12th Std Science Lesson Wise Questions in English – Part 1
12th Science Lesson 2 Questions in English
2] Chemistry in everyday life
1. In which domain Vladimir Prelog won the noble prize?
- Nuclear chemistry
- Stereo chemistry
- Organic chemistry
- Organisation of elements
Explanation
Prof. Vladimir Prelog was a Swiss Chemist who shared 1975 Nobel Prize for Chemistry with John W Cornforth for his work on Stereo Chemistry.
2. Which of the following statement about Vladimir Prelog is correct?
- He has done wide ranging research on alkaloids, antibiotics, enzymes and other natural compounds
- He was distinguished for his contribution to the development of modern stereo chemistry
- Prelog worked on problems of stereo chemistry like adamenline, boromycin analoids and rifamycins
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Prof. Vladimir Prelog has done wide ranging research on alkaloids, antibiotics, enzymes and other natural compounds. He was distinguished for his contribution to the development of modern stereo chemistry. Prelog synthesized many natural products and worked on problems of stereo chemistry like adamenline, boromycin analoids and rifamycins.
3. What does the French word drogue mean?
- Herb
- Dry herb
- Dip
- None
Explanation
The word drug is derived from the French word “drogue” meaning “dry herb”. A drug is a substance that is used to modify or explore physiological systems or pathological states for the benefit of the recipient.
4. Which of the following statement about Drug is incorrect?
- Drug is used for the purpose of diagnosis, prevention, cure/relief of a disease.
- The drug which interacts with macromolecular targets such as proteins to produce a therapeutic and useful biological response
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
A drug is used for the purpose of diagnosis, prevention, cure/relief of a disease. A drug which interacts with macromolecular targets such as proteins to produce a therapeutic and useful biological response is called medicine.
5. Which of the following features of ideal drug?
- Non- toxic
- Bio-compatible
- Bio- degradable
- Should have no side effects
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3, 4
- All the above
Explanation
An ideal drug is the one which is non-toxic, bio-compatible and bio-degradable, and it should not have any side effects.
6. The specific treatment of a disease using medicine is known as_______
- Hormone therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Precision therapy
Explanation
The specific treatment of a disease using medicine is known as chemotherapy. The drug which interacts with macromolecular targets such as proteins to produce a therapeutic and useful biological response is called medicine.
7. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Most of the drug molecules that are used now a days have the above properties at lower concentrations
- At higher concentrations, they have side effects and become toxic
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Generally, most of the drug molecules that are used now a days have the above properties at lower concentrations. However, at higher concentrations, they have side effects and become toxic.
8. Higher the value of therapeutic index, ___ is the drug
- Safer
- Less-safer
- Not-safer
- None
Explanation
The medicinal value of a drug is measured in terms of its therapeutic index. Higher the value of therapeutic index, safer is the drug.
9. Drugs are classified based on_____
- Chemical structure
- Pharmacological effect
- Target system
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Drugs are classified based on their properties such as chemical structure, pharmacological effect, target system, site of action, etc.
10. Which of the following medicines are classified under the group Penicillin?
- Amoxicillin
- Ampicillin
- Methicillin
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
In this classification, drugs with a common chemical skeleton are classified into a single group. For example, ampicillin, amoxicillin, methicillin, etc. all have similar structure and are classified into a single group called penicillin.
11.Which of the following drug groups have same biological action?
- Penicillin
- Steroids
- Barbiturates
- All the above
Explanation
Compounds having similar chemical structure are expected to have similar chemical properties. However, their biological actions are not always similar. For example, all drugs belonging to penicillin group have same biological action, while groups such as barbiturates, steroids etc. have different biological action.
12. Which of the following is not Antihypertensive drug?
- Atenolol
- Metoprolol Succinate
- Erythromycin
- Amlodipine
Explanation
Antibiotic drugs: amoxicillin, ampicillin, cefixime, cefpodoxime, erythromycin, tetracycline etc.
Antihypertensive drugs: propranolol, atenolol, metoprolol succinate, amlodipine etc.
13. _________ prevents the incorporation of new amino acids to the protein
- Atenolol
- Metoprolol Succinate
- Erythromycin
- Streptomycin
Explanation
Streptomycin inhibits the initiation of protein synthesis, while erythromycin prevents the incorporation of new amino acids to the protein.
14. Which of the following statement is correct?
- In all living systems, the biochemical reactions are catalysed by enzymes
- These enzyme actions are highly essential for the normal functioning of the system
- If their normal enzyme activity is inhibited, then the system may be affected
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
In all living systems, the biochemical reactions are catalysed by enzymes. Hence, these enzyme actions are highly essential for the normal functioning of the system. If their normal enzyme activity is inhibited, then the system will be affected. This principle is usually applied to kill many pathogens.
15. Which of the following statement is correct?
- If we want to block a message, a drug that binds to the receptor site should inhibit its natural function.
- Such drugs are called agonists.
- Agonists are used when there is lack of chemical messenger.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
If we want to block a message, a drug that binds to the receptor site should inhibit its natural function. Such drugs are called antagonists. In contrast, there are drugs which mimic the natural messenger by switching on the receptor. These types of drug are called agonists and are used when there is lack of chemical messenger.
16. Which of the following have been used to treat acidity?
- Aluminium hydroxide
- Calcium hydroxide
- Magnesium hydroxide
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
To treat acidity, we have been using weak bases such as aluminium and magnesium hydroxides. But these can make the stomach alkaline and trigger the production of much acid.
17. Which of the following statement about Tranquilizers is correct?
- They are neurologically active drugs.
- Haloperidol, clozapine are major tranquilizers
- Acts on the central nervous system by blocking the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Tranquilizers:
They are neurologically active drugs. Acts on the central nervous system by blocking the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain. It is used in treatment of stress, anxiety, depression, sleep disorders and severe mental diseases like schizophrenia.
Minor tranquilizers: Diazepam (Valium), alprazolam
Major tranquilizers: Haloperidol, clozapine
18. Which of the following statement about Analgesics?
- Analgesics reduce the pain without causing impairment of consciousness.
- They alleviate pain by reducing local inflammatory responses
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Analgesics reduce the pain without causing impairment of consciousness. They alleviate pain by reducing local inflammatory responses.
19. Which of the following is/are anti-inflammatory drug?
- Ibuprofen
- Asprin
- Paracetamol
- All the above
Explanation
Anti-inflammatory drugs:Acetaminophen or paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Asprin.
Antipyretics: Example Salicylates Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), Acetaminophen or Paracetamol
20. Which of the following are the uses of Analgesics?
- Used for short-term pain relief and for modest painlike headache
- These drugs have many other effects such as reducing fever (antipyretic) and preventing platelet coagulation
- Reduces fever by causing the hypothalamus to override a prostaglandin-induced increase in temperature.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Uses of Analgesics:
- Used for short-term pain relief and for modest painlike headache, muscle strain, bruising, or arthritis
- These drugs have many other effects such as reducing fever (antipyretic) and preventing platelet coagulation. Due to this property, aspirin finds useful in the prevention of heart attacks
- Reduces fever by causing the hypothalamus to override a prostaglandin-induced increase in temperature.
21. Which of the following statement about Opioids is correct?
- Relive pain and produce sleep.
- Used for either short term or long-term relief of severe pain.
- Morphine is an example of Opioids
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Opioids (Narcotic Analgesics):
Examples: Morphine, codeine
Relive pain and produce sleep. These drugs are addictive. In poisonous dose, these produces coma and ultimately death.
Uses: Used for either short-term or long-term relief of severe pain. Mainly used for post-operative pain, pain of terminal cancer.
22. Which of the following statement about local anaesthetics?
- It causes loss of sensation, in the area in which it is applied without losing consciousness
- They block pain perception that is transmitted via peripheral nerve fibres to the brain
- They are often used during major surgery
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Anaesthetics causes loss of sensation, in the area in which it is applied without losing consciousness. They block pain perception that is transmitted via peripheral nerve fibres to the brain. They are often used during minor surgical procedures.
23. Match the following
- Ester-linked local anaesthetic 1. Isoflurane
- Amide-linked local anaesthetic 2. Procaine
- Intravenous general anaesthetics 3. Lidocaine
- Inhalational general anaesthetics 4. Propofol
- 2, 1, 3, 4
- 2, 3, 4, 1
- 2, 1, 4, 3
- 1, 3, 2, 4
Explanation
Local anaesthetics:
Ester-linked local anaesthetic – Procaine
Amide-linked local anaesthetic – Lidocaine
General anaesthetics:
Intravenous general anaesthetics– Propofol
Inhalational general anaesthetics – Isoflurane
24. Which of the following statement about General anaesthetics is correct?
- Cause a controlled and reversible loss of consciousness by affecting central nervous system
- They are often used for major surgical procedures
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
General anaesthetics: Cause a controlled and reversible loss of consciousness by affecting central nervous system Uses: They are often used for major surgical procedures.
25. Which of the following are Antacids?
- Ranitidine
- Milk of Magnesia
- Omeprazole
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Antacids: Milk of Magnesia, Sodium bicarbonate, calcium bicarbonate, aluminium hydroxide Ranitidine, Cemitidine, Omeprazole, rabeprazole.
26, Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Neutralize the acid in the stomach that causes acidity
- They relieve symptoms such as burning sensation in the chest/ throat area
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Antacids: Neutralize the acid in the stomach that causes acidity.
Uses: To relieve symptoms such as burning sensation in the chest/ throat area (heart burns) caused by acid reflux.
27. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Cetirizine, levocetirizine, desloratadine are Antihistamines
- They Block histamine release from histamine-1 receptors
- They are used provide relief from the allergic effects
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Antihistamines: Cetirizine, levocetirizine, desloratadine, brompheniramine Terfenadine
They Block histamine release from histamine-1 receptors.
Uses: To provide relief from the allergic effects
28. Which of the following statement about Beta-Lactam is correct?
- Erythromycin, ampicillin are Antimicrobials
- They are used to treat skin infections, dental infections, ear infections, respiratory tract infections
- Inhibits bacterial cell wall biosynthesis
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Beta-Lactams: Penicillin, ampicillin, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams
Inhibits bacterial cell wall biosynthesis
Used to treat skin infections, dental infections, ear infections, respiratory tract infections, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and gonorrhoea
29. Which of the following are used to treat respiratory tract infection?
- Erythromycin
- Paracetamol
- Ampicillin
- All the above
Explanation
Macrolides: Erythromycin, azithromycin
Targets bacterial ribosomes and prevent protein production
Uses: To treat respiratory tract infections, genital, gastrointestinal tract and skin infections
30. Which of the following can be treated with Fluoroquinolones?
- Urinary tract infections
- Skin infections
- Pulmonary infections
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Fluoroquinolones can be used to treat urinary tract infections, skin infections, and respiratory infections (such as sinusitis, pneumonia, bronchitis), pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis.
31. Tetracyclines Inhibit the bacterial protein synthesis via interaction with the___ subunit of the
bacterial ribosome
- 30S
- 50S
- 60S
- 20S
Explanation
Tetracyclines:
Examples: Doxycycline, minocycline, oxytetracycline
Inhibit the bacterial protein synthesis via interaction with the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome
32. Which of the following are examples of Antiseptics?
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Benzalkonium chloride
- Povidone-iodine
- All the above
Explanation
Antiseptics Stop or slow down the growth of microorganisms – Applied to living tissue. Examples Hydrogen peroxide, povidone-iodine, benzalkonium chloride.
33. Which of the following statement about disinfectant is incorrect?
- Chlorine compounds, alcohol, Hydrogen peroxide are examples of disinfectants
- Generally used on inanimate objects
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Disinfectants:
Examples: Chlorine compounds, alcohol, Hydrogen peroxide.
Stop or slow down the growth of microorganisms – Generally used on inanimate objects.
34. Which of the following are the advantages of food additives?
- Flavouring agents enhance the aroma of the food
- Addition of vitamins and minerals reduces the mall nutrient
- Oxidants prevent the formation of potentially toxic oxidation products of lipids
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Advantages of food additives:
- Uses of preservatives reduce the product spoilage and extend the shelf-life of food
- Addition of vitamins and minerals reduces the mall nutrient
- Flavouring agents enhance the aroma of the food
- Antioxidants prevent the formation of potentially toxic oxidation products of lipids and other food constituents
35. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Preservatives are capable of inhibiting, retarding or arresting the process of fermentation, acidification or other decomposition of food by growth of microorganisms
- Alkyl esters of hydroxy benzoic acid are very effective in more acidic conditions
- Organic acids such as benzoic acid, sorbic acid and their salts are potent inhibitors of a number of fungi, yeast and bacteria
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Preservatives are capable of inhibiting, retarding or arresting the process of fermentation, acidification or other decomposition of food by growth of microorganisms. Organic acids such as benzoic acid, sorbic acid and their salts are potent inhibitors of a number of fungi, yeast and bacteria. Alkyl esters of hydroxy benzoic acid are very effective in less acidic conditions.
36. _____ is used mainly as a preservative for the preparation of pickles
- Formic acid
- Citric acid
- Malic acid
- Acetic acid
Explanation
Acetic acid is used mainly as a preservative for the preparation of pickles and for preserved vegetables.
37. Which of the following preservative methods can be used to preserve food?
- Pasteurisation
- Freezing
- Dehydration
- Irradiation
- 1, 2, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- 1, 3, 4
- All the above
Explanation
In addition to chemical treatment, physical methods such as heat treatment (pasteurisation and sterilisations), cold treatment (chilling and freezing) drying (dehydration) and irradiation are used to preserve food.
38. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Antioxidants are substances which retard the oxidative deteriorations of food
- Food containing fats and oils is easily oxidised and turn rancid
- To prevent the oxidation of the fats and oils, chemical BHT, BHA are added as food additives.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Antioxidants are substances which retard the oxidative deteriorations of food. Food containing fats and oils is easily oxidised and turn rancid. To prevent the oxidation of the fats and oils, chemical BHT (butyl hydroxy toluene), BHA (Butylated hydroxy anisole) are added as food additives. They are generally called antioxidants.
39. Which of the following are sugar substituents?
- Sorbitol
- Sucralose
- Xylitol
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Those compounds that are used like sugars (glucose, sucrose) for sweetening, but are metabolised without the influence of insulin are called sugar substituents. e.g. Sorbitol, Xylitol, Mannitol.
40. Which of the following are artificial sweeting agent?
- Saccharin
- Aspartame
- Alitame
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Synthetic compounds which imprint a sweet sensation and possess no or negligible nutritional value are called artificial sweeteners. Eg. Saccharin, Aspartame, sucralose, alitame etc…
41. Chemically soap is______
- Sodium or potassium salt of higher fatty acids
- Sodium or potassium salt of lower fatty acids
- Sodium salt of higher fatty acids
- Potassium salt of higher fatty acids
Explanation
Soaps and detergents are used as cleansing agents. Chemically soap is the sodium or potassium salt of higher fatty acids.
42. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Soaps are made from animal fats or vegetable oils.
- They contain glyceryl esters of long chain fatty acids
- When the glycerides are heated with a solution of sodium-hydroxide they become soap and glycerol.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Soaps are made from animal fats or vegetable oils. They contain glyceryl esters of long chain fatty acids. When the glycerides are heated with a solution of sodium-hydroxide they become soap and glycerol.
43. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The quality of a soap is described in terms of total fatty matter
- Lower the TFM quantity in the soap better is its quality
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The quality of a soap is described in terms of total fatty matter (TFM value). It is defined as the total amount of fatty matter that can be separated from a sample after splitting with mineral acids., Higher the TFM quantity in the soap better is its quality.
44. Which of the following statement is correct?
- As per BIS standards, Grade-1 soaps should have 76% minimum TFM
- Grade 3 must have 60%, minimum TFM
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
As per BIS standards, Grade-1 soaps should have 76% minimum TFM, while Grade-2 and 3 must have 70 and 60%, minimum respectively. The other quality parameters are lather, moisture content, mushiness, insoluble matter in alcohol etc.
45. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The nonpolar portion is hydrophobic while the polar end is hydrophilic
- The hydrophobic hydro carbon portion is soluble in water
- The hydrophilic carboxylate group is soluble in water.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The cleansing action of soap is directly related to the structure of carboxylate ions (palmitate ion) present in soap. The nonpolar portion is hydrophobic while the polar end is hydrophilic. The hydrophobic hydro carbon portion is soluble in oils and greases, but not in water. The hydrophilic carboxylate group is soluble in water.
46. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Synthetic detergents are formulated products containing either sodium salts of alkyl hydrogen sulphates
- There are three types of detergents
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Synthetic detergents are formulated products containing either sodium salts of alkyl hydrogen sulphates or sodium salts of long chain alkyl benzene sulphonic acids. There are three types of detergents.
47. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The term Polymer is derived from the Greek word ‘polumeres’ meaning “having many parts”.
- The constitution of a polymer is described in terms of its structural units called monomers
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The term Polymer is derived from the Greek word ‘polumeres’ meaning “having many parts”. The constitution of a polymer is described in terms of its structural units called monomers.
48. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Polymers consists of large number of monomer units derived from simple molecules
- Polymers can be classified based on the source of availability, structure, molecular forces and the mode of synthesis
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Polymers consists of large number of monomer units derived from simple molecules. For example: PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride). is a polymer which is obtained from the monomer vinyl chloride. Polymers can be classified based on the source of availability, structure, molecular forces and the mode of synthesis.
49. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The process of forming a very large, high molecular mass polymer from small structural units i.e., monomer is called polymerisation
- Addition polymerisation is also known as chain growth polymerisation
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The process of forming a very large, high molecular mass polymer from small structural units i.e., monomer is called polymerisation. Polymerisation occurs in the following two ways
- Addition polymerisation or chain growth polymerisation
- Condensation polymerisation or step growth polymerisation
50. How many mechanisms are there depending upon the reactive intermediate involved in Addition polymerisation?
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Explanation
The addition polymerisation can follow any of the following three mechanisms depending upon the reactive intermediate involved in the process.
- Free radical polymerisation
- Cationic polymerisation
- Anionic polymerisation
51. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Condensation polymers are formed by the reaction between functional groups an adjacent monomer with the elimination of simple molecules like H2O, NH3
- Nylon – 6,6 can be prepared by mixing equimolar adipic acid and hexamethylene – diamine to form a nylon salt
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Condensation polymers are formed by the reaction between functional groups an adjacent monomers with the elimination of simple molecules like H2O, NH3. Nylon – 6,6 can be prepared by mixing equimolar adipic acid and hexamethylene – diamine to form a nylon salt which on heating eliminate a water molecule to form amide bonds.
52. ___ is used in blending with cotton or wool fibres
- Teflon
- Bakelite
- Dacron
- All the above
Explanation
Terylene (Dacron) is used in blending with cotton or wool fibres and as glass reinforcing materials in safety helmets.
53. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Charles Good found that the rubber had become strong and elastic when he accidently dropped a mixture of natural rubber and sulphur onto a hot stove
- This discovery led to the process that Good year called vulcanization.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
In the year 1839, Charles Good year accidently dropped a mixture of natural rubber and sulphur onto a hot stove. He was surprised to find that the rubber had become strong and elastic. This discovery led to the process that Good year called vulcanization.
54. ___ is used in the manufacture of chemical containers, conveyer belts
- Neoprene
- Buna-N
- Buna-S
- Bakelite
Explanation
The free radical polymeristion of the monomer, 2-chloro buta-1,3-diene(chloroprene) gives neoprene. It is used in the manufacture of chemical containers, conveyer belts.
55. Which of the following are Biodegradable Polymers?
- Polyhydroxy butyrate
- Polyglycolic acid
- Poly (∈ caprolactone)
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Examples of Biodegradable Polymer:
- Polyhydroxy butyrate (PHB)
- Polyhydroxy butyrate-co-A- hydroxyl valerate (PHBV)
- Polyglycolic acid (PGA), Polylactic acid (PLA)
- Poly (∈ caprolactone) (PCL)
56. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The materials that are readily decomposed by microorganisms in the environment are called biodegradable.
- Natural polymers degrade on their own after certain period of time but the synthetic polymers do not
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The materials that are readily decomposed by microorganisms in the environment are called biodegradable. Natural polymers degrade on their own after certain period of time but the synthetic polymers do not. It leads to serious environmental pollution.
57. Which of these is not a criterion to classify the drugs?
a) Chemical structure
b) Disease causing agents
c) Target system
d) Site of action
Explanation
Drugs are classified based on their properties such as chemical structure, pharmacological effect, target system, site of action etc.
58. Assertion (A): Compounds having similar chemical structure may differ in chemical properties.
Reasoning(R): The biological actions of similar chemical structures are same.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) Both A and R is wrong.
d) A is correct But R is wrong.
Explanation
Compounds having similar chemical structure are expected to have similar chemical properties. However, their biological actions are not always similar. For example, all drugs belonging to penicillin group have same biological action, while groups such as barbiturates, steroids have different biological action.
59. What is the purpose of antagonists?
a) To block any one chemical messenger over the others in a cell.
b) To bind the active site of the receptors.
c) Transfer of message into the cell.
d) To increase the selectivity of one chemical messenger.
Explanation
The chemical messengers, the compounds that carry messages to cells, bind tothe active site of these receptors. This brings about the transfer of message into the cell. These receptors show high selectivity for one chemical messenger over the others. If we want to block a message, a drug that binds to the receptor site should inhibit its natural function. Such drugs are called antagonists.
60. Which of these is used to preserve fresh vegetables and fruits?
a) Potassium sulphate
b) Calcium carbonate
c) Sodium meta-sulphite
d) Magnesium sulphide
Explanation
Sodium meta-sulphite is used as preservatives for fresh vegetables and fruits.
61. What is the usage of sucrose esters with steric acids?
a) Presrvatives
b) Antibiotics
c) Emulsifiers
d) Additives
Explanation
Sucrose esterswith palmitic and steric acid are used as emulsifiers. In addition that some organic acids andtheir salts are used as preservatives.
62. What are the usages of Sulphur dioxide and sulphites?
a) Food additives
b) Antioxidants
c) Enzyme inhibitors
d) All the above
Explanation
Sulphur dioxide and sulphites are also used as foodadditives. They act as anti-microbial agents, antioxidants and enzyme inhibitors.
63. Which of the following are detergents?
a) Sodium salt of alkyl hydrogen sulphates
b) Sodium sulphates and sulphur dioxide
c) Sodium salt of Alkyl benzene sulphonic acids
d) Both a and c
Explanation
Detergent is sodium salt of alkyl hydrogen sulphates or alkyl benzene sulphonic acids.
64. Based on which a polymer is not classified?
a) Source of availability
b) Chemical reactions
c) Molecular forces
d) Mode of synthesis
Explanation
Polymers can be classified based on the source of availability, structure, molecular forces and the mode of synthesis.
65. How many types of polythene are available?
a) 5
b) 2
c) 4
d) 3
Explanation
Polytheneis an addition polymer of ethene. There are two types of polyethylene i) HDPE (HighDensity Polyethylene) ii) LDPE (Low Density polyethylene).
66. Which is used as catalyst in the production process of LDPE?
a) Carbon
b) Hydrogen
c) Oxygen
d) Argon
Explanation
LDPEis formed by heating ethene at 200 to 300°C under oxygen as a catalyst. The reactionfollows free radical mechanism. The peroxides formed from oxygen acts as a free radicalinitiator.It is used as insulation for cables, making toys.
67. Which of the following is not a property of HDPE?
a) High density
b) Used to make pipes.
c) High melting point
d) Used as insulation for cables.
Explanation
HDPEThe polymerization of ethylene is carried out at 373K and 6to7 atm pressure using Zeiglar– Natta catalyst .HDPE has high density and melting point and it is used tomake bottles, pipes.
68. In which of these conditions Teflon is produced?
a) High pressure
b) Low pressure
c) Vacuum
d) Low temperature
Explanation
Preparation of Teflon (PTFE): The monomer is tetrafluroethylene. When the monomer is heated with oxygen (or)ammonium persulphate under high pressure, Teflon is obtained.
69. Which of the following statement is not correct regarding the preparation of Bakelite’s?
a) Monomers used for Bakelite’s are phenol and formaldehyde.
b) Only acids are used as a catalyst in condensation polymerization.
c) Novolac is the linear polymer.
d) Heating of novolac with formaldehyde form backelites.
Explanation
Preparation of Bakelite: The monomers are phenol and formaldehyde. The polymer is obtained by the condensationpolymerization of these monomers in presence of either an acid or a base catalyst.Phenol reacts with methanol to form ortho or para hydroxyl methyl phenols which onfurther reaction with phenol give linear polymer called novolac. Novolac on further heatingwith formaldehyde undergo cross linkages to form backelites.
70. Which of the following statement is not correct?
a) Soft backelites are used for making glue.
b) Varnishes are hard backelites.
c) Navolac is used in paints.
d) Hard backelites are used to prepare combs and pens.
Explanation
Navolac is used in paints. Soft backelites are used for making glue for binding laminated wooden planks and in varnishes, Hard backelites are used to prepare combs, pens etc..
71. Assertion (A): Polymer containing same kinds of monomer units is called as co-polymer.
Reasoning(R): Co-polymers have same properties from the homo polymers.
a) Both A and R is correct and R is correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) Both A and R is wrong.
d) A is correct But R is wrong.
Explanation
A polymer containing two or more different kinds of monomer units is called a co-polymer. For example, SBR rubber (Buna-S) contains styrene and butadiene monomer units. Co-polymers have properties quite different from the homo-polymers.
72. Which of the following statements are not correct?
i) Rubber is obtained from the latex excludes from cuts in the bark of rubber tree.
ii) Thousands of isoprene units are linearly linked in natural rubber.
iii) Rubber is strong and elastic in nature.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Rubber is a naturally occurring polymer. It is obtained from the latex that excludes from cuts in the bark of rubber tree (Ficus elastic). The monomer unit of natural rubber is cisisoprene (2-methyl buta-1,3-diene). Thousands of isoprene units are linearly linked together in natural rubber. Natural rubber is not so strong or elastic. The properties of natural rubber can be modified by the process called vulcanization.
73. What percentage of sulphur used to make harder flexible rubber?
a) 0.3 to 50%
b) 3 to 10%
c) 1 to 3%
d) 50 to 100%
Explanation
The physical properties of rubber can be altered by controlling the amount of sulphur that is used for vulcanization. In sulphur rubber, made with about 1 to 3% sulphur is soft and stretchy. When 3 to 10% sulphuris used the resultant rubber is somewhat harder but flexible.
12th Science Lesson 3 Questions in English
3] Economically useful plants and entrepreneurial botany
1. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Pre-historic humans lived on berries, tubers, herbage, and the wild game which they collected and hunted that occupied whole of their time
- Domestication of plants and animals has led to the production of surplus food which formed the basis for civilizations
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The land and water of the earth sustain a vast assemblage of plants upon which all other living forms are directly or indirectly dependent. Pre-historic humans lived on berries, tubers, herbage, and the wild game which they collected and hunted that occupied whole of their time. Domestication of plants and animals has led to the production of surplus food which formed the basis for civilizations.
2. Which of the following type of plants are economically useful?
- food plants
- fodder plants
- fibre plants
- timber plants
- 1, 2, 4
- 1, 3, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- All the above
Explanation
Based on their utility, the economically useful plants are classified into food plants, fodder plants, fibre plants, timber plants, medicinal plants, and plants used in paper industries, dyes and cosmetics.
3. Which of the following are grass species?
- Fig
- Rice
- Wheat
- Maize
- 1, 2, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- 1, 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Currently about 10,000 food plants are being used of which only around 1,500 species were brought under cultivation. However, food base of majority of the population depends only on three grass species namely rice, wheat and maize.
4. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The word cereal is derived from Ceres, which according to the Roman mythology denotes “Goddess of agriculture”
- All cereals are members of grass family (Poaceae) that are grown for their edible starchy seeds.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The word cereal is derived from Ceres, which according to the Roman mythology denotes “Goddess of agriculture”. All cereals are members of grass family (Poaceae) that are grown for their edible starchy seeds.
5. Which of the following are the attributes of cereals?
- Greater adaptability and successful colonisation on every type of habitat
- High caloric value that provides energy
- The relative ease of cultivation
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The prominence of cereals as food plants is due to the following attributes:
i. Greater adaptability and successful colonisation on every type of habitat.
ii. The relative ease of cultivation
iii. Tillering property that produce more branches which results in higher yield per unit area.
iv. Compact and dry grains that they can be easily handled, transported and stored without undergoing spoilage.
v. High caloric value that provides energy
6. Which of the following nutrients does cereals include?
- Carbohydrates
- Minerals
- Proteins
- Fibres
- 1, 2, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- 1, 3, 4
- All the above
Explanation
The nutrients provided by cereals include carbohydrates, proteins, fibres and a wide range of vitamins and minerals.
7. What is the common name of Oryza sativa?
- Wheat
- Maize
- Paddy
- None
Explanation
Rice / Paddy
Botanical name: Oryza sativa
Paddy is a semi-aquatic crop and is grown in standing water.
8. Rice is the chief source of_____
- Protein
- Vitamin-c
- Minerals
- Carbohydrate
Explanation
Rice is an important food crop of the world, occupying the second position in terms of area under cultivation and production, next to wheat. Rice is the chief source of carbohydrate.
9. Earliest evidences of rice cultivation have been found in______
- Egypt
- India
- China
- Thailand
- 1, 2, 3
- 1, 3, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- All the above
Explanation
Earliest evidences of rice cultivation have been found in China, India and Thailand. It is mainly cultivated in Delta and irrigated regions of Tamil Nadu.
10. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Rice is the easily digestible calorie rich cereal food which is used as a staple food in Southern and North East India.
- Various rice products such as Flaked rice (Aval), Puffed rice / parched rice (Pori) are used as breakfast cereal or as snack food in different parts of India
- Rice bran oil obtained from the rice bran is used in culinary and industrial purposes
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Rice is the easily digestible calorie rich cereal food which is used as a staple food in Southern and North East India. Various rice products such as Flaked rice (Aval), Puffed rice / parched rice (Pori) are used as breakfast cereal or as snack food in different parts of India. Rice bran oil obtained from the rice bran is used in culinary and industrial purposes.
11. What is the common name of Triticum aestivum?
- Rice
- Wheat
- Maize
- Potato
Explanation
Wheat
Botanical name: Triticum aestivum
Earliest evidence for wheat cultivation comes from Fertile Crescent region.
12. Which state/s of India cultivate wheat?
- Punjab
- Bihar
- Uttar Pradesh
- All the above
Explanation
The common cultivated wheat, Triticum aestivum is cultivated for about 7,500 years. Wheat is mostly cultivated in the North Indian states such as Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Bihar.
13. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Wheat is the staple food in India
- Processed wheat flour, that has little fibre, is called Maida which is used extensively in making parota, naan and bakery products
- Malted wheat is a major raw material for producing alcoholic beverages and nutritive drinks
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Wheat is the staple food in Northern India. Wheat flour is suitable to make bread and other bakery products. Processed wheat flour, that has little fibre, is called Maida which is used extensively in making parota, naan and bakery products. Malted wheat is a major raw material for producing alcoholic beverages and nutritive drinks.
14. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The term pseudo-cereal is used to describe foods that are prepared and eaten as a whole grain, but are botanical outlier
- Quinoa is actually a seed from the Chenopodium quinoa plant belongs to the family Amaranthaceae
- It is a gluten-free, whole-grain carbohydrate, as well as a whole protein (meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids) and have been eaten for 6,000 years in Andes hill region
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The term pseudo-cereal is used to describe foods that are prepared and eaten as a whole grain, but are botanical outliers from grasses. Example: quinoa. It is actually a seed from the Chenopodium quinoa plant belongs to the family Amaranthaceae. It is a gluten-free, whole-grain carbohydrate, as well as a whole protein (meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids) and have been eaten for 6,000 years in Andes hill region.
15. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Most of the corn produced is used as food than fodder
- Corn syrup is used in the manufacture of infant foods
- Corn is a raw material in the industrial production of alcohol and alcoholic beverages
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Most of the corn produced is used as fodder than food. Corn syrup is used in the manufacture of infant foods. Corn is a raw material in the industrial production of alcohol and alcoholic beverages.
16. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The term millet is applied to a variety of very small seeds originally cultivated by ancient people in Africa and Asia
- They are gluten free and have less glycemic index
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The term millet is applied to a variety of very small seeds originally cultivated by ancient people in Africa and Asia. They are gluten free and have less glycemic index.
17. Ragi is rich in______
- Protein
- Carbohydrate
- Calcium
- Minerals
Explanation
Botanical name: Eleusine coracana
Finger millet is the crop of early introduction from East Africa into India. Ragi is rich in calcium.
18. Which of the following statement about ragi correct?
- It is used as a staple food in many southern hilly regions of India
- Ragi grains are made into porridge and gruel
- It is used as a source of fermented beverages.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Ragi is used as a staple food in many southern hilly regions of India. Ragi grains are made into porridge and gruel. Ragi malt is the popular nutrient drink. It is used as a source of fermented beverages.
19. Sorghum is native to______
- Asia
- USA
- Europe
- Africa
Explanation
Botanical name: Sorghum vulgare
Sorghum is native to Africa. It is one of the major millets in the world and is rich in calcium and iron.
20. Which of the following statement about Foxtail Millet is correct?
- This is one of the oldest millets used traditionally in India.
- Rich in protein, carbohydrate, vitamin B and C, Potassium and Calcium.
- It is domesticated first in China about 3000 years.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Foxtail Millet
Botanical name: Setaria italica
This is one of the oldest millets used traditionally in India. Which is domesticated first in China about 6000 years. Rich in protein, carbohydrate, vitamin B and C, Potassium and Calcium.
21. Which of the following statement about foxtail millet is correct?
- It supports in strengthening of heart and improves eye sight
- Thinai porridge is given to lactating mother.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Uses of foxtail millet:
It supports in strengthening of heart and improves eye sight. Thinai porridge is given to lactating mother.
22. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Kodo millet is originated from Asia, which is rich in fibre, protein and minerals
- Kodo millet is ground into flour and used to make pudding
- It is Good diuretic and cures constipation
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Kodo Millet
Botanical name: Paspalum scrobiculatum
Kodo millet is originated from West Africa, which is rich in fibre, protein and minerals. Uses Kodo millet is ground into flour and used to make pudding. Good diuretic and cures constipation. Helps to reduce obesity, blood sugar and blood pressure.
23. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The word Pulse is derived from the Latin words ‘puls’ or ‘pultis’ meaning “thick soup”.
- Pulses are the edible seeds that are harvested from the fruits of Fabaceae
- They provide vital source of plant-based protein, vitamins and minerals for people around the globe
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The word Pulse is derived from the Latin words ‘puls’ or ‘pultis’ meaning “thick soup”. Pulses are the edible seeds that are harvested from the fruits of Fabaceae. They provide vital source of plant-based protein, vitamins and minerals for people around the globe
24. What is the common name of Vigna mungo?
- Mango
- Black gram
- Sorghum
- Red gram
Explanation
Botanical name of black gram is Vigna mungo. Important states growing black gram in India are Uttar Pradesh, Chattisgarh and Karnataka.
25. Black gram is native to____
- China
- Thailand
- India
- Burma
Explanation
Black gram is native to India. Earliest archeo-botanical evidences record the presence of black gram about 3,500 years ago.
26. Which of the following statement about black gram is incorrect?
- Black gram is eaten whole or split, boiled or roasted or ground into flour
- Black gram batter is a major ingredient for the preparation of popular Southern Indian breakfast dishes.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Black gram is eaten whole or split, boiled or roasted or ground into flour. Black gram batter is a major ingredient for the preparation of popular Southern Indian breakfast dishes. Split pulse is used in seasoning Indian curries.
27. _____ is the only pulse native to Southern India
- White gram
- Black gram
- Red gram
- Blue gram
Explanation
Red gram / Pigeon pea is the only pulse native to Southern India. It is mainly grown in the states of Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Gujarat.
28. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Red gram is a major ingredient of sambar, a characteristic dish of Southern India
- Roasted seeds are consumed either salted or unsalted as a popular snack.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Red gram is a major ingredient of sambar, a characteristic dish of Southern India. Roasted seeds are consumed either salted or unsalted as a popular snack. Young pods are cooked and consumed.
29. Which of the following state cultivate green gram?
- Tamil Nadu
- Karnataka
- Madhya Pradesh
- All the above
Explanation
Green gram is a native of India and the earliest archaeological evidences are found in the state of Maharashtra. It is cultivated in the states of Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu
30. ____ is one of the ingredients of pongal, a popular breakfast dish in Tamil Nadu
- Black gram
- Red gram
- Green gram
- Blue gram
Explanation
Green gram is one of the ingredients of pongal, a popular breakfast dish in Tamil Nadu. Fried dehulled and broken or whole green gram is used as popular snack. The flour is traditionally used as a cosmetic, especially for the skin
31. Lady’s finger is a native of the Tropical______
- Asia
- Africa
- Australia
- South America
Explanation
Lady’s finger is a native of the Tropical Africa. Assam, Maharashtra and Gujarat are the important states where Lady’s finger is grown in abundance. Coimbatore, Dharmapuri and Vellore are the major cultivating regions of Tamil Nadu.
32. Which of the following are present in fruits?
- Potassium
- Fibre
- Folic acid
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Edible fruits are fleshy structures with a pleasant aroma and flavours. Fruits are sources of many nutrients including potassium, dietary fibre, folic acid and vitamins.
33. Which of the following are temperate fruits?
- Banana
- Apple
- Plum
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Depending on the climatic region in which fruit crops grow, they can be classified into temperate (apple, pear, plum) and tropical fruits (mango, jack, banana).
34. ______ is the national fruit of India?
- Banana
- Mango
- Apple
- Plum
Explanation
Mango (National fruit of India)
Botanical name: Mangifera indica
Family: Anacardiaceae
35. Which of the following statement about mango is correct?
- The mango is the native to Southern Asia, especially Burma and Eastern India
- It is the National fruit of India.
- Some of the major cultivars of mango in India are Alphonsa, Banganapalli, neelam and malgova
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The mango is the native to Southern Asia, especially Burma and Eastern India. It is the National fruit of India. Major mango producing States are Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Gujarat and Karnataka. Salem, Krishnagiri, Dharmapuri are the major mango producing districts of Tamil Nadu. Some of the major cultivars of mango in India are Alphonsa, Banganapalli, neelam and malgova
36. _____ is the major table fruit of India, which is rich in beta carotenes
- Banana
- Mango
- Apple
- Plum
Explanation
Mango is the major table fruit of India, which is rich in beta carotenes. It is utilized in many ways, as dessert, canned, dried and preserves in Indian cuisine. Sour, unripe mangoes are used in chutneys, pickles, side dishes, or may be eaten raw with salt and chili. Mango pulp is made into jelly. Aerated and non-aerated fruit juice is a popular soft drink.
37. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Nuts are simple dry fruits composed of a hard shell and an edible kernel
- They are packed with a good source of healthy fats, fibre, protein, vitamins, minerals and antioxidants.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Nuts are simple dry fruits composed of a hard shell and an edible kernel. They are packed with a good source of healthy fats, fibre, protein, vitamins, minerals and antioxidants.
38. Cashew has originated in______
- Burma
- Brazil
- England
- India
Explanation
Cashew has originated in Brazil and made its way to India in the 16th century through Portuguese sailors. Cashew is grown in Kerala, Karnataka, Goa, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Orissa.
39. What is the common name of Anacardium occidentale?
- Fig nut
- Cashew nut
- Walnut
- All the above
Explanation
Cashew nut
Botanical name: Anacardium occidentale
Family: Anacardiaceae
Uses:
Cashews are commonly used for garnishing sweets or curries, or ground into a paste that forms a base of sauces for curries or some sweets. Roasted and raw kernels are used as snacks.
40. Which of the following statement is correct?
- We can experience sweetness while eating the stems of sugarcane, roots of sugar beet, fruits of apple and while drinking palmyra sap
- Sugar is the generic name for sweet tasting soluble carbohydrate, which are used in foods and beverages.
- Sugars found in sugarcane and palmyra make them ideal for efficient extraction to make commercial sugar.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
We can experience sweetness while eating the stems of sugarcane, roots of sugar beet, fruits of apple and while drinking palmyra sap. This is due to the different proportions of sugars found in it. Sugar is the generic name for sweet tasting soluble carbohydrate, which are used in foods and beverages. Sugars found in sugarcane and palmyra make them ideal for efficient extraction to make commercial sugar.
41. _____ is the raw material for extracting white sugar
- Sugar cane
- Palmyra tree
- Gingelly
- All the above
Explanation
Sugar cane is the raw material for extracting white sugar. Sugarcane supports large number of industries like sugar mills producing refined sugars, distilleries producing liquor grade ethanol and millions of jaggery manufacturing units.
42. Molasses is the raw material for the production of_______
- Methyl alcohol
- Ethyl alcohol
- Propyl alcohol
- Butyl alcohol
Explanation
Fresh sugarcane juice is a refreshing drink. Molasses is the raw material for the production of ethyl alcohol.
43. Which of the following districts of Tamil Nadu does not cultivate sugar cane?
- Dharmapuri
- Nilgiris
- Kanyakumari
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The cultivated Saccharum officinarum has evolved by repeated back crossing of S.officinarum of New Guinea with wild S.spontaneum of India to improve the quality. All districts except Kanyakumari and Nilgiris of Tamil Nadu cultivate Sugarcane.
44. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Palmyra is native to tropical regions of Africa, Asia and New Guinea
- Palmyra grows all over Tamil Nadu, especially in coastal districts
- It is the state tree of Tamil Nadu
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Palmyra (State tree of Tamil Nadu): Palmyra is native to tropical regions of Africa, Asia and New Guinea. Palmyra grows all over Tamil Nadu, especially in coastal districts.
45. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Exudate from inflorescence axis is collected for preparing palm sugar
- Inflorescence is tapped for its sap which is used as health drink.
- Endosperm is used as a refreshing summer food.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Exudate from inflorescence axis is collected for preparing palm sugar. Inflorescence is tapped for its sap which is used as health drink. Sap is processed to get palm jaggery or fermented to give toddy. Endosperm is used as a refreshing summer food. Germinated seeds have an elongated embryo surrounded by fleshy scale leaf which is edible.
46. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The essential oils or volatile oils which possess aroma evaporate or volatilize in contact with air
- Any organ of a plant may be the source of essential oil
- Examples are flowers of Jasmine, fruits of orange and roots of ginger.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
There are two kinds of oils namely, essential oils and vegetable oils or fatty oils. The essential oils or volatile oils which possess aroma evaporate or volatilize in contact with air. Any organ of a plant may be the source of essential oil. For example, flowers of Jasmine, fruits of orange and roots of ginger. The vegetable oils or non-volatile oils or fixed oils that do not evaporate. Whole seeds or endosperm form the sources of vegetable oils.
47. Groundnut is native of______
- India
- Brazil
- Africa
- Indonesia
Explanation
Groundnut is native of Brazil. Portuguese introduced groundnut into Africa. The Spanish took it to the South East Asia and India via Philippines. In India Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan are top producers.
48. Ground Nuts contain about___ % oil
- 60
- 45
- 35
- 70
Explanation
Nuts contain about 45% oil. The kernels are also rich sources of phosphorous and vitamins, particularly thiamine, riboflavin and niacin. It is premium cooking oil because it does not smoke. Lower grade oil is used in manufacture of soaps and lubricants.
49. Sesamum indicum has originated from____
- India
- Brazil
- Africa
- Indonesia
Explanation
Sesamum indicum has originated from Africa. Sesame is cultivated as a dry land crop. West Bengal and Madhya Pradesh are the top producers in India during 2017-18. It is considered as a healthy oil in Southern Indian culture.
50. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Sesame oil is used for mostly culinary purposes in India
- Lower grades are used in manufacture of soaps, in paint industries, as a lubricant and as an illuminant
- Sesame seed snacks are popular throughout India.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Sesame oil is used for mostly culinary purposes in India. Lower grades are used in manufacture of soaps, in paint industries, as a lubricant and as an illuminant. In India, the oil is the basis of most of the scented oils used in perfumes. Sesame seed snacks are popular throughout India.
51.______ is the largest coffee producing state in India
- Karnataka
- Tamil Nadu
- Assam
- Kerala
Explanation
Coffea arabica is the prime source of commercial coffee which is native to the tropical Ethiopia An Indian Muslim saint, Baba Budan introduced coffee from Yemen to Mysore. Karnataka is the largest coffee producing state in India followed by Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Tamil Nadu is the largest consumer of coffee in India.
52. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Caffeine enhances release of acetylcholine in brain, which in turn enhances efficiency
- It may reduce the risk of type 1 diabetes
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Caffeine enhances release of acetylcholine in brain, which in turn enhances efficiency. It can lower the incidence of fatty liver diseases, cirrhosis and cancer. It may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
53. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Spices were used extensively throughout the world for several thousands of years.
- Majority of the spices are native to Mediterranean region, India and South East Asian countries.
- Records of use of garlic and onion dates back 500 years.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Spices were used extensively throughout the world for several thousands of years. Records of use of garlic and onion dates back 2500 years. Majority of the spices are native to Mediterranean region, India and South East Asian countries. Spices, especially pepper triggered the search for sea route to India and paved way for the exploratory voyages by Spanish and Portuguese.
54. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Spices are accessory foods mainly used for flavouring during food preparation to improve their palatability
- Spices are aromatic plant products and are characterized by bitter taste only
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Spices are accessory foods mainly used for flavouring during food preparation to improve their palatability. Spices are aromatic plant products and are characterized by sweet or bitter taste. Spices are added in minimal quantities during the cooking process. For example black pepper.
55. _____ is called as “Queen of Spices”
- Black pepper
- Cardamom
- Turmeric
- Tamarind
Explanation
Cardamom is indigenous to Southern India and Sri Lanka. Cardamom is called as “Queen of Spices”. In India it is one of the main cash crops cultivated in the Western Ghats, and North Eastern India.
56. Which of the following statement about cardamom is correct?
- The seeds have a pleasing aroma and a characteristic warm, slightly pungent taste
- The seeds are used in the preparation of curry powder, pickles and cakes.
- Medicinally, it is employed as a stimulant and carminative
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The cardamom seeds have a pleasing aroma and a characteristic warm, slightly pungent taste. It is used for flavouring confectionaries, bakery products and beverages. The seeds are used in the preparation of curry powder, pickles and cakes. Medicinally, it is employed as a stimulant and carminative. It is also chewed as a mouth freshener.
57. Black Pepper is indigenous to_____ of India
- Eastern ghats
- Western ghats
- Himalayas
- Deccan plateau
Explanation
Black Pepper is indigenous to Western Ghats of India. Botanical name of pepper is Piper nigrum. The characteristic pungency of the pepper is due to the presence of alkaloid Piperine.
58. _____ is one of the most important Indian spices referred to as the “King of Spices”
- Cardamom
- Black pepper
- Red pepper
- Bark leaves
Explanation
Pepper is one of the most important Indian spices referred to as the “King of Spices” and also termed as “Black Gold of India”. Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu are the top producers in India.
59. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Pepper is used for flavouring in the preparation of sauces, soups, curry powder and pickles
- It is used in medicine as an aromatic stimulant for enhancing salivary and gastric secretions and also as a stomachic.
- Pepper also enhances the bio-absorption of medicines.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Pepper is used for flavouring in the preparation of sauces, soups, curry powder and pickles. It is used in medicine as an aromatic stimulant for enhancing salivary and gastric secretions and also as a stomachic. Pepper also enhances the bio-absorption of medicines.
60. ______ in Tamil Nadu is the World’s largest wholesale turmeric market.
- Salem
- Coimbatore
- Erode
- Villupuram
Explanation
Turmeric is indigenous to Southern Asia India is the largest producer, consumer and exporter of turmeric. Erode in Tamil Nadu is the World’s largest wholesale turmeric market.
61. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Turmeric is one of the most important and ancient Indian spices and used traditionally over thousands of years for culinary, cosmetic, dyeing and for medicinal purposes
- It is an important constituent of curry powders
- It is also used for dyeing leather, fibre, paper and toys.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Turmeric is one of the most important and ancient Indian spices and used traditionally over thousands of years for culinary, cosmetic, dyeing and for medicinal purposes. It is an important constituent of curry powders. It is also used for dyeing leather, fibre, paper and toys.
62. ______ extracted from turmeric is responsible for the yellow colour.
- Indica
- Curcumin
- Cinchona
- None
Explanation
Curcumin extracted from turmeric is responsible for the yellow colour. Curcumin is a very good anti-oxidant which may help fight various kinds of cancer. It has anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal and antiviral activities. It stops platelets from clotting in arteries, which leads to heart attack
63. Capsicum is native to_____
- China
- South America
- Africa
- Europe
Explanation
Capsicum is native to South America and is popularly known as chillies or red pepper in English. India is leading producer and exporter. C. annuum and C. frutescens are important cultivated species of chillies.
64. Chillies are a good source of Vitamin___
- A, D, E
- B, C
- A, C, E
- A, D, K
Explanation
Capsaicin is an active component of chillies. It has pain relieving properties and used in pain relieving balms. Chillies are a good source of Vitamin C, A and E.
65. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Capsaicin is responsible for the pungency or spicy taste of chillies
- Pungency of Chillies is measured in Scoville Heat Units
- World’s hottest chilli, Carolina reaper pepper measures 220000 SHU
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Capsaicin is responsible for the pungency or spicy taste of chillies. Pungency of Chillies is measured in Scoville Heat Units (SHU). World’s hottest chilli, Carolina reaper pepper measures 2,200,000 SHU.
66. Tamarind is native of tropical______ region
- South American
- Africa
- Asia
- Australian
Explanation
Tamarind is native of tropical African region and was introduced into India several thousand years before. It is cultivated in India, Myanmar, south asian countries and several African and Central American countries.
67. Which of the following statement about tamarind is incorrect?
- It is used in flavouring sauces in the United States and Mexico.
- Sweet tamarinds are sold as table fruits in India imported from Thailand and Malaysia
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Tamarind is used in flavouring sauces in the United States and Mexico. In India, the fruit pulp is major ingredients for many culinary preparations. Sweet tamarinds are sold as table fruits in India imported from Thailand and Malaysia.
68. In India cotton is cultivated in_____
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
- Maharashtra
- All the above
Explanation
Commercial cotton comes from four cotton species: two from the new world and two from the old world. (1) G. hirsutum (2) G.barbadense are the New world species and (3) G. arboretum (4) G. herbaceum are the old world species. In India cotton is cultivated in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
69. Jute is an important cultivated commercial crop in Gangetic plains of____
- India
- China
- Bangladesh
- Burma
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- 2, 4
Explanation
Jute is derived from the two cultivated species (1) Corchorus capsularis and (2) C.olitorius is of African origin whereas C. capsularis, is believed to be Indo-Burmese origin. It is an important cultivated commercial crop in Gangetic plains of India and Bangladesh
70. About___ % of the jute produced is used for manufacturing sacks and bags
- 90
- 75
- 50
- 60
Explanation
About 75% of the jute produced is used for manufacturing sacks and bags. It is also used in manufacture of blankets, rags, curtains etc. It is also being used as a textile fibre in recent years.
71. Latex Rubber is a native of________
- Argentina
- Brazil
- India
- Myanmar
Explanation
Latex Rubber is a native of Brazil and was introduced outside its native range during the colonial period and has become an important cash crop.
72. Asia contributed_____ % of the world rubber production.
- 30
- 90
- 70
- 40
Explanation
Asia contributed 90% of the world rubber production. Kerala is the largest producer in India followed by Tamil Nadu.
73. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Tyre and other automobile parts manufacturing industries consume 50% of the rubber production
- Foamed latex is used in the manufacture of cushions, pillows and lifebelts
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Tyre and other automobile parts manufacturing industries consume 70% of the rubber production. Rubber is used in manufacturing footwear, wire and cable insulations, raincoats, household and hospital goods, shock absorbers, belts, sports goods, erasers, adhesives, and rubber-bands Hard rubber is used in the electrical and radio engineering industries Concentrated latex is used for making gloves, balloons and condoms. Foamed latex is used in the manufacture of cushions, pillows and lifebelts.
74. Charles Goodyear invented vulcanization in_____
- 1880
- 1839
- 1870
- 1779
Explanation
Charles Goodyear invented vulcanization in 1839. He found that the defects in rubber articles could be overcome by heating rubber with sulphur under pressure at 1500 C. The process was called vulcanization. The name was given from the Roman God of Fire, Vulcan. Because of this, solid rubber tyres were used for first time in 1867. That is why we smoothly travel on road.
75. Paper production is a_____ invention
- Indian
- African
- European
- Chinese
Explanation
The term paper is derived from the word ‘papyrus’ a plant (Cyperus papyrus) that was used by Egyptians to make paper-like materials. Paper production is a Chinese invention. The Chinese discovered the paper that was prepared from the inner bark of paper mulberry in 105 A.D.
76. When did Arabs learned the technique of paper making and improved it?
- 750 A.D.
- 750 B.C.
- 300 B.C.
- 600 B.C.
Explanation
For a long time, the art of paper making remained a monopoly of the Chinese until Arabs learned the technique and improved it around 750 A.D. Invention of printing increased the demand for paper.
77. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The ability to perceive colour is a wonderful aspect of human eyes and dyes add colour to the goods we use
- The earliest authentic records of dyeing were found in the tomb painting of ancient Egypt.
- Colourings on mummy cements (wrapping) included saffron and indigo.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The ability to perceive colour is a wonderful aspect of human eyes and dyes add colour to the goods we use. They have been in use since the ancient times. The earliest authentic records of dyeing were found in the tomb painting of ancient Egypt. Colourings on mummy cements (wrapping) included saffron and indigo. They can also be seen in rock paintings in India.
78. Henna is indigenous to_______
- North America
- North Africa
- South west Asia
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Henna is indigenous to North Africa and South-west Asia. It is grown mostly throughout India, especially in Gujarat, Madya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
79. Which of the following statement is correct?
- An orange dye ‘Henna’ is obtained from the leaves and young shoots of Lawsonia inermis
- It is used for colouring leather, for the tails of horses and in hair-dyes.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
An orange dye ‘Henna’ is obtained from the leaves and young shoots of Lawsonia inermis. The principal colouring matter of leaves ‘lacosone” is harmless and causes no irritation to the skin. This dye has long been used to dye skin, hair and finger nails. It is used for colouring leather, for the tails of horses and in hair-dyes.
80. Aloe is native to___________
- Sudan
- Egypt
- India
- Brazil
Explanation
Aloe Vera is a native of Sudan. It is cultivated on a large scale in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
81. Which of the following statement is correct?
- ‘Aloin’ (a mixture of glucosides) and its gel are used as skin tonic
- It has a cooling effect and moisturizing characteristics
- Products prepared from aloe leaves have multiple properties such as emollient, antibacterial, antioxidant, antifungal and antiseptic
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
‘Aloin’ (a mixture of glucosides) and its gel are used as skin tonic. It has a cooling effect and moisturizing characteristics and hence used in preparation of creams, lotions, shampoos, shaving creams, after shave lotions and allied products. It is used in gerontological applications for rejuvenation of aging skin. Products prepared from aloe leaves have multiple properties such as emollient, antibacterial, antioxidant, antifungal and antiseptic. Aloe vera gel is used in skin care cosmetics.
82. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The word perfume is derived from the Latin word Per (through) and fumus (to smoke), meaning through smoke
- Perfumes are added to baths and used for anointing the body
- Perfumes are manufactured from essential oil which are volatile and aromatic
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The word perfume is derived from the Latin word Per (through) and fumus (to smoke), meaning through smoke. It refers to the age-old tradition of burning scented woods at religious ceremonies. Perfumes are manufactured from essential oil which are volatile and aromatic. Essential oils are found at different parts of the plant such as leaves, (curry leaf, mint), flowers (rose, jasmine), fruits (citrus, straw berry) and wood (sandal, eucalyptus).
83. Which of the following statement is correct?
- ‘Madurai Malli’ is the pride of Madurai has a distinct reputation universally because of its uniqueness and has been given the Geographical Indications (GI)
- This is the third GI tag for Jasmine after ‘Mysore Malli’.
- Madurai malli has thick petals with long stalk equal to that of petals and the distinct fragrance is due to the presence of chemicals such as jasmine and alpha terpineol
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
‘Madurai Malli’ is the pride of Madurai has a distinct reputation universally because of its uniqueness and has been given the Geographical Indications (GI) mark by the Geographical indication Registry of India. Madurai malli has thick petals with long stalk equal to that of petals and the distinct fragrance is due to the presence of chemicals such as jasmine and alpha terpineol. This makes it easy to distinguish Madurai Malli from other places. This is the second GI tag for Jasmine after ‘Mysore Malli’.
84. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Jasmine, as a floral perfume, ranks next to the rose oil.
- Major species cultivated on the commercial scale is Jasminum grandiflorum, a native of the north-western Himalayas
- One ton of Jasmine blossom yields about 2.5 to 3 kg of essential oil, comprising 0.25 to 3% of the weight of the fresh flower.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Jasmine, as a floral perfume, ranks next to the rose oil. Major species cultivated on the commercial scale is Jasminum grandiflorum, a native of the north-western Himalayas. In Tamil Nadu, the major jasmine cultivation centres are Madurai and Thovalai of Kanyakumari District. The essential oil is present in the epidermal cells of the inner and outer surfaces of both the sepals and petals. One ton of Jasmine blossom yields about 2.5 to 3 kg of essential oil, comprising 0.25 to 3% of the weight of the fresh flower.
85. Which of the following statement is correct?
- India has a rich medicinal heritage.
- TSM in India can be broadly classified into institutionalized or documented and non-institutionalized or oral traditions.
- Institutionalized Indian systems include Siddha and Ayurveda which are practiced for about two thousand years.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
India has a rich medicinal heritage. A number of Traditional Systems of Medicine (TSM) are practiced in India some of which come from outside India. TSM in India can be broadly classified into institutionalized or documented and non-institutionalized or oral traditions. Institutionalized Indian systems include Siddha and Ayurveda which are practiced for about two thousand years. These systems have prescribed texts in which the symptoms, disease diagnosis, drugs to cure, preparation of drugs, dosage and diet regimes, daily and seasonal regimens.
86. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Siddha is the most popular, widely practiced and culturally accepted system in Tamil Nadu
- It is based on the texts written by 22 Siddhars
- The Siddhars are not only from Tamil Nadu, but have also come from other countries
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation Siddha is the most popular, widely practiced and culturally accepted system in Tamil Nadu. It is based on the texts written by 18 Siddhars. There are different opinions on the constitution of 18 Siddhars. The Siddhars are not only from Tamil Nadu, but have also come from other countries. The entire knowledge is documented in the form of poems in Tamil.
87. Which of the following statement is correct about Ayurveda is correct?
- Ayurveda supposed to have originated from Brahma.
- The core knowledge is documented by Charaka, Sushruta and Vagbhata in compendiums written by them
- The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India lists about 500 plants used as source of drugs
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Ayurveda supposed to have originated from Brahma. The core knowledge is documented by Charaka, Sushruta and Vagbhata in compendiums written by them. This system is also based on three humor principles namely, Vatha, Pitha and Kapha which would exist in equilibrium for a healthy living. This system Uses more of herbs and few animal parts as drug sources. Plant sources include a good proportion of Himalayan plants. The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India lists about 500 plants used as source of drugs.
88. Which of the following statement is correct?
- India is a treasure house of medicinal plants
- All institutional systems in India primarily use medicinal plants as drug sources
- Growing demand for herbal products has led to quantum jump in volume of plant materials traded within and across the countries
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
India is a treasure house of medicinal plants. They are linked to local heritage as well as to global-trade. All institutional systems in India primarily use medicinal plants as drug sources. At present, 90% collection of medicinal plants is from the non-cultivated sources. Growing demand for herbal products has led to quantum jump in volume of plant materials traded within and across the countries. Increasing demand exerts a heavy strain on the existing resources
89. Keezhanelli is a native of Tropical____ region
- African
- American
- Asian
- Australian
Explanation
The plant is a native of Tropical American region and is naturalised in India and other tropical countries. It is not cultivated and is collected from moist places in plains. Phyllanthus maderspatensis is also commonly sold in the medicinal plant markets collected from non-forest are as keezhanelli.
90. Which of the following can be treated with Phyllanthus?
- Malaria
- Jaundice
- Yellow fever
- Dengue
Explanation
Phyllanthus is a well-known hepato-protective plant generally used in Tamil Nadu for the treatment of Jaundice. Research carried out by Dr. S P Thyagarajan and his team from University of Madras has scientifically proved that the extract of P. amarus is effective against hepatitis B virus.
91. ____ known as the King of Bitters is traditionally used in Indian systems of medicines
- Andrographis paniculate
- Phyllanthus amarus
- Jasminum grandiflorum
- None
Explanation
Andrographis paniculata, known as the King of Bitters is traditionally used in Indian systems of medicines. Andrographis is a potent hepatoprotective and is widely used to treat liver disorders.
92. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Phytochemicals / drugs from some of the plants alter an individual’s perceptions of mind by producing hallucination are known as psychoactive drugs.
- These drugs are used in all ancient culture especially by Shamans and by traditional healers
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Phytochemicals / drugs from some of the plants alter an individual’s perceptions of mind by producing hallucination are known as psychoactive drugs. These drugs are used in all ancient culture especially by Shamans and by traditional healers. Here we focus on two such plants namely Poppy and Marijuana.
93. Which of the following states are licenced to cultivate opium?
- Rajasthan
- Madhya Pradesh
- Uttar Pradesh
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Opium poppy is native to South Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh are the licenced states to cultivate opium poppy.
94. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Opium is derived from the exudates of fruits of poppy plants
- It was traditionally used to induce sleep and for relieving pain.
- Opium yields Morphine, a strong analgesic which is used in surgery.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Opium is derived from the exudates of fruits of poppy plants. It was traditionally used to induce sleep and for relieving pain. Opium yields Morphine, a strong analgesic which is used in surgery. However, opium is an addiction forming drug.
95. Marijuana is native to_____
- India
- China
- Ghana
- Brazil
Explanation
Marijuana is native to China. States such as Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarkand, Uttarpradesh and Madhaya Pradesh have legally permitted to cultivate industrial hemp/Marijuana.
96. The active principle in Marijuana is_____
- Trans-tetra-hydrocanabinal
- Trans-penta-hydrocanabinal
- Tetrahydrocanabinal
- None
Explanation
The active principle in Marijuana is trans-tetra hydro-canabinal (THC). It possesses a number of medicinal properties. It is an effective pain reliever and reduces hypertension. THC is used in treating Glaucoma a condition in which pressure develops in the eyes.
97. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- THC is also used in reducing nausea of cancer patients undergoing radiation and chemotherapy.
- THC provides relief to bronchial disorders, especially asthma as it dilates bronchial vessels.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
THC is used in treating Glaucoma a condition in which pressure develops in the eyes. THC is also used in reducing nausea of cancer patients undergoing radiation and chemotherapy. THC provides relief to bronchial disorders, especially asthma as it dilates bronchial vessels. Because of these medicinal properties, cultivation of cannabis is legalized in some countries.
98. Match the following
- Holy basil 1. Vitaceae
- Indian gooseberry 2. Phyllanthaceae
- Vilvam 3. Lamiaceae
- Veldt grape 4. Rutaceae
- 2, 1, 3, 4
- 4, 2, 1, 3
- 3, 2, 4, 1
- 3, 4, 2, 1
Explanation
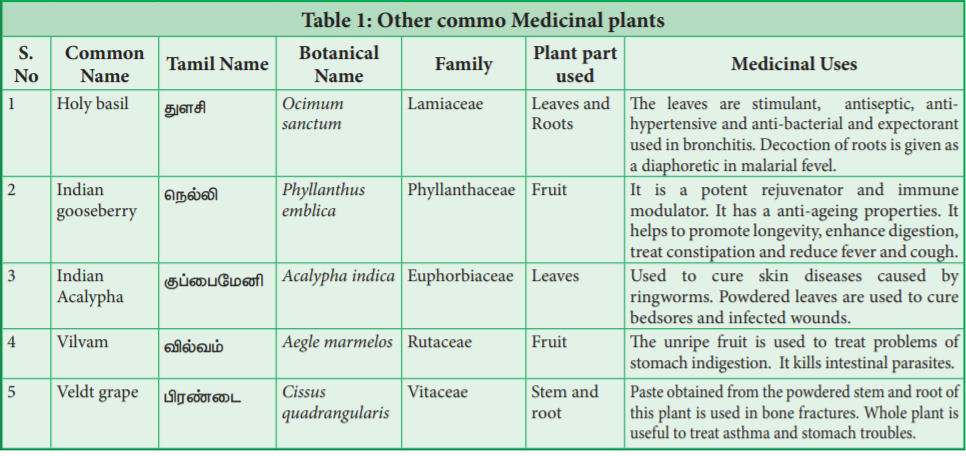
99. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Drug abuse and misuse can cause numerous health problems and in serious cases death can occur.
- The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) is the nodal drug law enforcement and intelligence agency of India and is responsible for fighting drug trafficking and the abuse of illegal substances
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation

100. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Entrepreneurial Botany is the study of how new businesses are created using plant resources as well as the actual process of starting a new business
- Entrepreneurship is now a popular topic for higher secondary students, with a focus on developing ideas to create new ventures among the young people.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Entrepreneurial Botany is the study of how new businesses are created using plant resources as well as the actual process of starting a new business. An entrepreneur is someone who has an idea and who works to create a product or service that people will buy, by building an organization to support the sales. Entrepreneurship is now a popular topic for higher secondary students, with a focus on developing ideas to create new ventures among the young people.
101. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Organic farming is an alternative agricultural system in which plants/crops are cultivated in natural ways by using biological inputs to maintain soil fertility and ecological balance thereby minimizing pollution and wastage.
- Indians were organic farmers by default until the green revolution came into practice.
- Use of biofertilizers is one of the important components of integrated organic farm management, as they are cost effective and renewable source of plant nutrients to supplement the chemical fertilizers for sustainable agriculture
- 1, 2
- 2, 3
- 1, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Organic farming is an alternative agricultural system in which plants/crops are cultivated in natural ways by using biological inputs to maintain soil fertility and ecological balance thereby minimizing pollution and wastage. Indians were organic farmers by default until the green revolution came into practice. Use of biofertilizers is one of the important components of integrated organic farm management, as they are cost effective and renewable source of plant nutrients to supplement the chemical fertilizers for sustainable agriculture. Several microorganisms and their association with crop plants are being exploited in the production of biofertilizers. Organic farming is thus considered as the movement directed towards the philosophy of Back to Nature.
102. Which of the following is not a majority grass based food species?
a) Rice
b) Groundnut
c) Wheat
d) Maize
Explanation
Currently about 10,000 food plants are being used of which only around 1,500 species were brought under cultivation. However, food base of majority of the population depends only on three grass species namely rice, wheat and maize.
103. Based on which property cereals are classified into two types?
a) Size
b) Cultivation period
c)Seed type
d)None of the above
Explanation
Cereals can be classified into two different types based on their size namely Major Cereals and Minor Cereals.
104. In which of these regions rice is cultivated in Tamil Nadu?
a) Coastal region
b) Hill Stations
c) Delta region
d) All the above
Explanation
South East Asia is considered as the centre of origin of rice.It is mainly cultivated in Delta and irrigated regions of Tamil Nadu.
105. Which is not a usage of rice husks?
a) Fuel
b) Cosmetics
c) Packing material
d) Fertilizer
Explanation
Husks are used as fuel, and in the manufacture of packing material and fertilizer.
106. Which variety of rice is called as miracle rice for fighting famine?
a)IR18
b)IR8
c)IR30
d)IR20
Explanation
IR8is a high-yielding semi-dwarf rice varietydeveloped by IRRI in the early 1960s andit is called as miracle rice, much celebratedfor fighting famine.
107. Which form of wheat is used for producing beverages and nutritive drinks?
a) Malted wheat
b) Wheat husk
c) Rice husk
d) Cereals husk
Explanation
Malted wheat is a major raw materialfor producing alcoholic beverages and nutritivedrinks.
108. Which crop was domesticated from the new world?
a) Jute
b) Cereals
c)Maize
d) Cotton
Explanation
Maize is the only cereal that has originated anddomesticated from the New World.
109. Which of the following is not a major maize growing belt in Tamil nadu?
a) Perambalur
b) Tirupur
c) Dindugul
d) Nagapattinam
Explanation
Perambalur, Ariyalur, Cuddalore,Dindigul and Tirupur are the major maize growing belts in Tamil Nadu.
110. Identify the Incorrect Match.
A. Foxtail Millet i) Setaria italic
B. Kodo Millet ii) Paspalumscrobiculatum
C. Finger Millet iii) Eleusinecoracana
D. Little Millet iv) Coffea arabica
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) iv only
Explanation
Finger Millet – Ragi, Botanical name:Eleusinecoracana
Little Millet Botanical name- Panicumsumatrense
Foxtail Millet Botanical name :Setaria italic
Kodo Millet Botanical name:Paspalumscrobiculatum
111. Which is the origin of the word Pulse?
a) Latin
b)Arab
c) Persian
d) Sanskrit
Explanation
The word Pulse is derived from the Latinwords ‘puls’ or ‘pultis’ meaning “thick soup”.
112. India contributes ____ of the global production of black gram.
a) 25%
b) 80%
c) 45%
d) 10%
Explanation
It is cultivated as a rain fed crop in drier parts of India. India contributes to 80% of the global production of black gram.
113. Which of these pulses is used as infant food formulae?
a) Chick pea
b) Groudnut
c) Black gram
d) Cashew nut
Explanation
Chick pea protein is rated high in terms ofamino acid content and digestibility. Infant foodformulae uses malted chick pea as an ingredient. Chick pea seed flour is a prime constituent ofmany forms of Indian confectionary.
114. Which of these are obtained from vegetables for health maintenance?
a) Potassium
b) Folic acid
c) Vitamins
d) All the above
Explanation
Vegetables are the important part ofhealthy eating and provide many nutrients,including potassium, fiber, folic acid andvitamins A, E and C. The nutrients in vegetablesare vital for maintenance of our health.
115. In which of the following places potato is cultivated in Tamil Nadu?
a) Perambalur
b) Palani hills
c) Cuddalore
d) Sivagangai
Explanation
Potato has originated from the highlandsof Peru and Bolivia.Nilgiri and Palani hills also contribute to the potatocultivation in Southern Indian hills.
116. What are the usages of potato tubers?
a) Brewing industry
b) Chips industry
c) Microbiological products
d) All the above
Explanation
Potato tubers are used in a variety of wayslike boiled, steamed, fried, baked, roastedor as an ingredient in soup, stews, pies andother dishes. It is the major raw material forthe chips industry, brewing industry andin the manufacture of products used formicrobiological and clinical applications.
117. Which of the following is not included in the curcurbitaceae family?
a) Squash
b) Potato
c) Melons
d) Cucumbers
Explanation
The cucurbits are the vining plants of the familyCucurbitaceae, which include cucumbers,squash, pumpkins, melons and gourds.
118. Which of the following fruit is loaded with potassium and essential vitamins?
a)Mango
b)Banana
c) Apple
d) Guava
Explanation
The banana fruit is loaded with potassium andessential vitamins, which can be eaten rawor cooked (deep fried, dehydrated, baked orsteamed).
119. Match the family name and the common name of fruits.
A. Date palm i) Caricaceae
B. Papaya ii) Myrtaceae
C. Fig iii) Arecaceae
D. Guava iv) Moraceae
a) ii, i, iv, iii
b) iii, i, iv, ii
c) i, iv, iii, ii
d) iv, ii, i, iii
120. What is the edible part of the pomegranate fruit?
a) Aril
b) Endocarp
c) Pericarp
d) Mesocarp
Explanation
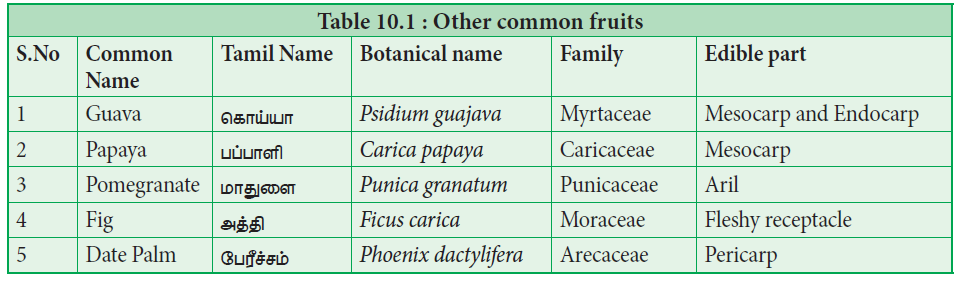
121. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Stevia is native to Brazil and Paraguay.
ii) In India Gujarat, Himachal pradesh and Tamil Nadu cultivates stevia.
iii) Stevia is an artificial sweetener used for medicinal purposes.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Stevia is a native to Brazil and Paraguay. It iscultivated in the states of Himachal Pradesh,Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.This is the most popular natural sweetenerand is a substitute for white sugar, hence itis extensively used by diabetic patients andhealth conscious people.
122. Which of the following is not a usage of coconut oil?
a) Edible – industrial oil
b)Fuel
c) Rubber and synthetic resin manufacturing
d)Soaps and detergents
Explanation
Coconut oil is classified as edible-industrial oil.Soaps obtained from coconut oil lathers well insoft and hard water. It is used in manufacture of rubber, synthetic resins, lubricants, brake fluids foraeroplanes and detergents. It is used as major hairoil and a base for applying medicinal powders.
123. Which country is native of Tea?
a) China
b) India
c) Chile
d) Iran
Explanation
Tea is native of China.Assam is the top tea producer in India,followed by Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
124. In which part of India coffee was introduced by a Muslim saint Baba Budan?
a) Delhi
b) Mysore
c) Mumbai
d) Bengal
Explanation
Coffea Arabica is the prime source of commercial coffeewhich is native to the tropical Ethiopia.An Indian Muslim saint, Baba Budan introducedcoffee from Yemen to Mysore.
125. Which of this state is the largest consumer of coffee in India?
a) Tamil Nadu
b) Karnataka
c) Gujarat
d) Madhya Pradesh
Explanation
Tamil Nadu is thelargest consumer of coffee in India.
126. Which of this state is the second largest producer of cocoa in India?
a) Andhra Pradesh
b) Karnataka
c) Gujarat
d) Madhya Pradesh
Explanation
Cocoa is native ofTropical American region. The word Theobroma(Theos means god, broma means food) means‘food of the Gods’. Kerala is the largest producerof Cocoa in India followed by Karnataka.
127. In which of these industries turmeric is used as a coloring agent?
a) Pharmacy
b) Food Industry
c) Confectionery
d) All the above
Explanation
Turmeric is used as a coloring agent in pharmacy, confectionery and food industry. Rice colored with turmeric (yellow) is considered sacred and auspicious which is used in ceremonies.
128. Which of the following statement is not correct regarding turmeric?
a) Curcumin extracted from turmeric is responsible for the yellow color.
b) Curcumin has anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal and antiviral activities.
c) Curcumin is a good anti-oxidant may help to fight various kinds of cancer.
d) Excess usage of Curcumin makes the platelets to clot in arteries leading to heart attack.
Explanation
Curcumin extracted from turmeric isresponsible for the yellow color. Curcumin isa very good anti-oxidant which may help fightvarious kinds of cancer. It has anti-inflammatory,anti-diabetic, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal and antiviralactivities.It stops platelets from clotting inarteries, which leads to heart attack.
129. Which of the following is used for its pain relieving properties?
a) Curcumin
b) Stevia
c) Capsaicin
d) Cocoa
Explanation
Capsaicin is an active component ofchillies. It has pain relieving properties andused in pain relieving balms.
130. What is the SHU measure of the commonly used cayenne pepper?
a) 10,000 SHU
b) 30,000 to 50,000 SHU
c) 2,00,000 to 4,00,000 SHU
d) Above 500 SHU
Explanation
Naga viper chilli is the hottest in India that measures 1,349,000 SHU. Commonly used cayenne pepper measures 30,000 to 50,000 SHU.
131. What is the origin of the name tamarind?
a) Arabian
b) Latin
c) French
d) Persian
Explanation
Tamarind has long been used in Africa and in Southern Asia. The name tamarindus is of Arabian origin, which means “dates of India”. (tamar – dates; Indus – India).
132. Identify the Incorrect Match.
A. Apiaceae i) Asafoetida
B. Myrtaceae ii) Cloves
C. Fabaceae iii) Fenugreek
D. Amarillidaceae iv) Onion
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) iv only
Explanation
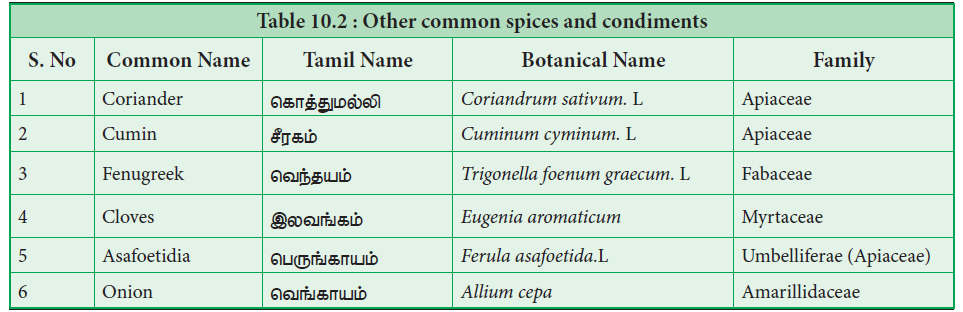
133. Which of this fibre is not used for making hats and furniture?
a) Cane
b) Lantana
c) Hemp
d) Vitex
134. Match
A. Filling fibre i) Jute
B. Plaiting fibre ii) Palm fibres
C. Textile fibre iii) Calotropis
D. Brush fibre iv) Cane
a)ii, iv, iii, i
b)iii,iv, i, ii
c)i, iii, ii, iv
d)ii, iii, i, iv
Explanation
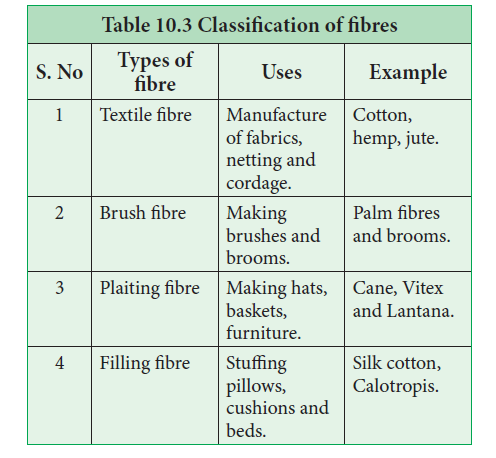
135. Choose the correct statements regarding commercial cotton.
i) Commercial cotton comes from three species from the new world.
ii) G. arboretum is the old world cotton species.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Commercial cotton comes fromfour cotton species: two from the new world and two from the old world.G. hirsutum,G.barbadense are the new world species andG. arboretum, G. herbaceumare the old world species.
136. Which of the following property is not associated with coconut fibres?
a) Elasticity
b) High resistance to sea water
c) Heavy mass
d) Insulating capacity
Explanation
Commercial coir is obtained from themesocarp of coconut. The fibre is known forits light mass, elasticity, high resistance to seawater and for its insulating capacity.
137. What are the main usages and properties of teak wood?
i) Durable
ii) Light mass
iii) Carpenter friendly
iv) Elasticity
v) Ships and bridge building woods.
a)i, iii, v only
b)i, ii, iv , v only
c)ii, iii, v only
d)ii, iv only
Explanation
Teak is known for itsdurability as it is immune to the attack of termites and fungi.The wood does not split or crack and isa carpenter friendly wood. It was the chiefrailway carriage and wagon wood in India. Ship building and bridge-building depends onteakwood. It is also used in making boats, toys,plywood, door frames and doors.
138. Which is not a major cultivation place of rose wood in India?
a) Bihar
b) Odisha
c) Rajasthan
d) Uttar Pradesh
Explanation
Rose woodis native to India it is cultivated in UttarPradesh, Bihar, Odisha, Central, Western andSouthern India.
139. What are the main usages of ebony?
a) Musical instruments
b) Whips and Umbrella handles
c) Furniture
d) All the above
Explanation
Ebony is used mainly for making piano keys, handlesof cutlery, musical instruments, making sticks,umbrella handles, whips and furniture.
140. Which of this latex is used for manufacturing cushions and life-belts?
a) Concentrated latex
b) Foamed latex
c) Derived latex
d) Combined latex
Explanation
Concentrated latex is used formaking gloves, balloons and condoms.Foamed latex is used in the manufacture ofcushions, pillows and life-belts.
141. Which of the following statements is correct?
i) Vulcanization process is not mandatory for rubber processing.
ii) Vulcanization is derived from the Sanskrit word Vulcan.
iii) In 1867 solid rubber tyres were used for the first time.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The process was calledvulcanization. The name was given from theRoman God of Fire, Vulcan. Because of this,solid rubber tyres were used for first time in 1867.
142. From which of this word the term paper was derived?
a) Papyrus
b) Paprika
c) Pyperus
d) Paaciferus
Explanation
The term paper is derived from the word‘papyrus’ a plant (Cyperus papyrus) thatwas used by Egyptians to make paper-likematerials.
143. By which of this process wood is converted to pulp in paper making process?
a) Bio-mechanical process
b) Electrical process
c) Mechanical and Chemical
d) Recycling process
Explanation
Woodis converted intopulp by mechanicaland chemicalprocesses.
144. In which of this manufacturing process purified dissolving pulp is used as a basic material?
a) Artificial silk
b) Plastics
c) Transparent films and fabrics
d) All the above
Explanation
Purified dissolving pulp isused as a basic material inthe manufacture of rayonor artificial silk, fabrics,transparent films (cellophane, cellulose acetate films), plastics. The viscose process ofmaking rayon is the most common process.
145. What is the color of the dye extracted from the leaves of Indigofera?
a) Black
b) Dark blue
c) Purple
d) Red
Explanation
A brilliant dark blue dye ‘indigo’ was extractedfrom the leaves of several species of Indigofera.The people of Asia, especially India have known the dye for over 4,000 years. It is also used inpainting of murals.
146. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The Indian farmers were forced to cultivate Indigofera during the British regime.
ii) Indigofera is a very important food crop.
iii) Gandhi started the first Satyagraha at Champaran village in support of the farmers.
a)i only
b)ii only
c)iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Indigofera is a veryimportant cash cropamong plants cultivatedin India during the British regime. Farmerswere forced to cultivate Indigofera instead of food crops. Gandhi started satyagraha at Champaran, a village in Bihar in supportof farmers. This was the first satyagraha inIndia by Gandhi.
147. Identify the incorrect match.
A. Leaves i) Mint
B. Wood ii) Teak
C. Flowers iii) Rose
D. Fruits iv) Citrus
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) iv only
Explanation
Perfumes are manufactured from essentialoil which arevolatile and aromatic. Essentialoils are found at different parts of the plantsuch as leaves, (curry leaf, mint), flowers (rose,jasmine), fruits (citrus, straw berry) and wood(sandal, eucalyptus).
148. Which of this place is native of the Jasminum grandiflorum?
a) Western Ghats
b) North-western Himalayas
c) South-east Asia
d) Northern America
Explanation
Jasmine, as a floral perfume, ranks next tothe rose oil. Major species cultivated on thecommercial scale is Jasminum grandiflorum,a native of the north-western Himalayas.
149. Which is the most expensive and oldest perfume oil?
a) Jasmine oil
b) Sandalwood oil
c) Rose oil
d) Mint oil
Explanation
Rose oil is one of the oldestand most expensive of perfume oils. The oil is concentrated in the epidermal cells on theinner surface of the petals.
150. Which is considered as the native of Sandal tree?
a) South East Asia
b) South Africa
c) South America
d) Mongolian region
Explanation
Sandal treeis native of South East Asia. Karnataka andTamil Nadu are states that possess large naturalpopulations of Santalum album in India.
151. Choose the correct statements.
i) The core knowledge of Ayurveda is documented by Charaka, Sushruta and Vagbhata.
ii) Ayurveda system is based on three principles vatha, pitha and kapha for healthy living.
a)i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Ayurveda supposed to have originated fromBrahma. The core knowledge is documentedby Charaka, Sushruta and Vagbhataincompendiums written by them. This systemis also based on three humor principlesnamely, Vatha, Pitha and Kapha which wouldexist in equilibrium for a healthy living.
152. Identify the Incorrect match
A. Indian Acalypha i) Asthma and stomach troubles
B. Holy Basil ii) Antiseptic
C. Vilvam iii) Kills intestinal parasites
D. Indian Gooseberry iv) Immune modulator and rejuvenator
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) iv only

153. In which year the university of Mississippi medical centre was granted patent for turmeric?
a) 1995
b) 1967
c) 1983
d) 1948
Explanation
University of Mississippimedical center, USAwas granted a patent for wound healing property of Turmericin 1995. The patent was granted both for oral and topical applications andprovides an exclusive right to sell and distribute.
154. Which of the following statements are not true regarding Opium?
a) Opium is derived from the exudates of fruits of poppy plants.
b) Opium is also derived from the edible fungus.
c) Opium is used to induce sleep and pain reliever.
d) Opium yields morphine a strong analgesic used for surgery.
Explanation
Opium is derived from the exudates offruits of poppy plants. It was traditionallyused to induce sleep and for relieving pain.Opium yields Morphine, a strong analgesicwhich is used in surgery.
155. Which part of edible fungi is known as mushroom?
a) Leaves
b) Stem
c) Fruit
d) Root
Explanation
Mushrooms are the fruiting body of ediblefungi and is the most priced commodity amongvegetables, not only because of its nutritivevalue but also for its characteristicaroma and flavor.M u s h r o o m sare also called white vegetable.
156. Which of these microorganisms are used for protein synthesize?
a) Fungi
b) Yeast
c) Bacteria
d) All the above
Explanation
Microorganisms that can be used forthe production of SCP have the capacity to synthesize proteins rapidly than higher livingorganisms. Microorganisms like algae, fungi,yeast and bacteria are used for this purpose.
157. Which of the following is not a usage of liquid seaweed?
a) Mosquito repellent
b) Foliar spray for fruit, flowers
c) Stimulates healthy growth for plants.
d) To withstand environmental stress and disease attack in plants.
Explanation
Liquid seaweed extract enhances healthy growthof plants, flowers and vegetables. Regular usewill help plants to withstand environmentalstress, pests and disease attack. It can be used asa foliar spray for fruit, flower, and vegetable crops aswell as for shrubs and trees. It stimulates healthy growth for all plants.
158. What is the usage of Azadirachta Indica?
a) Food preservatives
b) Pest repellent and Insecticide
c) Taste enhancers
d) Biomedicines
Explanation
Botanical pest repellentand insecticide made with the dried leaves of Azadirachta indica.
159. In which year the National Medicinal Plants Board was set up by the Government of India?
a) 2000
b) 1982
c) 1999
d) 1963
Explanation
Government of India has set up NationalMedicinal Plants Board (NMPB) on 24th November 2000. Currently this board isworking under AYUSH Government of India.
160. Which of the following parts are economically used in lemongrass?
a) Stem base
b) Flowers
c) Leaves
d) Both a and c
Explanation
Lemongrass is a tropical herb packed withstrong citrus flavor. The lemon taste is prizedin Asian cooking, as well as in tea, sauces, andsoups.Economic part: Stem base and leaves.
161. What are the contributions of CSIR in rural empowerment of aromatic plants?
a) Cultivation and processing
b) Value addition
c) Marketing
d) All the above
Explanation
The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) have Catalyzing Rural Empowerment through Cultivation, Processing, Value Addition and Marketing of Aromatic Plants”. This programs contributed significantly in the development, nurturing and positioning of essential oil-based aroma industry in the country.
12th Science Lesson 4 Questions in English
4] Applications of Biotechnology
1. Which of the following involves the manipulation of DNA and naturally occurring processes such as protein synthesis for a wide range of applications including the production of therapeutically important proteins?
- Genetic engineering
- Microbiology
- Cytology
- None of the above
Explanation
Genetic engineering involves the manipulation of DNA and naturally occurring processes such as protein synthesis for a wide range of applications including the production of therapeutically important proteins. This also involves extracting a gene from one organism and transferring it to the DNA of another organism, of the same or another species.
2. The DNA produced by genetic engineering is called as
- Genetical DNA
- Recombinant DNA
- Both a and b
- None of the above
Explanation
The DNA produced in genetic engineering is referred to as recombinant DNA (rDNA) and this technique as recombinant DNA technology. All these are part of the broad field biotechnology which can be defined as the applications of scientific and engineering principles to the processing of material by biological agents to provide goods and services.
3. Recombinant DNA technology has led to the large scale production of
- Hormones
- Protiens
- Both a and b
- None of the above
Explanation
The term biotechnology was first used before 20th century for such traditional activities as making idli, dosa, dairy products, bread or wine, but none of these would be considered biotechnology in the modern sense. Recombinant DNA technology has led to the large scale production of various hormones and proteins of therapeutic use.
4. The Human insulin is synthesized by the β cells of Islets of Langerhans in the
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Brain
- Stomach
Explanation
The Human insulin is synthesized by the β cells of Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. It is formed of 51 amino acids which are arranged in two polypeptide chains, A and B.
5. The Human insulin is is formed of 51 amino acids in which part A contains __ amino acids and part B contains ___ amino acids.
- 30 and 21
- 21 and 30
- 20 and 31
- 31 and 20
Explanation
The Human insulin is synthesized by the β cells of Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. It is formed of 51 amino-acids which are arranged in two polypeptide chains, A and B. Both A and B chains are attached together by disulphide bonds.
6. Insulin controls the levels of _____ in blood.
- Glucose
- Salt
- Energy
- Both a and c
Explanation
Insulin controls the levels of glucose in blood. It facilitates the cellular uptake and utilization of glucose for the release of energy. Deficiency of insulin leads to diabetes mellitus which is characterized by increased blood glucose concentration and a complex of symptoms which may lead to death, if untreated. A continuous program of insulin dependence is required to treat this deficiency
7. In early years insulin extracted from which animal was used to treat diabetes?
- Pig
- Cow
- Donkey
- Both a and b
Explanation
In the early years, insulin isolated and purified from the pancreas of pigs and cows was used to treat diabetic patients. Due to minor differences in the structure of the animal insulin as compared to human insulin, it resulted in the occurrence of allergic reactions in some diabetic patients. Production of insulin by recombinant DNA technology started in the late 1970s.
8. The recombinant DNA technique involved the insertion of human insulin gene on the plasmids of
- E. coli
- Escherchia coli
- Fungi
- Both a and b are same
Explanation
Production of insulin by recombinant DNA technology started in the late 1970s. This technique involved the insertion of human insulin gene on the plasmids of E.coli. The polypeptide chains are synthesized as a precursor called pre-pro insulin, which contains A and B segments linked by a third chain (C) and preceded by a leader sequence. The leader sequence is removed after translation and the C chain is excised, leaving the A and B polypeptide chains.
9. Which was the first ever pharmaceutical product of recombinant DNA technology administered to humans?
- Insulin
- Humulin
- Tubix
- Both a and b
Explanation
Insulin was the first ever pharmaceutical product of recombinant DNA technology administered to humans. The approval to use recombinant insulin for diabetes mellitus was given in 1982. In 1986 human insulin was marketed under the trade name Humulin.
10. Best and Banting in 1921, isolated insulin from the pancreatic islets of ____ and demonstrated its effectiveness against diabetes.
- Human
- Cow
- Dog
- None of the above
Explanation
Best and Banting in 1921, isolated insulin from the pancreatic islets of a dog and demonstrated its effectiveness against diabetes.
11. The first transgenic cow produced human protein enriched milk, which contained the human alpha lactalbumin was named as
- Comse
- Jersey
- Rosie
- Russel
Explanation
In 1997, Rosie, the first transgenic cow produced human protein enriched milk, which contained the human alpha lactalbumin. The protein rich milk (2.4 gm/litre) was a nutritionally balanced food for new born babies than the normal milk produced by the cows.
12. Interferons are proteinaceous, antiviral, species specific substances were discovered by
- Alick Isaacs
- Jean Lindemann
- Jena Alexa
- Both a and b
Explanation
Interferons are proteinaceous, antiviral, species specific substances produced by mammalian cells when infected with viruses. Interferons were discovered by Alick Isaacs and Jean Lindemann in 1957. Based on the structure of interferons they are classified as α, β and γ interferons
13. Which of the following is more suitable for production of recombinant interferons?
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- E. coli
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is more suitable for production of recombinant interferons than E. coli, since E. coli does not possess the machinery for glycosylation of proteins.
14. Interferons are used for the treatment of various diseases like
- Cancer
- AIDS
- Hepatitis
- All the above
Explanation
Interferons are used for the treatment of various diseases like cancer, AIDS, multiple sclerosis, hepatitis C and herpes zoster. In spite of the therapeutic applications interferons are not within the reach of the common man due to high cost for its production.
15. Vaccines that use components of a pathogenic organism rather than the whole organism are called
- United vaccines
- Subunit vaccines
- Liminto vaccines
- None of the above
Explanation
Vaccines that use components of a pathogenic organism rather than the whole organism are called subunit vaccines; recombinant DNA technology is very suited for developing new subunit vaccines. It includes components like proteins, peptides and DNAs of pathogenic organisms. The advantages of these vaccines include their purity in preparation, stability and safe use.
16. Which includes genetically modified pathogenic organisms (bacteria or viruses) that are made non- pathogenic and are used as vaccines?
- Subunit recombinant vaccines
- Attenuated recombinant vaccines
- DNA vaccines
- All the above
Explanation
Attenuated recombinant vaccines includes genetically modified pathogenic organisms (bacteria or viruses) that are made nonpathogenic and are used as vaccines. It is now possible to genetically engineer the organisms (bacteria or viruses) and use them as live vaccines and such vaccines are referred to as attenuated recombinant vaccines.
17. ___are prepared by molecular pharming using the science of genetic engineering.
- Subunit recombinant vaccines
- Attenuated recombinant vaccines
- DNA vaccines
- Edible vaccines
Explanation
Edible vaccines are prepared by molecular pharming using the science of genetic engineering. Selected genes are introduced into plants and the transgenic plants are induced to manufacture the encoded protein. Edible vaccines are mucosal targeted vaccines which cause stimulation of both systemic and mucosal immune response.
18. At present edible vaccines are produced for human and animal diseases like
- Cholera
- Foot and mouth disease
- Hepatitis
- All the above
Explanation
At present edible vaccines are produced for human and animal diseases like measles, cholera, foot and mouth disease and hepatitis.
19. Which Vaccine consists of a gene encoding an antigenic protein, inserted onto a plasmid, and then incorporated into the cells in a target animal?
- Subunit recombinant vaccines
- Attenuated recombinant vaccines
- DNA vaccines
- Edible vaccines
Explanation
DNA vaccine consists of a gene encoding an antigenic protein, inserted onto a plasmid, and then incorporated into the cells in a target animal. DNA instructs the cells to make antigenic molecules which are displayed on its surfaces. This would evoke an antibody response to the free floating antigen secreted by the cells.
20. Which was the first synthetic vaccine launched in 1997 which was marketed by trade names Recombivax and Engerix-B?
- Hepatitis B
- Astra zenaca
- Typhoid
- All the above
Explanation
The recombinant vaccine for hepatitis B (HbsAg) was the first synthetic vaccine launched in 1997 which was marketed by trade names Recombivax and Engerix-B. India is the fourth country in the world after USA, France and Belgium to develop an indigenous hepatitis B vaccine.
21. Which therapy which involves insertion of DNA into the genome to replace the missing gene product and Gene inhibition therapy?
- Somatic cell therapy
- Germ line gene therapy
- Gene Augmentation
- All the above
Explanation
At present most genetic diseases have no effective treatment and so gene therapy could offer hope for many people. There are two strategies involved in gene therapy namely; Gene augmentation therapy which involves insertion of DNA into the genome to replace the missing gene product and Gene inhibition therapy which involves insertion of the anti sense gene which inhibits the expression of the dominant gene .The two approaches to achieve gene therapy are somatic cell and germ line gene therapy.
22. Which therapy involves the insertion of a fully functional and expressible gene into a target somatic cell to correct a genetic disease permanently?
- Somatic cell therapy
- Germ line gene therapy
- Gene Augmentation
- All the above
Explanation
Somatic cell therapy involves the insertion of a fully functional and expressible gene into a target somatic cell to correct a genetic disease permanently whereas Germline gene therapy involves the introduction of DNA into germ cells which is passed on to the successive generations.
23. Which therapy involves isolation of a specific gene and making its copies and inserting them into target cells to make the desired proteins?
- Somatic cell therapy
- Germ line gene therapy
- Gene Augmentation
- All the above
Explanation
Gene therapy involves isolation of a specific gene and making its copies and inserting them into target cells to make the desired proteins. It is absolutely essential for gene therapists to ensure that the gene is harmless to the patient and it is appropriately expressed and that the body’s immune system does not react to the foreign proteins produced by the new genes.
24. _____ are undifferentiated cells found in most of the multi cellular animals.
- Nerve cells
- Neurons
- Stem cells
- None of the above
Explanation
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells found in most of the multi cellular animals. These cells maintain their undifferentiated state even after undergoing numerous mitotic divisions. Stem cell research has the potential to revolutionize the future of medicine with the ability to regenerate damaged and diseased organs.
25. The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 by French Anderson to a four year old girl with _____ deficiency.
- Melaimine
- Protien
- Adenosine deaminase
- None of the above
Explanation
The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 by French Anderson to a four year old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency. ADA deficiency or SCID (Severe combined immunodeficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder. It is caused by the deletion or dysfunction of the gene coding for ADA enzyme. In these patients the nonfunctioning T-Lymphocytes cannot elicit immune responses against invading pathogens. The right approach for SCID treatment would be to give the patient a functioning ADA which breaks down toxic biological products.
26. In some children ADA deficiency could be cured by
- Bone marrow transplantation
- Bone marrow manipulation
- Bone inoculation
- None
Explanation
In some children ADA deficiency could be cured by bone marrow transplantation, where defective immune cells could be replaced with healthy immune cells from a donor. In some patients it can be treated by enzyme replacement therapy, in which functional ADA is injected into the patient.
27. During gene therapy which of the following from the blood of the patient are removed and grown in a nutrient culture medium?
- Lymphocytes
- Eosinophils
- Phagocytes
- All the above
Explanation
During gene therapy the lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are removed and grown in a nutrient culture medium. A healthy and functional human gene, ADA cDNA encoding this enzyme is introduced into the lymphocytes using a retrovirus. The genetically engineered lymphocytes are subsequently returned to the patient. Since these cells are not immortal, the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes. The disease could be cured permanently if the gene for ADA isolated from bone marrow cells are introduced into the cells of the early embryonic stages.
28. Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent and can produce
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- All the above
Explanation
In mammals there are two main types of stem cells – embryonic stem cells (ES cells) and adult stem cells. ES cells are pluripotent and can produce the three primary germ layers ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. Embryonic stem cells are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate into a number of types of cells .
29. Which stem cell can divide and create another cell similar to it?
- Adult stem cell
- Embryonic stem cell
- Both a and b
- None of the above
Explanation
Adult stem cells are found in various tissues of children as well as adults. An adult stem cell or somatic stem cell can divide and create another cell similar to it. Most of the adult stem cells are multipotent and can act as a repair system of the body, replenishing adult tissues. The red bone marrow is a rich source of adult stem cells.
30. ______ is the ability of a single cell to divide and produce all of the differentiated cells in an organism.
- Totipotency
- Pluripotency
- Oligopotency
- None
Explanation
Totipotency (Toti-total) is the ability of a single cell to divide and produce all of the differentiated cells in an organism.
31.____ refers to a stem cell that has the potential to differentiate into any of the three germ layers- ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm.
- Totipotency
- Pluripotency
- Oligopotency
- None
Explanation
Pluripotency (Pluri-several) refers to a stem cell that has the potential to differentiate into any of the three germ layers-ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm.
32. Which refers to the stem cells that can differentiate into various types of cells that are related?
- Totipotency
- Pluripotency
- Oligopotency
- None of the above
Explanation
Multipotency (multi-Many) refers to the stem cells that can differentiate into various types of cells that are related. For example blood stem cells can differentiate into lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils etc.,
33. Lymphoid or myeloid stem cells can differentiate into B and T cells but not RBC are the examples of
- Totipotency
- Pluripotency
- Oligopotency
- None of the above
Explanation
Oligopotency (Oligo-Few) refers to stem cells that can differentiate into few cell types. For example lymphoid or myeloid stem cells can differentiate into B and T cells but not RBC. Unipotency (Uni- Single) refers to the ability of the stem cells to differentiate into only one cell type.
34. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Stem cell banking is the extraction, processing and storage of stem cells, so that they may be used for treatment in the future, when required
- Amniotic cell bank is a facility that stores stem cells derived from amniotic fluid for future use.
- Stem cells are stored in banks specifically for use by the individual from whom such cells have been collected and the banking costs are paid
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Stem cell banking is the extraction, processing and storage of stem cells, so that they may be used for treatment in the future, when required. Amniotic cell bank is a facility that stores stem cells derived from amniotic fluid for future use. Stem cells are stored in banks specifically for use by the individual from whom such cells have been collected and the banking costs are paid. Cord Blood Banking is the extraction of stem cells from the umbilical cord during childbirth. While the umbilical cord and cord blood are the most popular sources of stem cells, the placenta, amniotic sac and amniotic fluid are also rich sources in terms of both quantity and quality.
35. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Early diagnosis of infectious diseases or inherent genetic defects is essential for appropriate treatment
- Early detection of the disease is possible using conventional diagnostic methods like microscopic examinations, serum analysis and urine analysis
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Early diagnosis of infectious diseases or inherent genetic defects is essential for appropriate treatment. Early detection of the disease is not possible using conventional diagnostic methods like microscopic examinations, serum analysis and urine analysis. These laboratory techniques are indirect and not always specific.
36. Which of the following techniques can be used for early diagnosis of diseases?
- R-DNA technology
- ELISA
- PCR
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Scientists are continuously searching for specific, sensitive and simple diagnostic techniques for diagnosis of diseases. Recombinant DNA technology, Polymerase Chain Reactions (PCR) and Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) are some of the techniques that are reliable and help in early diagnosis.
37. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Presence of pathogens like virus, bacteria, etc., is detected only when the pathogen produces symptoms in the patient
- By the time the symptoms appear concentration of pathogen becomes very high in the body
- However very low concentration of a bacteria or a virus, even when the symptoms of the disease does not appear, can be detected by amplification of their nucleic acid.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Presence of pathogens like virus, bacteria, etc., is detected only when the pathogen produces symptoms in the patient. By the time the symptoms appear concentration of pathogen becomes very high in the body. However very low concentration of a bacteria or a virus, even when the symptoms of the disease does not appear, can be detected by amplification of their nucleic acid.
38. Which of the following presence can be detected in ELISA?
- Antigen
- Blood platelets
- Antibody
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
ELISA is a biochemical procedure discovered by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmanin (1971) to detect the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a sample of serum, urine, etc.,
39. Which of the following statement is correct about ELISA is correct?
- It is confirmatory test for HIV
- It is a very important diagnostic tool to determine if a person is HIV positive or negative
- ELISA is a tool for determining serum antibody concentrations
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
ELISA is a very important diagnostic tool to determine if a person is HIV positive or negative. ELISA is a tool for determining serum antibody concentrations (such as the antibodies produced in a person infected by pathogens such as HIV) and also for detecting the presence of specific antigens and hormones such as human chorionic gonadotropins. Western Blot is the confirmatory test for HIV
40. ______ is highly sensitive and can detect antigens in the range of a nanogram
- Western Blot
- ELISA
- PCR
- RT-PCR
Explanation
The intensity of the color is directly proportional to the amount of the antigen. ELISA is highly sensitive and can detect antigens in the range of a nanogram.
41. How many types of ELISA are there?
- 3
- 1
- 4
- 5
Explanation
There are four kinds of ELISA namely, Direct ELISA, Indirect ELISA, sandwich ELISA and competitive ELISA. It is a highly sensitive and specific method used for diagnosis. ELISA possesses the added advantages of not requiring radioisotopes or a radiation counting apparatus.
42. PCR technique was developed by_____
- Larry page
- Kary Mullis
- Eva Engvall
- Peter Perlmanin
Explanation
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an invitro amplification technique used for synthesising multiple identical copies (billions) of DNA of interest. The technique was developed by Kary Mullis (Nobel laureate, 1993) in the year 1983.
43. How many steps are involved in PCR?
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 3
Explanation
Denaturation, renaturation or primer annealing and synthesis or primer extension, are the three steps involved in PCR. The double stranded DNA of interest is denatured to separate into two individual strands by high temperature. This is called denaturation.
44. During denaturation the reaction mixture is heated to___ for a short time to denature the target DNA into single strands
- 900 C
- 950 C
- 800 C
- 850 C
Explanation
During denaturation the reaction mixture is heated to 950 C for a short time to denature the target DNA into single strands that will act as a template for DNA synthesis. Annealing is done by rapid cooling of the mixture, allowing the primers to bind to the sequences on each of the two strands flanking the target DNA.
45. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The PCR technique can also be used for amplifications of RNA in which case it is referred to as reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
- In this process the RNA molecules (mRNA) must be converted to complementary DNA by the enzyme reverse transcriptase
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The PCR technique can also be used for amplifications of RNA in which case it is referred to as reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR). In this process the RNA molecules (mRNA) must be converted to complementary DNA by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. The cDNA then serves as the template for PCR.
46. Which of the following statement is correct?
- PCR technique can also be used in the field of forensic medicine
- A single molecule of DNA from blood stains, hair, semen of an individual is adequate for amplification by PCR.
- PCR is also used in amplification of specific DNA segment to be used in gene therapy
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
PCR technique can also be used in the field of forensic medicine. A single molecule of DNA from blood stains, hair, semen of an individual is adequate for amplification by PCR. The amplified DNA is used to develop DNA fingerprint which is used as an important tool in forensic science. Thus, PCR is very useful for identification of criminals. PCR is also used in amplification of specific DNA segment to be used in gene therapy.
47. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Transgenesis is the process of introduction of extra (foreign/exogenous) DNA into the genome of the animals to create and maintain stable heritable characters
- The foreign DNA that is introduced is called the transgene and the animals that are produced by DNA manipulations are called transgenic animals
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Transgenesis is the process of introduction of extra (foreign/exogenous) DNA into the genome of the animals to create and maintain stable heritable characters. The foreign DNA that is introduced is called the transgene and the animals that are produced by DNA manipulations are called transgenic animals or the genetically engineered or genetically modified organisms.
48. Which of the following are transgenic animals?
- Cow
- Pig
- Fish
- All the above
Explanation
Demonstration of integration and expression of foreign gene in transgenic tissue or animals. Transgenic animals such as mice, rat, rabbit, pig, cow, goat, sheep and fish have been produced.
49. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Transgenesis is a powerful tool to study gene expression and developmental processes in higher organisms.
- Transgenesis helps in the improvement of genetic characters in animals
- Transgenic models exist for many human diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis and sickle cell anemia.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Transgenesis is a powerful tool to study gene expression and developmental processes in higher organisms. Transgenesis helps in the improvement of genetic characters in animals. Transgenic animals serve as good models for understanding human diseases which help in the investigation of new treatments for diseases. Transgenic models exist for many human diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis and sickle cell anemia. Transgenic animals are used to produce proteins which are important for medical and pharmaceutical applications.
50. Transgenesis is important for improving the quality and quantity of_____
- Milk
- Meat
- Egg
- All the above
Explanation
Transgenesis is important for improving the quality and quantity of milk, meat, eggs and wool production in addition to testing drug resistance.
51. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- A biological product is a substance derived from a living organism and used for the prevention or treatment of disease.
- These products include antitoxins, bacterial and viral vaccines, blood products and hormone extracts
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
A biological product is a substance derived from a living organism and used for the prevention or treatment of disease. These products include antitoxins, bacterial and viral vaccines, blood products and hormone extracts. These products may be produced through biotechnology in a living system, such as a microorganism, plant cell or animal cell, and are often more difficult to characterize than small molecule drugs.
52. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Animals are used as bioreactors to produce desirable proteins
- Monoclonal antibodies, which are used to treat cancer, heart disease and transplant rejection are produced by this technology
- Natural protein adhesives are non toxic, biodegradable and rarely trigger an immune response, hence could be used to reattach tendons and tissues, fill cavities in teeth, and repair broken bones
- 1 alone
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Animals are used as bioreactors to produce desirable proteins. Antibodies are substances that react against the disease-causing antigens and these can be produced using transgenic animals as bioreactors. Monoclonal antibodies, which are used to treat cancer, heart disease and transplant rejection are produced by this technology. Natural protein adhesives are non-toxic, biodegradable and rarely trigger an immune response, hence could be used to reattach tendons and tissues, fill cavities in teeth, and repair broken bones.
53. ____ was the first mammal (Sheep) clone developed by Ian Wilmut and Campbell
- Jersey
- Mully
- Dolly
- None
Explanation
Dolly was the first mammal (Sheep) clone developed by Ian Wilmut and Campbell in 1997. Dolly, the transgenic clone was developed by the nuclear transfer technique and the phenomenon of totipotency.
54. Ian Wilmut and Campbell removed___ cells from the udder of an adult sheep
- 200
- 277
- 227
- 727
Explanation
Ian Wilmut and Campbell removed 277 cells from the udder of an adult sheep and fused those cells with 277 unfertilised egg cells from which the nuclear material was removed. After culturing the resulting embryos for 6 days , they implanted 29 embryos into the surrogate mother’s womb and only one Dolly was produced.
55. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Biotechnology has given to the society cheap drugs, better friuts and vegetables, pest resistant crops, indigenious cure to diseases and lot of controversy.
- People fear that these genetic manipulations may lead to unknown consequences.
- The major apprehension of recombinant DNA technology is that unique microorganisms either inadvertently or deliberately for the purpose of war may be developed that could cause epidemics or environmental catastrophies
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Biotechnology has given to the society cheap drugs, better friuts and vegetables, pest resistant crops, indigenious cure to diseases and lot of controversy. This is mainly because the major part of the modern biotechnology deals with genetic manipulations. People fear that these genetic manipulations may lead to unknown consequences. The major apprehension of recombinant DNA technology is that unique microorganisms either inadvertently or deliberately for the purpose of war may be developed that could cause epidemics or environmental catastrophies. Although many are concerned about the possible risk of genetic engineering, the risks are in fact slight and the potential benefits are substantial.
56. In which year human insulin was marketed under the name Humulin?
a) 1986
b) 1972
c) 1960
d) 1956
Explanation
Insulin was the first ever pharmaceutical product of recombinant DNA technology
administered to humans. The approval to use recombinant insulin for diabetes mellitus was given in 1982. In 1986 human insulin was marketed under the trade name Humulin
57. Choose the correct statements,
i) α lactalbumin consists of 25% total protein found in human milk
ii) α lactalbumin binds calcium and zinc ions and possesses bactericidal and anti tumour activities.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
In human milk, α lactalbumin is the most abundant protein comprising 25% of total protein found in human milk. It is synthesized by the mammary glands. α lactalbumin binds calcium and zinc ions and possesses bactericidal and anti tumour activities
58. Interferons are classified based on the _____.
a) Structure
b) Origin
c) Size
d) Chemical reaction
Explanation
Based on the structure of interferons they are classified as α, β and γ interferons. They stimulate the cellular DNA to produce antiviral enzymes which inhibit viral replication and protect the cells.
59. Which of these components are included in the recombinant DNA technology?
a) Protein
b) Peptides
c) RNA
d) Pathogenic organism DNA
Explanation
Recombinant DNA technology is very suited for developing new subunit vaccines. It includes components like proteins, peptides and DNAs of pathogenic organisms. The advantages of these vaccines include their purity in preparation, stability and safe use.
60. Which of these are referred as the attenuated recombinant vaccines?
a) Live vaccines
b) Antibiotics
c) Modified RNA
d) Dead cells
Explanation
Attenuated recombinant vaccines: This includes genetically modified pathogenic organisms (bacteria or viruses) that are made nonpathogenic and are used as vaccines. It is now possible to genetically engineer the organisms (bacteria or viruses) and use them as live vaccines and such vaccines are referred to as attenuated recombinant vaccines.
61. Which of the following are the advantages of using DNA vaccines?
a) Inexpensive
b) Easy production
c) Easy design process
d) All the above
Explanation
The DNA vaccine cannot cause the disease as it contains only copies of a few of its genes. DNA vaccines are relatively easy and inexpensive to design and produce.
62. Which of these is not an advantage of vaccines produced by new techniques?
a) Produce target proteins
b) Trigger immune response
c) Increased toxic effects
d) Long lasting immunity
Explanation
Vaccines produced by these new techniques have definite advantages like producing target proteins, long lasting immunity and trigger immune response only against specific pathogens with less toxic effects.
63. Gene therapy is used as a corrective therapy for _______.
a) Hereditary disease
b) Auto Immune disease
c) Cardio vascular disease
d) All the above
Explanation
If a person is born with a hereditary disease, can a corrective therapy be given for such disease. Yes, this can be done by a process known as gene therapy. This process involves the transfer of a normal gene into a person’s cells that carries one or more mutant alleles. Expression of normal gene in the person results in a functional gene product whose action produces a normal phenotype.
64. Choose the correct statements.
i) Gene augmentation therapy inserts DNA into the genome to replace the missing gene product.
ii) Gene inhibition therapy inserts the anti-sense gene which inhibits the expression of the dominant gene.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Gene augmentation therapy which involves insertion of DNA into the genome to replace the missing gene product. Gene inhibition therapy which involves insertion of the anti-sense gene which inhibits the expression of the dominant gene.
65. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the somatic cell therapy?
a) Genes introduction in bone marrow cells and blood cells.
b) Therapeutic genes are transferred into somatic cells.
c) Not heritable in later generations.
d) Genes are introduced in eggs and sperms.
Explanation
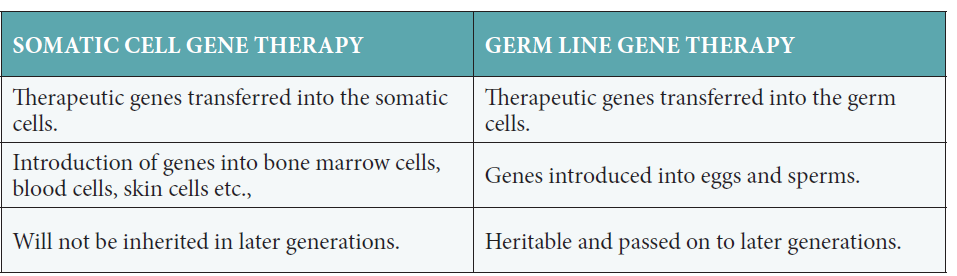
66. Which of the process is not involved in the gene therapy?
a) Isolating specific gene
b) Making copies of the isolated gene
c) Deletion of unwanted copies of genes
d) Inserting the gene copies into target cells
Explanation
Gene therapy involves isolation of a specific gene and making its copies and inserting them into target cells to make the desired proteins. It is absolutely essential for gene therapists to ensure that the gene is harmless to the patient and it is appropriately expressed and that the body’s immune system does not react to the foreign proteins produced by the new genes.
67. Choose the correct statements.
i) Stem cells are undifferentiated cells found in most of the multi cellular animals.
ii) Stem cells maintain their undifferentiated state even after undergoing numerous mitotic divisions.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells found in most of the multi cellular animals. These cells maintain their undifferentiated state even after undergoing numerous mitotic divisions.
68. Which of the following statements are not true regarding the stem cell?
a) Potential revolutionary to the future of medicine.
b) May cause mild damage to the immunity system.
c) Ability to regenerate damaged and diseased organs.
d) Stem cells can differentiate into all types of cells derived from any of the three germ layers.
Explanation
Stem cell research has the potential to revolutionize the future of medicine with the ability to regenerate damaged and diseased organs. Stem cells are capable of self-renewal and exhibit ‘cellular potency’. Stem cells can differentiate into all types of cells that are derived from any of the three germ layers ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm.
69. What is the rich source of adult stem cells?
a) Pituitary gland
b) Hypothalamus
c) Red bone marrow
d) Spleen
Explanation
The red bone marrow is a rich source of adult stem cells.
70. Identify the incorrect Match
A. Multipotency i) Differentiate various types of related cells
B. Pluripotency ii) Three germ layers
C. Totipotency iii) lymphoid / myeloid stem
D. Unipotency iv) Differentiate into only one cell type
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) iv only
Explanation
Totipotency (Toti-total) is the ability of a single cell to divide and produce all of the differentiated cells in an organism. Pluripotency (Pluri-several) refers to a stem cell that has the potential to differentiate into any of the three germ layers-ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm. Multipotency (multi-Many) refers to the stem cells that can differentiate into various types of cells that are related. For example blood stem cells can differentiate into lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils etc., Oligopotency (Oligo-Few) refers to stem cells that can differentiate into few cell types. For example lymphoid or myeloid stem cells can differentiate into B and T cells but not RBC. Unipotency (Uni- Single) refers to the ability of the stem cells to differentiate into only one cell type.
71. What are the sources of stem cells both in quantity and quality?
a) Placenta
b) Amniotic sac
c) Cord blood
d) All the above
Explanation
Cord Blood Banking is the extraction of stem cells from the umbilical cord during childbirth. While the umbilical cord and cord blood are the most popular sources of stem cells, the placenta, amniotic sac and amniotic fluid are also rich sources in terms of both quantity and quality.
72. Which of the following is not a type of ELISA test?
a) Direct ELISA
b) Derived ELISA
c) Indirect ELISA
d) Sandwich ELISA
Explanation
There are four kinds of ELISA namely, Direct ELISA, Indirect ELISA, sandwich ELISA and competitive ELISA. It is a highly sensitive and specific method used for diagnosis. ELISA possesses the added advantages of not requiring radioisotopes or a radiation counting apparatus.
73. Which of the following separates the double stranded DNA in denaturation?
a) High temperature
b) Low pressure
c) Acidic compounds
d) Natural proteins
Explanation
The double stranded DNA of interest is denatured to separate into two individual strands by high temperature . This is called denaturation
74. The sensitivity and specificity of PCR is useful to diagnose,
a) Inherited disorders only
b) Viral disease only
c) Bacterial diseases only
d) All the above
Explanation
The specificity and sensitivity of PCR is useful for the diagnosis of inherited disorders (genetic diseases), viral diseases, bacterial diseases.
75. Which of this disease does not use transgenic model as a good model?
a) Alzheimer’s
b) Lung cancer
c) Rheumatoid arthritis
d) Sickle cell anemia
Explanation
Transgenic animals serve as good models for understanding human diseases which help in the investigation of new treatments for diseases. Transgenic models exist for many human diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis and sickle cell anemia.
76. What are the usages of natural protein?
a) Repair broken bones
b) Fill cavities in teeth
c) Reattach tendons and tissues
d) All the above
Explanation
Natural protein adhesives are non-toxic, biodegradable and rarely trigger an immune response, hence could be used to reattach tendons and tissues, fill cavities in teeth, and repair broken bones.
77. By which of this technique Dolly, the transgenic clone was developed?
a) Totipotency
b) Oligopotency
c) Multipotency
d) Unipotency
Explanation
Dolly, the transgenic clone was developed by the nuclear transfer technique and the phenomenon of totipotency. Totipotency refers to the potential of a cell to develop different cells, tissues, organs and finally an organism.
78. What is the term used for organism carries inoperative genes by genetical engineering?
a) Gene knock out
b) Mutant genes
c) Null gene
d) Modified gene
Explanation
A gene ‘knock out’ is a genetically engineered organism that carries one or more genes in its chromosomes that have been made inoperative.
79. In which year the Indian government released the recombinant DNA safety guidelines?
a) 1982
b) 1967
c) 1990
d) 2011
Explanation
The biotechnology industry is governed by different enactments depending on theirrelevance and applicability on a case to case basis. “Recombinant DNA safety guidelines, 1990” were released by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) which covers areas of research involving genetically engineered organisms and these guidelines were further revised in 1994.
80. Define Biopiracy.
a) Use of bio resources without proper authorization from the countries and the people concerned.
b) Study of the ethical issues emerging from the advances in Biology and medicine.
c) Evaluating the risk factors of the technology used.
d) Analyzing and collecting the negative effects of the advancements.
Explanation
Biopiracy can be defined as “the use of bio resources by multinational companies and other organizations without proper authorization from the countries and the people concerned without compensatory payment”.
81. Which of the following is not an agricultural risk of GMO?
a) Big companies hold the legal rights for GM seeds.
b) Pesticide and herbicides are the major problems of GMO
c) Transferred genes can mutate and cause risks.
d) Pest toxins of GMO can increase the evolution of resistance of pest populations.
Explanation
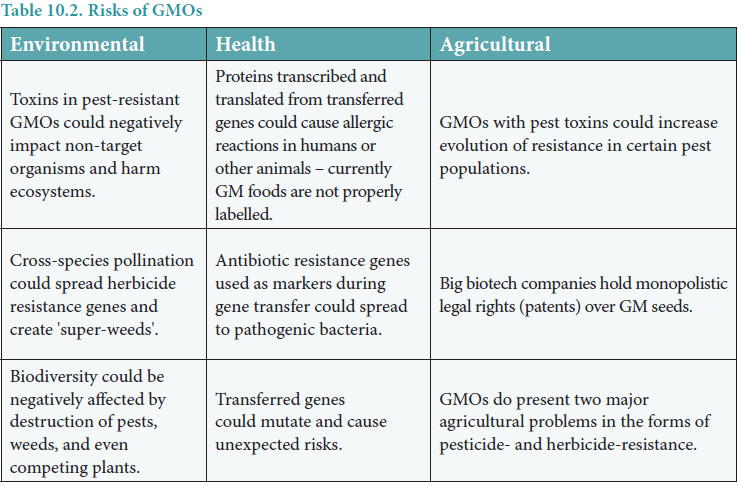
82. In which year the WHO built an informal group for biosafety?
a) 1991
b) 1972
c) 2001
d) 1956
Explanation
Due to the growing concerns arising from Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) throughout the globe the WHO has built an informal working group on biosafety in 1991.
83. Which of the following condition is not needed for patenting?
a) Invention must be novel and useful.
b) Product must be inventive and reproducible.
c) May be used for further research works.
d) Must provide the full description of the invention.
Explanation
The following criteria must be satisfied for patenting: The invention must be novel and useful. The product must be inventive and reproducible. The patent application should provide the full description of the invention and the invention must be patentable
84. Who patented the first genetically engineered living organism?
a) Sir C.V. Raman
b) Mohan Chakrabarty
c) Jagadish Chandra Bose
d) Nallakannu
Explanation
The first living organism that was patented was a genetically engineered species of bacteria – Pseudomonas putida in 1980 which was genetically engineered by Ananda Mohan Chakrabarty in 1971.
85. In which year the developed countries framed GATT?
a) 1948
b) 1970
c) 1929
d) 1901
Explanation
General agreement of tariffs and trade (GATT) and trade related IPRs (TRIPs) : GATT was framed in 1948 by developed countries to settle dispute, among the countries regarding share of world trade. The benefits of GATT were enjoyed only by developed countries. In 1988 US congress enacted a law ‘the omnibus trade and competitiveness act’ (OTCA) which gave powers to US to investigate the laws related to trade.
86. What was the first GI tagged product in India?
a) Thanjavur painting
b) Kerala coconut
c) Darjeeling tea
d) Mysore silk
Explanation
Darjeeling tea was the first GI tagged product in India in 2004-05. In Tamilnadu, Kancheepuram silk, Coimbatore wet grinder, Thanjavur paintings, Madurai Malli, Tirunelveli Halwa and Temple jewellery of Nagercoil are GI tagged.
87. Which of the following is subjected to copyright in the field of biotechnology?
a) Database of DNA sequence
b) Name of the research associate
c) Technology used
d) All the above
Explanation
In the field of biotechnology the data base of DNA sequences or any published forms, Photomicrographs are subject to copyright
12th Science Lesson 5 Questions in English
5] Atomic and Nuclear Physics
1. In which of these languages atom means as indivisible?
a) Greek
b) Latin
c) Rome
d) Persian
Explanation
The word atom in Greek means without division or indivisible.
2. Which of this scientist compared the sizes of atom, apple and earth?
a) J.J. Thomson
b) Albert Einstein
c) Richard P.Feynman
d) Neil’s Bohr
Explanation
An American Physicist Richard P. Feynman said that if the atom becomes the size of an apple, then the apple becomes the size of the earth.
3. Which of the following atom models explained the unsolved issues?
a) J.J. Thomson model
b) Bohr model
c) Rutherford model
d) All the above
Explanation
The Bohr atom model is more successful than J. J. Thomson and Rutherford atom models. It explained many unsolved issues in those days and also gave better understanding of chemistry.
4. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Scientist believed that atom is the fundamental entity for all the matters.
ii) Nucleus is made of proton and neutron.
iii) Quarks are the fundamental entities for the proton and neutron.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Later, scientists observed that even the atom is not the fundamental entity. It consists of electrons and nucleus. Around 1930, scientists discovered that nucleus is also made of proton and neutron. Further research discovered that even the proton and neutron are made up of fundamental entities known as quarks.
5. Assertion (A): Gases can conduct electricity only under special arrangements.
Reasoning(R): At normal atmospheric pressure gases don’t have free electrons for conduction.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Gases at normal atmospheric pressure are poor conductors of electricity because they do not have free electrons for conduction. But by special arrangement, one can make a gas to conduct electricity.
6. Which of the following statements are not true regarding the cathode rays?
a) Cathode rays possess energy and momentum.
b) Cathode ray travels in a straight line with speed 107 ms-1.
c) Cathode rays can be deflected by applying magnetic field only.
d) The deflected direction of cathode rays indicates the charge of the particles.
Explanation
Cathode rays possess energy and momentum and travel in a straight line with high speed of the order of 107m s -1. It can be deflected by application of electric and magnetic fields. The direction of deflection indicates that they are negatively charged particles.
7. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Cathode rays produce heat when they are allowed to fall on matter.
ii) Cathode rays do not affect the photographic plates.
iii) Cathode rays produce fluorescence on certain crystals and minerals.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
When the cathode rays are allowed to fall on matter, they produce heat. They affect the photographic plates and also produce fluorescence when they fall on certain crystals and minerals.
8. In which of these materials cathode rays fall to produce x-rays?
a) High atomic weight
b) Low density
c) High energy value
d) Vacuum space
Explanation
When the cathode rays fall on a material of high atomic weight, x-rays are produced.
9. What is the speed of cathode ray in terms of speed of light?
a) 1/2
b) 1/3rd
c) 2/3rd
d) 1/10th
Explanation
The speed of cathode rays is up to 1/ 10th of the speed of light.
10. Which of these values of cathode ray is measured by varying the electric and magnetic field?
a) Charge per unit mass
b) Specific charge
c) Normalized charge
d) All the above
Explanation
Thomson’s experiment is considered as one among the landmark experiments for the birth of modern physics. In 1887, J. J. Thomson made remarkable improvement in the scope of study of gases in discharge tubes. In the presence of electric and magnetic fields, the cathode rays are deflected. By the variation of electric and magnetic fields mass normalized charge or the specific charge (charge per unit mass) of the cathode rays is measured.
11. Which of these forces does not act on an oil droplet?
a) Gravitational force
b) Magnetic force
c) Buoyant force
d) Viscous force
Explanation
Let m be the mass of the oil drop and q be its charge. Then the forces acting on the droplet are gravitational force, electric force, buoyant force, viscous force.
12. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) J.J.Thomson atom model was based on static distribution of electric charges.
ii) Rutherford proposed the first dynamic model of an atom.
iii) Thomson and Rutherford models explained the stability of the atom.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
J. J. Thomson proposed a theoretical atom model which is based on static distribution of electric charges. Since this model fails to explain the stability of atom, one of his students E. Rutherford proposed the first dynamic model of an atom. Rutherford gave atom model which is based on results of an experiment done by his students (Geiger and Marsden). But this model also failed to explain the stability of the atom.
13. Which of this atomic model was proposed by Neil’s Bohr?
a) Hydrogen atom
b) Oxygen atom
c) Carbon atom
d) Nitrogen atom
Explanation
Neil’s Bohr who is also a student of Rutherford proposed an atomic model for hydrogen atom which is more successful than other two models. Neil’s Bohr atom model could explain the stability of the atom and also the origin of line spectrum.
14. Which of this explains that no stable equilibrium points in electrostatic configuration?
a) Einstein’s theorem
b) J.J.Thomson Atomic model
c) Earnshaw’s theorem
d) Neil’s Bohr Atomic model
Explanation
The atoms are electrically neutral; this implies that the total positive charge in an atom is equal to the total negative charge. According to the Neil’s model, all the charges are assumed to be at rest. But from classical electrodynamics, no stable equilibrium points exist in electrostatic configuration (this is known as Earnshaw’s theorem) and hence such an atom cannot be stable. Further, it fails to explain the origin of spectral lines observed in the spectrum of hydrogen atom and other atoms.
15. Who conducted the scattering of alpha particles by gold foil experiment?
a) Geiger and Marsden
b) J.J.Thomson
c) Neil’s Bohr
d) Earnshaw
Explanation
In 1911, Geiger and Marsden did a remarkable experiment based on the advice of their teacher Rutherford, which is known as scattering of alpha particles by gold foil.
16. What is the size of nucleus according to Rutherford?
a) 102m
b) 1012m
c) 10-14m
d) 10-5m
Explanation
Rutherford proposed that an atom has a lot of empty space and contains a tiny matter known as nucleus whose size is of the order of 10 -14m.
17. Choose the correct statements about Nucleus.
i) Most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in electrons.
ii) Nucleus is surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
iii) Electrons are at rest position around the nucleus.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The nucleus is positively charged and most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in nucleus. The nucleus is surrounded by negatively charged electrons. Since static charge distribution cannot be in a stable equilibrium, he suggested that the electrons are not at rest and they revolve around the nucleus in circular orbits like planets revolving around the sun.
18. What is the minimum distance between the nucleus center and the reflected alpha particle?
a) Contact distance
b) Minimum distance
c) Saturated point
d) Excited state
Explanation
The minimum distance between the center of the nucleus and the alpha particle just before it gets reflected back through 180° is defined as the distance of closest approach r0 (also known as contact distance).
19. What is the range of nucleus radius calculated by Rutherford?
a) 10-11 m to 10-15m
b) 10-14 m to 10-15m
c) 10-1 m to 10-9m
d) 10-8m to 10-15m
Explanation
Rutherford calculated the radius of the nucleus for different nuclei and found that it ranges from 10-14 m to 10-15m.
20. In which of these conditions the impact parameter is defined?
a) At equilibrium
b) At a large distance
c) Inside a vacuum space
d) At rest
Explanation
The impact parameter is defined as the perpendicular distance between the center of the gold nucleus and the direction of velocity vector of alpha particle when it is at a large distance.
21. Which of these values is decreased with increase in the impact parameter value?
a) Scattering angle
b) Radius of nucleus
c) Number of electrons
d) All the above
Explanation
When impact parameter increases the scattering angle decreases. Smaller the impact parameter, larger will be the deflection of alpha particles.
22. Which of these values were found by the Rutherford model?
a) Size of the atom
b) Stability of atom
c) Number of protons
d) None of the above
Explanation
Rutherford atom model helps in the calculation of the diameter of the nucleus and also the size of the atom.
23. What are the drawbacks of the Rutherford model?
a) Distribution of electrons around nucleus
b) Stability of the atom
c) Mass of the nucleus
d) Both a and b
Explanation
The Rutherford model fails to explain the distribution of electrons around the nucleus and also the stability of the atom.
24. Choose the correct statements.
i) According to electrodynamics theory accelerated charge emits electromagnetic radiations.
ii) The radius of orbit becomes smaller when the charge loses its energy.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
According to classical electrodynamics any accelerated charge emits electromagnetic radiations. Due to emission of radiations, it loses its energy. Hence, it can no longer sustain the circular motion. The radius of the orbit, therefore, becomes smaller and smaller (undergoes spiral motion) and finally the electron should fall into the nucleus and the atoms should disintegrate. But this does not happen.
25. What is the pattern of radiation emission according to the electrodynamics model?
a) Discrete
b) Continuous
c) Pulse
d) Hyperbola
Explanation
According to the electrodynamics model, emission of radiation must be continuous and must give continuous emission spectrum but experimentally we observe only line (discrete) emission spectrum for atoms.
26. Who was the first to give the theoretical model of the atom structure?
a) Neil’s Bohr
b) Rutherford
c) Marsden
d) J.J.Thomson
Explanation
In order to overcome the limitations of the Rutherford atom model in explaining the stability and also the line spectrum observed for a hydrogen atom, Neil’s Bohr made modifications of Rutherford atom model. He is the first person to give better theoretical model of the structure of an atom to explain the line spectrum of hydrogen atom.
27. Which of the following is not a postulate of Bohr atom model?
a) Electron moves around the nucleus in circular orbits in an atom.
b) The Coulomb force gives the centripetal force for the circular motion of electron.
c) Electrons revolve around the nucleus in all the orbits.
d) The discrete orbits do not radiate electromagnetic energy are stable orbits.
Explanation
Postulates of Bohr atom model: The electron in an atom moves around nucleus in circular orbits under the influence of Coulomb electrostatic force of attraction. This Coulomb force gives necessary centripetal force for the electron to undergo circular motion. Electrons in an atom revolve around the nucleus only in certain discrete orbits called stationary orbits where it does not radiate electromagnetic energy. Only those discrete orbits allowed are stable orbits.
28. Which is known as the angular momentum quantization condition?
a) h/2π
b) 2πh
c) 2♄
d) 2πr
Explanation
The angular momentum of the electron in these stationary orbits are quantized that is, it can be written as integer or integral multiples of h/ 2π called as reduced Planck’s constant that is the integer n is called as principal quantum number of the orbit. l =n♄ where ♄= h /2π this condition is known as angular momentum quantization condition.
29. Which is known as the de Broglie wavelength?
a) ♄
b) υ
c) λ
d) ϭ
Explanation
The de Broglie wavelength (λ) for an electron of mass m moving with velocity υ is λ=h/m υ where h is called Planck’s constant.
30. What is the energy value of the photon in the quantization of energy?
a) E
b) ΔE
c) πr
d) E/ 2πr
Explanation
Energy of orbits is not continuous but discrete. This is called the quantization of energy. An electron can jump from one orbit to another orbit by absorbing or emitting a photon whose energy is equal to the difference in energy (ΔE) between the two orbital levels.
31. In which of this state the velocity of electron is maximum?
a) Ground state
b) Excited state
c) Both a and b
d) Neither a nor b
Explanation
The velocity of electron decreases as the principal quantum number increases. This curve is the rectangular hyperbola. This implies that the velocity of electron in ground state is maximum when compared to excited states.
32. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The atomic mass of deuterium is thrice as the atomic mass of hydrogen atom.
ii) Bohr atomic model does not explain the isotopic shift.
iii) The Bohr atomic model considers the nuclear movement for calculating the wave length between hydrogen and deuterium.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
On calculating wavelength or wave number difference between the faint and bright spectral lines, atomic mass of deuterium is measured to be twice that of atomic mass of hydrogen atom. Bohr atom model could not explain this isotopic shift. Thus by considering nuclear motion (although the movement of the nucleus is much smaller, it is observed) into account in the Bohr atom model, the wave number or wavelength difference between hydrogen atom and deuterium is theoretically calculated which perfectly agreed with the spectroscopic measured values.
33. What is the difference between the hydrogen and deuterium atom?
a) Number of proton
b) Number of neutron
c) Number of electron
d) All the above
Explanation
The difference between hydrogen atom and deuterium is in the number of neutron. Hydrogen atom contains an electron and a proton, whereas deuterium has an electron, a proton and a neutron.
34. Assertion (A): Excitation energy is used to excite an electron from lower energy state to higher energy.
Reasoning(R): The first excitation energy excites an electron from first excited state to the ground state.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The energy required to excite an electron from lower energy state to any higher energy state is known as excitation energy. The excitation energy for an electron from ground state (n = 1) to first excited state (n = 2) is called first excitation energy.
35. What is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from an atom?
a) Binding energy
b) Electrostatic energy
c) Frictional energy
d) Magnetic energy
Explanation
The minimum energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the ground state is known as binding energy or ionization energy.
36. What is the ionization potential for a hydrogen atom?
a) 13.6 / n2 volt
b) 13 n volt
c) 13.6 volt
d) n2 volt
Explanation
Ionization potential is defined as ionization energy per unit charge.

Thus, for a hydrogen atom (Z =1), the ionization potential is V = 13.6/ n2volt.
37. Define the spectrum of the electromagnetic radiations from any heated materials?
a) Pulse spectrum
b) Continuous spectrum
c) Discrete spectrum
d) None of the above
Explanation
Materials in the solid, liquid and gaseous states emit electromagnetic radiations when they are heated up and these emitted radiations usually belong to continuous spectrum. For example, when white light is examined through a spectrometer, electromagnetic radiations of all wavelengths are observed which is a continuous spectrum.
38. By which of these emission electrons jump back to the ground state?
a) Spontaneous emission
b) Continuous emission
c) Long-term emission
d) Discrete emission
Explanation
Electrons in excited states have very small life time, these electrons jump back to ground state through spontaneous emission in a short duration of time (approximately 10 -8 s) by emitting the radiation with same wavelength (or frequency) corresponding to the colors it absorbed. This is called emission spectroscopy.
39. What is the value of the Rydberg constant?
a) 2.0945 x 10-7 m-1
b) 1.548 x 10 8 m-2
c) 1.09737 x 107 m-1
d) 10.737 x 10-8 m
Explanation
R is known as Rydberg constant whose value is 1.09737 x 107m-1 where m and n are positive integers such that m > n.
40. In which of the regions the Lyman series lies?
a) Ultra violet region
b) Infra-red region
c) Visible region
d) Far Infra-red region
Explanation

Lyman series: Put n = 1 and m = 2, 3, 4……. in the above equation. The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Lyman series which lies in ultra-violet region is v R m.
41. Which of these series have the value of n as 2?
a) Lyman series
b) Paschen series
c) Balmer series
d) Brackett series
Explanation

Balmer series: Put n = 2 and m = 3, 4, 5……. in the above equation. The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Balmer series which lies in visible region is v R m
42. Which of the following is not a limitation of the Bohr atomic model?
a) Bohr model is suitable for Hydrogen and some complex atoms.
b) The fine structure of hydrogen spectrum is not explained by the Bohr model.
c) Bohr atom model fails to explain the intensity variations in the spectral lines.
d) The electron distribution is not completely explained by Bohr atom model.
Explanation
The following are the drawbacks of Bohr atom model: Bohr atom model is valid only for hydrogen atom or hydrogen like-atoms but not for complex atoms. When the spectral lines are closely examined, individual lines of hydrogen spectrum is accompanied by a number of faint lines. These are often called fine structure. This is not explained by Bohr atom model. Bohr atom model fails to explain the intensity variations in the spectral lines. The distribution of electrons in atoms is not completely explained by Bohr atom model.
43. Choose the correct statements.
i) Atoms have a nucleus surrounded by electrons.
ii) The number of protons and electrons are equal.
iii) Neutrons are electrically neutral and protons have positive charge.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Atoms have a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. The neutrons are electrically neutral (q = 0) and the protons have positive charge (q = + e) equal in magnitude of the charge of the electron (q = –e).
44. What is the value of the mass number if the number of neutrons is N and atomic number is Z?
a) Z + N
b) Z * N
c) Z – N
d) Z / N
Explanation
The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number and it is denoted by Z. The number of neutrons in the nucleus is called neutron number (N). The total number
of neutrons and protons in the nucleus is called the mass number and it is denoted by A. Hence, A = Z+N.
45. Which of these are collectively called as nucleons?
a) Electrons and Neutrons
b) Protons and Nucleus
c) Neutrons and Protons
d) Protons and Electrons
Explanation
The two constituents of nucleus namely neutrons and protons, are collectively called nucleons.
46. Choose the correct statements.
i) The mass of a proton is greater than the mass of the electron.
ii) Mass of a neutron is slightly lesser than the mass of the proton.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The mass of a proton is 1.6726×10-27kg which is roughly 1836 times the mass of the electron. The mass of a neutron is slightly greater than the mass of the proton and it is equal to 1.6749×10-27 kg.
47. What does X represents in the notation Z A X?
a) Multiply
b) Mass number
c) Number of protons
d) Chemical symbol of the element
Explanation
To specify the nucleus of any element, we use the following general notation Z AX where X is the chemical symbol of the element, A is the mass number and Z is the atomic number.
48. Choose the incorrect statement about the atoms.
i) Nucleus contains positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons.
ii) The overall charge of the nucleus is positive.
iii) The number of electrons in the atom is equal to the number of nucleus.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The nucleus is made up of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons, the overall charge of the nucleus are positive and it has the value of +Ze. But the atom is electrically neutral which implies that the number of electrons in the atom is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus.
49. Define isotope.
a) Same number of electrons and different number of protons.
b) Equal number of neutrons and electrons.
c) Same atomic number and different mass number.
d) Different number of protons and atomic number.
Explanation
In nature, there are atoms of a particular element whose nuclei have same number of protons but different number of neutrons. These kinds of atoms are called isotopes. In other words, isotopes are atoms of the same element having same atomic number Z, but different mass number A.
50. Which of these used to determine the chemical properties of any atom?
a) Atomic number
b) Electrons
c) Nucleus structure
d) Number of protons
Explanation
The chemical properties of any atom are determined only by electrons, the isotopes of any element have same electronic structure and same chemical properties. So the isotopes of the same element are placed in the same location in the periodic table.
51. Isobars are the atoms of different elements having same ____ and different ______.
a) Mass number, Atomic number
b) Number of protons, Mass number
c) Atomic number, Number of electrons
d) Number of neutrons, Number of protons
Explanation
Isobars are the atoms of different elements having the same mass number A, but different atomic number Z. In other words, isobars are the atoms of different chemical element which has same number of nucleon.
52. Assertion (A): Isobars are chemically different elements.
Reasoning(R): Isobars have same chemical property and different physical property.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Unlike isotopes, isobars are chemically different elements. They have different physical and chemical properties.
53. Which of the value is same for various isotone elements?
a) Number of neutrons
b) Number of protons
c) Number of Atomic number
d) Number of electrons
Explanation
Isotones are the atoms of different elements having same number of neutrons. 512B and 613C are examples of isotones which 7 neutrons.
54. Assertion (A): Atomic Mass unit is used to represent the mass of nuclei.
Reasoning(R): The mass of nuclei is very small which is about 10-25 kg or less.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The mass of nuclei is very small when it expressed in SI units (about 10-25 kg or less). Therefore, it is more convenient to express it in terms of another unit namely, the atomic mass unit (u).
55. Which is the most abundant natural isotope of carbon?
a) 612C
b) 10 20C
c) 2 8C
d) 4 10C
Explanation
One atomic mass unit (u) is defined as the 1/12th of the mass of the isotope of carbon 6 12C the most abundant naturally occurring isotope of carbon.
56. Which of this instrument determines the atomic mass experimentally?
a) Bainbridge Mass Spectrometer
b) Electron Microscope
c) Emission spectroscopy
d) Aneroid barometer
Explanation
Experimentally the atomic mass is determined by the instrument called Bainbridge mass spectrometer. If we determine the atomic mass of the element without considering the effect of its isotopes, we get the mass averaged over different isotopes weighted by their abundances.
57. What is the approximate shape of nuclei?
a) Spherical
b) Parabola
c) Hemisphere
d) Hyperbola
Explanation
The nuclei are found to be approximately spherical in shape. It is experimentally found that radius of nuclei for Z > 10, satisfies the following empirical formula R = Ro A1/3
58. Which of this value is independent of the nuclear density?
a) Mass Number
b) Atomic Number
c) Atomic Mass
d) All the above
Explanation
The empirical formula R = Ro A1/3shows that the nuclear density is independent of the mass number A.
59. Choose the correct statements.
i) Above Z> 100 all the nuclei have same density and it is an important characteristic.
ii) The mass of any nuclei is always less than the sum of the mass of its individual constituents.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
In other words, all the nuclei (Z > 10) have the same density and it is an important characteristic of the nuclei. It is experimentally found out that the mass of any nucleus is always less than the sum of the mass of its individual constituents.
60. What is the difference between the total mass value and the individual constituents mass?
a) Mass defect
b) Mass number
c) Atomic Mass
d) Nucleus Mass number
Explanation
The experimental mass of carbon-12 nucleus is less than the total mass of its individual constituents by Δm = 0.09888 u . This difference in mass Δm is called mass defect. In general, if M, mp, and mn are mass of the nucleus ( A ZX ), the mass of a proton and the mass of a neutron respectively, then the mass defect is given by
![]()
61. According to Einstein theory which of this value is converted to energy and vice versa?
a) Mass
b) Intensity
c) Temperature
d) Mole
Explanation
Albert Einstein with the help of famous mass-energy relation (E = mc ) 2 . According to this relation, the mass can be converted into energy and energy can be converted into mass.
62. Choose the correct statements.
i) Binding energy is released by the mass defect when protons and neutrons combine to form the nucleus.
ii) To separate the nucleus into individual constituents we must supply energy greater than the binding energy of the nucleus.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
In the case of the carbon-12 nucleus when 6 protons and 6 neutrons combine to form carbon-12 nucleus, mass equal to mass defect disappears and the corresponding energy is released. This is called the binding energy of the nucleus (BE) and is equal to (Δm)c2 . In fact, to separate the carbon-12 nucleus into individual constituents, we must supply the energy equal to binding energy of the nucleus.
63. In which of these units the atomic mass unit is expressed?
a) MeV
b) J/s
c) J
d) Both a and c
Explanation
Using Einstein’s mass-energy equivalence, the energy equivalent of one atomic mass unit 1υ = 1.66 * 10-27 x (3x 108)2 = 14.94x 10-11 J ≏931 Me V
64. Which energy is required to separate single nucleon from the nucleus?
a) Average Binding energy
b) Mass defect
c) Atomic Mass
d) Average Mass value
Explanation
The average binding energy per nucleon is the energy required to separate single nucleon from the particular nucleus.
65. Assertion (A): The strong nuclear is the attractive force holds the nucleus together.
Reasoning(R): A strong attractive force is needed to overcome the repulsive Coulomb’s force between protons.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
There must be a strong attractive force between protons to overcome the repulsive Coulomb’s force. This attractive force which holds the nucleus together is called strong nuclear force.
66. Which of these is not a property of strong nucleus force?
a) The short range of nucleus force acts up to a few Fermi distance.
b) Strong nuclear force acts on the electrons to alter the chemical properties of atom.
c) Coulomb forces are weaker than the strong nuclear force.
d) Strong nucleus forces are repulsive and acts with unequal strength between the constituents.
Explanation
A few properties of strong nuclear force are: The strong nuclear force is of very short range, acting only up to a distance of a few Fermi. But inside the nucleus, the repulsive Coulomb force or attractive gravitational forces between two protons are much weaker than the strong nuclear force between two protons. Similarly, the gravitational force between two neutrons is also much weaker than strong nuclear force between the neutrons. So nuclear force is the strongest force in nature. The strong nuclear force is attractive and acts with an equal strength between proton-proton, proton-neutron, and neutron – neutron. Strong nuclear force does not act on the electrons. So it does not alter the chemical properties of the atom.
67. Above which of the atomic number value the elements have a unstable nuclei?
a) 82
b) 42
c) 70
d) 25
Explanation
In the binding energy curve, the stability of the nucleus that has Z > 82 starts to decrease and these nuclei are called unstable nuclei. Some of the unstable nuclei decay naturally by emitting some kind of particles to form a stable nucleus.
68. Which of these particles are emitted by radioactive nuclei?
a) α-decay
b) β-decay
c) γ -decay
d) All the above
Explanation
The elements of atomic number Z > 82 and isotopes of lighter nuclei belong to naturally-occurring radioactive nuclei. Each of these radioactive nuclei decays to another nucleus by the emission of 2 4He nucleus (α-decay) or electron or positron (β-decay) or gamma rays ( γ -decay).
69. Which of these are called as radio isotopes?
a) Isotopes of lighter elements
b) Isotopes of heavy elements
c) All isotopes
d) Both a and b
Explanation
Emission of highly penetrating radiations such as α, β and γ rays by an element is called radioactivity and the substances which emit these radiations are called radioactive elements. These radioactive elements can be heavy elements (Z > 82), isotopes of lighter and heavy elements and these isotopes are called radioisotopes.
70. Choose the correct statements.
i) After the decaying of the radioactive materials the mass of the nuclei is reduced.
ii) According to Einstein’s relation the mass difference between the initial and final nuclei is greater than zero, it appears as the energy.
iii) Radioisotopes have various applications like carbon dating and cancer treatment.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Radioisotopes have a variety of applications such as carbon dating, cancer treatment, etc. When radioactive nucleus undergoes decay, the mass of the system decreases – that is, the mass of the initial nucleus before decay is always greater than the sum of the mass of the final nucleus and that of the emitted particle. When this difference in mass Δm < 0 , it appears as the energy according to Einstein’s relation E = Δm c2 .
71. Who discovered the radioactivity phenomenon in 1896?
a) Henri Becquerel
b) Albert Einstein
c) Marie Curie
d) J.J. Thomson
Explanation
The phenomenon of radioactivity was first discovered by Henri Becquerel in 1896. Later, Marie Curie and her husband Pierre Curie did a series of experiments in detail to understand the phenomenon of radioactivity.
72. In which of this place the Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics is situated?
a) Bangalore
b) New Delhi
c) Kolkata
d) Patna
Explanation
In India, Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics (SINP), Kolkata is the premier institute pursuing active research in nuclear physics.
73. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The radioactive nucleus emits both electron and positron.
ii) The positron is an anti-particle of an electron with same mass and opposite charge.
iii) Positron and electron are referred as beta particles.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
In beta decay, a radioactive nucleus emits either electron or positron. If electron (e–) is emitted, it is called β- decay and if positron (e+) is emitted, it is called β+ decay. The positron is an anti-particle of an electron whose mass is same as that of electron and charge is opposite to that of electron – that is, +e. Both positron and electron are referred to as beta particles.
74. Which of this decay is used in the smoke detectors?
a) Alpha decay
b) Gamma decay
c) Beta decay
d) All the above
Explanation
A very interesting application of alpha decay is in smoke detectors which prevent us from any hazardous fire.
75. What is the purpose of the third particle proposed by W.Pauli?
a) To control the amount of decay
b) To neutralize charge differences
c) Carry away the missing charge and momentum
d) Compensate the mass difference of the nucleus.
Explanation
After a detailed theoretical and experimental study, in 1931 W.Pauli proposed a third particle which must be present in beta decay to carry away missing energy and momentum.
76. Who named the third particle as neutrino?
a) Fermi
b) Bohr
c) Einstein
d) Pauli
Explanation
Fermi later named this particle the neutrino (little neutral one) since it has no charge, have very little mass.
77. Who was awarded Nobel Prize for the experiment discovery of neutrino?
a) W. Pauli
b) Henry Becquerel
c) Fredrick Reines
d) Neil’s Bohr
Explanation
For many years, the neutrino (symbol ν, Greek nu) was hypothetical and could not be verified experimentally. Finally, the neutrino was detected experimentally in 1956 by Fredrick Reines and Clyde Cowan. Later Reines received Nobel Prize in physics in the year 1995 for his discovery.
78. Which of the following is not a property of a neutrino?
a) Tiny mass
b) Negative charge
c) Weak interaction with matter
d) Anti-neutrino is the antiparticle of neutrino
Explanation
The neutrino has the following properties· It has zero charge,· It has an antiparticle called anti-neutrino,· Recent experiments showed that the neutrino has very tiny mass, · It interacts very weakly with the matter. Therefore, it is very difficult to detect. In fact, in every second, trillions of neutrinos coming from the sun are passing through our body without any interaction.
79. What is the life time of the excited state of the daughter nucleus of α and β decay?
a) 10-11s
b) 1015s
c) 10-9s
d) 105s
Explanation
In α and β decay, the daughter nucleus is in the excited state most of the time. The typical life time of excited state is approximately 10-11s. So this excited state nucleus immediately returns to the ground state or lower energy state by emitting highly energetic photons called γ rays.
80. Which of these emits a high energetic proton of energy when returning to ground state?
a) Atom
b) Electron
c) Nucleus
d) Neutron
Explanation
When the atom is in the excited state, it returns to the ground state by emitting photons of energy in the order of few eV. But when the excited state nucleus returns to its ground state, it emits a highly energetic photon (γ rays) of energy in the order of MeV
81. The decay rate of a radioactive material is directly proportional to_____.
a) Number of Nuclei
b) Number of protons
c) Mass Number
d) Atomic Number
Explanation
In a radioactive sample which contains a vast number of the radioactive nuclei and not all the radioactive nucleus in sample decay at the same time and this decay is basically a random process. It implies that we cannot predict which nucleus is going to decay or rather we can determine like probabilistic basis (like tossing a coin). We can calculate approximately how many nuclei in a sample are decayed over a period of time. At any instant t, the number of decays per unit time called rate of decay dN / dt is proportional to the number of nuclei (N) at the same instant.
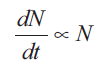
82. What is the polarity of the decay constant of a radioactive material?
a) Neutral
b) Positive
c) Zero
d) Negative
Explanation
The proportionality constant λ is called decay constant which is different for different radioactive sample and the negative sign in the equation implies that the N is decreasing with time. By rewriting the equation we get dN =−λ N dt, Here dN represents the number of nuclei decaying in the time interval dt.
83. Assertion (A): The half-life of a radioactive material is the time required for the number of atoms reduces to one half of the initial amount.
Reasoning(R): The shorter half-life sample will have a higher radio activity.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
We can define the half-life T1/2 as the time required for the number of atoms initially present to reduce to one half of the initial amount. The half-life is the important characteristic of every radioactive sample. Some radioactive nuclei are known to have half-life as long as 1014 years and some nucleus have very shorter life time. The shorter half-life sample will have higher activity and it is more ‘radioactive’ which is more harmful.
84. What is the range of the life time for each radio-active nucleus?
a) Zero to infinity
b) One to Hundred
c) Zero to negative value
d) None of the above
Explanation
When the radioactive nucleus undergoes the decay, the nucleus which disintegrates first has zero life time and the nucleus which decays last has an infinite lifetime. The actual life time for each nucleus varies from zero to infinity. Therefore, it is meaningful to define average life or mean life time t, that the nucleus survives before it decays.
85. Which is known as the ratio of integration of all life times to the total number of initial nuclei?
a) Average life time
b) Mean life time
c) Total life time
d) Active life time
Explanation
The mean life time of the nucleus is the ratio of sum or integration of life times of all nuclei to the total number nuclei present initially.
86. Choose the correct statements.
i) The beta decay of radioactive material is used in carbon dating applications.
ii) All living organism absorbs carbon dioxide in which very small part of 612C is radioactive.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The interesting application of beta decay is radioactive dating or carbon dating. Using this technique, the age of an ancient object can be calculated. All living organisms absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from air to synthesize organic molecules. In this absorbed CO2, the major part is 612C and very small fraction (1.3x 10-12) is radioactive 614C whose half-life is 5730 years.
87. Assertion (A): The ratio of 6 14C to 6 12C is nearly constant in all the living organisms.
Reasoning(R): The continuous production and decay of 6 14C in the atmosphere keeps the carbon ratio constant.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Carbon-14 in the atmosphere is always decaying but at the same time, cosmic rays from outer space are continuously bombarding the atoms in the atmosphere which produces 614C. So the continuous production and decay of 6 14C in the atmosphere keep the ratio of 6 14C to 6 12C always constant. Since our human body, tree or any living organism continuously absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere, the ratio of 6 14C to 6 12C in the living organism is also nearly constant.
88. Choose the correct statements.
i) Keezhadi is an important archeological places of Tamil Nadu located at the banks of river Vaigai.
ii) The artifacts unearthed in Keezhadi gave a substantial evidence for an ancient urban civilization.
iii) A 200g charcoal was used for the carbon dating to determine the age of the materials found in Keezhadi.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Keezhadi (கீழடி), a small hamlet, has become one of the very important archeological places of Tamil Nadu. It is located in Sivagangai district. A lot of artifacts (gold coins, pottery, beads, iron tools, jewelry and charcoal, etc.) have been unearthed in Keezhadi which have given substantial evidence that an ancient urban civilization had thrived on the banks of river Vaigai. To determine the age of those materials, the charcoal of 200 g sent for carbon dating.
89. Which of this material was bombarded with α particle in the experiment conducted by Bothe and Becker in the year 1930?
a) Beryllium
b) Gold
c) Tungsten
d) Boron
Explanation
In 1930, two German physicists Bothe and Becker found that when beryllium was bombarded with α particle highly penetrating radiation was emitted. This radiation was capable of penetrating the thick layer of lead and was unaffected by the electric and magnetic fields. Initially, it was thought as γ radiation.
90. Who discovered the neutrons in the year 1932?
a) James Chadwick
b) Henry Becquerel
c) Marie Curie
d) Neil’s Bohr
Explanation
In the year 1932, James Chadwick discovered that those radiations found in the Bothe and Becker experiment are not EM waves but they are particles of mass little greater than the mass of the proton and had no charge. He called them as neutrons.
91. Assertion (A): Neutrons are stable only inside the nucleus and unstable outside the nucleus.
Reasoning(R): The free neutron outside the nucleus decays with the emission of proton.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Neutrons are stable inside the nucleus. But outside the nucleus they are unstable. If the neutron comes out of the nucleus (free neutron), it decays with emission of proton.
92. Based on which property neutrons are classified?
a) Stability
b) Chemical reactions
c) Kinetic energy
d) Mass
Explanation
Neutrons are classified according to their kinetic energy as slow neutrons (0 to 1000 eV), fast neutrons (0.5 MeV to 10 MeV).
93. Thermal neutrons are neutrons with _____ energy in ______.
a) High, Stable
b) Peak, Atmosphere
c) Low, Vacuum
d) Average, Thermal equilibrium
Explanation
The neutrons with average energy of about 0.025 eV in thermal equilibrium are called thermal neutron, because at 298K, the thermal energy kT 0.025eV. Slow and fast neutrons play a vital role in nuclear reactors.
94. Who discovered the idea of high energy release when breaking nucleus with neutron?
a) Murray Gellman and George Zweig
b) Otto Hahn and F. Strassman
c) Murray Gellman and George Zweig
d) Bothe and Becker
Explanation
In 1939, German scientists Otto Hahn and F. Strassman discovered that when uranium nucleus is bombarded with a neutron, it breaks up into two smaller nuclei of comparable masses with the release of energy.
95. Which of these constitutes for the energy release in the nuclear fission?
a) Neutrons
b) Protons
c) Electrons
d) All the above
Explanation
The process of breaking up of the nucleus of a heavier atom into two smaller nuclei with the release of a large amount of energy is called nuclear fission. The fission is accompanied by the release of neutrons.
96. Choose the correct statements.
i) Energy released in the nuclear fission is greater than a chemical reaction.
ii) Uranium undergoes nuclear fission in 90 different ways.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The energy that is released in the nuclear fission is of many orders of magnitude greater than the energy released in chemical reactions. Uranium undergoes fission reaction in 90 different ways.
97. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Huge amount of energy released even by one nucleus in a nuclear fission process.
ii) Each one of a fission reaction releases more neutrons which further reacts and produces more neutrons.
iii) The number of neutrons in a nuclear fission goes on increasing in a geometric progression.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
When one 92235U nucleus undergoes fission the energy released might be small. But from each fission reaction, three neutrons are released. These three neutrons cause further fission in another three 92235U nuclei which in turn produce nine neutrons. These nine neutrons initiate fission in another 27 92 235U nuclei and so on. This is called a chain reaction and the number of neutrons goes on increasing almost in geometric progression.
98. How many types of chain reaction are possible in a nuclear fission?
a) 2
b) 4
c) 3
d) 5
Explanation
There are two kinds of chain reactions: uncontrolled chain reaction and controlled chain reaction.
99. Assertion (A): The Atom bomb is an example of nuclear fission by an uncontrolled chain reaction.
Reasoning(R): The neutrons multiply indefinitely in an uncontrolled chain reaction and the energy releases in a fraction of a second.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
In an uncontrolled chain reaction, the number of neutrons multiplies indefinitely and the entire amount of energy released in a fraction of second. The atom bomb is an example of nuclear fission in which uncontrolled chain reaction occurs. Atom bombs produce massive destruction for mankind.
100. Choose the correct statements.
i) In the controlled chain reaction the average numbers of neutrons are released in each stage so as to store the released energy.
ii) Nuclear Reactors use the controlled chain reaction to produce energy for power generation and research purposes.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
If the chain reaction is controllable then we can harvest an enormous amount of energy for our needs. It is achieved in a controlled chain reaction. In the controlled chain reaction, the average number of neutron released in each stage is kept as one such that it is possible to store the released energy. In nuclear reactors, the controlled chain reaction is achieved and the produced energy is used for power generation or for research purpose.
101. Assertion (A): The energy produced in a nuclear reactor is through the nuclear fission in a self-sustained controlled manner.
Reasoning(R): The Nuclear reactor produces the energy for power generation or for the research purpose.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Nuclear reactor is a system in which the nuclear fission takes place in a self-sustained controlled manner and the energy produced is used either for research purpose or for power generation.
102. Which country built the first nuclear reactor?
a) USA
b) Germany
c) Soviet Union
d) China
Explanation
The first nuclear reactor was built in the year 1942 at Chicago, USA by physicist Enrico Fermi.
103. Which of the following is not an important part of a Nuclear reactor?
a) Moderator
b) Transformer
c) Control rods
d) Fuel
Explanation
The main parts of a nuclear reactor are fuel, moderator and control rods. In addition to this, there is a cooling system which is connected with power generation set up.
104. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Uranium and plutonium are the fuels used as a fissionable material.
ii) Additional neutron source is added to the fuel to initiate the chain reaction initially.
iii) Fast neutrons are preferred for the sustained nuclear reactions.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Fuel: The fuel is fissionable material usually uranium or plutonium. In addition to this, a neutron source is required to initiate the chain reaction for the first time. A mixture of beryllium with plutonium or polonium is used as the neutron source. During fission only fast neutrons are emitted but the probability of initiating fission by it in another nucleus is very low. Therefore, slow neutrons are preferred for sustained nuclear reactions.
105. Which of the following is used to convert fast neutrons to slow neutrons?
a) Control rod
b) Steam
c) Moderator
d) Coolant
Explanation
Moderators: The moderator is a material used to convert fast neutrons into slow neutrons.
106. Assertion (A): Moderators are chose to be very light nucleus with comparable mass of the neutrons.
Reasoning(R): The Light nuclei collide with fast neutrons to reduce the speed of the neutrons.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Usually the moderators are chosen in such a way that it must be very light nucleus having mass comparable to that of neutrons. Hence, these light nuclei undergo collision with fast neutrons and the speed of the neutron is reduced.
107. Which of these is not used as a moderator?
a) Heavy water
b) Carbon
c) Graphite
d) Normal water
Explanation
Most of the reactors use water, heavy water (D2O) and graphite as moderators. The blocks of uranium stacked together with blocks of graphite (the moderator) to form a large pile.
108. What is the main purpose of the control rod?
a) Reaction rate control
b) Control the energy release
c) Temperature of the reaction
d) All the above
Explanation
Control rods: The control rods are used to adjust the reaction rate. During each fission, on an average 2.5 neutrons are emitted and in order to have the controlled chain reactions only one neutron is allowed to cause another fission and the remaining neutrons are absorbed by the control rods.
109. Which material is used as a control rod?
a) Boron
b) Carbon
c) Lead
d) Manganese
Explanation
Usually cadmium or boron acts as control rod material and these rods are inserted into the uranium blocks.
110. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The average number of neutrons produced per fission depends on the insertion depth of the control rod.
ii) If the average number of neutrons produced per fission is greater than one it is in critical state.
iii) In the super-critical state the reactor may explode and cause massive destruction.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Depending on the insertion depth of control rod into the uranium, the average number of neutrons produced per fission is set to be equal to one or greater than one. If the average number of neutrons produced per fission is equal to one, then reactor is said to be in critical state. In fact, all the nuclear reactors are maintained in critical state by suitable adjustment of control rods. If it is greater than one, then reactor is said to be in super-critical and it may explode sooner or may cause massive destruction.
111. Which of these are used as the coolant?
a) Heavy water
b) Liquid sodium
c) Normal water
d) All the above
Explanation
Cooling system: The cooling system removes the heat generated in the reactor core. Ordinary water, heavy water and liquid sodium are used as coolant since they have very high specific heat capacity and have large boiling point under high pressure.
112. How many nuclear reactors are operated in India?
a) 22
b) 2
c) 18
d) 35
Explanation
India has 22 nuclear reactors in operation. Nuclear reactors are constructed in two places in Tamilnadu, Kalpakkam and Koodankulam. Even though nuclear reactors are aimed to cater to our energy need, in practice nuclear reactors now are able to provide only 2% of energy requirement of India.
113. Choose the correct statements.
i) In Nuclear fusion two or more light nuclei combine to form a heavy nucleus.
ii) The mass of the resultant nuclei is greater than the sum of the masses of original light nuclei.
iii) The nuclear fusion occurs at room temperature.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
When two or more light nuclei (A<20) combine to form a heavier nucleus, then it is called nuclear fusion. In the nuclear fusion, the mass of the resultant nucleus is less than the sum of the masses of original light nuclei. The mass difference appears as energy. The nuclear fusion never occurs at room temperature unlike nuclear fission. It is because when two light nuclei come closer to combine, it is strongly repelled by the coulomb repulsive force.
114. In which of this temperature value the thermonuclear fusion reaction occurs?
a) Less than 303 K
b) Equal to 0 K
c) Greater than 107K
d) Less than 100K
Explanation
To overcome this repulsion, the two light nuclei must have enough kinetic energy to move closer to each other such that the nuclear force becomes effective. This can be achieved if the temperature is very much greater than the value 107 K. When the surrounding temperature reaches around 107K, lighter nuclei start fusing to form heavier nuclei and this resulting reaction is called thermonuclear fusion reaction.
115. Assertion (A): The cores of the stars are the natural place where nuclear fusion occurs.
Reasoning(R): Most of the stars including Sun fuse hydrogen into helium by this nuclear fusion.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The natural place where nuclear fusion occurs is the core of the stars, since its temperature is of the order of 107K. In fact, the energy generation in every star is only through thermonuclear fusion. Most of the stars including our Sun fuse hydrogen into helium and some stars even fuse helium into heavier elements.
116. Which of the following statements is not true regarding the nuclear fusion of stars?
a) Stars are early in the form of cloud and dust.
b) The Gravitational energy of stars is converted into kinetic energy and to heat.
c) The Thermonuclear fusion is initiated in the stars when the temperature starts cooling down.
d) The enormous energy release of stars stabilizes the star and prevents it from further collapse.
Explanation
The early stage of a star is in the form of cloud and dust. Due to their own gravitational pull, these clouds fall inward. As a result, its gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy and finally into heat. When the temperature is high enough to initiate the thermonuclear fusion, they start to release enormous energy which tends to stabilize the star and prevents it from further collapse.
117. What will happen when the Sun enters into a Red giant phase?
a) Total hydrogen is burnt out.
b) The size of Sun will shrink.
c) Helium and Hydrogen fuse to become carbon.
d) Carbon is burnt to produce helium.
Explanation
The sun’s interior temperature is around 1.5×107K. The sun is converting 6×1011kg hydrogen into helium every second and it has enough hydrogen such that these fusion lasts for another 5 billion years. When the hydrogen is burnt out, the sun will enter into new phase called red giant where helium will fuse to become carbon. During this stage, sun will expand greatly in size and all its planets will be engulfed in it.
118. How many steps are involved in the fusion reaction cycle of the sun according to Hans Bethe?
a) 10
b) 3
c) 7
d) 5
Explanation
According to Hans Bethe, the sun is powered by proton-proton cycle of fusion reaction. This cycle consists of three steps.
119. Which of this scientist theoretically proposed quark as the elementary particle?
a) Murray Gellman and George Zweig
b) Hans Bethe
c) Otto Hahn and F. Strassman
d) Bothe and Becker
Explanation
In 1964, physicist Murray Gellman and George Zweig theoretically proposed that protons and neutrons are not fundamental particles in fact they are made up of quarks. These quarks are now considered elementary particles of nature.
120. Which of these is an elementary particle?
a) Atom
b) Nucleus
c) Electrons
d) Protons
Explanation
Electrons are fundamental or elementary particles because they are not made up of anything.
121. Which of this organization discovered the quarks?
a) The University of Cambridge
b) Stanford Linear Accelerator Center
c) The French National Centre for Scientific Research
d) Helmholtz Association of German Research Centers
Explanation
In the year 1968, the quarks were discovered experimentally by Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC), USA.
122. How many quarks are classified with their antiparticles?
a) 5
b) 7
c) 4
d) 6
Explanation
There are six quarks namely, up, down, charm, strange, top and bottom and their antiparticles. All these quarks have fractional charges. For example, charge of up quark is + 2 /3 e and that of down quark is − 1/3 e.
123. State the combinations of proton according to quark model?
a) Two up quarks and Two down quarks
b) One up quark and Two down quarks
c) Two up quarks and One down quark
d) One up quark and One down quark
Explanation
According to quark model proton is made up of two up quarks and one down quark and neutron is made up of one up quark and two down quarks.
124. Assertion (A): A gravitational force is universal in nature.
Reasoning(R): Planets are bound to the sun through the gravitational force.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
It is known that there exists gravitational force between two masses and it is universal in nature. Our planets are bound to the sun through gravitational force of the sun.
125. Which of these is not the fundamental force of nature?
a) Gravitational forces
b) Frictional forces
c) Weak forces
d) Electromagnetic forces
Explanation
Gravitational, electromagnetic, strong and weak forces are called fundamental forces of nature. It is very interesting to realize that, even for our day-to-day life we require these four fundamental forces.
12th Science Lesson 6 Questions in English
6] Electrostatics
1. The forces we experience in everyday life are electromagnetic in nature except ____
- Friction
- Gravity
- Repulsion
- All the above
Explanation
The technological developments of the modern 21st century are primarily due to our understanding of electromagnetism. The forces we experience in everyday life are electromagnetic in nature except gravity. It is now understood that except gravity, all forces which we experience in every day life (tension in the string, normal force from the surface, friction etc.) arise from electromagnetic forces within the atoms.
2. Which among the following statement is correct
- When an object is pushed, the atoms in our hand interact with the atoms in the object and this interaction is basically electromagnetic in nature. When we stand on Earth’s surface, the gravitational force on us acts downwards and the normal force acts upward to counter balance the gravitational force.
- It arises due to the electromagnetic interaction of atoms on the surface of the Earth with the atoms present in the feet of the person. Though, we are attracted by the gravitational force of the Earth, we stand on Earth only because of electromagnetic force of atoms.
- When an object is moved on a surface, static friction resists the motion of the object. This static friction arises due to electromagnetic interaction between the atoms present in the object and atoms on the surface. Kinetic friction also has similar origin. This branch of electricity which deals with stationary charges is called Electrostatics.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
3. Two millenniums ago, Who, noticed that amber after rubbing with animal fur attracted small pieces of leaves and dust?
- Aryans
- Greeks
- Romans
- None of the above
Explanation
Two millenniums ago, Greeks noticed that amber (a solid, translucent material formed from the resin of a fossilized tree) after rubbing with animal fur attracted small pieces of leaves and dust. The amber possessing this property is said to be ‘charged’.
4. Which among the following statement is correct
- Consider a charged rubber rod hanging from a thread. Suppose another charged rubber rod is brought near the first rubber rod; the rods repel each other. Now if we bring a charged glass rod close to the charged rubber rod, they attract each other.
- At the same time, if a charged glass rod is brought near another charged glass rod, both the rods repel each other. From these observations, the following inferences are made (i) The charging of rubber rod and that of glass rod are different from one another. (ii) The charged rubber rod repels another charged rubber rod, which implies that ‘like charges repel each other’.
- We can also arrive at the same inference by observing that a charged glass rod repels another charged glass rod. (iii) The charged rubber rod attracts the charged glass rod, implying that the charge in the glass rod is same kind of charge present in the rubber. Thus, like charges attract each other
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
We can also arrive at the same inference by observing that a charged glass rod repels another charged glass rod. (iii) The charged rubber rod attracts the charged glass rod, implying that the charge in the glass rod is not the same kind of charge present in the rubber. Thus unlike charges attract each other.
5. In the 18th century, who called one type of charge as positive (+) and another type of charge as negative (–)?
- J. J. Thomson
- Benjamin Franklin
- Rutherford
- John Dalton
Explanation
In the 18th century, Benjamin Franklin called one type of charge as positive (+) and another type of charge as negative (–). Based on Franklin’s convention, rubber and amber rods are negatively charged while the glass rod is positively charged. If the net charge is zero in the object, it is said to be electrically neutral.
6. Charging the objects through rubbing is called _____
- Cosmoelectric charging
- Triboelectric charging
- Neoelectric charging
- Hostelectric charging
Explanation
When an object is rubbed with another object (for example rubber with silk cloth), some amount of charge is transferred from one object to another due to the friction between them and the object is then said to be electrically charged. Charging the objects through rubbing is called triboelectric charging.
7. The SI unit of charge is ____
- Newton
- Joule
- Coulomb
- Pascal
Explanation
Most objects in the universe are made up of atoms, which in turn are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons. These particles have mass, an inherent property of particles. Similarly, the electric charge is another intrinsic and fundamental property of particles. The SI unit of charge is coulomb.
8. Which among the following statement is correct
- Benjamin Franklin argued that when one object is rubbed with another object, charges get transferred from one to the other. Before rubbing, both objects are electrically neutral and rubbing simply transfers the charges from one object to the other.
- He concluded that charges are neither created or nor destroyed but can only be transferred from one object to other. This is called conservation of total charges and is one of the fundamental conservation laws in physics.
- It is stated more generally in the following way. The total electric charge in the universe is constant and charge can neither be created nor be destroyed. In any physical process, the net change in charge will always be zero.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
9. Who in n his famous experiment found that the value of e = 1.6 × 10–19 C?
- James Chadwick
- Harvey Fletcher
- Robert Millikan
- Rutherford
Explanation
Robert Millikan in his famous experiment found that the value of e = 1.6 × 10–19 C. The charge of an electron is −1.6 × 10–19 C and the charge of the proton is +1.6 × 10–19 C.
10. Calculate the number of electrons in one coulomb of negative charge?
- n = 1.38 × 1018 electrons
- n = 3.18 × 1018 electrons
- n = 6.25 × 1018 electrons
- n = 9.18 × 1018 electrons
Explanation
According to the quantisation of charge, q = ne
Here q = 1C. So, the number of electrons in 1 coulomb of charge is n = q / e.
n = 1C / 1.6 ×10-19
n = 6.25 × 1018 electrons.
11. Which among the following statement is correct regarding coulomb’s law?
- In the year 1786, Coulomb deduced the expression for the force between two stationary point charges in vacuum or free space. Consider two-point charges q1 and q2 at rest in vacuum, and separated by a distance of r. According to Coulomb, the force on the point charge q1 exerted by another point charge q2 is F21 = K r12.
- Coulomb’s law states that the electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of the two-point charges and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two-point charges.
- The force on the charge q2 exerted by the charge q1 always lies along the line joining the two charges. r12 is the unit vector pointing from charge q1 to q2. Likewise, the force on the charge q1 exerted by q2 is along r12 (i.e., in the direction opposite to r12). The magnitude of the electrostatic force between two charges each of one coulomb and separated by a distance of 1 m is calculated as follows: |F| = 9 × 109 N.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
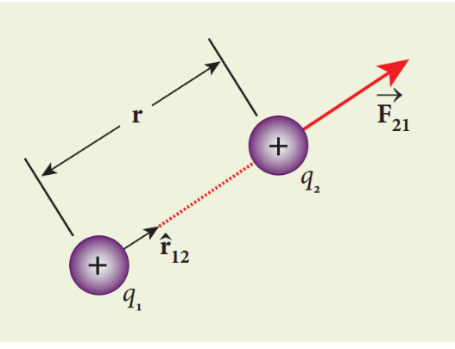
In the year 1786, Coulomb deduced the expression for the force between two stationary point charges in vacuum or free space. Consider two-point charges q1 and q2 at rest in vacuum, and separated by a distance of r. According to Coulomb, the force on the point charge q2 exerted by another point charge q1 is F21 = K r12.
12. By Coulomb’s law, in S.I units, k = and its value is _____
- 9×109 N m C
- 9×109 N m2 C
- 9×109 N m C2
- 9×109 N m2 C–2
Explanation
By Coulomb’s law, in S.I units, k = and its value is 9 ×109 N m2 C–2.
13. Which among the following statement is correct regarding coulombs law?
- Coulomb’s law has same structure as Newton’s law of gravitation. Both are inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the particles. The electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of two-point charges and gravitational force is directly proportional to the product of two masses.
- But there are some important differences between these two laws. The gravitational force between two masses is always attractive but Coulomb force between two charges can be attractive or repulsive, depending on the nature of charges.
- The gravitational force between two masses is dependent of the medium. For example, if 1 kg of two masses are kept in air or inside water, the gravitational force between two masses remains different. Thus, electrostatic force between the two charges depends on nature of the medium in which the two charges are kept at rest.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
The gravitational force between two masses is independent of the medium. For example, if 1 kg of two masses are kept in air or inside water, the gravitational force between two masses remains the same. But the electrostatic force between the two charges depends on nature of the medium in which the two charges are kept at rest.
14. What is the value of Gravitational constant?
- G = 4.91 × 10–8 N m2 kg–2
- G = 5.82 × 10–11 N m2 kg–2
- G = 6.67 × 10–11 N m2 kg–2
- G = 7.83 × 10–11 N m2 kg–2
Explanation
The value of the gravitational constant G = 6.67 × 10–11 N m2 kg–2. The value of the constant k in Coulomb law is k = 9 × 109 N m2 C–2. Since k is much greater than G, the electrostatic force is always greater in magnitude than gravitational force for smaller size objects.
15. Which principle explains the interaction between multiple charges?
- Multitude principle
- Superposition principle
- Nanoconduction principle
- Compressive principle
Explanation
Coulomb’s law explains the interaction between two-point charges. If there are more than two charges, the force on one charge due to all the other charges needs to be calculated. Coulomb’s law alone does not give the answer. The superposition principle explains the interaction between multiple charges.
16. Which among the following statement is correct regarding superposition principle?
- According to this superposition principle, the total force acting on a given charge is equal to the vector sum of forces exerted on it by all the other charges. Consider a system of n charges, namely q1 , q2 , q3 ….qn. The force on q1 exerted by the charge q2,
- F12 = K r21. where r21 is the unit vector from q2 to q1 along the line joining the two charges and r21 is the distance between the charges q1 and q2. The electrostatic force between two charges is not affected by the presence of other charges in the neighbourhood.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
17. Consider a point charge kept at a point in space. If another point charge is placed at some distance from the first point charge, it experiences either an attractive force or repulsive force. This is called ____
- Consideration at a distance
- Action at a distance
- Motion at a distance
- Flexible at a distance
Explanation
Consider a point charge kept at a point in space. If another point charge is placed at some distance from the first point charge, it experiences either an attractive force or repulsive force. This is called ‘action at a distance’.
18. Who introduced the concept of field?
- James Maxwell
- Heinrich Hertz
- Humphry Davy
- Michael Faraday
Explanation
Michael Faraday introduced the concept of field.
19. Which among the following statement is correct
- According to Faraday, every charge in the universe creates an electric field in the surrounding space, and if another charge is brought into its field, it will interact with the electric field at that point and will experience a force. It may be recalled that the interaction of two masses is similarly explained using the concept of gravitational field.
- Both the electric and gravitational forces are contact forces, hence the field concept is required to explain action at a distance. Consider a source point charge q located at a point in space. Another point charge qo (test charge) is placed at some point P which is at a distance r from the charge q.
- The electrostatic force experienced by the charge qo due to q is given by Coulomb’s law. F = r, where K = The charge q creates an electric field in the surrounding space within which its effect can be felt by another charge. It is measured in terms of a quantity called electric field intensity or simply called electric field E.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Both the electric and gravitational forces are non-contact forces, hence the field concept is required to explain action at a distance. Consider a source point charge q located at a point in space. Another point charge qo (test charge) is placed at some point P which is at a distance r from the charge q.
20. The electric field at the point P at a distance r from the point charge q is given by ____
- E = r
- E = r
- E = r
- E = qr
Explanation
The electric field at the point P at a distance r from the point charge q is defined as the force that would be experienced by a unit positive charge placed at that point P and is given by E = r.
21. Which among the following statement is correct regarding electric field?
- If the charge q is positive then the electric field points away from the source charge and if q is negative, the electric field points towards the source charge q. If the electric field at a point P is ρ E, then the force experienced by the test charge qo placed at the point P is F = q0E.
- The equation E = r implies that the electric field is independent of the test charge qo and it depends only on the source charge q. Since the electric field is a vector quantity, at every point in space, this field has unique direction and magnitude.
- In the definition of electric field, it is assumed that the test charge q0 is taken sufficiently small, so that bringing this test charge will not move the source charge. In other words, the test charge is made sufficiently small such that it will not modify the electric field of the source charge.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and3
- All 1, 2 and 3
22. How many kinds of electric field are there?
- Three
- Four
- Six
- Two
Explanation
There are two kinds of the electric field: uniform (constant) electric field and non-uniform electric field. Uniform electric field will have the same direction and constant magnitude at all points in space. Non-uniform electric field will have different directions or different magnitudes or both at different points in space.
23. The electric field at an arbitrary point due to a collection of point charges is simply equal to the vector sum of the electric fields created by the individual point charges. This is called ____
- Superposition of electric pulse
- Superposition of electric currents
- Superposition of electric fields
- Superposition of electro magnets
Explanation
Suppose a number of point charges are distributed in space. To find the electric field at some point P due to this collection of point charges, superposition principle is used. The electric field at an arbitrary point due to a collection of point charges is simply equal to the vector sum of the electric fields created by the individual point charges. This is called superposition of electric fields.
24. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Electric field due to continuous charge distribution?
- The electric charge is quantized microscopically. While dealing with the electric field due to a charged sphere or a charged wire etc., it is very difficult to look at individual charges in these charged bodies.
- Therefore, it is assumed that charge is distributed continuously on the charged bodies and the discrete nature of charges is not considered here. The electric field due to such continuous charge distributions is found by invoking the method of calculus.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
25. Which among the following statement is correct
- Electric field vectors are visualized by the concept of electric field lines. They form a set of continuous lines which are the visual representation of the electric field in some region of space. The following rules are followed while drawing electric field lines for charges.
- The electric field lines start from a positive charge and end at negative charges or at infinity. For a positive point charge the electric field lines point radially outward and for a negative point charge, the electric field lines point radially inward.
- Note that for an isolated negative point charge the electric field line starts from the charge and ends only at infinity. For an isolated positive point charge the electric field lines start at infinity and end at the negative charge.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Note that for an isolated positive point charge the electric field line starts from the charge and ends only at infinity. For an isolated negative point charge the electric field lines start at infinity and end at the negative charge. The electric field vector at a point in space is tangential to the electric field line at that point.
26. Which among the following statement is correct regarding electric field lines?
- The electric field lines are denser (more closer) in a region where the electric field has small magnitude and high dense in a region where the electric field is of large magnitude. In other words, the number of lines passing through a given surface area perpendicular to the lines is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field in that region.
- The magnitude of the electric field for a point charge decreases as the distance increases {|E| ∝ }. So the electric field has greater magnitude at the surface A than at B. Therefore, the number of lines crossing the surface A is greater than the number of lines crossing the surface B. Note that at surface B the electric field lines are farther apart compared to the electric field lines at the surface A.
- No two electric field lines intersect each other. If two lines cross at a point, then there will be two different electric field vectors at the same point. As a consequence, if some charge is placed in the intersection point, then it has to move in two different directions at the same time, which is physically impossible. Hence, electric field lines do not intersect.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
The electric field lines are denser (more closer) in a region where the electric field has larger magnitude and less dense in a region where the electric field is of smaller magnitude. In other words, the number of lines passing through a given surface area perpendicular to the lines is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field.
27. Two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance constitute an _____
- Electric potential
- Electric dipole
- Electric constant
- Electric volt
Explanation
Two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance constitute an electric dipole. In many molecules, the centres of positive and negative charge do not coincide. Such molecules behave as permanent dipoles. Examples: CO, water, ammonia, HCl etc.
28. Which among the following statement is correct
- Consider two equal and opposite point charges (+q, –q) that are separated by a distance 2a. The electric dipole moment is defined as p = qr+ + (−q) r_. where r+ is the position vector of +q from the origin and ρ r_ is the position vector of –q from the origin.
- The electric dipole moment vector lies perpendicular to the line joining two charges and is directed from +q to ̶ q. The electric field lines for an electric dipole. For simplicity, the two charges are placed on the y-axis. If the two charges are placed on x or z-axis, dipole moment will point from –q to +q.
- The magnitude of the electric dipole moment is equal to the product of the magnitude of one of the charges and the distance between them, |p| = 2qa. Though the electric dipole moment for two equal and opposite charges is defined, it is possible to define and calculate the electric dipole moment for a collection of point charges. The electric dipole moment for a collection of n point charges is given by p = .
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
The electric dipole moment vector lies along the line joining two charges and is directed from –q to +q. The electric field lines for an electric dipole. For simplicity, the two charges are placed on the x-axis. Even if the two charges are placed on y or z-axis, dipole moment will point from –q to +q.
29. What is the S.I. unit of dipole moment?
- Newton metre
- Newton / metre
- Coulomb metre
- Coulomb / metre
Explanation
The SI unit of dipole moment is coulomb metre (Cm).
30. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Torque experienced by an electric dipole in the uniform electric field?

- Consider an electric dipole of dipole moment p placed in a uniform electric field E whose field lines are equally spaced and point in the same direction. The charge +q will experience a force q E in the direction of the field and charge –q will experience a force –q E in a direction opposite to the field.
- Since the external field E is uniform, the total force acting on the dipole is zero. These two forces acting at different points will constitute a couple and the dipole experience a torque. This torque tends to rotate the dipole. The total torque on the dipole about the point O
- Using right-hand corkscrew rule, it is found that total torque is perpendicular to the plane of the paper and is directed into it. The magnitude of the total torque τ = qE.2a sin θ. where θ is the angle made by ρ p with ρ E . Since p = 2aq, the torque is written in terms of the vector product as τ = pE sin θ and is maximum when θ = 90ο.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
31. A sample of HCl gas is placed in a uniform electric field of magnitude 3 × 104 N C–1. The dipole moment of each HCl molecule is 3.4 × 10–30 Cm. Calculate the maximum torque experienced by each HCl molecule?
- τmax = 8.19 × 10−26 Nm
- τmax = 10.2 × 10−26 Nm
- τmax = 12.7 × 10−26 Nm
- τmax = 15.6 × 10−26 Nm
Explanation
The maximum torque experienced by the dipole is when it is aligned perpendicular to the applied field
τmax = pE sin900 = 3.4 × 10-30 × 3 × 104
τmax = 10.2 × 10-26 Nm.
32. Which among the following is not the conservative forces?
- Gravitational force
- Coulomb force
- Frictional force
- None of the above
Explanation
In mechanics, potential energy is defined for conservative forces. Since gravitational force is a conservative force, its gravitational potential energy. Since Coulomb force is an inversesquare-law force, its also a conservative force like gravitational force. Therefore, we can define potential energy for charge configurations.
33. Which among the following statement is correct
- Consider a positive charge q kept fixed at the origin which produces an electric field ρ E around it. A positive test charge q′ is brought from point R to point P against the repulsive force between q and q′. Work must be done to overcome the repulsion between the charges and this work done is stored as potential energy of the system.
- The test charge q′ is brought from R to P with constant velocity which means that external force used to bring the test charge q′ from R to P must be equal and opposite to the coulomb force (Fext = ̶ Fcoulomb) . The work done is W = .dr.
- Since coulomb force is conservative, work done is dependent of the path and it is independent of on the initial and final positions of the test charge. If potential energy associated with q′ at P is UP and that at R is UR, then difference in potential energy is defined as the work done to bring a test charge q′ from point R to P and is given as UP × UR = W = ΔU.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Since coulomb force is conservative, work done is independent of the path and it depends only on the initial and final positions of the test charge. If potential energy associated with q′ at P is UP and that at R is UR, then difference in potential energy is defined as the work done to bring a test charge q′ from point R to P and is given as UP – UR = W = ΔU.
34. The electric potential at a point P is equal to the work done by an external force to bring a unit positive charge with constant velocity from infinity to the point P in the region of the external electric field E. Mathematically this is written as _____
- VP =
- VP =
- VP =
- VP =
Explanation
The electric potential at a point P is equal to the work done by an external force to bring a unit positive charge with constant velocity from infinity to the point P in the region of the external electric field E. Mathematically this is written as VP = . The electric potential energy difference can be written as ∆U = q′ ∆V. P
35. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Electric potential due to a point charge?
- Consider a positive charge q kept fixed at the origin. Let P be a point at distance r from the charge q. The electric potential at the point P is V = = . The electric potential due to a point charge q at a distance r is V = .
- If the source charge q is positive, V > 0. If q is negative, then V is negative and equal to V = ̶ . It is clear that the potential due to positive charge decreases as the distance increases, but for a negative charge the potential increases as the distance is increased. At infinity (r = ∞) electrostatic potential is zero (V = 0).
- In the case of gravitational force, mass moves from a point of lower gravitational potential to a point of higher gravitational potential. Similarly, a positive charge moves from a point of lower electrostatic potential to a point of higher electrostatic potential. However, a negative charge moves from lower electrostatic potential to higher electrostatic potential.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
In the case of gravitational force, mass moves from a point of higher gravitational potential to a point of lower gravitational potential. Similarly, a positive charge moves from a point of higher electrostatic potential to a point of lower electrostatic potential. However, a negative charge moves from lower electrostatic potential to higher electrostatic potential.
36. What is the S.I unit of electric field?
- Newton coulomb
- Newton / coulomb
- Newton metre
- Newton / metre
Explanation
The electric field is a vector quantity and its SI unit is newton per coulomb (NC–1).
37. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Electrostatic potential at a point due to an electric dipole?
- Consider two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance 2a. The point P is located at a distance r from the midpoint of the dipole. Let θ be the angle between the line OP and dipole axis AB. Total potential at the point P, V = q.
- Now we can write p cosθ = p × r, where r is the unit vector from the point O to point P. Hence the electric potential at a point P due to an electric dipole is given by V = This is valid for distances very large compared to the size of the dipole. But for a point dipole, the equation is valid for any distance.
- The potential due to an electric dipole falls as 1/r2 and the potential due to a single point charge falls as 1/r. Thus, the potential due to the dipole falls faster than that due to a monopole (point charge). As the distance increases from electric dipole, the effects of positive and negative charges nullify each other.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
38. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Equi-potential Surface?
- Consider a point charge q located at some point in space and an imaginary sphere of radius r is chosen by keeping the charge q at its centre. The electric potential at all points on the surface of the given sphere is the same. Such a surface is called an equipotential surface.
- An equipotential surface is a surface on which all the points are at the different electric potential. For a point charge the equipotential surfaces are concentric spherical surfaces. Each spherical surface is an equipotential surface but the value of the potential is same for different spherical surfaces.
- For a uniform electric field, the equipotential surfaces form a set of planes normal to the electric field E. The work done to move a charge q between any two points A and B, W = q (VB – VA). If the points A and B lie on the same equipotential surface, work done is zero because VA = VB.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
An equipotential surface is a surface on which all the points are at the same electric potential. For a point charge the equipotential surfaces are concentric spherical surfaces. Each spherical surface is an equipotential surface but the value of the potential is different for different spherical surfaces. The electric field is normal to an equipotential surface. If it is not normal, then there is a component of the field parallel to the surface.
39. Which among the following equation gives Relation between electric field and potential?
- E =
- E =
- E =
- E =
Explanation
Consider a positive charge q kept fixed at the origin. To move a unit positive charge by a small distance dx towards q in the electric field E, the work done is given by dW = −E dx. The minus sign implies that work is done against the electric field. This work done is equal to electric potential difference. Therefore, E = .
40. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Electrostatic potential energy for collection of point charges?
- The electric potential at a point at a distance r from point charge q1 is given by V = . This potential V is the work done to bring a unit negative charge from infinity to the point. Now if the charge q2 is brought from infinity to that point at a distance r from q1, the work done is the product of q2 and the electric potential at that point. Thus, we have W = q + V.
- This work done is stored as the electrostatic potential energy U of a system of charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance r. Thus, we have U = q2 V = . The electrostatic potential energy depends only on the distance between the two-point charges. In fact, the expression is derived by assuming that q1 is fixed and q2 is brought from infinity.
- The equation holds true when q2 is fixed and q1 is brought from infinity or both q1 and q2 are simultaneously brought from infinity to a distance r between them. Since the Coulomb force is a conservative force, the electrostatic potential energy is independent of the manner in which the configuration of charges is arrived at.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
The electric potential at a point at a distance r from point charge q1 is given by V = . This potential V is the work done to bring a unit positive charge from infinity to the point. Now if the charge q2 is brought from infinity to that point at a distance r from q1, the work done is the product of q2 and the electric potential at that point. Thus, we have W = q2 V.
41. Which among the following work on the principle of torque acting on an electric dipole?
- Air cooler
- Microwave
- Turbine
- All the above
Explanation
Microwave oven works on the principle of torque acting on an electric dipole. The food we consume has water molecules which are permanent electric dipoles. Oven produces microwaves that are oscillating electromagnetic fields and produce torque on the water molecules.
42. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Electrostatic potential energy of a dipole in a uniform electric field?
- Consider a dipole placed in the uniform electric field ρ E as shown in the Figure 1.29. A dipole experiences a torque when kept in an uniform electric field ρ E . This torque rotates the dipole to align it with the direction of the electric field. To rotate the dipole (at constant angular velocity) from its initial angle θ′ to another angle θ against the torque exerted by the electric field, an equal and opposite external torque must be applied on the dipole.
- The work done by the external torque to rotate the dipole from angle θ′ to θ at constant angular velocity is W = . Since τext is equal and opposite to τE = p × E, we have W p = E(cosƟ’ ̶ cosƟ). The potential energy stored in the system of dipole kept in the uniform electric field is given by U p =− pE cosƟ
- In addition to p and E, the potential energy also depends on the orientation θ of the electric dipole with respect to the external electric field. The potential energy is maximum when the dipole is aligned parallel (θ = π) to the external electric field and minimum when the dipole is aligned anti-parallel (θ = 0) to the external electric field.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
In addition to p and E, the potential energy also depends on the orientation θ of the electric dipole with respect to the external electric field. The potential energy is maximum when the dipole is aligned anti-parallel (θ = π) to the external electric field and minimum when the dipole is aligned parallel (θ = 0) to the external electric field.
43. The number of electric field lines crossing a given area kept normal to the electric field lines is called _____
- Electric conductor
- Electric magnitude
- Electric flux
- Electric vector
Explanation
The number of electric field lines crossing a given area kept normal to the electric field lines is called electric flux.
44. Electric flux is usually denoted by the Greek letter ____
- µE
- ƟE
- ΦE
- ∈E
Explanation
Electric flus is usually denoted by the Greek letter ΦE.
45. Which among the following statement is correct
- The electric field of a point charge is drawn in this figure. Consider two small rectangular area elements placed normal to the field at regions A and B. Even though these elements have the same area, the number of electric field lines crossing the element in region A is more than that crossing the element in region B.
- Therefore, the electric flux in region A is more than that in region B. Since electric field strength for a point charge decreases as the distance increases, electric flux also decreases as the distance increases. The above discussion gives a qualitative idea of electric flux. However, a precise definition of electric flux is needed.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 1
- None
46. What is the unit of Electric flux?
- N m C
- N m C2
- N m2 C ̶ 1
- N m-2 C-1
Explanation
The unit of Electric flux N m2 C–1. Electric flux is a scalar quantity and it can be positive or negative.
47. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Electric flux for uniform Electric field?
- Consider a uniform electric field in a region of space. Let us choose an area A normal to the electric field lines. The electric flux for this case is ΦE = EA. Suppose the same area A is kept parallel to the uniform electric field, then no electric field lines pass through the area A ,. The electric flux for this case is zero. ΦE = 0
- If the area is inclined at an angle θ with the field, then the component of the electric field perpendicular to the area alone contributes to the electric flux. The electric field component parallel to the surface area will not contribute to the electric flux. For this case, the electric flux. ΦE = (E cosθ) A.
- Further, θ is also the angle between the electric flux and the direction normal to the area. Hence in general, for uniform electric field, the electric flux is defined as ΦE = E A = EA cosθ. If θ = 90o. Therefore ΦE = E A cos900 = E A
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Further, θ is also the angle between the electric field and the direction normal to the area. Hence in general, for uniform electric field, the electric flux is defined as ΦE = ⋅ E A = EA cosθ. If θ = 90o. Therefore, ΦE = ⋅ E A = 0.
48. The total electric flux over the closed surface is written as _____
- ΦE =
- ΦE =
- ΦE =
- ΦE =
Explanation
The total electric flux over this closed surface is written as ΦE = . The total electric flux over a closed surface can be negative, positive or zero.
49. In general, the electric flux is negative if the electric field lines _____
- Enters the closed surface
- Leaves the closed surface
- Both entered and leaves the closed surface
- None of the above
Explanation
In general, the electric flux is negative if the electric field lines enter the closed surface and positive if the electric field lines leave the closed surface.
50. Which law states that if a charge Q is enclosed by an arbitrary closed surface, then the total electric flux ΦE through the closed surface is ΦE = = .
- Pascal law
- Joules law
- Gauss law
- Coulomb law
Explanation
Gauss’s law states that if a charge Q is enclosed by an arbitrary closed surface, then the total electric flux ΦE through the closed surface is ΦE = = .
51. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Gauss law?
- The total electric flux through the closed surface depends only on the charges enclosed by the surface and the charges present outside the surface will not contribute to the flux and the shape of the closed surface which can be chosen arbitrarily. The total electric flux is independent of the location of the charges inside the closed surface.
- To arrive at equation ., we have chosen a spherical surface. This imaginary surface is called a Gaussian surface. The shape of the Gaussian surface to be chosen depends on the type of charge configuration and the kind of symmetry existing in that charge configuration.
- The electric field is spherically asymmetric for a point charge, therefore spherical Gaussian surface is chosen. Cylindrical and planar Gaussian surfaces also be chosen for same kinds of charge configurations. The electric field E is due to charges present inside the Gaussian surface not for outside but the charge Qencl denotes the charges which lie both inside and outside the Gaussian surface
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
The electric field is spherically symmetric for a point charge, therefore spherical Gaussian surface is chosen. Cylindrical and planar Gaussian surfaces can be chosen for other kinds of charge configurations. The electric field E is due to charges present inside and outside the Gaussian surface but the charge Qencl denotes the charges which lie only inside the Gaussian surface.
52. Electric field due to any arbitrary charge configuration cannot be calculated using which among the following law?
- Gauss law
- Coulomb law
- Pascal law
- None of the above
Explanation
Electric field due to any arbitrary charge configuration can be calculated using Coulomb’s law or Gauss law. If the charge configuration possesses some kind of symmetry, then Gauss law is a very efficient way to calculate the electric field.
53. Which among the following statement is correct regarding application of Gauss law onElectric field due to charged infinite plane sheet?
- Consider an infinite plane sheet of charges with uniform surface charge density σ (charge present per unit area). Let P be a point at a distance of r from the sheet. Since the plane is infinitely large, the electric field should be same at all points equidistant from the plane and radially directed outward at all points.
- A cylindrical Gaussian surface of length 2r and two flats surfaces each of area A is chosen such that the infinite plane sheet passes perpendicularly through the middle part of the Gaussian surface. Total electric flux linked with the cylindrical surface, ΦE = = .
- Since the magnitude of the electric field at these two equal flat surfaces is uniform, E is taken out of the integration and Qencl is given by Q A encl = σ , we get 2E. The total area of surface either at P or P′, . Hence E = .
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
54. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Electric field due to two parallel charged infinite sheets?
- Consider two infinitely large charged plane sheets with equal and opposite charge densities +σ and -σ which are placed parallel to each other. The electric field between the plates and outside the plates is found using Gauss law. The magnitude of the electric field due to an infinite charged plane sheet is and it points perpendicularly outward if σ > 0 and points inward if σ < 0.
- At the points P2 and P3 , the electric field due to both plates are unequal in magnitude and same in direction. As a result, electric field at a point outside the plates is infinite. But between the plates, electric fields are in the same direction i.e., towards the right and the total electric field at a point P1 is Einside = + = .
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
At the points P2 and P3 , the electric field due to both plates are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. As a result, electric field at a point outside the plates is zero. But between the plates, electric fields are in the same direction i.e., towards the right and the total electric field at a point P1 is Einside = + = .
55. Gauss law is a powerful technique whenever a given charge configuration possesses ____
- Spherical symmetry
- Cylindrical symmetry
- Planar symmetry
- All the above
Explanation
Gauss law is a powerful technique whenever a given charge configuration possesses spherical, cylindrical or planar symmetry, then the electric field due to such a charge configuration can be easily found. If there is no such symmetry, the direct method (Coulomb’s law and calculus) can be used. For example, it is difficult to use Gauss law to find the electric field for a dipole since it has no spherical, cylindrical or planar symmetry.
56. Which among the following statement is correct
- An electrical conductor has a minimum number of mobile charges which are free to move in the material. In a metallic conductor, these mobile charges are free electrons which are bound to many atoms and therefore are restricted to move on the surface of the conductor.
- When there is no external electric field, the free electrons are in continuous random motion in all directions. As a result, there is no net motion of electrons along any particular direction which implies that the conductor is in electrostatic equilibrium. Thus, at electrostatic equilibrium, there is no net current in the conductor.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
An electrical conductor has a large number of mobile charges which are free to move in the material. In a metallic conductor, these mobile charges are free electrons which are not bound to any atom and therefore are free to move on the surface of the conductor.
57. Which among the following statement is correct
- The electric field is zero everywhere inside the conductor. This is true regardless of whether the conductor is solid or hollow. This is an experimental fact. Suppose the electric field is not zero inside the metal, then there will be a force on the mobile charge carriers due to this electric field.
- As a result, there will be a net motion of the mobile charges, which contradicts the conductors being in electrostatic equilibrium. Thus the electric field is zero everywhere inside the conductor. We can also understand this fact by applying an external uniform electric field on the conductor. Before applying the external electric field, the free electrons in the conductor are uniformly distributed in the conductor.
- When an electric field is applied, the free electrons accelerate to the right causing the right plate to be negatively charged and the left plate to be positively charged Due to this realignment of free electrons, there will be an internal electric field created inside the conductor which decrease until it nullifies the external electric field. Once the external electric field is nullified the conductor is said to be in electrostatic equilibrium.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
When an electric field is applied, the free electrons accelerate to the left causing the left plate to be negatively charged and the right plate to be positively charged. Due to this realignment of free electrons, there will be an internal electric field created inside the conductor which increases until it nullifies the external electric field. Once the external electric field is nullified the conductor is said to be in electrostatic equilibrium.
58. Which among the following statement is correct
- There is more net charge inside the conductors. The charges must reside on both the surface of the conductors. We can prove this property using Gauss law. Consider an arbitrarily shaped conductor. A Gaussian surface is drawn inside the conductor such that it is very close to the surface of the conductor.
- Since the electric field is zero everywhere inside the conductor, the net electric flux is also zero over this Gaussian surface. From Gauss’s law, this implies that there is no net charge inside the conductor. Even if some charge is introduced inside the conductor, it immediately reaches the surface of the conductor.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
There is no net charge inside the conductors. The charges must reside only on the surface of the conductors. We can prove this property using Gauss law. Consider an arbitrarily shaped conductor. A Gaussian surface is drawn inside the conductor such that it is very close to the surface of the conductor.
59. Which among the following statement is correct
- The electric field outside the conductor is perpendicular to the surface of the conductor and has a magnitude of σ / where σ is the surface charge density at that point. If the electric field has components parallel to the surface of the conductor, then free electrons on the surface of the conductor would experience acceleration.
- This means that the conductor is in equilibrium. Therefore, at electrostatic equilibrium, the electric field must be parallel to the surface of the conductor. We now prove that the electric field has magnitude σ / just inside the conductor’s surface. Consider a small cylindrical Gaussian surface. One half of this cylinder is embedded inside the conductor.
- Since electric field is normal to the surface of the conductor, the curved part of the cylinder has zero electric flux. Also, inside the conductor, the electric field is zero. Hence the bottom flat part of the Gaussian surface has no electric flux. Therefore, the top flat surface alone contributes to the electric flux. The electric field is parallel to the area vector and the total charge inside the surface is σA. By applying Gauss’s law EA = .
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
This means that the conductor is not in equilibrium. Therefore, at electrostatic equilibrium, the electric field must be perpendicular to the surface of the conductor. We now prove that the electric field has magnitude σ / just outside the conductor’s surface. Consider a small cylindrical Gaussian surface. One half of this cylinder is embedded inside the conductor.
60. Which among the following statement is correct
- The electrostatic potential has the same value on the surface and inside of the conductor. We know that the conductor has no parallel electric component on the surface which means that charges can be moved on the surface without doing any work.
- This is possible only if the electrostatic potential is constant at end points on the surface and there is potential difference between any two points on the surface. Since the electric field is zero inside the conductor, the potential is maximum at the surface of the conductor. Thus, at electrostatic equilibrium, the conductor is always at equipotential.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
This is possible only if the electrostatic potential is constant at all points on the surface and there is no potential difference between any two points on the surface. Since the electric field is zero inside the conductor, the potential is the same as the surface of the conductor. Thus, at electrostatic equilibrium, the conductor is always at equipotential.
61. Charging a conductor without actual contact is called _____
- Electrostatic potential
- Electrostatic resistant
- Electrostatic induction
- Electrostatic convection
Explanation
Whenever a charged rod is touched by another conductor, charges start to flow from charged rod to the conductor. Is it possible to charge a conductor without any contact? yes. This type of charging a conductor without actual contact is called electrostatic induction.
62. Which among the following statement is correct regarding electrostatic induction
- Consider an uncharged (neutral) conducting sphere at rest on an insulating stand. Suppose a negatively charged rod is brought near the conductor without touching it. The negative charge of the rod repels the electrons in the conductor to the opposite side. As a result, positive charges are induced near the region of the charged rod while negative charges on the farther side.
- Before introducing the charged rod, the free electrons were distributed uniformly on the surface of the conductor and the net charge is zero. Once the charged rod is brought near the conductor, the distribution is no longer uniform with more electrons located on the farther side of the rod and positive charges are located closer to the rod. But the total charge is zero.
- Now the conducting sphere is connected to the ground through a conducting wire that removes the electron from the conducting sphere. Note that positive charges will not flow to the ground because they are attracted by the negative charges of the rod. When the grounding wire is removed from the conductor, the positive charges remain near the charged rod. Now the positive charge gets distributed uniformly on the surface of the conductor By this process, the neutral conducting sphere becomes positively charged.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
63. A sensitive electrical instrument which is to be protected from external electrical disturbance can be kept inside this cavity. This is called _____
- Electrostatic capacitor
- Electrostatic receiver
- Electrostatic shielding
- Electrostatic potential
Explanation
Consider a cavity inside the conductor. Whatever be the charges at the surfaces and whatever be the electrical disturbances outside, the electric field inside the cavity is zero. A sensitive electrical instrument which is to be protected from external electrical disturbance can be kept inside this cavity. This is called electrostatic shielding.
64. Which is an instrument used to demonstrate Electrostatic shielding?
- Maxwell cage
- Faraday cage
- Coulomb cage
- Thomson cage
Explanation
Faraday cage is an instrument used to demonstrate Electrostatic shielding. It is made up of metal bars. If an artificial lightning jolt is created outside, the person inside is not affected. During lightning accompanied by a thunderstorm, it is always safer to sit inside a bus than in open ground or under a tree. The metal body of the bus provides electrostatic shielding, since the electric field inside is zero.
65. Which is a non-conducting material and has no free electrons?
- Bipolar
- Transmitter
- Dielectric
- All the above
Explanation
A dielectric is a non-conducting material and has no free electrons. The electrons in a dielectric are bound within the atoms.
66. Which among the following is not the example of dielectrics?
- Ebonite
- Tin
- Glass
- Mica
Explanation
Ebonite, glass and mica are some examples of dielectrics. When an external electric field is applied, the electrons are not free to move anywhere but they are realigned in a specific way. A dielectric is made up of either polar molecules or non-polar molecules.
67. Which is one in which centres of positive and negative charges coincide?
- Polar molecule
- Non-polar molecule
- Both polar molecule and Non-polar molecule
- None of the above
Explanation
A non-polar molecule is one in which centres of positive and negative charges coincide. As a result, it has no permanent dipole moment. When an external electric field is applied, the centres of positive and negative charges are separated by a small distance which induces dipole moment in the direction of the external electric field. Then the dielectric is said to be polarized by an external electric field.
68. Which among the following is not the example of Non-polar molecule?
- H2
- O2
- HCL
- None of the above
Explanation
Examples of non-polar molecules are hydrogen (H2 ), oxygen (O2 ), and carbon dioxide (CO2 ) etc.
69. Which among the following is not the example of Polar molecule?
- H2O
- N2O
- NH3
- None of the above
Explanation
Examples of polar molecules are H2 O, N2 O, HCl, NH3.
70. Which among the following statement is correct regarding polar molecules?
- In polar molecules, the centres of the positive and negative charges are separated even in the absence of an external electric field. They have a permanent dipole moment. Due to thermal motion, the direction of each dipole moment is oriented randomly.
- Hence the net dipole moment is maximum in the absence of an external electric field. When an external electric field is applied, the dipoles inside the material tend to align in the opposite direction of the electric field. Hence a net dipole moment is induced in it. Then the dielectric is said to be polarized by an external electric field.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Hence the net dipole moment is zero in the absence of an external electric field. When an external electric field is applied, the dipoles inside the material tend to align in the direction of the electric field. Hence a net dipole moment is induced in it. Then the dielectric is said to be polarized by an external electric field.
71. Which is defined as the total dipole moment per unit volume of the dielectric?
- Capacitance
- Conductance
- Polarisation
- Alignment
Explanation
In the presence of an external electric field, the dipole moment is induced in the dielectric material. Polarisation ρ P is defined as the total dipole moment per unit volume of the dielectric. For most dielectrics (linear isotropic), the Polarisation is directly proportional to the strength of the external electric field. P = XeEext.
72. In P = Xe Eext, Xe is a constant called _____
- Electric susceptibility
- Electric alignment
- Electric conductance
- Electric orientation
Explanation
In P = Xe Eext, Xe is a constant called the electric susceptibility which is a characteristic of each dielectric.
73. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Induced Electric field inside the dielectric?
- When an external electric field is applied on a conductor, the charges are aligned in such a way that an internal electric field is created which tends to cancel the external electric field. But in the case of a dielectric, which has no free electrons, the external electric field only realigns the charges so that an internal electric field is produced.
- The magnitude of the internal electric field is smaller than that of external electric field. Therefore, the net electric field inside the dielectric is not zero but is parallel to an external electric field with magnitude less than that of the external electric field. For example, let us consider a rectangular dielectric slab placed between two oppositely charged plates.
- The uniform electric field between the plates acts as an external electric field Eext which polarizes the dielectric placed between plates. The positive charges are induced on one side surface and negative charges are induced on the other side of surface. But inside the dielectric, the net charge is zero even in a small volume.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
74. When the external electric field applied to a dielectric is very large, it tears the atoms apart so that the bound charges become free charges. Then the dielectric starts to conduct electricity. This is called _____
- Dielectric resistance
- Dielectric strength
- Dielectric breakdown
- All the above
Explanation
When the external electric field applied to a dielectric is very large, it tears the atoms apart so that the bound charges become free charges. Then the dielectric starts to conduct electricity. This is called dielectric breakdown.
75. The maximum electric field the dielectric can withstand before it breaks down is called ___
- Dielectric strength
- Dielectric capacitance
- Dielectric resistance
- Dielectric potential
Explanation
The maximum electric field the dielectric can withstand before it breaks down is called dielectric strength. For example, the dielectric strength of air is 3 × 106 V m–1. If the applied electric field increases beyond this, a spark is produced in the air.
76. Which is a device used to store electric charge and electrical energy?
- Inductor
- Resistor
- Capacitor
- None of the above
Explanation
Capacitor is a device used to store electric charge and electrical energy. It consists of two conducting objects (usually plates or sheets) separated by some distance. Capacitors are widely used in many electronic circuits and have applications in many areas of science and technology.
77. Which among the following substance has highest Dielectric strength?
- Teflon
- Mica
- Paper
- Air
Explanation
Mica – 100 × 106Vm–1, Teflon – 60 × 106Vm–1, Paper – 16 × 106Vm–1, Air – 3 × 106Vm–1, Pyrex glass – 14 × 106Vm–1.
78. Which among the following statement is correct?
- A simple capacitor consists of two parallel metal plates separated by a small distance. When a capacitor is connected to a battery of potential difference V, the electrons are transferred from one plate to the other plate by battery so that one plate becomes negatively charged with a charge of –Q and the other plate positively charged with +Q.
- The potential difference between the plates is equivalent to the battery’s terminal voltage. If the battery voltage is increased, the amount of charges stored in the plates decrease. In general, the charge stored in the capacitor is inverse to the potential difference between the plates. Q = C/V.
- where the C is the proportionality constant called capacitance. The capacitance C of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of the magnitude of charge on either of the conductor plates to the potential difference existing between them. C = .
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
The potential difference between the plates is equivalent to the battery’s terminal voltage. If the battery voltage is increased, the amount of charges stored in the plates also increase. In general, the charge stored in the capacitor is proportional to the potential difference between the plates. Q = C/V.
79. What is the S.I unit of capacitance?
- Farad
- Joule
- Coulomb
- Weber
Explanation
The SI unit of capacitance is coulomb per volt or farad (F) in honour of Michael Faraday. Farad is a larger unit of capacitance. In practice, capacitors are available in the range of microfarad (1µF = 10–6 F) to picofarad (1pF = 10–12 F). Note that the total charge stored in the capacitor is zero (Q – Q = 0). When we say the capacitor stores charges, it means the amount of charge that can be stored in any one of the plates.
80. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor?
- Consider a capacitor with two parallel plates each of cross-sectional area A and separated by a distance d. The electric field between two infinite parallel plates is uniform and is given by E = σ / ∈0 where σ is the surface charge density on either plates (σ = ).
- If the separation distance d is very much smaller than the size of the plate (d2 << A), then the above result can be used even for finite–sized parallel plate capacitor. The electric field between the plates is E = Q / A∈0.
- Since the electric field is uniform, the electric potential difference between the plates having separation d is given by V = Ed = . Therefore, the capacitance of the capacitor is given by C = = . From the equation it is evident that capacitance is directly proportional to the area of cross section and is inversely proportional to the distance between the plates.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
81. The energy stored per unit volume of space is defined as _____
- Energy resistance
- Energy potential
- Energy density
- Energy potential
Explanation
The energy stored per unit volume of space is defined as energy density uE = . From equation we get uE = ∈0 E2.
82. Which among the following statement is correct
- Capacitor not only stores the charge but also it stores energy. When a battery is connected to the capacitor, electrons of total charge –Q are transferred from one plate to the other plate. To transfer the charge, work is done by the battery. This work done is stored as electrostatic potential energy in the capacitor.
- To transfer an infinitesimal charge dQ for a potential difference V, the work done is given by dW = V dQ. Where V = . The total work done to charge a capacitor is W = dQ = . It is important to note that the energy density depends only on the electric field and not on the size of the plates of the capacitor.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
83. Which among the following statement is correct regarding applications of capacitors?
- Flash capacitors are used in digital cameras for taking photographs. The flash which comes from the camera when we take photographs is due to the energy released from the capacitor, called a flash capacitor.
- During cardiac arrest, a device called heart defibrillator is used to give a sudden surge of a large amount of electrical energy to the patient’s chest to retrieve the normal heart function.
- Capacitors are used in the ignition system of automobile engines to increase sparking. Capacitors are used to increase power fluctuations in power supplies and to increase the efficiency of power transmission.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Capacitors are used in the ignition system of automobile engines to eliminate sparking. Capacitors are used to reduce power fluctuations in power supplies and to increase the efficiency of power transmission. However, capacitors have disadvantage as well. Even after the battery or power supply is removed, the capacitor stores charges and energy for some time.
84. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- Effect of dielectrics in capacitors when the battery is disconnected charge (Q) is constant, voltage (V), electric field (E) and energy (U) decreases while capacitance (C) increases.
- Effect of dielectrics in capacitors when the battery is connected charge (Q) is constant, voltage (V), electric field (E) and energy (U) increase while capacitance (C) decrease.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Effect of dielectrics in capacitors when the battery is connected charge (Q) is increased, voltage (V), electric field (E) are constant while capacitance (C) and Energy (U) increase.
85. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Capacitor in series?
- Consider three capacitors of capacitance C1 ,C2 and C3 connected in series with a battery of voltage V. As soon as the battery is connected to the capacitors in series, the electrons of charge –Q are transferred from negative terminal to the right plate of C3 which pushes the electrons of same amount –Q from left plate of C3 to the right plate of C2 due to electrostatic induction.
- Similarly, the left plate of C2 pushes the charges of –Q to the right plate of C1 which induces the positive charge +Q on the left plate of C1. At the same time, electrons of charge –Q are transferred from left plate of C1 to positive terminal of the battery. By these processes, each capacitor stores the same amount of charge Q.
- The capacitances of the capacitors are in general different, so that the voltage across each capacitor is also different and are denoted as V1, V2 and V3 respectively. The sum of the voltages across the capacitor must be equal to the voltage of the battery V=V1+V2 + V3. If three capacitors in series are considered to form an equivalent single capacitor Cs, (1/Cs) = (1/C1) + (1/C2) + (1/C3).
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
86. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Capacitance in parallel

- Consider three capacitors of capacitance C1 , C2 and C3 connected in parallel with a battery of voltage V. Since corresponding sides of the capacitors are connected to the same positive and negative terminals of the battery, the voltage across each capacitor is equal to the battery’s voltage. Since capacitances of the capacitors are different the charge stored in each capacitor is not the same.
- Let the charge stored in the three capacitors be Q1 , Q2, and Q3 respectively. According to the law of conservation of total charge, the sum of these three charges is equal to the charge Q transferred by the battery, Q = Q1 +Q2 +Q3. Since Q = CV, we have Q = C1 V + C2 V + C3 V.
- If these three capacitors are considered to form a single equivalent capacitance CP which stores the total charge Q, then we can write Q = CP V. Substituting this in equation we get, 1/ (CP V) = 1/C1V + 1/C2V + 1/C3V. Thus, 1/CP = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + 1/C3. Thus, the equivalent capacitance of capacitors connected in parallel is equal to the sum of the reciprocal of individual capacitances. The equivalent capacitance CP in a parallel connection is always smaller than the largest individual capacitance.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
If these three capacitors are considered to form a single equivalent capacitance CP which stores the total charge Q, then we can write Q = CP V. Substituting this in equation, we get CP V = C1 V + C2 V + C3 V. Thus, CP = C1 + C2 + C3. the equivalent capacitance of capacitors connected in parallel is equal to the sum of the individual capacitances. The equivalent capacitance CP in a parallel connection is always greater than the largest individual capacitance.
87. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Distribution of charges in a conductor
- Consider two conducting spheres A and B of radii r1 and r2 respectively connected to each other by a thin conducting wire. The distance between the spheres is much smaller than the radii of either spheres. If a charge Q is introduced into any one of the spheres, this charge Q is redistributed into both the spheres such that the electrostatic potential is different in both the spheres.
- They are now uniformly charged and attain electrostatic equilibrium. Let q1 be the charge residing on the surface of sphere A and q2 is the charge residing on the surface of sphere B such that Q = q1 + q2 . The charges are distributed only on the surface and there is no net charge inside the conductor
- The electrostatic potential at the surface of the sphere A is given by VA = . The electrostatic potential at the surface of the sphere B is given by VB = . The surface of the conductor is an equipotential. Since the spheres are connected by the conducting wire, the surfaces of both the spheres together form an equipotential surface. This implies that VA = VB. we know q = 4πrσ. Thus, σ1 r1 = σ2 r2. from which we conclude that σr = constant
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Consider two conducting spheres A and B of radii r1 and r2 respectively connected to each other by a thin conducting wire. The distance between the spheres is much greater than the radii of either spheres. If a charge Q is introduced into any one of the spheres, this charge Q is redistributed into both the spheres such that the electrostatic potential is same in both the spheres.
88. Lightning arrester or lightning conductor works on the principle of ______
- Resistance discharge
- Capacitance discharge
- Corona discharge
- Potential discharge
Explanation
Lightning arrester or lightning conductor is a device used to protect tall buildings from lightning strikes. It works on the principle of action at points or corona discharge.
89. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding Action of points?
- Consider a charged conductor of irregular shape. We know that smaller the radius of curvature, the larger is the charge density. The end of the conductor which has larger curvature (smaller radius) has a large charge accumulation.
- As a result, the electric field near this edge is very low and it deionizes the surrounding air. The positive ions are attracted at the sharp edge and negative ions are repelled towards the sharper edge. This reduces the total charge of the conductor near the sharp edge. This is called action of points or corona discharge.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
As a result, the electric field near this edge is very high and it ionizes the surrounding air. The positive ions are repelled at the sharp edge and negative ions are attracted towards the sharper edge. This reduces the total charge of the conductor near the sharp edge. This is called action of points or corona discharge.
90. Who in the year 1929, designed a machine which produces a large amount of electrostatic potential difference, up to several million volts (10-7 V)?
- Robert Van de Graaff
- Nikola Tesla
- Albert Einstein
- Benjamin Franklin
Explanation
In the year 1929, Robert Van de Graaff designed a machine which produces a large amount of electrostatic potential difference, up to several million volts (10-7 V). This Van de Graff generator works on the principle of electrostatic induction and action at points. The high voltage produced in this Van de Graaff generator is used to accelerate positive ions (protons and deuterons) for nuclear disintegrations and other applications.
91. What is the charge of a proton according to Robert Millikan experiment?
a) – 1.6 x 10-9C
b) + 1.6 x 10-19 C
c) -1.9 x 10-19 C
d) -2.6 x 10-19 C
Explanation
Robert Millikan in his famous experiment found that the value of e = 1.6 × 10–19 C. The charge of an electron is −1.6 × 10–19 C and the charge of the proton is +1.6 × 10–19 C.
92. According to coulomb’s law the electrostatic force is inversely proportional to the ___.
a) Distance between charges
b) Square root of the distance between two charges
c) Square of the distance between the charges
d) Product of the magnitude of point charges
Explanation
Coulomb’s law states that the electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of the two point charges and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two point charges.
93. What measure of electrical charges is used in the day to day life?
a) Micro coulomb
b) Milli coulomb
c) Nano coulomb
d) Both a and c
Explanation
Most of the electrical phenomena in day-to-day life involve electrical charges of the order of μC (micro coulomb) or nC (nano coulomb).
94. What is the value of electrostatic force for smaller objects?
a) Always greater than gravitational force.
b) More or less equal to unity.
c) Equal to the gravitational force
d) Less than the gravitational force
Explanation
The electrostatic force is always greater in magnitude than gravitational force for smaller size objects.
95. Choose the correct statements.
i) Superposition principle is not needed to coulomb’s law application for charges.
ii) Superposition principle and Coulomb’s law explain all the phenomena in electrostatics.
iii) Both the Super position principle and coulomb’s law are derivable from each other.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Without the superposition principle, Coulomb’s law will be incomplete when applied to more than two charges. Both the superposition principle and Coulomb’s law form fundamental principles of electrostatics and explain all the phenomena in electrostatics. But they are not derivable from each other.
96. What is the SI unit for the electric field?
a) Newton per coulomb
b) Newton per meter square
c) Newton per meter
d) Newton meter
Explanation
The electric field is a vector quantity and its SI unit is Newton per coulomb (NC–1).
97. Define the electric field path for a isolated negative point charge?
a) Start from the negative charge and ends at infinity.
b) Start and ends at negative charge itself.
c) Start at infinity and ends at the negative charge
d) Start and ends at infinity.
Explanation
For an isolated positive point charge the electric field line starts from the charge and ends only at infinity. For an isolated negative point charge the electric field lines start at infinity and end at the negative charge.
98. Which of the following is not permanent dipole?
a) Water
b) H2S
c) CO
d) HCl
Explanation
In many molecules, the centers of positive and negative charge do not coincide. Such molecules behave as permanent dipoles. Examples: CO, water, ammonia, HCl etc.
99. For which value of θ the magnitude of torque is maximum?
a) 90°
b) 180°
c) 0°
d) 45°
Explanation
The magnitude of this torque is τ θ = pEsin and is maximum when θ=90.
100. What is the value of the torque on the dipole if it is aligned with the electric field?
a) Zero
b) Unity
c) Infinity
d) Negative value
Explanation
This torque tends to rotate the dipole and align it with the electric field E. Once it is aligned with E, the total torque on the dipole becomes zero.
101. Choose the correct statements.
i) Microwave oven works on the principle of torque acting on an electric dipole.
ii) Water molecules are permanent electric dipoles.
iii) Oscillating microwaves produce torque on the water molecules to rotate very fast and produce thermal energy.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Microwave oven works on the principle of torque acting on an electric dipole. The food we consume has water molecules which are permanent electric dipoles. Oven produces microwaves that are oscillating electromagnetic fields and produce torque on the water molecules. Due to this torque on each water molecule, the molecules rotate very fast and produce thermal energy. Thus, heat generated is used to heat the food.
102. The electrostatic potential energy is ______.
a) Independent of the configuration of charges.
b) Dependent on the total momentum of charges.
c) Dependent on the point charges.
d) Independent on the charges.
Explanation
The Coulomb force is a conservative force, the electrostatic potential energy is independent of the manner in which the configuration of charges is arrived at.
103. Choose the correct statements.
i) The potential energy depends on the orientation of the electric dipole.
ii) The potential energy is maximum when the dipole is aligned anti-parallel to the external electric field.
iii) Minimum potential energy if when the dipole is aligned parallel to the external electric field.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
In addition to p and E, the potential energy also depends on the orientation θ of the electric dipole with respect to the external electric field. The potential energy is maximum when the dipole is aligned anti-parallel (θ = π) to the external electric field and minimum when the dipole is aligned parallel (θ = 0) to the external electric field.
104. The electric flux on a surface is dependent on,
i) Electric field pattern
ii) Orientation of the surface
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The electric flux for a given surface depends on both the electric field pattern on the surface area and orientation of the surface with respect to the electric field.
105. The electric field between the plates is _____ everywhere.
a) Zero
b) Unity
c) Uniform
d) Varying
Explanation
The direction of the electric field between the plates is directed from positively charged plate to negatively charged plate and is uniform everywhere between the plates.
106. Choose the incorrect statements.
i) The Electric field is zero outside the conductor.
ii) The potential is same as the surface of the conductor.
iii) At electrostatic equilibrium conductor is always at equipotential.
- i only
- ii only
- iii only
- None of the above
Explanation
The electric field is zero inside the conductor, the potential is the same as the surface of the conductor. Thus at electrostatic equilibrium, the conductor is always at equipotential.
107. Which of these are inversely proportional to the acceleration of the object?
a) Maximum height
b) Velocity
c) Range
d) Time of flight
Explanation
The time of flight, maximum height, range are all inversely proportional to the acceleration of the object.
108. Which of the following is not a type of capacitor?
a) Ceramic
b) Electrolytic
c) Disk
d) Tantalum
Explanation
Capacitors available in various shapes (cylindrical, disk) and types (tantalum, ceramic and electrolytic).
109. In how many ways a dielectric can be inserted into the plates?
a) Two
b) Only one
c) Infinite
d) Based on the voltage difference
Explanation
The dielectric can be inserted into the plates in two different ways. (i) when the capacitor is disconnected from the battery. (ii) when the capacitor is connected to the battery.
110. What value of charge is increased in a capacitor when a dielectric is inserted between the plates?
a) eo
b) ereo
c) er
d) Greater than eo
Explanation
The potential difference V0 across the plates remains constant. But it is found experimentally (first shown by Faraday) that when dielectric is inserted, the charge stored in the capacitor is increased by a factor er.