8th Std Science Lesson Wise Questions in English – Part 2
8th Science Lesson 13 Questions in English
13] Movements
1. Define movement.
a) Act of changing the position by one part of the body.
b) Variation in the place and position.
c) Act of changing of the place or position by one or more parts of the body.
d) Maximum variation in the position of the body.
Explanation
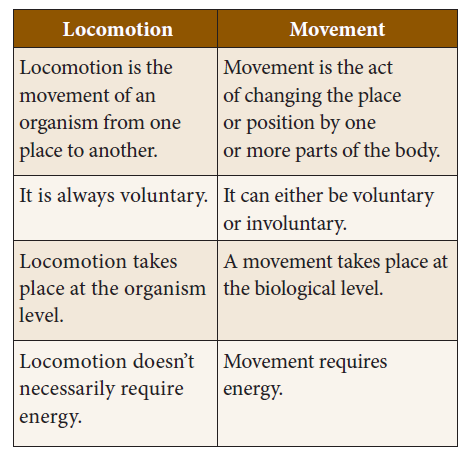
Movement is generally defined “as the act of changing the place or position by one or more parts of the body”.
2. Choose the correct statements.
i) Movements are used to change the position of an organism.
ii) Movements also help to pump blood to different parts of the body.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Movement helps to perform necessary functions such as pumping of blood to different parts of the body in an organism.
3. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Movement is defined as the action of involuntary actions only.
ii) Walking is a voluntary movement.
iii) Breathing is an involuntary movement.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Movement can be both voluntary and involuntary. For example walking is a voluntary movement while breathing is an involuntary movement.
4. What are the uses of locomotion?
a) To find food.
b) Avoid harsh weather conditions.
c) Escape from their predator
d) All the above
Explanation
The movement of an organism from one place to another is known as locomotion. Locomotion helps an organism to find food, avoid harsh weather conditions, escape from their predator etc.
5. What are the types of locomotion?
a) Walking
b) Running
c) Swimming
d) All the above
Explanation
Walking, running and swimming are few examples for different types of locomotion. In this process, there is the action of appendages such as limbs, wings, flagella and cilia.
6. What are the movements of the most aquatic animals?
a) Wave-like muscle contractions.
b) Ciliary movement.
c) Amoeboid movement
d) Muscular movement
Explanation
In most of the aquatic animals such as fish, whales, and shark, the locomotion results from a series of wave-like muscle contractions.
7. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Locomotion can be voluntary and involuntary actions.
ii) Locomotion takes place at the organism level.
iii) Locomotion does not require energy.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
8. Assertion (A): Movement is act of change of place or position by one or more parts of the body.
Reasoning(R): Movement takes place at the biological level and requires energy.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
9. Choose the correct statements.
i) Movement is the basic mechanism of the vertebrates including human.
ii) Animals exhibit a mono type of movements.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Movement is one of the significant features of living beings. This is the basic mechanism used in majority of the vertebrates including human. Animals exhibit a wide range of movements.
10. Which of these in earthworm body used to get grip on the ground?
a) Muscles
b) Setae
c) Rings
d) Nerves
Explanation
The body of earthworm is made up of many rings joined end to end. It has muscles which help to extend and shorten the body. Under its body it has large number of bristles called setae which are connected with muscles. These bristles help to get grip on the ground.
11. Assertion (A): Earthworms move forward by a repeating muscle contractions and relaxation movement.
Reasoning(R): A slimy substance secreted by the body is used for the movement of an earthworm.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Earthworm makes it move forward by small distances. Repeating such muscle contraction and relaxation the earthworm can move through soil. A slimy substance secreted by its body helps this movement.
12. Choose the correct statements.
i) A cockroach has two pairs of legs and two pairs of wings.
ii) Cockroaches can walk, run, climb and fly.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
A cockroach has three pairs of jointed legs, which help it to walk, run and climb. It also has two pairs of wings for flying.
13. Name the protective material in the cockroach body?
a) Chitin
b) Bristles
c) Setae
d) Wings
Explanation
Large and strong muscles help in the movement of legs. The body is covered by chitin, a light protective material. Chitin is shed regularly so that the body can grow.
14. Choose the correct statements.
i) Birds can walk and fly and some birds can also swim in the water.
ii) The bones of the birds are light and strong.
iii) The breast bones of the birds are modified as flight muscles to move the wings.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Birds can walk on the ground and fly as well. Some birds can also swim in the water. A bird has streamlined body. Its bones are light and strong. They are hollow and have air spaces between them. The hind limbs of birds are modified as claws which help them to walk and to perch. The breast bones are modified to hold massive flight muscles which help in moving wings up and down.
15. Which of these are used for the flying movement of birds?
a) Wings
b) Tails
c) Long feathers
d) All the above
Explanation
Birds have special flight muscles and the forelimbs are modified as wings. The wings and tail have long feathers which help in flying.
16. How many types of flight are shown by birds?
a) 2
b) 5
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation
Birds show two types of flight: gliding and flapping.
17. Which of the bird movement uses the air current to go up and down?
a) Gliding
b) Linear
c) Flapping
d) Waving
Explanation
Gliding: During gliding the bird has its wings and tail spread out. In this movement the bird uses air currents for going up and down.
18. Which of these are used by the birds in the flapping movement?
a) Air current
b) Sea current
c) Flight feathers
d) Thermal points
Explanation
Flapping: This is an active flight. The bird beats the air by flapping its wings. They use flight feathers for this purpose.
19. Assertion (A): The Snake body consists of a large number of vertebrae.
Reasoning(R): The skin and the adjoining vertebrae ribs are inter-connected by the slender body muscles.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The body of snake consists of a large number of vertebrae. The adjoining vertebrae ribs and skin are inter-connected with slender body muscles.
20. Name the movement of a snake.
a) Flapping
b) Sliding
c) Slithering
d) Gliding
Explanation
When the snake moves, it makes many loops on its sides. The forward push of the loops against the surface makes the snake move forward. Movement of snake is called slithering movement. Many snakes can swim in water also.
21. Which of these are used by the snakes for their movement?
a) Tissues and bones
b) Muscles and scales
c) Scales only
d) Nerves and bones
Explanation
Since snakes do not have legs they use their muscles and their scales to move.
22. How many paired fins are present in the body of the fish?
a) 3
b) 4
c) 2
d) 1
Explanation
Fish swims with the help of fins. They have two paired fins and an unpaired fin.
23. What is the use of the streamlined body of the fish?
a) To reduce the friction when moving in water.
b) For opposing the water current.
c) To provide strength.
d) To protect the internal organs.
Explanation
The body of a fish is streamlined to reduce friction while moving in water. They have strong muscles which help in swimming.
24. Which of the following is used to change the direction of movement of a fish?
a) Paired fin
b) Streamlined body structure
c) Tail fin
d) Exoskeleton system
Explanation
When a fish swims its front part curves to one side and the tail part stays in the opposite direction. In the next move, the front part curves to the opposite side and the tail part also changes its position to another side. The caudal or tail fin helps in changing direction.
25. Which of these used to maintain the balance in a fish movement?
a) Muscles
b) Fins
c) Tail
d) All the above
Explanation
Fish have streamlined body structure which helps them to move smoothly with the flow of water. Muscles and fins on the body and the tail help to keep the balance.
26. Assertion (A): Human body is made up of a frame work of bones called skeleton.
Reasoning(R): Humans can move all the body parts in different directions using the skeleton system.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Humans can move some parts of their body in different directions; however some body parts can be moved only in one direction. Our body is made up of a frame work of bones called skeleton helps in the movement of the body.
27. Which of these are the human body movements?
a) Head and neck movement
b) Heart muscle movement
c) Arms and legs movement
d) All the above
Explanation
Some of the movements in body parts of human are: Movement of eyelids, Movement of the heart muscles, Movement of teeth and jaw, Movement of arms and legs, Movements of head, Movements of neck.
28. Assertion (A): Human movement is possible along the meeting points of two or more bones.
Reasoning(R): Some human organs movement happens due to the combined action of bones and muscles.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Movement of some organs happens because of the combined action of bones and muscles. In such cases, movement is possible along a point where two or more bones meet.
29. Which of the following is not true?
a) Dolphin is the fastest mammal can swim up to 35 miles per hours.
b) Cheetah can run 76 kilometer per hour.
c) Cockroach is the fastest animal which covers 100 meters per second.
d) Hippopotamus can run faster than a man.
Explanation
- A Cheetah can run 76 kilometer per hour.
- A Hippopotamus can run faster than a man.
- Cockroach is the fastest animal on 6 legs covering a meter per second.
- The fastest mammal, the Dolphin can swim up to 35 miles per hours
30. Which of these causes the amoeboid movement in a cell?
a) Pseudopodia
b) Flagella
c) Hair
d) Cell wall
Explanation
Amoeboid movement: It is brought about by pseudopodia which are appendages which move with movement of protoplasm within a cell.
31. Choose the correct statements.
i) Ciliary movement is brought by cilia, hair-like extensions of the epithelium.
ii) Ciliary movement is seen with the cells of the lymphatic system.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Ciliary movement: This movement is brought about by appendages called as cilia which are the hair-like extensions of the epithelium. Both these kinds of movements are seen with cells of the lymphatic system.
32. Which of these movements is seen in the higher vertebrates?
a) Muscular movement
b) Amoeboid movement
c) Ciliary movement
d) Linear movement
Explanation
Muscular movement: It is a more complex movement which is brought about by the musculoskeletal system. This type of movement is seen in the higher vertebrates.
33. How many number of movements are classified based on the type of movements?
a) 5
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation
The point at which two separate bones meet is called a joint. Depending on the type of movement they allow, joints can be of three types: fixed, slightly moveable and moveable joints.
34. Which is an example of fixed or Immovable joints in the human body?
a) Structures between the bones of the skull box.
b) Ankle joint bones
c) Vertebrae bones joints
d) Hip joint bones
Explanation
Fixed or Immoveable joints: In this type of joint no movement is possible between the two bones. The structures between the bones of the skull box are examples of immoveable joints.
35. Assertion (A): Slightly movable joints have partial movement between the bones.
Reasoning(R): The joint between a rib and the breast bone is an example of slightly movable joint.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Slightly moveable joints: Here, only very little (partial) movement occurs between the two bones. The joint between a rib and the breast bone or between the vertebrae is the example for slightly movable joint.
36. How many major types of movable joints are classified in a human body?
a) 5
b) 3
c) 6
d) 10
Explanation
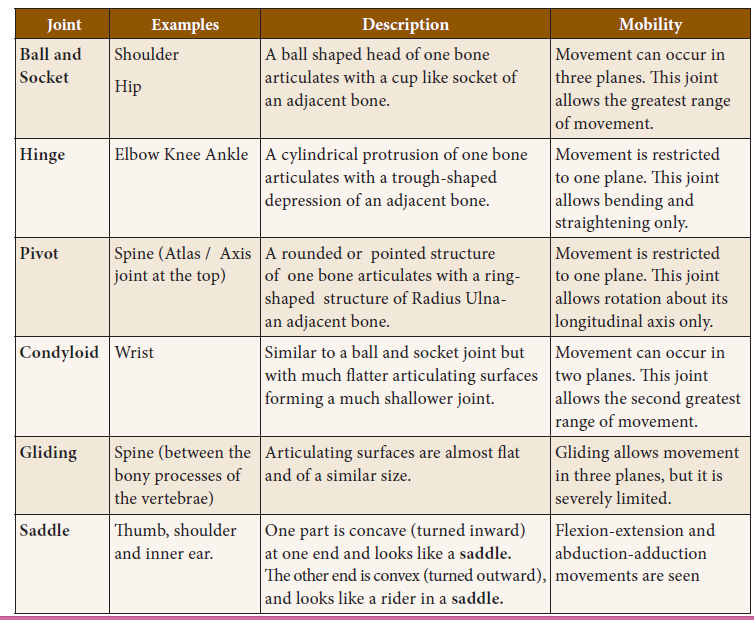
Freely movable joints: In this type, varying degree of movements is possible between the two bones forming the joint. There are six major types of movable joints.
37. In which of these joints the movement can occur freely in three planes?
a) Pivot
b) Hinge
c) Ball and socket
d) Saddle
38. Name the type of joint bones in the wrist of human?
a) Condyloid
b) Hinge
c) Gliding
d) Pivot
39. In which of this human part the bone movement is restricted to one plane?
a) Thumb
b) Shoulder
c) Spine
d) Hips
40. Which of these joints is used for straightening and bending movements only?
a) Hinge
b) Saddle
c) Ball and socket
d) Pivot
41. Which of the following statements are not true regarding the types of movable joints?
a) Pivot joints allow rotation about its longitude axis only.
b) Gliding movement is allowed in three planes with severe limits.
c) Thumb bones the saddle joints allow the greatest range of movements in human body.
d) Flexion-extension and abduction-adduction movements are seen in human shoulder bones.
42. Match
A. Elbow Knee ankle i) Gliding
B. Spine (between the vertebrae bones) ii) Saddle
C. Hip iii) Hinge
D. Inner ear iv) Ball and Socket
a) iv, i, iii, ii
b) iii, i, iv, ii
c) ii, iv, i, iii
d) iii, iv, ii, i
43. Choose the correct statements.
i) In gliding joints the articulating surfaces are almost flat and of similar size.
ii) The Condyloid joints are similar to pivot with flatter articulating surfaces.
iii) Saddle joints have concave and convex ends to look like a saddle and a rider.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Types of movable joints.
44. Define the Diarthrosis joint.
a) A cylindrical protrusion of one bone articulates with a trough-shaped depression.
b) A rounded or pointed structure of one bone articulates with a ring-shaped structure.
c) Connection between two bones filled with cartilage cavity fluid.
d) A ball shaped head of one bone articulates with a cup like socket of an adjacent bone.
Explanation
A synovial joint is a joint which makes connection between two bones consisting of a cartilage lined cavity filled with fluid which is known as a diarthrosis joint.
45. What are the causes for the joint inflammation or Arthritis disease?
a) Lack of synovial fluid in the joints.
b) Friction of the articulating cartilage.
c) Deposition of uric acid crystals in the joints.
d) All the above
Explanation
Inflammation of joints is a condition that usually results either due to friction of articulating cartilage or due to lack of synovial fluid in the joint. During this condition, the person feels acute pain in joints particularly while moving joints. This disease is referred to as arthritis. Arthritis is however also caused due to the deposition of uric acid crystals in the joints.
46. Which of the following substance is present in the joint cavity?
a) Synovial fluid
b) Joint capsule
c) Ligament
d) Articular cartilage
47. State the function of the articular cartilage?
a) For bone to bone connection.
b) Strengthen the joints.
c) Absorbs shock and prevent friction between the ends of the bone joints.
d) Reduces friction between the articular cartilages at the joints.
48. How many fibrous layers are present in the joint capsule?
a) 5
b) 2
c) 6
d) 3
Explanation

49. Assertion (A): The Skeleton system provides the hard structure to the human body.
Reasoning(R): Skeleton system consists of bones, cartilages, tendons and ligaments to provide movement in the human body.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The skeleton system provides the hard structure or framework to the human body which supports and protects the body. It is composed of connective tissues like bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments. If the skeleton is without joints, no movement would take place and the significance of human body will be no more than a stone.
50. On what basis the skeleton is categorized into two types?
a) Functionalities
b) Presence in the body
c) Originating species.
d) Usage of the skeleton
Explanation
On the basis of presence in the body, skeleton is of two types.
51. What are the major features of exoskeleton?
a) Found on the exterior layer.
b) It is dead and it protects and preserves the inner organs.
c) Originates from embryonic ectoderm or mesoderm.
d) All the above
Explanation
Exoskeleton: It is the skeleton that is found on the exterior layer of the body and it basically originates from embryonic ectoderm or mesoderm. Like scales in the fishes, outer hard layer of the tortoise and feathers of the birds it is dead and it protects and preserves the inner organs.
52. From which of these the endoskeleton is originated?
a) Mesoderm
b) Endoderm
c) Mesenchyme
d) Pectoderm
Explanation
Endoskeleton: It is the skeleton that is found inside the human body and it originates from the mesoderm. These are found in almost all vertebrates and form the main body structure.
53. Which of the following is not a function of the human skeletal system?
a) Acts as levers for muscular actions.
b) Produces red blood cells in the bone marrow.
c) Provides mental and physical growth.
d) Supports and surrounds the internal organs of the human body.
Explanation
Functions of skeleton: The skeletal system serves five important functions in the human body. It provides structure and shape to the body. It supports and surrounds the internal organs of the body. Calcium and phosphorus, the two minerals that the body needs for important regulatory functions, are stored inside the bones. Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow. The bones of the skeletal system act as levers for muscular action. Muscular movement would not be possible without tendons (fibrous cords of tissue that attach muscle to bone) and ligaments (fibrous cords of tissue that attach bone to bone).
54. Which of these minerals is stored in the human bones?
a) Sodium
b) Calcium
c) Magnesium
d) Zinc
Explanation
Calcium and phosphorus, the two minerals that the body needs for important regulatory functions, are stored inside the bones.
55. Assertion (A): The Femur or thigh bone is the longest and lightest bone of the human body.
Reasoning(R): The stapes in the middle ear is the smallest and strongest bone of the human skeleton.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The femur or thighbone is the longest and strongest bone of the human skeleton. The stapes in the middle ear is the smallest and lightest bone of the human skeleton.
56. Which of the following is not true?
a) Human skeleton consists of bone, cartilages and ligaments.
b) Ligaments used to bind the bones together.
c) Bones supports the projecting external ears and the tip of the nose.
d) Cartilages are the supporting and connecting structures.
Explanation
Human skeleton consists of bone, cartilages and ligaments. Bones comprise the hard framework of the body. Cartilages are the supporting and connecting structures. For example, the cartilage supports the projecting external ears and the tip of the nose. Ligaments bind the bones together.
57. Match
A. Flat bones i) Legs
B. Long bones ii) Vertebral column
C. Short bones iii) Ribs
a) iii, i, ii
b) ii, iii, i
c) i, iii, ii
d) ii, i, iii
Explanation
There are different types of bones in human skeletal system. They are:
Long bones: Found in arms and legs.
Short bones: Found in wrist ankle, vertebral column.
Flat bones: Found in skull, ribs, shoulder and hips.
58. Which of the following is not an irregular bone?
a) Palatine
b) Hyoid
c) Wrist ankle
d) Mandible
Explanation
Irregular bones: Found in spine and vertebral column, mandible, palatine, inferior nasal concha, and hyoid.
59. Choose the correct statements.
i) The skeletal system consists of bones and related structures for the movement of body.
ii) Skeletal system is divided into three major parts.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The skeletal system is composed of bones and the related structures that aid body movement. It is divided into two major parts: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
60. Which of these are included in the axial skeleton?
a) Skull
b) Vertebral column
c) Sternum
d) All the above
Explanation
The axial skeleton consists of the bones along the axis, or central line of the human body. The axial skeleton consists of the skull, facial bones, sternum, ribs, and vertebral column.
61. How many bones are fused to form the face in a human skull?
a) 22
b) 14
c) 10
d) 8
Explanation
Skull is a hard structure made up of small bones. It is formed by 22 bones out of which 8 bones are fixed together to form the cranium and 14 bones fuse to form the face.
62. Assertion (A): The Skull placed on the top of back bone can be moved only up and down.
Reasoning(R): Lower jaw is one of the bones which have a movable joint.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The only bone which has movable joint is the lower jaw. This movable joint is supported by muscles and ligaments. Skull placed on the top of the backbone can be moved up, down and side wards.
63. Which of these are not called as vertebral column?
a) Spine
b) Thigh bone
c) Vertebrae bones
d) Backbone
Explanation
Vertebral column: Vertebral column running at the back of the body is also called as spine or the backbone. It is in the trunk region to offer support to the upper part of the body. Vertebral column is made up of individual bones called as vertebrae.
64. Match
A. Fused sacral i) 7
B. Cervical vertebrae ii) 12
C. Coccygeal vertebrae iii) 5
D. Lumbar vertebrae iv) 3
a) iii, i, iv, ii
b) ii, iv, i, iii
c) ii, iii, iv, i
d) iv, iii, ii, i
Explanation
Total vertebral column consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 lumbar vertebrae, 5 fused sacral and 3 fused coccygeal vertebrae.
65. Which of these joints the vertebrae bones?
a) Pelvic girdle
b) Gliding points
c) Circular joints
d) Soft tissues
Explanation
Vertebral column runs from the base of the skull to the hip bone forming a tube. Spinal cord passes through this hollow tube. Vertebrae are joined by gliding points which allow the body to be bent back, front or side wards.
66. Which of these are the functions of vertebral column?
a) Protects the spinal cord and supports the head.
b) Provides movement for the human skeleton.
c) Supports the pectoral and pelvic girdle.
d) All the above
Explanation
The functions of vertebral column are given below.
• It protects the spinal cord.
• It supports the head.
• It serves as an attachment for the ribs.
• It provides support and place of attachment for the pectoral and pelvic girdle.
• It provides movement for the human skeleton.
• It helps in walking and standing erect with correct posture.
67. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Sternum cage or Rib cage occupies the chest region of the human body.
ii) Rib cage is a Tree-shaped structure made up of 10 pairs of ribs.
iii) Ribs are attached to the vertebrae at the back curve to form a cage.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Sternum or Rib cage: Rib cage occupies the chest region. It is a cone-shaped structure made up of 12 pairs of ribs. Ribs are attached to vertebrae at the back which curve around to form a cage.
68. How many pairs of free floating ribs are present in the rib cage?
a) 2
b) 4
c) 10
d) 12
Explanation
10 pairs of ribs are attached to the breast bone at the front. 2 pairs of lower ribs are free at front. These are called as free-floating ribs.
69. Which of this organ is not protected by the rib cage?
a) Lungs
b) Heart
c) Kidney
d) Part of liver
Explanation
Rib cage is set up in such a way that it can contract and expand during the process of breathing. Rib cage protects the underlying lungs, heart and some part of liver.
70. Assertion (A): The vertebrae in a giraffe’s neck are much larger than human.
Reasoning(R): Human’s and Giraffes have the same number of bones in the necks.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Humans and giraffes have the same number of bones in the necks, but the vertebrae in a giraffe’s neck are much, much larger.
71. Which of these are included in the appendicular skeleton of the human body?
a) Shoulder girdle
b) Pelvic girdle
c) Foot and hand bones
d) All the above
Explanation
Specifically, the appendicular skeleton comprises the shoulder girdle; the arm, wrist, and hand bones; the pelvic girdle; and the leg, ankle, and foot bones.
72. Which of these make the shoulder bone?
a) Leg bones
b) Pelvic bones
c) Thigh bones
d) Collar bone
Explanation
Shoulder bone is formed by collar bone at the front and the shoulder blade at the back. The collar bone is supported by breast bone at one end and the shoulder blade at the other end. The shoulder bone encloses a socket like cavity into which fixes the ball of the upper arm. This forms a ball and socket joint. This girdle is also called as pectoral girdle.
73. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Pelvic bone is also called as pelvic girdle.
ii) Pelvic girdle is formed by ten fused vertebrae at the back.
iii) Pelvic bone is made up of strong bones to balance entire weight of the body.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Pelvic bone is also called as pelvic girdle. It is made up of strong bones to balance entire weight of the body. Pelvic girdle is formed by five fused vertebrae at the back and form a cavity in the center while reaching the front part. The thigh bones are attached to either side of the girdle with a ball and socket joint.
74. Which of the following is not true regarding the arm bone?
a) Arm bone is the upper limb.
b) Arm bone includes fore-arm, wrists, palm and fingers.
c) All the bones are joined by hinge joints.
d) The arm bone can move in many directions.
Explanation
Arm bone is the upper limb made up of humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals and phalanges. All these bones are joined by hinge joints which allow the limb to move only in one direction.
75. Identify the Incorrect match.
A. Fingers i) Phalanges
B. Palm ii) Metacarpals
C. Wrist iii) Radius
D. Humerus iv) Upper arm
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) iv only
Explanation
Humerus makes up the upper arm. Fore-arm is made up of radius and ulna. Wrist is made up of carpals. Palm is made up of metacarpals. Fingers are made up of phalanges.
76. Which of the following is not present in the leg bone?
a) Ulna
b) Tibia
c) Tarsals
d) Femur
Explanation
Leg bone is the lower limb made up of femur, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals and phalanges. All these bones are joined by hinge joints which allow the limb to move only in one direction.
77. Match
A. Knee i) Tarsals
B. Toes ii) Patella
C. Ankle iii) Thigh bone
D. Femur iv) Phalanges
a) ii, i, iii, iv
b) ii, iv, i, iii
c) i, iv, ii, iii
d) iii, i, ii, iv
Explanation
Knee is covered by a cap like structure called as patella or a knee cap. Femur makes up the thigh bone. Leg is made up of tibia and fibula. Ankle is made up of tarsals. Foot is made up of metatarsals. Toes are made up of phalanges.
78. What are the usages of muscles?
a) Provides all type of movements.
b) Cover the skeletal framework.
c) Helps to maintain body posture
d) All the above
Explanation
The muscles in the body provide the means of all movements. They cover the skeletal framework and also give shape to the body. Muscles help to maintain body posture while sitting, standing or walking.
79. Choose the correct statements.
i) A muscle has a fixed end and a movable end.
ii) Only some of the muscles are long bundles of contractile tissue.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Most muscles are long bundles of contractile tissue. Each muscle usually has two ends – a fixed end where the muscle originates and a movable end which pulls some other part. This moveable end is drawn out to form a tough structure the tendon which is attached to the bone.
80. Assertion (A): A Muscle can contract, relax and some can lengthen.
Reasoning(R): In a movement a muscle contracts and pulls the bone at the movable end.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
When stimulated by a nerve the muscle contracts to become shorter and thicker and thus it pulls the bone at the moveable end. Muscles can only contact and relax, they cannot lengthen.
81. Which is the hardest working muscle in the human body?
a) Eye
b) Thighs
c) Arm
d) Brain
Explanation
There are muscles in the root of your hair that give you goose bumps. It takes 17 muscles to smile and 42 muscles to frown. The hardest working muscle is in eye.
82. Name the muscles work against each other in pairs?
a) Biceps pairs
b) Regulating pairs
c) Antagonistic pairs
d) Coordinating pairs
Explanation
Muscles often work in pairs which work against each other. These are called antagonistic pairs. The muscles in the upper arm control the bending and straightening of the arm. The two muscles, the biceps and triceps are working against each other. When the biceps contracts the lower arm is raised and the arm bends. In this position the triceps muscle is relaxed. To straighten the arm the reverse happens. The triceps contracts straightening the arm while the biceps relaxes. Antagonistic muscles can be found all over the body.
83. How many set of muscles are present in the iris of the eye?
a) 2
b) 10
c) 7
d) 4
Explanation
In the iris of the eye there are two sets of muscle. There are radial muscles which radiate from the pupil like spokes of a bicycle and there are circular muscles. The radial muscles make the pupil of the eye wider, while the circular muscles make the pupil smaller.
84. Which of the following is not a type of higher vertebrate muscle?
a) Striated muscles
b) Stretched muscles
c) Smooth muscles
d) Cardiac muscles
Explanation
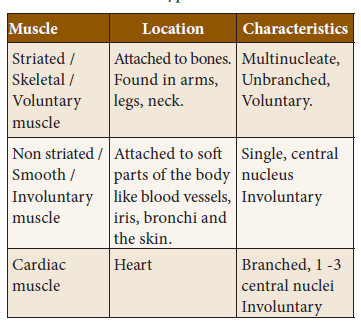
Muscles found in higher vertebrates are of three types: Striated or skeletal muscles or voluntary muscles. Unstriated or smooth muscles or involuntary muscles and Cardiac muscles
85. Which of the following is a voluntary muscle?
a) Cardiac muscle
b) Smooth muscle
c) Skeletal muscle
d) Non-striated muscle
86. Which of this muscle is attached to the soft parts of the human body?
a) Voluntary muscle
b) Non-striated muscle
c) Cardiac muscle
d) Skeletal muscle
87. Match
A. Cardiac Muscle i) Un-branched
B. Striated Muscle ii) Branched
C. Smooth Muscle iii) Single
a) ii, iii, i
b) iii, i, ii
c) i, iii, ii
d) ii, i, iii
Explanation
88. Choose the correct statements.
i) Muscles have to be in a coordinated action for any kind of movement.
ii) Most of the human actions require combined actions of several muscles.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Coordination of Muscles: Most actions in our body like standing, walking, running, playing tennis require combined action of several muscles. To a great extent the muscles have to be coordinated for a particular kind of movement.
89. Assertion (A): Muscles work in pairs of flexors and extensors.
Reasoning(R): Muscles can pull bones but they can’t push them back to the position.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Muscles move body parts by contracting and then relaxing. Muscles can pull bones but they can’t push them back to the original position. So they work in pairs of flexors and extensors.
90. Choose the correct statements.
i) The flexor contracts to bend a muscle at a joint.
ii) The extensor contracts to extend or to straighten the limb at the joint.
iii) The Biceps muscle is a flexor and the triceps muscle is an extensor muscle.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The flexor contracts to bend a limb at a joint. Then, when the movement is completed, the flexor relaxes and the extensor contracts to extend or straighten the limb at the same joint. For example, the biceps muscle in the front of the upper arm is a flexor, and the triceps, at the back of the upper arm, is an extensor. When you bend your elbow the biceps contracts then the biceps relaxes and the triceps contracts to straighten the elbow.