratio
c) Crystallization
d) All the above
Explanation
Double Salts: Double salts are formed by the combination of the saturated solution of two simple salts in equimolar ratio followed by crystallization. For example, potash alum is a mixture of potassium sulphate and aluminum sulphate. KAl(SO4)2·12H2O
67. Choose the correct statements.
i) Salts are mostly liquids which boil at high temperature.
ii) All Salts are soluble in water.
iii) Salts are hygroscopic in nature.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Properties of Salts: Salts are mostly solids which melt as well as boil at high temperature. Most of the salts are soluble in water. For example, chloride salts of potassium and sodium are soluble in water. But silver chloride is insoluble in water. They are odorless, mostly white, cubic crystals or crystalline powder with salty taste. Salt is hygroscopic in nature.
68. Assertion (A): Salts having water of crystallization are hydrated salts.
Reasoning (R): Water molecules of salts are known as water of crystallization.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Many salts are found as crystals with water molecules. These water molecules are known as water of crystallization. Salts that contain water of crystallization are called hydrated salts.
69. Choose the correct statements.
i) The water molecules hydrated to a salt is indicated after a dot in the chemical formula.
ii) Copper sulphate pentahydrate has five water molecules only.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The number of molecules of water hydrated to a salt is indicated after a dot in its chemical formula. For example, copper sulphate crystal has five molecules of water for each molecule of copper sulphate. It is written as CuSO4.5H2O and named as copper sulphate pentahydrate. This water of crystallization makes the copper sulphate blue. When it is heated, it loses its water molecules and becomes white.
70. What are the qualities of an anhydrous salt?
a) Not soluble in water
b) Highly concentrated carbon atoms
c) Does not contain water of crystallization
d) Not soluble in any liquids
Explanation
Salts that do not contain water of crystallization are called anhydrous salt. They are generally found as powders.
71. Which of these studies are made by physically examining a salt?
a) Color
b) Smell
c) Density
d) All the above
Explanation
The physical examination of the unknown salt involves the study of color, smell and density. This test is not much reliable.
72. What is the end product of salts reacting with concentrated Hydrochloric acid?
a) Chlorides
b) Carbonates
c) Nitrates
d) Sulphate
Explanation
Flame Test: Certain salts on reacting with concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl) form their chlorides. The paste of the mixture with con. HCl is introduced into the flame with the help of platinum wire.
73. Match the color of flame and the inferred compounds.
A. K+ i) Green Fleshes
B. Na+ ii) Brick red
C. Ca2+ iii) Pink violet
D. Zn2+ iv) Golden yellow
a) i, iv, ii, iii
b) i, iii, ii, iv
c) ii, iii, i, iv
d) iii, iv, ii, i
Explanation
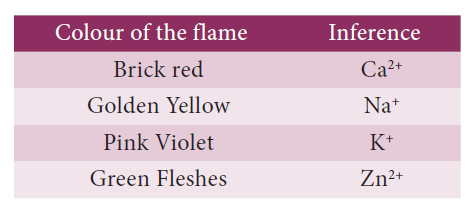
74. What gas is resulted if HCl is added with a carbonate salt?
a) CO2
b) O2
c) Cl2
d) H2
Explanation
When HCl is added with a carbonate salt it gives off CO2 gas with brisk effervescence.
75. Which of these is known as common salt?
a) Sodium Bicarbonate
b) Sodium Carbonate
c) Sodium Chloride
d) Sodium Hydroxide
Explanation
Common Salt (Sodium Chloride – NaCl) It is used in our daily food and used as a preservative.
76. What are the uses of Sodium Carbonate?
a) Glass Industries
b) Soap Making
c) Paper Industries
d) All the above
Explanation
Washing Soda (Sodium Carbonate-Na2CO3) is used in softening hard water. It is used in glass, soap and paper industries.
77. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding Sodium bicarbonate.
i) NaHCO3 is the formula for the Sodium bicarbonate also known as Baking soda.
ii) Baking powder consists of baking soda and Oxalic acid.
iii) It is also used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Baking Soda (Sodium bicarbonate -NaHCO3): It is used in making of baking powder which is a mixture of baking soda and tartaric acid. It is used in soda-acid fire extinguishers. Baking powder is used to make cakes and bread, soft and spongy. It neutralizes excess acid in the stomach and provides relief.
78. What is the chemical name for the bleaching powder?
a) Calcium Oxychloride
b) Formaldehyde
c) Hydrogen Peroxide
d) Sodium Hypo chloride
Explanation
Bleaching powder (Calcium Oxychloride – CaOCl2): It is used as disinfectant. It is used in textile industry for bleaching cotton and linen.
79. What is the chemical formula for the Plaster of Paris?
a) KaSO4
b) CaSO4. H2O
c) CaSO4. 1/2H2O
d) MgSO3. H2O
Explanation
Plaster of Paris (Calcium Sulphate Hemihydrate – CaSO4 .½ H2O)
i. It is used for plastering bones.
ii. It is used for making casts for statues.
80. Which of the following is a double salt?
a) Potash Alum
b) Copper Sulphate
c) Sodium bicarbonate
d) Potassium Chloride
Explanation
Potash alum is a chemical compound widely used as the potassium sulfate dodecahydrate. It is double salt that is used commonly in medicine and the water treatment process.
9th Science Lesson 15 Questions in English
15] Carbon And Its Compounds
1. Carbon is the _______ element denoted by the symbol ______.
a) Non-metallic, C
b) Metallic, CO
c) Organic, CO2
d) Non-metallic, c
Explanation
Carbon is one of the most important non-metallic elements. It is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6.
2. Who named carbon from the Latin word Carbo?
a) Benjamin Brodie
b) Berzelius
c) Antoine Lavoisier
d) Carl Scheele
Explanation
Antoine Lavoisier named Carbon from the Latin word ‘Carbo’ meaning coal.
3. Assertion (A): Carbon is the main constituent of coal and present in all the living forms.
Reasoning (R): Coal is a fossil fuel developed from the decomposition of buried plants and animals.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Carbon is the main constituent of coal. Coal is a fossil fuel developed from prolonged decomposition of buried plants and animals. So it is clear that all the life forms contain carbon.
4. What percentage of carbon dioxide is present in the earth’s atmosphere?
a) 0.73%
b) 0.33%
c) 3.33%
d) 0.03%
Explanation
The earth atmosphere has only 0.03% of carbon dioxide (i.e.300 parts per million by weight).
5. Assertion (A): Earth crust contains 0.032% of carbon in various forms.
Reasoning (R): Carbon compounds are very important element in everyday life of human.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The earth’s crust contains only 0.032% of carbon (i.e.320 parts per million by weight) in the form of minerals like carbonates, coal and petroleum. Even though available in small amount in nature, carbon compounds have an immense importance in everyday life.
6. In which of these substances carbon is not present?
a) Human blood
b) Air
c) Graphite
d) Glass
Explanation
Carbon is present in our muscles, bones, organs, blood and other components of living matter.
7. What is the other name of the Carbon chemistry?
a) Plant Chemistry
b) Inorganic Chemistry
c) Living Chemistry
d) Human Chemistry
Explanation
Carbon Chemistry is also called as Living Chemistry. Without carbon there is no possibility for the existence of plants and animals including human.
8. What are known forms of carbon from the ancient times?
a) Diamonds
b) Charcoal
c) Graphite
d) All the above
Explanation
Carbon has been known since ancient times in the form of soot, charcoal, graphite and diamonds.
9. What was the conclusion of the experiments done by Antoine Lavoisier in 1772?
a) Sun rays burn diamonds.
b) Diamond and Charcoal were made of carbon.
c) Diamond is the highest form of carbon.
d) Carbon is essential for human lives.
Explanation
In 1772, French scientist Antoine Lavoisier pooled resources with other chemists to buy a diamond, which they placed in a closed glass jar they focused the Sun’s rays on the diamond with a remarkable giant magnifying glass and saw the diamond burn and disappear. Lavoisier noted that the overall weight of the jar was unchanged and that when it burned, the diamond had combined with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. He concluded that diamond and charcoal were made of the same element – carbon.
10. Name the scientist who showed burnt graphite forms carbon dioxide?
a) Benjamin Brodie
b) Smithson Tennant
c) Berzelius
d) Carl Scheele
Explanation
In 1779, Swedish scientist Carl Scheele showed that graphite also burned to form carbon dioxide.
11. Who proved that diamond is a pure carbon?
a) Smithson Tennant
b) Antoine Lavoisier
c) Berzelius
d) Francis Bundy
Explanation
In 1796, English chemist Smithson Tennant established that diamond is pure carbon and not a compound of carbon and it burned to form only carbon dioxide.
12. What was the conclusion of the experiments done by Francis Bundy at General Electric company?
a) Graphite is an Inorganic carbon compound.
b) Graphite is a purest form of carbon.
c) Graphite could be transformed into diamond at high temperature and pressure.
d) Diamond and Graphite can be transformed to coal.
Explanation
In 1855, English chemist Benjamin Brodie produced pure graphite from carbon, proving graphite is a form of carbon. Although it had been previously attempted without success, in 1955 American scientist Francis Bundy and his co-workers at ‘General Electric’ company finally demonstrated that graphite could be transformed into diamond at high temperature and pressure.
13. In which year a new form of carbon, fullerenes were discovered by scientists?
a) 1855
b) 1985
c) 1796
d) 1955
Explanation
In 1985, Robert Curl, Harry Kroto and Richard Smalley discovered fullerenes, a new form of carbon in which the atoms are arranged in soccer-ball shapes.
14. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding Graphene.
i) It consists of single layer of carbon atoms in hexagon arrangement.
ii) It was discovered in the year 1985.
iii) Kostya Novoselov and Andre Geim discovered graphene.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Graphene consists of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in hexagons. Graphene’s discovery was announced in 2004 by Kostya Novoselov and Andre Geim.
15. Which of these statements is true?
a) Carbon is found in Free State only
b) Carbon is excessively present in earth’s layer.
c) Carbon is found in both Free State and combined state in nature.
d) Carbon is metallic element.
Explanation
Carbon is found both in Free State as well as combined state in nature.
16. On what basis Berzelius classifies the carbon compounds?
a) Source
b) Usage
c) Chemical properties
d) Atomic values
Explanation
In the early 19th century, Berzelius classified carbon compounds based on their source.
17. Match the origin of the scientists.
A. Smithson Tennant i) France
B. Carl Scheele ii) England
C. Antoine Lavoisier iii) America
D. Francis Bundy iv) Sweden
a) ii, iv, i, iii
b) ii, iii, iv, i
c) ii, iv, i, iii
d) iv, iii, ii, i
Explanation
French scientist Antoine Lavoisier, Swedish scientist Carl Scheele, English chemist Smithson Tennant, American scientist Francis Bundy did various experiments on carbon and its compounds.
18. Which of these carbon compounds are found in living organisms?
a) Ethanol
b) Cellulose
c) Starch
d) All the above
Explanation
Organic Carbon Compounds: These are the compounds of carbon obtained from living organisms such as plants and animals. e.g. Ethanol, cellulose, Starch.
19. Assertion (A): Calcium carbonate is an inorganic carbon compound.
Reasoning (R): Inorganic carbon compounds are obtained from the non-living matters.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Inorganic Carbon Compounds: These are the compounds containing carbon but obtained from non-living matter. e.g. Calcium Carbonate, Carbon Monoxide, Carbon dioxide.
20. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Organic carbon compounds are connected with elements like hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
ii) Organic carbon compounds are classified based on their sources.
iii) Hydrocarbons, alcohols and amino acids are various organic carbon compounds.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
There are millions of organic carbon compounds available in nature and also synthesized manually. Organic carbon compounds contain carbon connected with other elements like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur etc. Thus, depending on the nature of other elements and the way in which they are connected with carbon, there are various classes of organic carbon compounds such as hydrocarbons, alcohols, aldehydes and ketones, carboxylic acids, amino acids.
21. Which is not a major class of Inorganic carbon compounds?
a) Bicarbonates
b) Ketones
c) Cyanides
d) Carbides
Explanation
As compared to organic compounds the number of inorganic carbon compounds is limited. Among them oxides, carbides, sulphides, cyanides, carbonates and bicarbonates are the major classes of inorganic carbon compounds.
22. Which of these are added to the atmosphere by incomplete combustion of fuels?
a) CO
b) CS2
c) CaCO3
d) NaHCO3
Explanation
Carbon monoxide (CO) is not a natural component of air. Mainly added to atmosphere due to incomplete combustion of fuels.
23. Which is a main component of the water gas?
a) Carbon disulphide
b) Carbon dioxide
c) Carbon monoxide
d) Calcium carbonate
Explanation
Carbon monoxide is the main component of water gas (CO+H2).
24. Assertion (A): Carbon dioxide is found in combined forms in nature.
Reasoning (R): Combined forms of carbon dioxide are found in minerals.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is False but R is True.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Carbon dioxide occurs in nature as free and combined forms. Combined form is found in minerals like limestone, magnesite. It is formed by complete combustion of carbon or coke.
25. In which of these carbon dioxide is not used?
a) Fire extinguisher
b) To prepare acetylene gas for welding
c) Fruits preservation and bread making
d) Dry ice
Explanation
Uses of CO2: Fire extinguisher, preservative for fruits, making bread, to manufacture urea, carbonated water, nitrogenous fertilizers, dry ice in refrigerator.
26. Which of this carbon compound is not colorless?
a) CO
b) CO2
c) CaC2
d) CS2
27. Choose the correct statements regarding Calcium carbide.
i) It appears as a Greyish black solid.
ii) Prepared by heating calcium oxide and coke.
iii) Used to manufacture graphite and hydrogen.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation

28. Which is not a property of carbon disulphide?
a) Colorless
b) Greyish solid
c) Inflammable
d) Highly poisonous gas
Explanation
Carbon disulphide (CS2) is a Colorless, inflammable, highly poisonous gas.
29. Which of this compound is insoluble in water?
a) Carbon monoxide
b) Calcium carbonate
c) Calcium carbide
d) Sodium bicarbonate
Explanation
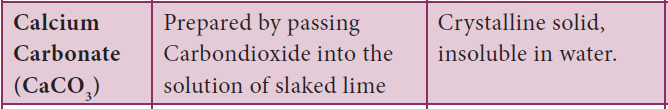
30. Carbon disulphide is prepared from _____ and ______.
a) Carbon, Sulphur
b) Carbon, Sulphate
c) Calcium, Sulphur
d) Carbonates, Sulphate
Explanation
Carbon disulphide (CS2) is directly prepared from Carbon and Sulphur.
31. What are the uses of carbon disulphide?
a) Fungicides and insecticides
b) Solvent for sulphur
c) Rayon manufacture
d) All the above
Explanation
Uses of Carbon disulphide: Solvent for sulphur, to manufacture rayon, fungicide, insecticide.
32. Which of these are used to produce Calcium carbonate?
a) Carbon monoxide, Coke
b) Carbon dioxide, slaked lime solution
c) Calcium oxide, Coke
d) Complete combustion of carbon
Explanation
Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) : Prepared by passing Carbon dioxide into the solution of slaked lime.
33. What is the color of sodium bicarbonate?
a) Colorless
b) Grey
c) Black
d) White
Explanation
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3): White crystalline substance, sparingly soluble in water.
34. Match
A. Carbon disulphide i) Antacid
B. Calcium Carbonate ii) Baking powder
C. Sodium bicarbonate iii) Acetylene gas
D. Calcium Carbide iv) Rayon
a) iii, iv, ii, i
b) iv, i, ii, iii
c) iv, iii, i, i
d) ii, iv, iii, i
Explanation
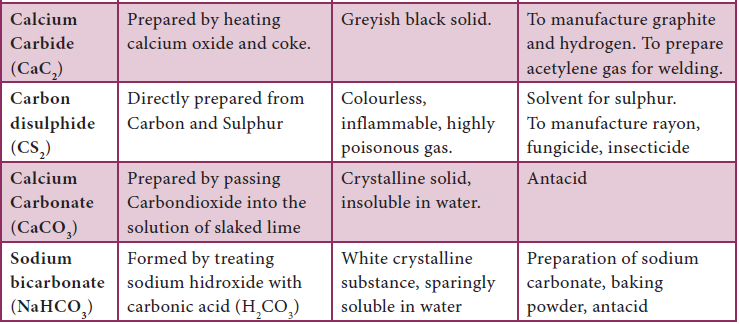
35. Catenation,
i) Binding of an element to itself.
ii) Form open chains by covalent bonds.
iii) Binding of an element to itself or with other elements.
iv) Covalent bonds form open chains or close chain compounds
a) i , iii, only
b) ii, iii, iv only
c) iii, iv only
d) i, iv only
Explanation
Catenation is binding of an element to itself or with other elements through covalent bonds to form open chain or closed chain compounds.
36. Which of these chain structures are formed by the carbon atoms through covalent bonds?
a) Linear chain
b) Branched chain
c) Ring
d) All the above
Explanation
Carbon is the most common element which undergoes catenation and forms long chain compounds. Carbon atom links repeatedly to itself through covalent bond to form linear chain, branched chain or ring structure.
37. Which of the carbon property is dealt by the organic chemistry?
a) Catenation
b) Tetravalency
c) Isomerism
d) None of the above
Explanation
This property of catenations carbon itself is the reason for the presence of large number of organic carbon compounds. So organic chemistry essentially deals with catenated carbon compounds.
38. How many electrons are in the outermost orbit of carbon?
a) 2
b) 6
c) 4
d) 8
Explanation
Another versatile nature of carbon is its tetravalency. The shell electronic configuration of carbon is 2, 4 (Atomic no: 6). It has four electrons in its outermost orbit.
39. Which is the nearest noble gas that could be reached by tetravalency of carbon?
a) Oxygen
b) Neon
c) Helium
d) Fluorine
Explanation
According to Octet Rule, carbon requires four electrons to attain nearest noble gas (Neon) electronic configuration. So carbon has the tendency to share its four electrons with other atoms to complete its octet. This is called its tetravalency.
40. Which of this bond is used for combining tetravalent carbon with other elements?
a) Single bond
b) Double bond
c) Triple bond
d) All the above
Explanation
The tetravalency carbon is able to combine with other elements or with itself through single bond, double bond and triple bond.
41. Assertion (A): The nature of bonding is a primary factor of a compound.
Reasoning (R): The physical and chemical characteristics of a compound are determined by the nature of bonding.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The nature of bonding in a compound is the primary factor which determines the physical and chemical characteristics of a compound.
42. What is the main reason for the existence of various classes of carbon compounds?
a) Multiple bonds
b) Isomerism
c) Easily available
d) Simple structure
Explanation
The ability of carbon to form multiple bonds is the main reason for the existence of various classes of carbon compounds.
43. Match
A. Ethene i) Alkane
B. Methane ii) Alkyne
C. Ethyne iii) Alkene
a) i, iii, ii
b) ii, iii, i
c) iii, i, ii
d) ii, i, iii
Explanation
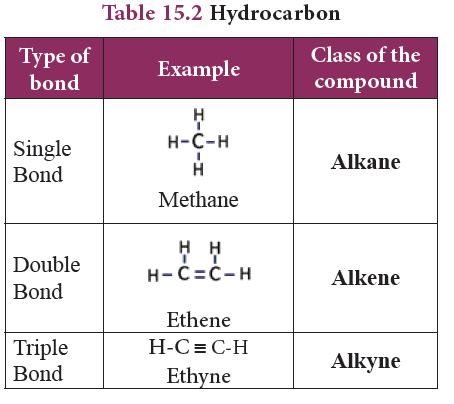
44. Which of this hydrocarbon has a triple bond configuration?
a) Methane
b) Ethyne
c) Ether
d) None of the above
Explanation
Alkyne class of compounds has triple bond configuration example is Ethyne.
45. Which of these elements replace the hydrogen in hydrocarbons to form various functional groups?
a) O
b) N
c) S
d) All the above
Explanation
When one or more hydrogen in hydrocarbons is replaced by other elements like O, N, S, halogens, etc., a variety of compounds having different functional groups is produced.
46. What is the special feature of catenated organic carbon compounds?
a) Isomerism
b) Pentavalent
c) Tetravalent
d) All the above
Explanation
Isomerism is another special feature of carbon compounds especially found in catenated organic compounds.
47. Assertion (A): The total number of atoms is represented in the molecular formula of an organic compound.
Reasoning (R): The molecular formula denotes the arrangement of atoms and the structure.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The molecular formula of an organic compound represents only the number of different atoms present in that compound. It does not tell about the way in which the atoms are arranged and hence its structure. Without knowing the structure, we can’t name it.
48. Define isomerism.
a) Same molecular formula with different structures.
b) Different structural arrangement of compounds.
c) Similar chemical properties.
d) All the above
Explanation
A given molecular formula may lead to more than one arrangement of atoms. Such compounds are having different physical and chemical properties. This phenomenon in which the same molecular formula may exhibit different structural arrangement is called isomerism.
49. Which is the origin of the word isomers?
a) Latin
b) Persian
c) Greek
d) Arabic
Explanation
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formula are called isomers (Greek, isos = equal, meros = parts).
50. Assertion (A): Allotropy elements can exist in more than one form.
Reasoning (R): The physical and chemical characteristics are same for allotropes.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Allotropy is a property by which an element can exist in more than one form that is physically different and chemically similar.
51. What is the main reason for the existence of allotropes?
a) Various sources
b) Formation and preparation methods
c) Multiple bonding
d) All the above
Explanation
The different forms of that element are called its allotropes. The main reason for the existence of allotropes of an element is its method of formation or preparation.
52. How many allotropes of carbon are classified based on their physical nature?
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Explanation
53. Choose the correct statements about Diamond.
i) Each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds.
ii) Atoms are arranged in tetrahedral fashion.
iii) The arrangement of diamond is the reason for the hardness and rigidity.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Diamond: In diamond, each carbon atom shares its four valence electrons with four other carbon atoms forming four covalent bonds. Here the atoms are arranged in repeated tetrahedral fashion which leads to a three dimensional structure accounting for its hardness and rigidity.
54. Why graphite is softer than diamond?
a) Three carbon atoms are bonded through covalent bonds.
b) Hexagonal layer arrangement
c) Weak Vander Waals forces
d) All the above
Explanation
Graphite: In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms through covalent bonds in the same plane. This arrangement forms hexagonal layers which are held together one over other by weak Vander Waals forces. Since the layers are held by weak forces graphite is softer than diamond.
55. How many carbon atoms are present in the Buckminster fullerene?
a) 30
b) 50
c) 60
d) 20
Explanation
Fullerene: The third crystalline allotrope of carbon is fullerene. The best known fullerene is Buckminster fullerene, which consists of 60 carbon atoms joined together in a series of 5- and 6- membered to form spherical molecule resembling a soccer ball. So its formula is C60.
56. What is the shape of the molecular arrangement of the Buckminster fullerene?
a) Linear
b) Spherical
c) Ring
d) Tree
Explanation
The best known fullerene is Buckminster fullerene, which consists of 60 carbon atoms joined together in a series of 5- and 6- membered to form spherical molecule resembling a soccer ball.
57. What is the pet name for the Buckminster fullerene?
a) Bucky Ball
b) Bucky tubes
c) Bucky Onions
d) Magic molecule
Explanation
The allotrope was named as Buckminster fullerene after the American architect Buckminster fuller. Because its structure reminded the framework of dome shaped halls designed by Fuller for large international exhibitions, it is called by the pet name Bucky Ball.
58. Which is the highest fullerene available?
a) C70
b) C540
c) C80
d) C200
Explanation
A large family of fullerenes exists, starting at C20 and reaching up to C540.
59. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding Diamond.
i) Each carbon in diamond has four covalent bonds.
ii) Diamonds are Hard, heavy and transparent.
iii) It is a conductor of heat and electricity.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation

60. The Graphite,
i) Each carbon has three covalent bonds
ii) Planar layers of hexagon units.
iii) Soft, slippery to touch and opaque.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation

61. What is the shape of arrangement of the carbon atoms in the Graphene?
a) Spherical
b) Loop
c) Honeycomb
d) Ring
Explanation
Graphene is most recently produced allotrope of carbon which consists of honeycomb shaped hexagonal ring repeatedly arranged in a plane.
62. Assertion (A): Graphene is the thinnest compound and the lightest known material.
Reasoning (R): Graphene is stronger than steel.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Graphene is the thinnest compound known to man at one atom thick. It is the lightest material known (with 1 square metres weighing around 0.77 milligrams) and the strongest compound discovered (100-300 times stronger than steel). It is a best conductor of heat at room temperature.
63. Which of these results in the stacking of graphene layers?
a) Graphite
b) Coal
c) Diamond
d) Fullerene
Explanation
Layers of graphene are stacked on top of each other to form graphite, with an inter planar spacing of 0.335 nanometers. The separate layers of graphene in graphite are held together by Vander Waals forces.
64. What is the property of an amorphous form of carbon?
a) Ring arrangement of atoms
b) Linear arrangement of atoms
c) Random arrangements of atoms
d) Spherical arrangement of atoms
Explanation
In amorphous form of carbon, carbon atoms are arranged in random manner. These forms of carbon are obtained when wood is heated in the absence of air. E.g., charcoal
65. Assertion (A): All the Allotropic compounds of carbon are available as hard solids
Reasoning (R): Carbon is a metal compound.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Carbon is a non-metal found in various allotropic forms from soft powder to hard solid.
66. In which of these forms the allotropic carbon compounds are available?
a) Solid
b) Liquid
c) Gas
d) All the above
Explanation
All the allotropic forms of carbon are solids whereas its compounds exist in solid, liquid and gaseous state.
67. Which of the carbon forms are black in color?
a) Amorphous
b) Isomers
c) Crystalline
d) Carbon compounds
Explanation
Amorphous forms of carbon and graphite are almost black in color and opaque. Diamond is transparent and shiny.
68. The ______ forms of carbon have low _____.
a) Crystalline, Melting point
b) Amorphous, Melting and Boiling point
c) Crystalline, Boiling point
d) Amorphous, Boiling point
Explanation
Carbon amorphous forms have low melting and boiling point compared to crystalline forms.
69. Assertion (A): Carbon is insoluble in water and other solvents.
Reasoning (R): Ethanol is a compound of carbon is soluble in water.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Carbon is insoluble in water and other common solvents. But some of its compounds are soluble in water and other solvents. e.g., Ethanol, CO2 are soluble in water.
70. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Elemental carbon undergoes no reaction at room temperature.
ii) Carbon compounds are limited number of reactions at elevated temperatures.
iii) Carbon compounds undergo large number of reactions at room temperature.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Elemental carbon undergoes no reaction at room temperature and limited number of reactions at elevated temperatures. But its compounds undergo large number of reactions even at room temperature.
71. Which of this reaction produces the oxides of carbon?
a) Neutralization
b) Oxidation
c) Double replacement
d) Decomposition
Explanation
Oxidation – (Reaction with oxygen) Carbon combines with oxygen to form its oxides like carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) with evolution of heat.
72. Which of this carbon produces flame in the combustion?
a) Inorganic compounds
b) Organic compounds
c) Crystalline compounds
d) Amorphous
Explanation
Organic carbon compounds like hydrocarbon also undergo oxidation to form oxides and steam with evolution of heat and flame. This is otherwise called combustion.
2C(s) + O2(g) → 2CO(g)+ heat
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + heat
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g)+ 2H2O(g) + heat
73. Which of these are resulted in the reaction of steam and carbon?
a) Carbon monoxide, Hydrogen
b) Carbon monoxide, water
c) Carbon dioxide, Nitrogen
d) Carbon dioxide, water
Explanation
Carbon reacts with steam to form carbon monoxide and hydrogen. C(s) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + H2(g)
74. What is the other name of the carbon monoxide and hydrogen mixture?
a) Sea water
b) Sea foam
c) Water gas
d) Smog
Explanation
The mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen is called water gas.
75. In which of these conditions carbon reacts with sulphur?
a) Room temperature
b) High temperature
c) Low temperature
d) Elevated temperature
Explanation
With sulphur, carbon forms its disulphide at high temperature.
C(s) + 2S(g) → CS2(g)
76. Which of these react with carbon and produces its carbides?
a) Iron
b) Tungsten
c) Titanium
d) All the above
Explanation
At elevated temperatures carbon reacts with some metals like iron, tungsten, titanium to form their carbides. Tungsten + Carbon → Tungsten carbide
77. Which of this carbon compound is not harmful to human?
a) Plastic
b) Calcium carbonate
c) Cyanide
d) Carbon monoxide
Explanation
Even though carbon and its compounds are vital for modern life, some of its compounds like CO, cyanide and certain types of plastics are harmful to humans.
78. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Plastics are major class of catenated Inorganic carbon compounds.
ii) Plastics are made from the long chain compounds called as polymer resins.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Plastics are a major class of catenated organic carbon compounds. They are made from long chain organic compounds called ‘polymer resins’ with chemical additives that give them different properties.
79. Why the plastic materials are recycled?
a) Breaking down microbes for plastics are few in nature.
b) Complex atomic structure
c) Hazardous compounds
d) None of the above
Explanation
Drawbacks of plastics: Plastics take a very long time to fully break down in nature. The microbes that break down plastic are too few in nature to deal with the quantity of plastics we produce.
80. What are the environmental effects of plastic usage?
a) Some chemical additives to plastics are harmful for human health.
b) Burning of plastics releases toxic gases result in climate change.
c) One time use plastics pollute the environment.
d) All the above
Explanation
A lot of plastic does not get recycled and ends up polluting the environment. Some types of plastics contain harmful chemical additives that are not good for human health. Burning of plastics releases toxic gases that are harmful to our health and contribute to climate change. One-time use and throwaway plastics end up littering and polluting the environment.
81. Which of these represent the type of polymer used to make the plastic?
a) Color of the plastic
b) Manufacturing date
c) Resin codes
d) Usage of the plastics
Explanation
In order to know which plastics are harmful, you will need to learn the secret ‘language’ of plastics (resin codes).The resin code represents the type of polymer used to make the plastic.
82. In which year the resin codes of plastics were designed?
a) 1976
b) 1988
c) 1955
d) 1945
Explanation
The resin codes of plastics were designed in 1988 and are a uniform way of classifying the different types of plastic which help recyclers in the sorting process.
83. Assertion (A): The Resin codes are represented by three chasing arrows in a triangle with a number or alphabet.
Reasoning (R): The number or alphabet represents the recycle level of the plastic.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The secret resin codes are shown as three chasing arrows in a triangle. There is a number in the middle or letters under the triangle (an acronym of that plastic type). This is usually difficult to find. It can be found on the label or bottom of a plastic item. The resin codes look very similar to the recycling symbol, but this does not mean that all plastics with a code can be recycled.
84. What are the maximum numbers used in resin codes?
a) 5
b) 7
c) 6
d) 3
Explanation
The resin codes are numbered from 1 to 7. Resin codes #1 to #6 each identify a certain type of plastic that is often used in products. Resin code #7 is a category which is used for every other plastic (since 1988) that does not fit into the categories #1 to #6.
85. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Some type of plastics contains harmful chemicals to human health.
ii) Plastics are harmful only when they are burned.
iii) One time use plastics cause pollution to the environment.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Plastics in our everyday life can be harmful for two reasons. The first reason is that some types of plastic contain chemicals that are harmful to our health. The second reason is that a lot of plastics are designed to be used just for one time. This use and throwaway plastic cause’s pollution to our environment.
86. Match
A. PC/ABS i) 6
B. PVC ii) 7
C. PS iii) 3
a) ii, iii, i
b) i, iii, ii
c) iii, ii, i
d) iii, i, ii
Explanation
There are three types of plastic that use toxic and harmful chemicals. These chemicals are added to plastics to give them certain qualities such as flexibility, strength, color and fire or UV resistance. The three unsafe plastics are: PVC (resin code #3), PS (resin code #6 also commonly called Thermocol) and PC/ABS (resin code #7).
87. Which is not true regarding the PVC?
a) Polyvinyl chloride plastics are called as PVC.
b) Burning PVC releases dioxins.
c) Light metals are added to PVC.
d) Phthalates is a chemical additive added to PVC.
Explanation
PVC – Polyvinyl Chloride plastics: Phthalates (chemical additive) copy our hormones. Burning PVC releases dioxins (one of the most toxic chemicals known to humans).
88. Which of these metals are not added to PVC plastic?
a) Cadmium
b) Lithium
c) Lead
d) Tin
Explanation
Heavy metals like cadmium & lead are added to PVC.
89. What is the basis of the PS plastics?
a) Styrene
b) Organic compounds
c) Metals
d) Non metals
Explanation
PS (Polystyrene plastics) Styrene is a building block of this plastic and may cause cancer.
90. What are the disadvantages of PS plastics?
a) It takes up to 1 million years to break down.
b) Styrene in PS may cause cancer to human.
c) Hot and oily foods result in high amount of toxic in food items.
d) All the above
Explanation
PS plastics takes very long time to break-down (100- 1 million years). Higher amounts of toxic styrene leak into our food and drinks when they are hot or oily.
91. What does the Polycarbonate plastics contain?
a) Bisphenol A
b) Ethanol
c) Ether
d) Styrene
Explanation
PC – Polycarbonate plastics: PC plastic contains Bisphenol A (BPA). BPA leaks out of PC products used for food and drinks.
92. What is the effect of BPA of polycarbonate carbonates in the human body?
a) Increases cancer cells
b) Decreases the white blood cells
c) Hormonal changes
d) Affects the nervous system
Explanation
BPA increases or decreases certain hormones and changes the way our bodies work.
93. Choose the correct statements regarding ABS plastics.
i) The Styrene in ABS damages the human skin, digestive system and lungs.
ii) Brominated Flame Retardants are added often in ABS.
iii) Toxic chemicals leak from this type of plastic.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
ABS – Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
• Styrene causes problems for our eyes, skin, digestive system and lungs.
• Brominated Flame Retardants (BFRs) are often added.
• Studies show that toxic chemicals leak from this plastic.
94. By which year amendment the Government of India took initiatives to stop plastic pollution?
a) 1988
b) 1972
c) 1956
d) 1977
Explanation
The Government of India is progressively taking various legal initiatives to stop plastic pollution by making some provisions and amendments in the Environment (Protection) Act, 1988.
95. Which of this department of Tamil Nadu government passed the GO to ban the usage of plastic items?
a) Rural Development and Panchayat Raj Department
b) Agriculture Department
c) Environment and Forests Department
d) Social Reforms Department
Explanation
With reference to this act, Government of Tamil Nadu has taken a step forward to ban the usage of some kind of plastic items (Environment and Forests Department, T.N. G.O. No: 84, dated 25/06/2018).
96. When the Tamil Nadu Government banned the usage of one-time use and throwaway plastics?
a) August 15, 2019
b) January 1, 2019
c) January 15, 2018
d) November 1, 2017
Explanation
As per the government order cited above, the Tamil Nadu Government has banned the usage of one-time use and throwaway plastics from 1st January 2019. This excellent legislation is designed to protect Tamil Nadu from plastic pollution.
97. Which of this item is not banned in Tamil Nadu?
a) Plastic Sheets
b) Plastic Straws
c) Plastic carry bags and Plates
d) PVC pipes
Explanation
As per the key aspects of new rules along with science-based facts these items have been banned in Tamil Nadu Plastic carry bags, Plastic plates, Water pouches, Plastic straws and Plastic sheets.
98. By which of these material most of the plastic one-time plates are made?
a) Polystyrene
b) Bisphenol A
c) Brominated Flame Retardants
d) Lead
Explanation
Most of the one-time use plates are made from Polystyrene (resin code # 6) which is harmful to our health.
99. What are the safety measures for plastic usage in daily life?
a) Do not litter the environment by throwing and burning the plastic items.
b) Avoid using one-time use or throwaway plastics, tea cups, Thermocol plates and plastic straws.
c) Educate to identify the resin codes and avoid unsafe plastics.
d) All the above
Explanation
RULES TO PRACTICE IN DAILY LIFE
