10th Std Science Lesson Wise Questions in English – Part 3
10th Science Lesson 16 Questions in English
16] Plant And Animal Hormones
1. What does the word ‘Hormone’?
- Message
- Messenger
- To excite
- To react
Explanation
The word hormone is derived from the Greek word “hormon” meaning “to excite”. Both Plants and animals have hormone.
2. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The function of control and coordination in plants is performed by chemical substances produced by the plants called plant hormones.
- In plants several cells are capable of producing hormones
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The function of control and coordination in plants is performed by chemical substances produced by the plants called plant hormones. In plants several cells are capable of producing hormones. The phytohormones are transported to different parts of the plants to perform various physiological functions.
3. ____ acts through chemical messengers, which are produced by specialized glands
- Endocrine
- Exocrine
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
Endocrine glands in vertebrate animals possess a diversified communication system to co-ordinate physiological and metabolic functions by chemical integration. The endocrine system acts through chemical messengers known as hormones which are produced by specialized glands.
4. Which of the following process are controlled by hormones?
- Digestion
- Metabolism
- Growth
- Reproduction
- 1, 2, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- 1, 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Physiological processes such as digestion, metabolism, growth, development and reproduction are controlled by hormones.
5. Which of the following responses in plants are controlled by plant hormones?
- Morphology
- Physiology
- Biochemical response
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Plant hormones are organic molecules that are produced at extremely low concentration in plants. These molecules control morphological, physiological and biochemical responses.
6. How many major classes of plant hormones are there?
- 5
- 6
- 3
- 9
Explanation
There are five major classes of plant hormones. They are:
- Auxins
- Cytokinin
- Gibberellins
- Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Ethylene
7. Which of the following plant hormone inhibit plant growth?
- Auxins
- Abscisic acid
- Ethylene
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Among all these plant hormones auxins, cytokinin and gibberellins promote plant growth while abscisic acid and ethylene inhibit plant growth.
8. Which of the following was the 1st plant hormone to be discovered?
- Auxin
- Ethylene
- Cytokinin
- Abscisic acid
Explanation
Auxins (Gk. auxein = to grow) were the first plant hormones discovered. The term auxin was introduced by Kogl and HaagenSmith (1931).
9. Where does the Auxin are produced?
- Petals
- Tip of root
- Tip of stem
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Auxins are produced at the tip of stems and at the tip of roots from where they migrate to the zone of elongation.
10. Who concluded that some ‘influence’ was transmitted from tip of the coleoptile to basal region?
- Darwin
- Einstein
- Went
- Mendel
Explanation
Charles Darwin (1880), observed unilateral growth and curvature of canary grass (Phalaris canariensis) coleoptiles. He came to the conclusion that some ‘influence’ was transmitted from the tip of the coleoptile to the basal region. This ‘influence’ was later identified as Auxin by Went.
11. Who demonstrated the effect of auxin in plants?
- Darwin
- Einstein
- Went
- Mendel
Explanation
Frits Warmolt Went (1903– 990), a Dutch biologist demonstrated the existence and effect of auxin in plants. He did a series of experiments in Avena coleoptiles.
12. What does the term “Auxin” mean?
- To grow
- To move
- To elongate
- To reach
Explanation
From his experiments Went concluded that a chemical diffusing from the tip of coleoptiles was responsible for growth, and he named it as “Auxin” meaning ‘to grow”.
13. How many types of Auxins are there?
- 2
- 5
- 4
- 3
Explanation
Types of Auxins: Auxin is a growth hormone. Auxins are classified into two types, namely natural auxins and synthetic auxins.
14. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Auxins produced by the plants are called natural auxins
- 2, 4 D (2,4 Di-chloro-phenoxy Acetic Acid) is natural auxins
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Natural Auxins: Auxins produced by the plants are called natural auxins. Example: IAA (Indole – 3 – Acetic Acid)
Synthetic Auxins: Artificially synthesized auxins that have properties like auxins are called as synthetic auxins. Example: 2, 4 D (2,4 Dichlorophenoxy Acetic Acid).
15. Which of the following are the effects produced by Auxin?
- Formation of seed
- Elongation of stems
- Apical dominance
- Formation of abscission layer
- 1, 2, 3
- 1, 3, 4
- 2, 3, 4
- All the above
Explanation
Auxins bring about a variety of physiological effects in different parts of the plant body. Auxins promote the elongation of stems and coleoptiles which makes them to grow. Auxins induce root formation at low concentration and inhibit it at higher concentration. The auxins produced by the apical buds suppress growth of lateral buds. This is called apical dominance. Auxins prevent the formation of abscission layer.
16. Which of the following fruit cannot be produced by Parthenocarpy method?
- Watermelon
- Lime
- Grapes
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Seedless fruits without fertilization are induced by the external application of auxins. (Parthenocarpy). Examples: Watermelon, Grapes, Lime etc.
17. Which of the following are synthetic acetic acid?
- Phenyl Acetic Acid
- Indole 3 Butyric Acid
- α-Naphthalene Acetic Acid
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Phenyl Acetic Acid (PAA), and Indole 3 Acetonitrile (IAN) are natural auxins. Indole 3 Butyric Acid (IBA), Indole-3- Propionic Acid, α-Naphthalene Acetic Acid (NAA), 2, 4, 5-T (2,4,5 Tri-chloro-phenoxy Acetic Acid) are some of the synthetic auxins.
18. Which plant hormones that promote cell division?
- Auxin
- Renin
- Cytokinin
- Pepsin
Explanation
Cytokinin (Cytos – cell; kinesis – division) are the plant hormones that promote cell division or cytokinesis in plant cells. It was first isolated from Herring fish sperm
19. Zeatin was the cytokinin isolated from______
- Rice
- Wheat
- Zea Mays
- Coconut
Explanation
Zeatin was the cytokinin isolated from Zea mays. Cytokinin is found abundantly in coconut milk.
20. Which of the following are the effects of Cytokinin?
- Cell division in absence of Auxin
- It delays the process of ageing in plants
- It promotes the growth of lateral buds even in the presence of apical bud
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Physiological effects of Cytokinins:
- Cytokinin induces cell division (cytokinesis) in the presence of auxins.
- Cytokinin also causes cell enlargement
- Cytokinin promote the growth of lateral buds even in the presence of apical bud
- Application of cytokinin delays the process of ageing in plants. This is called Richmond Lang effect.
21. Which of the following hormones in plant are essential for Morphogenesis?
- Auxin
- Renin
- Cytokinin
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Both auxins and cytokinin are essential for the formation of new organs from the callus in tissue culture (Morphogenesis).
22. Kurosawa (1926) observed Bakanae disease in____ crops
- Rice
- Wheat
- Maize
- None
Explanation
Gibberellins are the most abundantly found plant hormones. Kurosawa (1926) observed Bakanae disease or foolish seedling disease in rice crops
23. Internodal elongation in rice was caused by_______
- Virus
- Fungus
- Bacteria
- All the above
Explanation
The internodal elongation in rice was caused by fungus Gibberella fujikuroi. The active substance was identified as Gibberellic acid.
24. Application of which of the following stimulate extraordinary elongation of internode?
- Auxin
- Cytokinin
- Renin
- Gibberellins
Explanation
Application of gibberellins on plants stimulate extraordinary elongation of internode. e.g.Corn and Pea.
25. Treatment of rosette plants with ____ induces sudden shoot elongation
- Auxin
- Cytokinin
- Renin
- Gibberellins
Explanation
Treatment of rosette plants with gibberellin induces sudden shoot elongation followed by flowering. This is called bolting.
26. _________ is a growth inhibitor
- Auxin
- Cytokinin
- Abscisic acid
- Gibberellins
Explanation
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a growth inhibitor which regulates abscission and dormancy. It increases tolerance of plants to various kinds of stress.
27. Which of the following is called as stress hormone?
- Auxin
- Cytokinin
- Abscisic acid
- Gibberellins
Explanation
Abscisic Acid is also called as stress hormone. It is found in the chloroplast of plants. ABA promotes the process of abscission (separation of leaves, flowers and fruits from the branch). During water stress and drought conditions ABA causes stomatal closure.
28. As the banana continues to ripen, it produces_______ gas
- Methane
- Ethylene
- Methylene
- Nitrogen
Explanation
Banana is placed in first bag. Tomato is placed in second bag. As the banana continues to ripen in the first bag, it produces ethylene gas. The gas trapped in the bag will cause tomatoes to ripen. The tomatoes remain unripe in the second bag.
29. Which of the following are the effects of Abscisic acid?
- Promotes senescence
- Induces bud dormancy
- Inhibitor of lateral bud growth
- All the above
Explanation
ABA promotes senescence in leaves by causing loss of chlorophyll. ABA induces bud dormancy towards the approach of winter in trees like birch. ABA is a powerful inhibitor of lateral bud growth in tomato.
30. ______ is a gaseous plant hormone.
- Methane
- Ethylene
- Methylene
- Nitrogen
Explanation
Ethylene is a gaseous plant hormone. It is a growth inhibitor. It is mainly concerned with maturation and ripening of fruits.
31. Maximum synthesis of ethylene occurs during ripening of fruits like______
- Apples
- Melons
- Bananas
- All the above
Explanation
Maximum synthesis of ethylene occurs during ripening of fruits like apples, bananas and melons.
32.Which of the following are the effects of ethylene?
- Promotes the ripening of fruits
- Inhibits the elongation of stem and root in dicots
- Breaks the dormancy of buds, seeds and storage organs
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Physiological effects of ethylene:
- Ethylene promotes the ripening of fruits. e.g Tomato, Apple, Mango, Banana, etc.
- Ethylene inhibits the elongation of stem and root in dicots.
- Ethylene hastens the senescence of leaves and flowers.
- Ethylene stimulates formation of abscission zone in leaves, flowers and fruits. This leads to premature shedding
- Ethylene breaks the dormancy of buds, seeds and storage organs.
33. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Endocrine glands in animals possess a versatile communication system to coordinate biological functions
- Exocrine glands and endocrine glands are two kinds of glands found in animals.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Endocrine glands in animals possess a versatile communication system to coordinate biological functions. Exocrine glands and endocrine glands are two kinds of glands found in animals.
34. Which of the following statement is correct about Endocrine gland?
- Endocrine glands are found in different regions of the body of animals as well as human beings.
- They are ductless glands
- Their secretions are called hormones which are produced in minute quantities
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Endocrine glands are found in different regions of the body of animals as well as human beings. These glands are called ductless glands. Their secretions are called hormones which are produced in minute quantities. They act on specific organs which are referred as target organs.
35. Who is the father of ‘Endocrinology’?
- Thomas Hardy
- Thomas Addison
- E.H. Starling
- W. M. Bayliss
Explanation
Th e branch of biology which deals with the study of the endocrine glands and its physiology is known as ‘Endocrinology’. Thomas Addison is known as Father of Endocrinology.
36. Which was the first hormone discovered?
- Prolactin
- Vasopressin
- Secretin
- GTH
Explanation
English physiologists W. M. Bayliss and E. H. Starling introduced the term hormone in 1909. They first discovered the hormone secretin.
37. Which of the following is/are exocrine gland?
- Salivary gland
- Sweat gland
- Mammary gland
- All the above
Explanation
Exocrine glands have specific ducts to carry their secretions e.g salivary glands, mammary glands, sweat glands.
38. Which of the following is not an Endocrine gland?
- Pituitary gland
- Pancreas
- Gonads
- Sweat gland
Explanation
Endocrine glands present in human and other vertebrates are:
- Pituitary gland
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid gland
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Adrenal gland (Adrenal cortex and Adrenal medulla)
- Gonads (Testes and Ovary)
- Thymus gland
39. Pituitary gland is attached to the base of_____
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
Explanation
Th e pituitary gland or hypophysis is a pea shaped compact mass of cells located at the base of the midbrain attached to the hypothalamus by a pituitary stalk.
40. How many lobes does pituitary gland have?
- 2
- 4
- 5
- 1
Explanation
Th e pituitary gland is anatomically composed of two lobes and perform different functions. They are the anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) and the posterior lobe (neurohypophysis). Th e intermediate lobe is non-existent in humans.
41. Which of the following gland is known as master gland?
- Pineal gland
- Pancreas
- Pituitary gland
- Liver
Explanation
The pituitary gland forms the major endocrine gland in most vertebrates. It regulates and controls other endocrine glands and so is called as the “Master gland”.
42. Hormones secreted by ____ lobe of pituitary
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Both a and b
- None
Explanation
Hormones secreted by the anterior lobe (Adenohypophysis) of pituitary. Pituitary gland are the anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) and the posterior lobe (neurohypophysis). The intermediate lobe is non-existent in humans.
43. Which of the following hormone is not secreted by pituitary gland?
- Prolactin
- Growth Hormone
- Melatonin
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Explanation
The hormones secreted by anterior pituitary are:
- Growth Hormone
- Thyroid stimulating Hormone
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
- Gonadotropic Hormone which comprises the Follicle Stimulating Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone
- Prolactin
44. Which of the following statement is correct?
- The anterior pituitary is composed of different types of cells
- They secrete hormones which stimulates the production of hormones by other endocrine glands
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The anterior pituitary is composed of different types of cells and secrete hormones which stimulates the production of hormones by other endocrine glands.
45. Which of the following organ growth are stimulated by Growth Hormone?
- Muscles
- Bones
- Long bones
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
GH promotes the development and enlargement of all tissues of the body. It stimulates the growth of muscles, cartilage and long bones. It controls the cell metabolism.
46. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Dwarfism is caused by over-secretion of growth hormone
- The characteristic features are stunted growth, delayed skeletal formation and mental disability
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Dwarfism is caused by decreased secretion of growth hormone in children. The characteristic features are stunted growth, delayed skeletal formation and mental disability.
47. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Over-secretion of growth hormone leads to gigantism in adult
- Individuals attain abnormal increase in height.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Over-secretion of growth hormone leads to gigantism in children. It is characterised by overgrowth of all body tissues and organs. Individuals attain abnormal increase in height.
48. Which causes abnormal enlargement of head, face, hands and feet in adult?
- Dwarfism
- Gigantism
- Acromegaly
- None
Explanation
Acromegaly:
Excess secretion of growth hormone in adults may lead to abnormal enlargement of head, face, hands and feet.
49. ____ controls the growth of thyroid gland
- GT
- ACTH
- TSH
- GTH
Explanation
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) controls the growth of thyroid gland, coordinates its activities and hormone secretion.
50. ______ stimulates adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland for the production of its hormones
- GT
- ACTH
- TSH
- GTH
Explanation
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland for the production of its hormones. It also influences protein synthesis in the adrenal cortex.
51. ____ hormones are follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone.
- GT
- ACTH
- TSH
- GTH
Explanation
The gonadotropic hormones are follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone which are essential for the normal development of gonads.
52. _____ stimulates the germinal epithelium of testes for formation of sperms
- Follicle stimulating hormone
- Luteinizing hormone
- Melatonin
- Oxytocin
Explanation
In male, Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the germinal epithelium of testes for formation of sperms. In female it initiates the growth of ovarian follicles and its development in ovary.
53. ____ causes ovulation in female
- Follicle stimulating hormone
- Luteinizing hormone
- Melatonin
- Oxytocin
Explanation
In male, Luteinizing hormone promotes the Leydig cells of the testes to secrete male sex hormone testosterone. In female, it causes ovulation (rupture of mature graafian follicle), responsible for the development of corpus luteum and production of female sex hormones oestrogen and progesterone.
54. _____ is also called lactogenic hormone
- Follicle stimulating hormone
- Luteinizing hormone
- Melatonin
- Prolactin
Explanation
Prolactin (PRL) is also called lactogenic hormone. This hormone initiates development of mammary glands during pregnancy and stimulates the production of milk after child birth.
55. _____ is known as a ‘time messenger’.
- Follicle stimulating hormone
- Luteinizing hormone
- Melatonin
- Prolactin
Explanation
Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland. It is known as a ‘time messenger’. It signals night time information throughout the body.
56. Exposure to light of____ at night can decrease melatonin production
- Short wavelength
- Long wavelength
- Medium wavelength
- All the above
Explanation
Exposure to light at night, especially short-wavelength light, can decrease melatonin production interrupting sleep. Suppression of melatonin has been implicated in sleep disturbances and related metabolic disorders.
57. Which of the following hormones are produced by posterior lobe (Neurohypophysis) of pituitary?
- Vasopressin
- Melatonin
- Oxytocin
- Both a and c
Explanation
Hormones secreted by the posterior lobe (Neurohypophysis) of pituitary:
The hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary are:
- Vasopressin or Antidiuretic hormone
- Oxytocin
58. _____ increases reabsorption of water in kidney tubules
- Vasopressin
- Melatonin
- Oxytocin
- Both a and c
Explanation
In kidney tubules it increases reabsorption of water. It reduces loss of water through urine and hence the name antidiuretic hormone or Vasopressin.
59. Deficiency of ADH causes___________
- Diabetes insipidus
- Diabetes mellitus
- Both a and b
- Renal failure
Explanation
Deficiency of ADH reduces reabsorption of water and causes an increase in urine output (polyuria). This deficiency disorder is called Diabetes insipidus.
60. _____ helps in the contraction of the smooth muscles of uterus at the time of child birth
- Vasopressin
- Melatonin
- Oxytocin
- Both a and c
Explanation
Oxytocin helps in the contraction of the smooth muscles of uterus at the time of child birth and milk ejection from the mammary gland after child birth.
61. How many lobes does thyroid gland have?
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Explanation
The thyroid gland is composed of two distinct lobes lying one on either side of the trachea. The two lobes are connected by means of a narrow band of tissue known as the isthmus.
62. Which of the following are involved in thyroid formation?
- Iodine
- Calcium
- Amino acid tyrosine
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
An amino acid tyrosine and iodine are involved in the formation of thyroid hormone. The hormones secreted by the thyroid gland are
- Triiodothyronine (T3)
- Tetraiodothyronine or Thyroxine (T4)
63. Which of the following about thyroid hormone is correct?
- Increases oxygen consumption in tissues
- Influences the activity of central nervous system.
- Production of energy by maintaining the Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) of the body
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Functions of thyroid hormones:
- Increases oxygen consumption in tissues
- Production of energy by maintaining the Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) of the body.
- Helps to maintain normal body temperature.
- Influences the activity of central nervous system.
- Controls the growth of body, bone formation and development of gonads.
64. Which of the following regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism?
- Thyroid Gland
- Thymus gland
- Adrenal gland
- Parathyroid gland
Explanation
The functions of thyroid hormones are:
- Essential for normal physical, mental and personality development. It is also known as personality hormone.
- Regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism.
65. Who among the following first crystallised thyroxine hormone?
- Edward C. Kendal
- George Barger
- Charles Harrington
- Charles Hammlock
Explanation
Edward C. Kendal in 1914 first crystallised thyroxine hormone. Charles Harrington and George Barger identified the molecular structure of thyroxine in 1927. Thyroid gland requires “120 µg” of iodine every-day for the production of thyroxine.
66. Which of the following are the abnormal conditions are simple goitre?
- Simple goitre
- Cretinism
- Myxoedema
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Hypothyroidism is caused due to the decreased secretion of the thyroid hormones. The abnormal conditions are simple goitre, cretinism and myxoedema.
67. In which of the following region of India Goitre is mostly prevalent?
- Western ghats
- Eastern ghats
- Deccan Plateau
- Himalayan region
Explanation
Goitre is caused due to the inadequate supply of iodine in our diet. This is commonly prevalent in Himalayan regions due to low level of iodine content in the soil. It leads to the enlargement of thyroid gland which protrudes as a marked swelling in the neck and is called as goitre.
68. Cretinism is caused in______
- Adults
- Children
- Old age people
- All the above
Explanation
Cretinism is caused due to decreased secretion of the thyroid hormones in children. The conditions are stunted growth, mental defect, lack of skeletal development and deformed bones. They are called as cretins.
69. Myxoedema is caused in____
- Adults
- Children
- Old age people
- All the above
Explanation
Myxoedema is s caused by deficiency of thyroid hormones in adults. They are mentally sluggish, increase in body weight, puffiness of the face and hand, oedematous appearance.
70. Which of the following statement about Hyperthyroidism?
- It is caused due to the excess secretion of the thyroid hormones which leads to Grave’s disease
- The symptoms are protrusion of the eyeballs, profuse sweating, loss of body weight and nervousness.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Hyperthyroidism is caused due to the excess secretion of the thyroid hormones which leads to Grave’s disease. The symptoms are protrusion of the eyeballs (Exopthalmia), increased metabolic rate, high body temperature, profuse sweating, loss of body weight and nervousness.
71. In Which surface of thyroid, parathyroid glands are located?
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Dorsal
- Ventral
Explanation
The parathyroid glands are four small oval bodies that are situated on the posterior surface of the thyroid lobes. The chief cells of the gland are mainly concerned with secretion of parathormone.
72. Which of the following metabolism are regulated by parathormone?
- Calcium
- Iron
- Phosphorous
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
The parathormone regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism in the body. They act on bone, kidney and intestine to maintain blood calcium levels.
73. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Removal of parathyroid glands during thyroidectomy (removal of thyroid) causes decreased secretion of parathormone
- Muscle spasm known as Tetany (sustained contraction of muscles in face, larynx, hands and feet)
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The secretion of parathyroid hormone can be altered due to the following conditions. Removal of parathyroid glands during thyroidectomy (removal of thyroid) causes decreased secretion of parathormone. The conditions are:
- Muscle spasm known as Tetany (sustained contraction of muscles in face, larynx, hands and feet).
- Painful cramps of the limb muscles.
74. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Pancreas is an elongated, yellowish gland situated in the loop of stomach and Ileum
- It is exocrine and endocrine in nature
- The endocrine portion is made up of Islets of Langerhans.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Pancreas is an elongated, yellowish gland situated in the loop of stomach and duodenum. It is exocrine and endocrine in nature. The exocrine pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which plays a role in digestion while, the endocrine portion is made up of Islets of Langerhans.
75. Human insulin was first discovered by____
- Fredrick Banting
- Charles Best
- MacLeod
- All the above
Explanation
Human insulin was first discovered by Fredrick Banting, Charles Best and MacLeod in 1921. Insulin was first used in treatment of diabetes on 11th January 1922.
76. The Islets of Langerhans consists of___ types of cells
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 7
Explanation
The Islets of Langerhans consists of two types of cells namely alpha cells and beta cells. The alpha cells secrete glucagon and beta cells secrete insulin.
77. A balance between____ and____ production is necessary to maintain blood glucose
- Insulin
- Glucagon
- Thyroxine
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
A balance between insulin and glucagon production is necessary to maintain blood glucose concentration.
78. Which of the following statement about Insulin is correct?
- It promotes the transport of glucose into the cells.
- Insulin helps in the conversion of glucose into glycogen which is stored in Bile
- It decreases the concentration of glucose in blood.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Insulin:
- Insulin helps in the conversion of glucose into glycogen which is stored in liver and skeletal muscles
- It promotes the transport of glucose into the cells.
- It decreases the concentration of glucose in blood.
79. _____ helps in the breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver
- Insulin
- Glucagon
- zona glomerulosa
- zona fasciculata
Explanation
Glucagon:
- Glucagon helps in the breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver.
- It increases blood glucose levels.
80. Match the following:
- Hyper-glycemia 1. Increase in appetite
- Polyuria 2. Frequent urination
- Polydipsia 3. Increase in blood sugar level
- Polyphagia 4. Increased thirst
- 2, 1, 3, 4
- 4, 1, 2, 3
- 3, 2, 4, 1
- 3, 4, 2, 1
Explanation
- Increase in blood sugar level (Hyper-glycemia).
- Excretion of excess glucose in the urine (Glycosuria).
- Frequent urination (Polyuria).
- Increased thirst (Polydipsia).
- Increase in appetite (Polyphagia).
81. Which gland also called supra renal glands?
- Thyroid
- Pancreas
- Adrenal
- Gonads
Explanation
The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. They are also called supra renal glands. The outer part is the adrenal cortex and the inner part is the adrenal medulla. The two distinct parts are structurally and functionally different.
82. How many layers are there in adrenal cortex?
- 2
- 4
- 3
- 5
Explanation
The adrenal cortex consists of three layers of cells. They are zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis.
83. The glucocorticoids secreted by______
- Zona glomerulosa
- Zona fasciculata
- Zona reticularis
- All the above
Explanation
The glucocorticoids secreted by the zona fasciculata are cortisol and corticosterone
- They regulate carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism.
- It stimulates the formation of glucose from glycogen in the liver.
- It is an anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic agent.
84. The mineralocorticoids secreted by______
- Zona glomerulosa
- Zona fasciculata
- Zona reticularis
- All the above
Explanation
The mineralocorticoids secreted by zona glomerulosa is aldosterone
- It helps to reabsorb sodium ions from the renal tubules.
- It causes increased excretion of potassium ions.
- It regulates electrolyte balance, body fluid volume, osmotic pressure and blood pressure
85. _____ hormones of adrenal cortex serve to maintain the body in living condition
- Cortisol
- Corticosterone
- Epinephrine
- Norepinephrine
Explanation
The cortisol hormones of adrenal cortex serve to maintain the body in living condition and recover it from the severe effects of stress reactions. Thus, an increased output of cortisol is “life-saving” in “shock conditions”. It is also known as life-saving hormone
86. _______ is composed of chromaffin cells
- Pancreas
- Kidney
- Adrenal Medulla
- Adrenal Cortex
Explanation
The adrenal medulla is composed of chromaffin cells. They are richly supplied with sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves.
87. Which of the following hormone is not secreted by adrenal medulla?
- Glucocorticoids
- Adrenaline
- Noradrenaline
- All the above
Explanation
Hormones of Adrenal Medulla:
- Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
- Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline)
88. Which of the following hormones are called as Emergency hormones?
- Glucocorticoids
- Adrenaline
- Noradrenaline
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Adrenaline and Noradrenaline are together called as “Emergency hormones”. It is produced during conditions of stress and emotion. Hence it is also referred as “flight, fright and fight hormone”.
89. Which of the following are the functions of Epinephrine?
- It promotes the conversion of glycogen to glucose in liver and muscles.
- It decreases blood flow through the skin
- It increases heart beat and blood pressure.
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Functions of adrenal medullary hormones:
Epinephrine (Adrenaline):
• It promotes the conversion of glycogen to glucose in liver and muscles. • It increases heart beat and blood pressure. • It increases the rate of respiration by dilation of bronchi and trachea. • It causes dilation of the pupil in eye. • It decreases blood flow through the skin.
Norepinephrine (Noradrenalin): Most of its actions are similar to those of epinephrine.
90. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- The sex glands are of two types the testes and the ovaries
- The testes are present in male, while the ovaries are present in female.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
The sex glands are of two types the testes and the ovaries. The testes are present in male, while the ovaries are present in female.
91. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Testes are the reproductive glands of the males.
- They are composed of seminiferous tubules, Leydig cells and Sertoli cells
- They secrete the male sex hormone called progesterone
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Testes are the reproductive glands of the males. They are composed of seminiferous tubules, Leydig cells and Sertoli cells. Leydig cells form the endocrine part of the testes. They secrete the male sex hormone called testosterone
92. Which of the following are the functions of testosterone?
- It influences the process of spermatogenesis.
- It stimulates protein synthesis and controls muscular growth.
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Functions of testosterone:
- It influences the process of spermatogenesis.
- It stimulates protein synthesis and controls muscular growth.
- It is responsible for the development of secondary sexual characters (distribution of hair on body and face, deep voice pattern, etc).
93. Which of the following hormone is not secreted by Ovary?
- Estrogen
- Prolactin
- Progesterone
- None
Explanation
The ovaries are the female gonads located in the pelvic cavity of the abdomen. They secrete the female sex hormones:
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
Prolactin is secreted by Pituitary gland.
94. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Estrogen is produced by the Graafian follicles of the ovary
- Progesterone from the corpus luteum that is formed in the ovary
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Estrogen is produced by the Graafian follicles of the ovary and progesterone from the corpus luteum that is formed in the ovary from the ruptured follicle during ovulation.
95. Which of the following are the functions of Estrogen?
- It brings about the changes that occur during puberty.
- It stimulates the maturation of ovarian follicles in the ovary.
- It promotes the development of secondary sexual characters
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 2, 3
- All the above
Explanation
Functions of estrogens:
- It brings about the changes that occur during puberty.
- It initiates the process of oogenesis.
- It stimulates the maturation of ovarian follicles in the ovary.
- It promotes the development of secondary sexual characters (breast development, high pitched voice etc).
96. Which of the following gland is partly an endocrine gland and partly a lymphoid gland?
- Thyroid
- Parathyroid
- Thymus
- Testes
Explanation
Thymus is partly an endocrine gland and partly a lymphoid gland. It is located in the upper part of the chest covering the lower end of trachea. Thymosin is the hormone secreted by thymus.
97. Which of the following are the functions of Thymosin?
- It has a stimulatory effect on the immune function
- It stimulates the production and differentiation of lymphocytes
- 1 alone
- 2 alone
- 1, 2
- None
Explanation
Functions of Thymosin:
- It has a stimulatory effect on the immune function.
- It stimulates the production and differentiation of lymphocytes.
10th Science Lesson 17 Questions in English
17] Reproduction In Plants And Animals
1. Assertion (A): All living organisms have the ability to produce of its own kind by reproduction.
Reasoning(R): Reproduction ensures continuity and survival of the species on earth.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
“Living organisms cannot survive for an indefinite period on earth. All living organisms have the ability to produce more of its own kind by the process called reproduction. Reproduction is the unfolding of life forms where new individuals are formed. It ensures continuity and survival of the species. This process is to preserve individual species and it is called as self-perpetuation.
2. Which of these contain the genetic materials of living organisms?
a) Gametes
b) Embryo
c) Estrogen
d) Placenta
Explanation
In sexual reproduction off springs are produced by the union of male and female gametes (sperm and egg). The male and female gametes contain the genetic material or genes present on the chromosomes which transmit the characteristic traits to the next generation.
3. Which of the following is not a plant reproduction method?
a) Vegetative
b) Chemical
c) Asexual
d) Sexual
Explanation
There are three types of reproduction in plants namely i) Vegetative ii) Asexual and iii) Sexual reproduction.
4. Choose the incorrect statements about the vegetative reproduction method.
i) New plants are formed from vegetative cells or from the plant organs.
ii) Part of a plant detached from the parent body and grows into an independent plant.
iii) No mitotic division and only has the gametic fusion.
iv) The daughter plants are genetically different from the parent plant.
a) i, iii, iv only
b) ii, iv only
c) i, ii only
d) iii, iv only
Explanation
In this type, new plantlets are formed from vegetative (somatic) cells, buds or organs of plant. The vegetative part of plant (root, stem, leaf or bud) gets detached from the parent body and grows into an independent daughter plant. It has only mitotic division, no gametic fusion and daughter plants are genetically similar to the parent plant.
5. Which of these plant parts can produce the vegetative reproduction?
a) Bulbils
b) Leaves
c) Roots
d) All the above
Explanation
Vegetative reproduction may take place through leaves, stems, roots and bulbils.
6. In which of these plants leaves are involved in reproduction?
a) Pteridophytes
b) Drosophila
c) Bryophyllum
d) Bryophytes
Explanation
Leaves: In Bryophyllum small plants grow at the leaf notches.
7. Which part of strawberry plant is involved in vegetative reproduction?
a) Stems
b) Leaves
c) Fruits
d) Roots
Explanation
Stems: In strawberry aerial weak stems touch the ground and give off adventitious roots and buds. When the connections with the parent plant are broken, the offspring become independent.
8. Which of the following does not reproduce using its roots?
a) Asparagus
b) Sweet potato
c) Agave
d) Parsnip
Explanation
Root: Tuberous roots (Asparagus and Sweet potato) can be used for vegetative propagation.
9. Which part of plants is modified as bulbils in some plants?
a) Roots
b) Flower buds
c) Leaves
d) Stems
Explanation
Bulbils: In some plants the flower buds modified into globose which are called as bulbils, when these falls on the ground they grow into new plants. e.g. Agave.
10. Which of these is not a type of vegetative reproduction?
a) Fragmentation
b) Gametes fusion
c) Budding
d) Regeneration
Explanation
Other types of Vegetative Reproduction: Fragmentation, Fission, Budding and Regeneration.
11. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Fragmentation is breaking the filamentous algae into many fragments.
ii) Each fragment has at least one cell to form a new filament of algae by cell division.
iii) Agave is an example for the fragmentation reproduction.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Fragmentation: In filamentous algae breaking of the filament into many fragments is called fragmentation. Each fragment having at least one cell, may give rise to a new filament of the algae by cell division e.g. Spirogyra.
12. Identify the Incorrect match.
A. Regeneration i) Planaria
B. Fission ii) Asparagus
C. Fragmentation iii) Spirogyra
D. Budding iv) Yeast
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) iv only
Explanation
Fission: In this type the parent cell divides into two daughter cells and each cell develops into a new adult organism e.g. Amoeba.
Budding: Formation of a daughter individual from a small projection, the bud, arising on the parent body is called budding. e.g. Yeast.
Regeneration: The ability of the lost body parts of an individual organism to give rise to an whole new organism is called regeneration. It takes place by specialized mass of cells e.g Hydra and Planaria.
13. How many daughter cells are divided from the parent cell by the fission method?
a) 4
b) 10
c) 2
d) 5
Explanation
Fission: In this type the parent cell divides into two daughter cells and each cell develops into a new adult organism e.g. Amoeba.
14. Choose the correct statements about the asexual reproduction method.
i) Offspring is produced by a single parent without forming fusion of gametes.
ii) Both the mitotic and meiosis cell divisions occur.
iii) Parent and the off springs are not identical and they are genetically different.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Production of an offspring by a single parent without the formation and fusion of gametes is called asexual reproduction. It involves only mitotic cell divisions and meiosis does not occur. Offspring produced by asexual reproduction are not only identical to parents but are also exact copies of their parent.
15. Which of these reproduce by the asexual reproduction method?
a) Amoeba
b) Hydra
c) Bacteria
d) Yeast
Explanation
Asexual reproduction occurs by spore formation. This is the most common method of asexual reproduction in fungi and bacteria.
16. Arrange the correct order of the asexual reproduction process.
i) Each nucleus with small amount of cytoplasm develops into a spore.
ii) Asexual reproduction occurs by spore formation.
iii) Nucleus is divided several times within the sporangium.
iv) Spores are liberated and developed as a new hypha after reaching ground or substratum.
v) Sporangium is developed from the fungal hypha.
a) i, iv, ii, iii, v
b) ii, v, iii, i, iv
c) iii, iv, v, i, ii
d) iv, iii, i, ii, v
Explanation
Asexual reproduction occurs by spore formation. During spore formation a structure called sporangium develops from the fungal hypha. The nucleus divides several times within the sporangium and each nucleus with small amount of cytoplasm develops into a spore. The spores are liberated and they develop into new hypha after reaching the ground or substratum.
17. Assertion (A): In a sexual reproduction process two gametes are fused to produce off springs.
Reasoning(R): Male and female sex organs are needed to produce gametes in sexual reproduction.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Sexual reproduction is the process in which two gametes (male and female) are fused to produce offspring of their own kind. In such cases both sexes, male and female sex organs are needed to produce gametes.
18. Match the flower parts.
A. Gynoecium i) Petals
B. Calyx ii) Carpels
C. Androecium iii) Sepals
D. Corolla iv) Stamens
a) i, iii, iv, ii
b) iv, iii, i, ii
c) ii, iii, iv, i
d) iv, i, ii, iii
Explanation
A flower is a modified shoot with limited growth to carry out sexual reproduction. A flower consists of four whorls borne on a thalamus. These whorls are from outside
Calyx – consisting of sepals
Corolla – consisting of petals
Androecium – consisting of stamens
Gynoecium or pistil – consisting of carpels
19. Which of these parts of plants take part in sexual reproduction?
a) Gynoecium
b) Leaves
c) Calyx
d) Corolla
Explanation
The two outermost whorls calyx and corolla are non–essential or accessory whorls as they do not directly take part in the reproduction. The other two whorls androecium and gynoecium are known as the essential whorls, because both take part directly in reproduction.
20. In which part of the plant pollen grains are produced?
a) Calyx
b) Anther
c) Corolla
d) Stems
Explanation
Androecium: Androecium, the male part of flower is composed of stamens. Each stamen consists of a stalk called the filament and a small bag like structure called anther at the tip. The pollen grains are produced in the anther within the pollen sac.
21. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Pollen grains are usually disc like shaped with a three layered wall.
ii) The Hard outer layer is known as exine with germpores.
iii) Intine is a thin inner layer made up of cellulose and pectin.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Pollen grain: Pollen grains are usually spherical in shape. It has two layered wall. The hard outer layer is known as exine. It has prominent apertures called germpore. The inner thin layer is known as intine. It is a thin and continuous layer made up of cellulose and pectin.
22. Which of these pollen cells divides mitotically?
a) Vegetative cell
b) Nucleus
c) Generative cell
d) Cellulose
Explanation
Mature pollen grains contain two cells, the vegetative and the generative cell. Vegetative cell contains a large nucleus. The generative cell divides mitotically to form two male gametes.
23. Which is not a part of gynoecium?
a) Ovary
b) Intine
c) Style
d) Stigma
Explanation
Gynoecium: Gynoecium is the female part of the flower and is made up of carpels. It has three parts: Ovary, Style and Stigma
24. Assertion (A): Androecium is the male part of plant composed of stamens.
Reasoning(R): The female part of plant is made up of carpels called as Gynoecium.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Androecium, the male part of flower is composed of stamens. Gynoecium is the female part of the flower and is made up of carpels.
25. Which of these statements are not true regarding the gynoecium part of a plant?
a) Nucellus is the main part of the ovule.
b) Nucellus is enclosed by two integuments and an opening called micropyle.
c) Ovule is attached to the ovary by carpels.
d) Chalaza is the basal part.
Explanation
The main part of the ovule is the nucellus which is enclosed by two integuments leaving an opening called as micropyle. The ovule is attached to the ovary wall by a stalk known as funiculus. Chalaza is the basal part.
26. How many cells are there in an embryo sac?
a) 7
b) 5
c) 3
d) 2
Explanation
The embryo sac contains seven cells and the eighth nuclei located within the nucellus.
27. Choose the correct statements about the cells of embryo sac.
i) Five cells at the chalaza end are called as antipodal cells.
ii) Two nuclei cells found in the center are called as polar nuclei.
iii) The egg apparatus contain two egg cells and single synergids.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Three cells at the micropylar end form the egg apparatus and the three cells at the chalaza end are the antipodal cells. The remaining two nuclei are called polar nuclei found in the center. In the egg apparatus one is the egg cell (female gamete) and the remaining two cells are the synergids.
28. Which is a process of sexual reproduction in the flowering plants?
a) Pollination and Fertilization
b) Fragmentation and Fission
c) Spore formation
d) Cell division
Explanation
Process of sexual reproduction in flowering plants involves: Pollination and Fertilization
29. Define pollination.
a) Meiosis cell division method.
b) Producing spores by asexual reproduction.
c) Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of a flower.
d) Producing the gametes used for reproduction.
Explanation
The transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of a flower is called as pollination.
30. Which of these are not the significances of pollination?
a) Asexual reproduction
b) Fruits and seed formation
c) Fertilization
d) Cross pollination for creating new varieties.
Explanation
Importance of Pollination: It results in fertilization which leads to the formation of fruits and seed. New varieties of plants are formed through new combination of genes in case of cross pollination.
31. Which of this plant is an example for self-pollination or Autogamy?
a) Bryophyllum
b) Asparagus
c) Hibiscus
d) Hydra
Explanation
Self-pollination (Autogamy): Self-pollination is also known as autogamy. The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of same flower or another flower borne on the same plant is known as self-pollination. e.g. Hibiscus.
32. What are the advantages of self-pollination?
a) Possible in bisexual flowers.
b) Does not depend on pollination agents.
c) No wastage of pollen grains.
d) All the above
Explanation
Advantages of self-pollination: Self-pollination is possible in bisexual flowers. Flowers do not depend on agents for pollination. There is no wastage of pollen grains.
33. Which is not a disadvantage of self-pollination?
a) Less number of seeds.
b) Very big endosperm.
c) New varieties are not possible.
d) Seeds produce weak plants.
Explanation
Disadvantages of self-pollination: The seeds are less in numbers. The endosperm is minute. Therefore, the seeds produce weak plants. New varieties of plants cannot be produced.
34. Which of these plants reproduce by cross-pollination?
a) Apples
b) Grapes
c) Plums
d) All the above
Explanation
Cross-pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anthers of a flower to the stigma of a flower on another plant of the same species e.g. apples, grapes, plum, etc.
35. Which of the following are the advantages of cross pollination?
a) Better plants by proper germination.
b) New varieties of plants are possible.
c) More viable seeds are produced.
d) All the above
Explanation
Advantages of cross pollination: The seeds produced as a result of cross pollination, develop and germinate properly and grow into better plants, cross pollination leads to the production of new varieties. More viable seeds are produced.
36. Which of the following is not a disadvantage of cross pollination?
a) Failure in pollination due to distance barrier.
b) Less wastage of pollen grains.
c) Unwanted characters may be introduced in plants.
d) External agencies are needed for pollination.
Explanation
Disadvantages of cross-pollination: Pollination may fail due to distance barrier. More wastage of pollen grains. It may introduce some unwanted characters Flowers depend on the external agencies for pollination.
37. Which of the following are the agents for cross pollination?
a) Animals
b) Water
c) Wind
d) All the above
Explanation
In order to bring about cross pollination, it is necessary that the pollen should be carried from one flower to another of a different plant. This takes place through the agency of animals, insects, wind and water.
38. Choose the correct statements.
i) Anemophily is the pollination method carried out by the wind.
ii) The anemophilous flowers produce enormous amount of pollen grains.
iii) Pollen grains off this pollination are small, smooth, dry and light weighted.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The pollination with the help of wind is called anemophily. The anemophilous flowers produce enormous amount of pollen grains. The pollen grains are small, smooth, dry and light in weight. Pollen of such plants is blown off at a distance of more than 1,000 km. The stigmas are comparatively large, protruding and sometimes hairy to trap the pollen grains. e.g. Grasses and some cacti.
39. Assertion (A): Pollination with the help of insects is called as entomophily.
Reasoning(R): The flowers attract the insects by their bright color, smell and nectar.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Pollination with the help of insects like honey bees, flies are called entomophily. To attract insects these flowers are brightly colored, have smell and nectar. The pollen grains are larger in size, the exine is pitted, spiny etc., so they can be adhered firmly on the sticky stigma.
40. Which of these insect does the major entomophily pollination?
a) Ants
b) Bumble bees
c) Honey bees
d) Grass hoppers
Explanation
Approximately, 80% of the pollination done by the insects is carried by honey bees.
41. By which of this method the aquatic plants are pollinated?
a) Hydrophily
b) Entomophily
c) Anemophily
d) Zoophily
Explanation
Pollination by water: The pollination with the help of water is called hydrophily. This takes place in aquatic plants. Pollen grains are produced in large numbers. Pollen grains float on surface of water till they land on the stigma of female flowers e.g. Hydrilla, Vallisneria.
42. Which of these pollinates the silk cotton tree?
a) Sun bird
b) Squirrels
c) Honey bees
d) Lady bug
Explanation
Pollination by Animals: When pollination takes place with the help of animals, it is called Zoophily. Flowers of such plants attract animals by their bright color, size, scent etc. e.g. sun bird pollinates flowers of Canna, Gladioli etc., Squirrels pollinate flowers of silk cotton tree.
43. Match
A. Zoophily i) Cacti
B. Anemophily ii) Honey bees
C. Entomophily iii) Hydrilla
D. Hydrophily iv) Canna flowers
a) iii, iv ,i, ii
b) iv, iii, ii, i
c) iv, i, ii, iii
d) iii, i, ii, iv
Explanation
The pollination with the help of wind is called anemophily. E.g. Grasses and some cacti. Pollination with the help of insects like honey bees, flies are called entomophily. The pollination with the help of water is called hydrophily. E.g. Hydrilla, Vallisneria. When pollination takes place with the help of animals, it is called Zoophily. E.g. sun bird pollinates flowers of Canna, Gladioli etc., Squirrels pollinate flowers of silk cotton tree.
44. What is termed as double fertilization?
a) The process of two types of fusion syngamy and triple fusion in embryo sac.
b) Sperm fuses with the secondary nucleus to form the nucleus.
c) Sperm fuses with the egg and forms a triploid zygote.
d) None of the above
Explanation
One sperm fuses with the egg (syngamy) and forms a diploid zygote. The other sperm fuses with the secondary nucleus (Triple fusion) to form the primary endosperm nucleus which is triploid in nature. Since two types of fusion syngamy and triple fusion take place in an embryo sac the process is termed as double fertilization.
45. What is the significance of the fertilization?
a) Seedling under appropriate conditions.
b) New character from two different individuals.
c) Stimulating ovary to develop into fruit.
d) Both b and c
Explanation
Significance of Fertilization: It stimulates the ovary to develop into fruit. It helps in development of new characters from two different individuals.
46. What are the post fertilization changes?
a) Seed development from the ovule.
b) Development of seed coat by the integuments of the ovule.
c) Fruit development by the enlargement of ovary.
d) All the above
Explanation
Post fertilization changes: The ovule develops into a seed. The integuments of the ovule develop into the seed coat. The ovary enlarges and develops into a fruit.
47. Which of these contains the future plant?
a) Seed
b) Gamete
c) Zygote
d) Embryo
Explanation
The seed contains the future plant or embryo which develops into a seedling under appropriate conditions.
48. Assertion (A): Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two haploid cells to form a diploid zygote.
Reasoning(R): Reproductive organs are divided into primary and secondary sex organs.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two haploid gametes (male and the female gametes) to form a diploid individual (zygote). Organs of the reproductive system are divided into primary and secondary (accessory) sex organs.
49. Which of the following is not an accessory sex organ of a male?
a) Vas deferens
b) Cervix
c) Seminal vesicle
d) Epididymis
Explanation
Primary reproductive organs include the gonads (Testes in male and Ovaries in female). Accessory sex organs Male: Vas deferens, epididymis, seminal, vesicle, prostate gland and penis. Female: Fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix and vagina.
50. In which of this process the secondary sex organs are involved?
a) Ovulation process
b) Fertilization
c) Foetus development and child birth
d) All the above
Explanation
The secondary (accessory) sex organs include those structures which are involved in the Process of ovulation, Fusion of the male and female gametes (fertilization), Division of the fertilized egg up to the formation of embryo, Pregnancy, Development of foetus and Child birth.
51. Which of these are true regarding the testes of male?
a) Oval shaped reproductive gland of male.
b) Testes are kept inside a sac like structure scrotum.
c) Lies outside the abdominal cavity of a man.
d) All the above
Explanation
Testes are the reproductive glands of the male that are oval shaped organs which lie outside the abdominal cavity of a man in a sac like structure called scrotum.
52. Which of this tissue covers the testes of male reproductive system?
a) Seminiferous tubules
b) Tunica albuginea
c) Sertoli cells
d) Haploid cells
Explanation
Each testis is covered with a layer of fibrous tissue called tunica albuginea. Many septa from this layer divide the testes into pyramidal lobules, in which lie seminiferous tubules, cells of Sertoli, and the Leydig cells (interstitial cells).
53. Which of the following cells support and provide nutrients to the developing sperms?
a) Follicle cells
b) Haploid cells
c) Leydig cells
d) Sertoli cells
Explanation
The process of spermatogenesis takes place in the seminiferous tubules. The Sertoli cells are the supporting cells and provide nutrients to the developing sperms.
54. Which of these initiates the spermatogenesis process?
a) Luteinizing hormones
b) Leydig cells
c) Mitochondria
d) Graafian follicle
Explanation
The Leydig cells are polyhedral in shape and lie between the seminiferous tubules and secrete testosterone. It initiates the process of spermatogenesis.
55. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The ovaries are located on the right side of the lower abdomen.
ii) Ovaries lie near the lateral end of fallopian tube.
iii) Ovary is a compact structure of an outer cortex and an inner medulla layer.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The ovaries are located on either side of the lower abdomen composed of two almond shaped bodies each lying near the lateral end of fallopian tube. Each ovary is a compact structure consisting of an outer cortex and an inner medulla.
56. Which of these cells in the ovum forms the primary follicle?
a) Haploid cells
b) Cytoplasm
c) Granulosa cells
d) Gametes
Explanation
The cortex is composed of a network of connective tissue called as stroma and is lined by the germinal epithelium. The epithelial cells called the granulosa cells surround each ovum in the ovary together forming the primary follicle.
57. Name the fluid that fills the grown ovum.
a) Graafian follicle
b) Haploid
c) Perivitelline
d) Hyaluronidase
Explanation
As the egg grows larger, the follicle also enlarges and gets filled with the fluid and is called the Graafian follicle.
58. Which of the following is not a function of gametogenesis?
a) Sperm formation in male and ovum in the female
b) Involves spermatogenesis and oogenesis process.
c) Produce gametes with haploid cells.
d) Provides sperm motility in fertilization.
Explanation
The formation of the sperm in male and the ovum in female is called gametogenesis. It involves spermatogenesis (formation of spermatozoa) and oogenesis (the formation of ova). Gametes with haploid cells are produced through gametogenesis.
59. Which part of the spermatozoa is formed by the condensation of nucleus?
a) Sperm head
b) Tail part
c) Middle piece
d) All the above
Explanation
The spermatozoa consist of head a middle piece and tail. The sperm head is elongated and formed by the condensation of nucleus.
60. Name the cap like structure of the anterior part of spermatozoa?
a) Ribosome
b) Acrosome
c) Lysosome
d) None of the above
Explanation
The anterior portion of spermatozoan has a cap like structure called acrosome. It contains hyaluronidase an enzyme that helps the sperm to enter the ovum during fertilization.
61. What are the significances of the middle part of the spermatozoan?
a) Contains the mitochondria.
b) Energy supply for the tail movement.
c) Provides sperm motility for fertilization.
d) All the above
Explanation
The spermatozoan has a short neck connects the head and middle piece which comprises the centrioles. The middle piece contains the mitochondria provides energy for the movement of tail. It brings about sperm motility which is essential for fertilization.
62. Choose the Incorrect statements about the human ovum.
i) The shape of a mature ovum or egg is spherical.
ii) The ovum contains the yolk in the middle.
iii) Ovum contains cytoplasm and the nucleus.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
The mature ovum or egg is spherical in shape. The ovum is almost free of yolk. It contains abundant cytoplasm and the nucleus.
63. How many membranes surround the ovum?
a) 5
b) 7
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation
The ovum is surrounded by three membranes. The plasma membrane is surrounded by inner thin zona pellucida and an outer thick corona radiata. The corona radiata is formed of follicle cells.
64. Which of these membranes forms the surface layer of the ovum?
a) Vitelline Membrane
b) Mucous Membranes
c) Serous Membranes
d) Epithelial Membranes
Explanation
The membrane forming the surface layer of the ovum is called vitelline membrane. The fluid-filled space between zona pellucida and the surface of the egg is called Perivitelline space.
65. Choose the correct statements.
i) In the puberty period the female reproductive system becomes functional.
ii) Girls reach puberty between 11 to 13 years.
iii) Puberty starts earlier in males than in females.
iv) Onset of puberty is triggered by the testosterone hormone in male.
a) i, ii only
b) i, iii, iv only
c) ii, iv only
d) iii, iv only
Explanation
Puberty: The reproductive system in both males and females becomes functional and an increase in sex hormone production resulting in puberty. This phenomenon tends to start earlier in females than in males. Generally boys attain puberty between the ages of 13 to 14 years, while girls reach puberty between 11 to 13 years. In male, the onset of puberty is triggered by the secretion of the hormone testosterone in the testes, in female the secretion of estrogens and progesterone from the ovary.
66. Which of the following is responsible for the secretion of both male and female hormones?
a) Luteinizing Hormone and Follicle stimulating hormone
b) Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
c) Estrogen and Progesterone
d) Anti-Mullerian Hormone
Explanation
The secretion of both male and female hormones is under the control of the pituitary gonadotropins luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH).
67. What are the significances of the menstrual cycle in female human?
a) Cyclic events during the reproductive period of a women’s life.
b) Menstrual cycle starts at the age of 11-13 years.
c) It marks the onset of the puberty and called as menarche.
d) All the above
Explanation
The cyclic events that take place in a rhythmic fashion during the reproductive period of a woman’s life is called menstrual cycle. In human females the menstrual cycle starts at the age of 11-13 years which marks the onset of puberty and is called menarche, and ceases around 48-50 years of age and this stage is termed menopause.
68. What is the minimum time repetition duration for a healthy menstrual flow?
a) 35 days
b) 15 days
c) 28 days
d) 45 days
Explanation
The reproductive period is marked by characteristic events repeated almost every month in physiologically normal women (28 days with minor variation) in the form of a menstrual flow.
69. Which is not a menstrual cycle phase?
a) Fertilization phase
b) Destructive phase
c) Proliferative phase
d) Ovulatory phase
Explanation
The menstrual cycle consists of 4 phases: Menstrual or Destructive Phase, Follicular or Proliferative Phase, Ovulatory Phase and Luteal or Secretory Phase.
70. What are the hormonal changes in the menstrual phase of women?
a) FSH and estrogen increase
b) LH and FSH decrease
c) Decrease in progesterone and estrogen
d) Peak LH
71. What are the changes in the follicular phase of a women cycle?
a) Increase in endometrial thickness.
b) Primary follicles grow to become a fully mature Graafian follicle.
c) Breakdown of uterine endometrial lining leads to bleeding.
d) Development of primary follicles.
72. In which day of the women menstrual cycle the ovulatory phase begin?
a) 14th day
b) 4th day
c) 28th day
d) 7th day
73. Which of these hormones is at peak in the ovulatory phase?
a) FSH
b) LH
c) Estrogen
d) Progesterone
74. Which of these statements is not true regarding the luteal phase of women?
a) Emptied Graafian follicle develops into corpus luteum.
b) Occurs from the 15th–28th day of menstrual cycle.
c) Increase in endometrial thickness.
d) Endometrium is prepared for implantation if fertilization of egg takes place.
75. In which phase of the menstrual cycle the emptied Graafian follicle develops into corpus luteum?
a) Luteal phase
b) Follicular phase
c) Menstrual phase
d) Ovulatory phase
Explanation
Events of Menstrual Cycle and the Role of Hormones
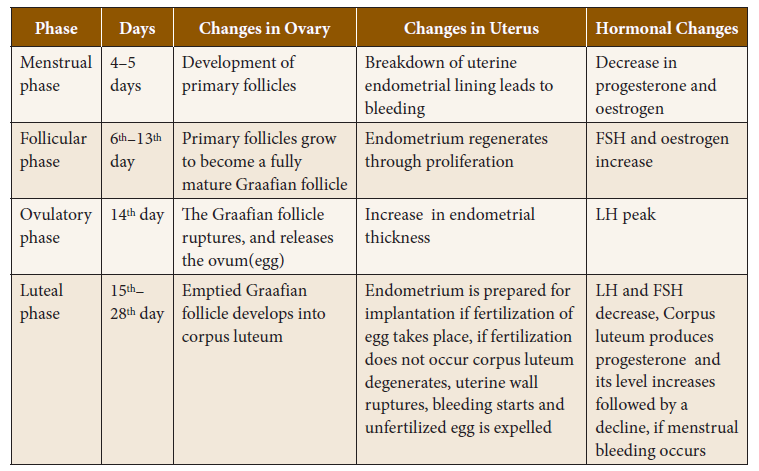
76. Which of these hormones does not make changes in the ovary and the uterus?
a) Estrogen hormone
b) Calcitonin hormone
c) Progesterone hormone
d) Follicle stimulating hormone
Explanation
Changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by the pituitary hormones (LH and FSH) and ovarian hormones (estrogen and progesterone).
77. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Human fertilization is internal and occurs at the female genital tract.
ii) Fertilization takes place in the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
iii) Fertilization must take place within 24 days.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Fertilization in human is internal and occurs in the oviduct of the female genital tract. It takes place usually in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. An oocyte is alive for about 24 hours after it is released from the follicle. Fertilization must take place within 24 hours.
78. Which is called as a fertilized ovum?
a) Gastrula
b) Zygote
c) Cleavage
d) Blastocyst
Explanation
The sperm enters into the ovum and fuses with it, resulting in the formation of a ‘zygote’. This process is called fertilization. The zygote is a fertilized ovum.
79. What is a cleavage in the process of fertilization?
a) Forming a zygote in the ovum.
b) Rearrangement of cells.
c) Series of rapid mitotic zygote divisions.
d) Attaching the blastocyst into the uterine.
Explanation
The first cleavage takes place about 30 hours after fertilization. Cleavage is a series of rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote to form many celled blastula (Blastocyst) which comprises an outer layer of smaller cells and inner mass of larger cells.
80. Define implantation.
a) Process of attaching the fertilized egg (blastocyst) to the uterine wall.
b) Formation of germ layers.
c) Transformation of blastula into gastrula.
d) The sperm enters into the ovum and fuses with to form a zygote.
Explanation
Implantation: The blastocyst (fertilized egg) reaches the uterus and gets implanted in the uterus. The process of attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine wall (endometrium) is called implantation.
81. After how many days the fertilized egg is implanted in the uterus?
a) 15 to 20 days
b) 2 to 3 days
c) 6 to 7 days
d) 10 to 20 days
Explanation
The fertilized egg becomes implanted in about 6 to 7 days after fertilization.
82. What are the functions of gastrulation stage?
a) Transformation of blastula into gastrula.
b) Formation of primary germ layers.
c) Takes place after the implantation process.
d) All the above
Explanation
Gastrulation: The transformation of blastula into gastrula and the formation of primary germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm) by rearrangement of the cells is called gastrulation. This takes place after the process of implantation.
83. Which of these is not a germ layer?
a) Ectoderm
b) Endometrium
c) Mesoderm
d) Endoderm
Explanation
The establishment of the germ layers namely ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm initiates the final phase of embryonic development.
84. At what stage the organs of the foetus attain a functional state?
a) Gastrulation
b) Lactation
c) Organogenesis
d) Implantation
Explanation
Organogenesis: During organogenesis the various organs of the foetus are established from the different germ layers attaining a functional state.
85. Assertion (A): The placenta is a disc shaped structure attached to the uterine wall of the mother.
Reasoning(R): Placenta is a permanent association between the developing embryo and maternal tissues.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Formation of Placenta: The placenta is a disc shaped structure attached to the uterine wall and is a temporary association between the developing embryo and maternal tissues.
86. What are the usages of the placenta?
a) Exchange of food materials only.
b) Oxygen diffusion and carbon dioxide elimination.
c) Excretion of nitrogenous wastes.
d) All the above
Explanation
Placenta allows the exchange of food materials, diffusion of oxygen, excretion of nitrogenous wastes and elimination of carbon dioxide.
87. Which of these are connected by the umbilical cord?
a) Placenta and the foetus
b) Pituitary and the placenta
c) Foetus and the uterus
d) Foetus and the embryo
Explanation
A cord containing blood vessels that connects the placenta with the foetus is called the umbilical cord.
88. What is defined as the gestation period?
a) Time duration for the embryo to develop in the uterus.
b) Process of milk production after the child’s birth.
c) Expulsion of young one’s from the mother’s uterus.
d) Development of two-identical twins.
Explanation
Pregnancy (Gestation): It is the time period during which the embryo attains its development in the uterus.
89. What is the normal gestation period of human?
a) 500 days
b) 625 days
c) 280 days
d) 150 days
Explanation
Normally gestation period of human last for about 280 days. During pregnancy the uterus expands up to 500 times of its normal size.
90. Choose the correct statements regarding Parturition.
i) It is the end of gestation period and expulsion of young one from the mother’s uterus.
ii) Oxytocin from the posterior pituitary stimulates the contractions and forces to expel the baby from the uterus.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Parturition (Child Birth): Parturition is the expulsion of young one from the mother’s uterus at the end of gestation. Oxytocin from the posterior pituitary stimulates the uterine contractions and provides force to expel the baby from the uterus, causing birth.
91. Assertion (A): Two eggs from ovaries fertilized by a different sperm results in Non-identical Twins.
Reasoning(R): Identical twins are developed by a single egg, fertilized and divided into two foetus.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Sometimes ovaries releases two eggs and each is fertilized by a different sperm, resulting in Non-Identical Twins (Fraternal Twins). If single egg is fertilized and then divides into two fetuses, Identical Twins develop.
92. Which of the following statements is not true regarding lactation?
a) The process of milk production after child birth from the mammary glands is called lactation.
b) Colostrum is the first liquid released from the mammary glands after child birth.
c) Milk production from the alveoli of mammary glands is stimulated from the posterior pituitary.
d) The milk ejection is stimulated by the oxytocin hormone.
Explanation
Lactation: The process of milk production after child birth from mammary glands of the mother is called lactation. The first fluid which is released from the mammary gland after child birth is called as colostrum. Milk production from alveoli of mammary glands is stimulated by prolactin secreted from the anterior pituitary. The ejection of milk is stimulated by posterior pituitary hormone oxytocin.
93. Choose the correct statements.
i) Colostrum is the milk produced during the first 2 to 3 days of child birth.
ii) Colostrum contains immune substances and provides immunity to the new born child.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The milk produced from the breast during the first 2 to 3 days after child birth is called colostrum. It contains immune substances and provides immunity to the new born which is essential for the body.
94. Which of these are included as the reproductive health by World Health Organization?
a) Ability to reproduce and regulate fertility.
b) Safe child birth.
c) Maternal and infant survival and well-being.
d) All the above
Explanation
According to World Health Organization (WHO) reproductive health means a total well-being in all aspects of reproduction, ability to reproduce and regulate fertility, women’s ability to undergo pregnancy and safe child birth, maternal and infant survival and well-being.
95. Which of these are included in the national Family Welfare Program scheme?
i) Nutritional supplement to pregnant women and children.
ii) Primary education for children below 14.
iii) Maternal and child health care.
iv) Contraception with health education.
a) i, iv only
b) ii, iii, iv only
c) i, iii, iv only
d) iv only
Explanation
Family welfare program: The National Family Welfare Programme is a comprehensive scheme which includes:
1. Maternal and child health care (MCH)
2. Immunization of mothers, infants and children.
3. Nutritional supplement to pregnant women and children.
4. Contraception with health education, to motivate couples to accept contraceptive methods and to have small family norms which improve economic status, living status and the quality of life.
96. Which of these is not included in the Reproductive and Child Health Care program?
a) Pregnancy and child birth
b) Population control
c) Postnatal care of mother and the child
d) Prevention of reproductive tract infections and sexually transmitted diseases.
Explanation
Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) Programme: It has integrated all services which include Pregnancy and child birth , Postnatal care of the mother and child, Importance of breast feeding and Prevention of reproductive tract infections and sexually transmitted diseases.
97. When did Indian government launch the nation-wide family planning program?
a) 1952
b) 1970
c) 1959
d) 1968
Explanation
Population explosion defined as the sudden and rapid rise in the size of population especially human population. Realizing the dangers inherent in population growth, the Government of India has taken several measures to check population growth and introduced family planning. India has been one of the first countries in the world to launch the nation-wide family planning program in 1952.
98. Which is considered to be the best birth control measure?
a) Family Planning
b) Knowledge about the population effects.
c) Contraception devices
d) None of the above
Explanation
Contraception is one of the best birth control measures. A number of techniques or methods have been developed to prevent pregnancies in women. The devices used for contraception are called contraceptive devices.
99. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the barrier method.
i) Barrier methods use the pills or tablets to stop the release of egg from the ovary.
ii) These methods can be used to protect against sexually transmitted diseases like syphilis and AIDS.
iii) Condoms and Diaphragm or Cervical cap are used in barrier method to prevent sperms to meet the ovum.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Barrier Methods: This method prevents sperms from meeting the ovum. Its entry into the female reproductive tract is prevented by barrier. Condom: Condom prevents deposition of sperms in the vagina. Condoms are made of thin rubber or latex sheath. Condom also protect against sexually transmitted diseases (STD) like syphilis, AIDS. Diaphragm (Cervical cap): Vaginal diaphragm fitting into the vagina or a cervical cap fitting over the cervix. This prevents the entry of sperms into the uterus.
100. Which of these method use pills and tablets for interfere with ovulation process?
a) Hormonal method
b) Barrier method
c) Intra-Uterine devices
d) Tubectomy
Explanation
Hormonal Methods: Hormonal preparations are in the form of pills or tablets (contraceptive pills). These hormones stop (interfere with ovulation) the release of egg from the ovary.
101. Which of the following statements are not true regarding the Intra-uterine devices?
a) Lippe’s loop and Copper-T are the synthetic devices commonly used in India.
b) It is used for reducing the sperm fertilizing capacity and prevents implantation.
c) IUD devices are used for permanent birth control.
d) IUD devices help to give adequate time interval between pregnancies.
Explanation
Intra-Uterine Devices (IUDs): The intrauterine device (IUD) is contraceptive devices inserted into the uterus. There are two synthetic devices commonly used in India are Lippe’s Loop and Copper-T made of copper and plastic (non-irritant). This can remain for a period of 3 years. This reduces the sperm fertilizing capacity and prevents implantation. This also helps to give adequate time interval between pregnancies.
102. Assertion (A): The surgical contraception or sterilization techniques are terminal methods for permanent birth control.
Reasoning(R): The surgical procedure for male is vasectomy and for female it is Tubectomy.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Surgical contraception or sterilization techniques are terminal methods to prevent any pregnancy. This procedure in males is vasectomy (ligation of vas deferens) and in females it is tubectomy (ligation of fallopian tube). These are methods of permanent birth control.
103. Which is not a type of Urinary Tract Infection?
a) Asymptomatic Bacteriuria
b) Thyroid fluctuation
c) Kidney Infection
d) Cystitis Infection
Explanation
Many diseases affect both women and men, but a few diseases occur at a higher frequency in woman. Women are susceptible to UTI from the bacteria that are present on skin, rectum or vagina. This will enter the urethra, before moving upwards. The types of UTI are: Cystitis or Bladder infection, Kidney Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria.
104. What are the main aspects of hygiene?
a) Food hygiene
b) Body hygiene
c) Environment hygiene
d) All the above
Explanation
Hygiene is the practice of healthy living and personal cleanliness. Personal hygiene is caring of one’s own body and health. Social hygiene is proper care of the surrounding environment. The main aspect of hygiene is body hygiene, food hygiene, sanitary hygiene and hygienic environment.
105. What are the measures to be taken for maintaining toilet hygiene?
a) Washing hands before and after using toilets.
b) Clean and dry toilet floors to avoid infection and bad odor.
c) All the materials used inside toilet must be cleaned with disinfectants.
d) All the above
Explanation
The following measures can ensure toilet hygiene: The floors of the toilet should be maintained clean and dry. This helps to reduce the bad odor and also infection. Toilet flush handles, door knobs, faucets, paper towel dispensers, light switches and walls should be cleaned with disinfectants to kill harmful germs and bacteria. Hands should be washed thoroughly with soap before and after toilet use.
106. On which day the world menstrual hygiene day is observed?
a) May 28th
b) March 20th
c) June 1st
d) August 26th
Explanation
Every year May 28 is observed as Menstrual Hygiene day to make girls and women aware of maintaining menstrual hygiene and importance of menstrual hygiene for good health. By way of awareness through films discussions and campaigns menstrual hygiene has taken quite the center stage in recent days.
107. In which year the Indian government launched the menstrual hygiene scheme?
a) 1993
b) 2011
c) 2001
d) 1972
Explanation
The menstrual hygiene scheme to provide subsidized sanitary napkins was launched by the Health ministry in 2011. In Tamil Nadu, UNICEF has developed an affordable incinerator that uses firewood to handle sanitary napkin waste at schools and special wells are equipped where sanitary napkins are composted.
10th Science Lesson 18 Questions in English
18] Genetics
1. Assertion (A): The Genes transfer the characters of parents to the next generation.
Reasoning(R): Genes are responsible for the physical outlook and all the biological functions.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
We inherit characters from one generation to another. It is because of the genes we inherit from our parents. These genes are responsible for the physical outlook and biological functions.
2. Which of the following is not dealt with the study of genetics?
a) Genes
b) Genetic variation
c) Economic status
d) Heredity of organisms
Explanation
The branch of biology that deals with the genes, genetic variation and heredity of living organisms is called genetics.
3. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) Heredity is called as the character transmission from one generation to next generation.
ii) Chromosomes of the living organisms are responsible for the heredity and the variations in the off springs.
iii) Variation refers to the differences in the individuals of different species of off springs and the parents.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Heredity is transmission of characters from one generation to the next generation while variation refers to the differences shown by the individuals of the same species and also by the offspring of the same parents. All these can happen only due to chromosomes.
4. Who discovered the basic principles of heredity?
a) Gregor Mendel
b) John Ray
c) Carolus Linnaeus
d) Adolf Engler
Explanation
Mendel (1822-1884) was an Austrian monk who discovered the basic principles of heredity through his experiments.
5. Which of this plant was used by Mendel for the heredity experiments?
a) Mushrooms
b) Pea plant
c) Beans
d) Grass
Explanation
The reasons for Mendel’s success are he chose the pea plant as it was advantageous for experimental work in many aspects. His experiments are the foundation for modern genetics.
6. Which of these characters is not an advantage of the pea plant?
a) Naturally self-pollinating
b) Long life span
c) Bisexual flowers
d) Defined contrasting characters
Explanation
The advantages of the pea plant are, it is naturally self-pollinating and so is very easy to raise pure breeding individuals. It has a short life span as it is an annual and so it was possible to follow several generations. It is easy to cross-pollinate. It has deeply defined contrasting characters. The flowers are bisexual.
7. How many pairs of contrast characters was chosen by Mendel for his study?
a) 10
b) 7
c) 5
d) 8
Explanation
Mendel had chosen 7 pairs of contrasting characters for his study as shown in the table.
8. Which of these are called as the monohybrid cross?
a) Inheritance of one pair of character.
b) Inheriting two pairs of same characters.
c) Inheritance of one pair of contrasting characters.
d) Inheritance of three pairs of same characters.
Explanation
Crosses involving inheritance of only one pair of contrasting characters are called monohybrid crosses. For example it is a cross between two forms of a single trait like a cross between tall and dwarf plant.
9. What is the character of the F1 generation obtained by Mendel’s Monohybrid Cross parental experiments?
a) Tall and Monohybrid
b) Round seeds and Monohybrid
c) Blue colored flower
d) All the above
Explanation
Mendel’s Explanation of Monohybrid Cross Parental generation: Pure breeding tall plant and a pure breeding dwarf plant. F1 generation: Plants raised from the seeds of pure breeding parental cross in F1 generation were tall and monohybrids.
10. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the monohybrid experiments by Mendel.
i) The Selfing of the F1 monohybrids resulted in the F2 generation plants.
ii) The F2 generation of monohybrid cross experiment resulted with round seed and blue colored plant.
iii) External expression of the particular trait is called as phenotype and its ratio is 3:1 for the monohybrid experiment done by Mendel.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
F2 generation: Selfing of the F1 monohybrids resulted in tall and dwarf plants respectively in the ratio of 3:1. The actual number of tall and dwarf plants obtained by Mendel was 787 tall and 277 dwarf. External expression of a particular trait is known as phenotype. So the phenotypic ratio is 3:1.
11. How many types of plants were obtained by the Mendel’s Monohybrid experiement?
a) 2
b) 5
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation
In the F2 generation 3 different types were obtained:
Tall Homozygous – TT (Pure) – 1
Tall Heterozygous – Tt – 2
Dwarf Homozygous – tt – 1
12. What is the genotypic ratio of the F2 generation obtained by the Mendel’s monohybrid experiment?
a) 1:3:3:1
b) 1:1:2
c) 1:2:1
d) 3:1
Explanation
A genotype is the genetic expression of an organism. The genotypic ratio of F2 generation obtained by Mendel was 1:2:1.
13. Which of the following are the observations made by Mendel’s experiments?
i) Some of the factors are passed on from one generation to another.
ii) The contrasting factors of the generation occur in pairs and may be different from the breeding plants.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Based on the observations it was confirmed by Mendel that ‘factors’ are passed on from one generation to another, now referred to as genes. Tallness and Dwarfness are determined by a pair of contrasting factors tall plant possess a pair of factors (represented by T- taking the first letter of the dominant character) and a plant is dwarf because it possess factors for Dwarfness (represented as t- recessive character).
14. Assertion (A): The homozygous pairs are alike the pure breeding plants.
Reasoning(R): The Unlike pair of plants from the parents are called as Heterozygous.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The contrasting factors occur in pairs and may be alike as in pure breeding tall plants (TT) and dwarf plants (tt). This is referred to as homozygous. If they are unlike (Tt) they are referred to as heterozygous.
15. Choose the correct statements.
i) The two factors making up a pair of same characters are called as alleles.
ii) Phenotype expression of alleles is called as Allelomorphs.
iii) Both the members of each pair are contributed by the dominant parent.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Two factors making up a pair of contrasting characters are called alleles. Phenotypic expressions of alleles are called allelomorphs. One member of each pair is contributed by one parent.
16. Assertion (A): Fertilization brings the two different factors of alternative expression together in a trait.
Reasoning(R): Dominant condition expresses its character by itself and recessive condition masks the character.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
When two factors for alternative expression of a trait are brought together by fertilization the character which expresses itself is called dominant (Tallness) condition and that which is masked is called recessive condition (Dwarfness).
17. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The Gametes gets both the alternative factors from the fertilization process.
ii) The Tallness or dwarfness factor is separate entities present inside a gamete.
iii) The F1 hybrids are self-crossed to produce the two entities separate and unite independently.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
The factors are always pure and when gametes are formed, the unit factors segregate so that each gamete gets one of the two alternative factors. It means that factors for tallness (T) and dwarfness (t) are separate entities and in a gamete either T or t is present. When F1 hybrids are self-crossed the two entities separate and then unite independently, forming tall and dwarf plants.
18. Which of the following statements are not correct regarding the Punnett square?
a) R.C.Punnett devised the Punnett square for the study of genetics.
b) Punnett square is a checker board form graphical representation.
c) Punnett square is a mathematical formula used for predicting the genitival off springs.
d) It is used to calculate the probability of all possible genotypes of off springs in a genetic cross.
Explanation
Punnett square is a checker board form devised by a British geneticist R.C.Punnett for study of genetics. It is a graphical representation to calculate the probability of all possible genotypes of off springs in a genetic cross.
19. Which of this following characters was chosen by Mendel for Dihybrid cross inheritance?
a) Tall and dwarf
b) Shape and color of seed
c) Flower position and color
d) Pod shape and color
Explanation
Di hybrid cross involves the inheritance of two pairs of contrasting characteristics (or contrasting traits) at the same time. The two pairs of contrasting characteristics chosen by Mendel were shape and color of seeds: round-yellow seeds and wrinkled-green seeds.
20. Which of these plants were produced in the first generation in the Mendel’s Dihybrid cross experiment?
a) Round yellow seeds
b) Wrinkled yellow seeds
c) Round green seeds
d) Wrinkled green seeds
Explanation
Mendel crossed pea plants having round yellow seeds with pea plants having wrinkled green seeds. Mendel made the following observations: Mendel first crossed pure breeding pea plants having round-yellow seeds with pure breeding pea plants having wrinkled green seeds and found that only round yellow seeds were produced in the first generation (F1). No wrinkled-green seeds were obtained in the F1 generation. From this it was concluded that round shape and yellow color of the seeds were dominant traits over the wrinkled shape and green color of the seeds.
21. Which of these combinations were not obtained in the second generation of Mendel’s Dihybrid experiment?
a) Round yellow seeds
b) Inflated yellow pods
c) Wrinkled green seeds
d) Wrinkled yellow seeds
Explanation
When the hybrids of F1 generation pea plants having round-yellow seeds were cross-bred by self- pollination then four types of seeds having different combinations of shape and color were obtained in second generation or F2 generation. They were round yellow, round-green, wrinkled yellow and wrinkled-green seeds.
22. State the phenotype Dihybrid ratio of Mendel’s experiment?
a) 9:3:1
b) 9:3
c) 9:3:3:1
d) 1:3
Explanation
The ratio of each phenotype (or appearance) of seeds in the F2 generation is 9:3:3:1. This is known as the Dihybrid ratio.
23. Which of the following results were obtained by Mendel’s Dihybrid cross experiment?
i) Two types of off springs were produced by second generation dihybrid cross.
ii) Four new combinations of traits with green, round, wrinkled and yellow seed appeared in F2 generation.
iii) The F2 generation contains 9 with two dominant traits and one with two recessive traits.
iv) The second generation had 3 plants with one dominant trait and one recessive trait and 3 with another dominant trait and another recessive trait.
a) i, ii only
b) iii, iv only
c) i, iii, iv only
d) ii, iv only
Explanation
Results of a Dihybrid Cross: Mendel got the following results from his dihybrid cross Four Types of Plants: A dihybrid cross produced four types of F2 off springs in the ratio of 9 with two dominant traits, 3 with one dominant trait and one recessive trait, 3 with another dominant trait and another recessive trait and 1 with two recessive traits. New Combination: Two new combinations of traits with round green and wrinkled yellow had appeared in the dihybrid cross (F2 generation).
24. Which of the following is the Law of Dominance?
a) Two homozygous individuals crossed the dominant characters appear in F1.
b) Heterozygous individuals are selfed and the recessive characters appear in F1.
c) Both Homozygous and Heterozygous characters are in F1.
d) All the above
Explanation
Law of Dominance: “When two homozygous individuals with one or more sets of contrasting characters are crossed, the characters that appear in the F1 hybrid are dominant and those that do not appear in F1 are recessive characters”.
25. How many factors enter the gamete when a pair of two contrasting factors brought in F1?
a) None
b) Two
c) One
d) Three
Explanation
Law of Segregation or Law of purity of gametes: “When a pair of contrasting factors are brought together in a F1 hybrid. The two factors of the allelic pair remain together without mixing and when gametes are formed, the two separate out, so that only one enters each gamete.”
26. Define the law of independent assortment.
a) Inheritance of two pairs will assort a single pair of genes of the other pair.
b) Inheritance of two or more pairs simultaneously, genes of one pair assort out independently of the other pair.
c) Only one factors of the gene will be present in the first generation if two pairs are inherited simultaneously.
d) None of the above.
Explanation
Law of independent assortment: “In case of inheritance of two or more pairs of characters simultaneously, the factors or genes of one pair assort out independently of the other pair.”
27. For which of these discoveries T.H.Morgan was awarded Nobel Prize in the year 1993?
a) Determining the role of chromosomes in heredity.
b) Role of mutation.
c) Law of purity of gametes.
d) Structure of DNA.
Explanation
T.H. Morgan was awarded Nobel Prize in 1993 for determining the role of chromosomes in heredity.
28. Who coined the term chromosome in 1888?
a) Waldeyer
b) T.H.Morgan
c) Linnaeus
d) Mendel
Explanation
The human body is made up of million cells. The nucleus of each cell contains thin thread like structures called chromosomes. The term ‘chromosomes’ was first coined by Waldeyer in 1888.
29. Which of these contain the heredity information?
a) Nerves
b) Blood cells
c) Chromosomes
d) Nucleus
Explanation
The chromosomes are the carrier of genetic material which contains the heredity information.
30. Choose the correct statements.
i) Chromosomes are highly condensed coiled chromatin fibers packed with the DNA.
ii) Genes are the segments of DNA which is responsible for the inheritance of a particular character.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
The chromosomes are highly condensed coiled chromatin fibres packed with the DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) that forms the genetic material. Genes are segments of DNA, which are responsible for the inheritance of a particular phenotypic character.
31. In which of these the gene is present on a chromosome?
a) Layer
b) Locus
c) Wall
d) Nucleus
Explanation
Each gene is present at a specific position on a chromosome called its locus. During cell division, the genetic information present in the genes is passed from one generation to another.
32. Choose the correct statements.
i) Chromosomes are thin, long and thread like structures consists of two identical strands.
ii) Each chromatid is made up of spirally coiled thin structure called chromonema.
iii) The sister chromatids are held together by the centromere.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The chromosomes are thin, long and thread like structures consisting of two identical strands called sister chromatids. They are held together by the centromere. Each chromatid is made up of spirally coiled thin structure called chromonema.
33. Name the bead like structures in the chromosomes?
a) Chromatid
b) Chromonema
c) Centromere
d) Chromomeres
Explanation
The chromonema has number of bead-like structures along its length which are called chromomeres.
34. Which of these makes the chromosomes?
a) DNA and RNA
b) Chromosomal protein
c) Metallic ions
d) All the above
Explanation
The chromosomes are made up of DNA, RNA, chromosomal proteins (histones and non-histones) and certain metallic ions. These proteins provide structural support to the chromosome.
35. Which of the following is not true regarding the primary constriction region of chromosome?
a) Two arms of a chromosome meet at a point called primary constriction.
b) Centromere region spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes during cell division.
c) Primary constriction is also known as the Nuclear region.
d) Primary constriction is also known as the centromere.
Explanation
A chromosome consists of the following regions: Primary constriction: The two arms of a chromosome meet at a point called primary constriction or centromere. The centromere is the region where spindle fibres attach to the chromosomes during cell division.
36. What is the significance of the Secondary constriction of a chromosome?
a) Nuclear zone
b) Nucleolar organizer
c) Formation of the nucleolus in the nucleus
d) All the above
Explanation
Secondary constriction: Some chromosomes possess secondary constriction at any point of the chromosome. They are known as the nuclear zone or nucleolar organizer (formation of nucleolus in the nucleus).
37. Which of these provides the stability to the chromosomes?
a) Telomere
b) Centromere
c) Nucleolus
d) Chromatids
Explanation
Telomere: The end of the chromosome is called telomere. Each extremity of the chromosome has a polarity and prevents it from joining the adjacent chromosome. It maintains and provides stability to the chromosomes.
38. Name the chromosomes with satellites at one end?
a) Sat-chromosomes
b) Telomere
c) Sister strand
d) Centromere
Explanation
Satellite: Some of the chromosomes have an elongated knob-like appendage at one end of the chromosome known as satellite. The chromosomes with satellites are called as the sat-chromosomes.
39. What is the main function of the Telomeres?
a) Aging clock in every cell.
b) Carry the inherited characters.
c) Energy provider.
d) Mutation agent.
Explanation
Telomeres act as aging clock in every cell. Telomeres are protective sequences of nucleotides found in chromosomes. As a cell divides every time they become shorter. Telomeres get too short to do their job, causing our cells to age.
40. Which of the following is not a type of centromere?
a) Telocentric
b) Nucleocentric
c) Acrocentric
d) Metacentric
Explanation
Based on the position of centromere, the chromosomes are classified as Telocentric, Acrocentric, Sub metacentric and Metacentric.
41. Match
A. Metacentric i) One end
B. Acrocentric ii) Proximal end
C. Sub-metacentric iii) Center
D. Telocentric iv) Near the center
a) i, iii, iv, ii
b) ii, iv, iii, i
c) iii, i, iv, ii
d) iv, i, iii, ii
Explanation
Telocentric– The centromere is found on the proximal end. They are rod shaped chromosomes.
Acrocentric – The centromere is found at the one end with a short arm and a long arm. They are also rod-shaped chromosomes.
Sub metacentric – The centromere is found near the center of the chromosome thus forming two unequal arms. They are J shaped or L shaped chromosomes.
Metacentric – The centromere occurs in the center of the chromosome and form two equal arms. They are V shaped chromosomes.
42. Which of these are the J shaped chromosomes?
a) Telocentric
b) Sub metacentric
c) Metacentric
d) Acrocentric
Explanation
Sub metacentric – The centromere is found near the center of the chromosome thus forming two unequal arms. They are J shaped or L shaped chromosomes.
43. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The eukaryotic chromosomes are classified into autosomes and allosomes.
ii) Autosomes contain genes that determine the somatic (body) characters.
iii) Male and female have unequal number of autosomes.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
The eukaryotic chromosomes are classified into autosomes and allosomes. Autosomes contain genes that determine the somatic (body) characters. Male and female have equal number of autosomes.
44. Which of these chromosomes is used to determine the sex of an individual?
a) Allosomes
b) Sex chromosomes
c) Hetero- chromosomes
d) All the above
Explanation
Allosomes are chromosomes which are responsible for determining the sex of an individual. They are also called as sex chromosomes or hetero-chromosomes. There are two types of sex chromosomes, X and Y- chromosomes. Human male have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome and human female have two X chromosomes.
45. Choose the correct statements.
i) The number of chromosomes in any living organism is not constant.
ii) In Human each cell contains 23 pair of chromosomes.
iii) Human has 22 pair of allosomes and 23rd pair is an autosome.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
The number of chromosomes in any living organism (animal or plant) is constant. In human, each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. Out of which 22 pairs are autosomes and the 23rd pair is the allosomes or sex chromosome.
46. Assertion (A): The human body cells have pairs of chromosomes which are known as diploid condition.
Reasoning(R): The gametes are said to be haploid as it contains a single set of chromosomes.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
In the body cells of sexually reproducing organisms, the chromosomes generally occur in pairs. This condition is called diploid (2n). The gametes produced by the organisms contain a single set of chromosomes. Hence the gametes are said to be haploid (n).
47. Which of these are known as the karyotype of the cell nucleus of an organism?
a) Number of chromosomes
b) Size of the chromosomes
c) Shape of the chromosomes
d) All the above
Explanation
Karyotype is the number, size and shape of chromosomes in the cell nucleus of an organism.
48. Choose the correct statements.
i) Idiogram is the diagrammatic representation of Karyotype of a species.
ii) Idiogram consists of all the metaphasic chromosomes arranged in heterogeneous pairs.
iii) The heterogeneous pairs are arranged in the decreasing length, thickness, position of centromere and shape.
iv) The sex chromosomes are placed at the end.
a) i, iv only
b) ii, iii, iv only
c) iii only
d) iii, iv only
Explanation
Idiogram is the diagrammatic representation of karyotype of a species. It consists of all the metaphasic chromosomes arranged in homologous pairs according to decreasing length, thickness, position of centromere, shape etc., with the sex chromosomes placed at the end.
49. Choose the correct statements.
i) DNA is the most important constituent of the chromosome as it contains the genetic information.
ii) The double helical structure of James Watson and Francis Crick is the most accepted structure of DNA.
iii) The 3-D model of DNA is based on the X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
DNA is the hereditary material as it contains the genetic information. It is the most important constituent of a chromosome. The most widely accepted model of DNA is the double helical structure of James Watson and Francis Crick. They proposed the three-dimensional model of DNA on the basis of X-ray diffraction studies of DNA obtained by Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins.
50. In which year Watson, Crick and Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize for their discoveries?
a) 1943
b) 1978
c) 1962
d) 1954
Explanation
In appreciation of their discoveries on the molecular structure of nucleic acids Watson, Crick and Wilkins were awarded Nobel Prize for Medicine in 1962.
51. Which of the following is not a component of a polynucleotide or DNA?
a) Protein Molecules
b) Deoxyribose sugar
c) Nitrogenous base
d) Phosphate group
Explanation
Chemical Composition of DNA molecule DNA is a large molecule consisting of millions of nucleotides. Hence, it is also called a polynucleotide. Each nucleotide consists of three components. Sugar molecules – Deoxyribose sugar, a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group
52. Which of these are the types of nitrogenous bases of DNA?
a) Adenine
b) Guanine
c) Cytosine
d) All the above
Explanation
There are two types of nitrogenous bases in DNA. They are Purines (Adenine and Guanine) and Pyrimidines (Cytosine and Thymine)
53. By which of these the nucleotides are formed in a DNA?
a) Purines
b) Proteins
c) Pyrimidines
d) Both a and c
Explanation
Nucleoside and Nucleotide
Nucleoside = Nitrogen base + Sugar
Nucleotide = Nucleoside + Phosphate
The nucleotides are formed according to the purines and pyrimidines present in them.
54. Which of these are the features of Watson and Crick model of DNA?
a) Nitrogenous bases in the center are linked to sugar-phosphate units are the backbone of DNA.
b) DNA molecule consists of two polynucleotide chains forming a double helix structure with two strands run anti-parallel to one another.
c) The nucleotides in a helix are joined by phosphodiester bonds.
d) All the above
Explanation
Watson and Crick model of DNA: DNA molecule consists of two polynucleotide chains. These chains form a double helix structure with two strands which run anti-parallel to one another. Nitrogenous bases in the center are linked to sugar-phosphate units which form the backbone of the DNA. The nucleotides in a helix are joined together by phosphodiester bonds.
55. Choose the correct statements.
i) The Complimentary base pairing is done between the nitrogenous bases of DNA.
ii) Adenine is linked with Thymine with two hydrogen bonds (A=T).
iii) Three hydrogen bonds link the Cytosine and Guanine (C ≡ G).
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Pairing between the nitrogenous bases is very specific and is always between purine and pyrimidine linked by hydrogen bonds. Adenine (A) links Thymine (T) with two hydrogen bonds (A = T). Cytosine (C) links Guanine (G) with three hydrogen bonds(C ≡ G). This is called complementary base pairing.
56. Which of these stabilizes the DNA molecules?
a) Hydrogen bonds
b) Chromosomes
c) Enzymes
d) All the above
Explanation
Hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases make the DNA molecule stable.
57. How many base pairs are in a complete turn of a DNA?
a) 2
b) 4
c) 10
d) 22
Explanation
Each turn of the double helix is 34 A° (3.4 nm). There are ten base pairs in a complete turn.
58. Define the Chargaff rule of DNA base pairing.
a) The proportion of Adenine is always equal to Thymine.
b) The Proportion of Guanine is always equal to Cytosine.
c) The proportion of Adenine is less than Guanine.
d) Both a and b
Explanation
Chargaff rule of DNA base pairing: Erwin Chargaff states that in DNA, the proportion of adenine is always equal to that of thymine and the proportion of guanine always equal to that of cytosine.
59. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) DNA molecule produces exact copies of its own structure during replication process.
ii) The nucleotides of each strand provide the information needed to produce a new strand.
iii) The two resulting daughter cells contain the contrast genetic information of the parent cell.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
DNA replication is one of the basic process that occurs within a cell. DNA molecule produces exact copies of its own structure during replication process. The two strands of a DNA molecule have complementary base pairs the nucleotides of each strand provide the information needed to produce its new strand. The two resulting daughter cells contain exactly the same genetic information as the parent cell.
60. Which of the following are true about the origin of replication?
i) Specific points on the DNA where the replication begins is the origin of replication.
ii) The two strands open and separate at the origin to form the replication fork.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) Both i and ii
d) Neither i nor ii
Explanation
Origin of replication: The specific points on the DNA where the replication begins, is the site of origin of replication. The two strands open and separate at this point form the replication fork.
61. What is the function of the enzyme Helicase?
a) Bind to the origin of replication site.
b) Synthesize the RNA primer.
c) Separates the double helix.
d) Forms the DNA templates.
Explanation
Unwinding of DNA molecule: The enzyme called helicase, bind to the origin of replication site. Helicase separates the two strands of the DNA.
62. Which of the following enzyme removes the twists formed by the unwinding process?
a) Primase
b) Helicase
c) Topoisomerase
d) Lipase
Explanation
The enzyme called topoisomerase separates the double helix above the replication fork and removes the twists formed during the unwinding process. Each of the separated DNA strands function as a template.
63. Which of these forms the RNA primer?
a) Short segment of RNA nucleotides.
b) DNA template
c) Complementary strand
d) Replication strand
Explanation
Formation of RNA primer: An RNA primer is a short segment of RNA nucleotides. The primer is synthesized by the DNA template close to the origin of replication site.
64. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The DNA polymerase adds the nucleotides to the RNA primer.
ii) A new complementary strand of DNA is formed from each of the parent strand.
iii) The synthesis of new complementary strand from the parent strand is bidirectional.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Synthesis of new complementary strand from the parent strand: After the formation of RNA primer nucleotides are added with the help of an enzyme DNA polymerase and a new complementary strand of DNA is formed from each of the parent strand. The synthesis is unidirectional.
65. Assertion (A): The Leading strand is a continuously synthesized daughter strand.
Reasoning(R): The short segments of DNA are synthesized in the other strand known as lagging strand.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
In one strand, the daughter strand is synthesized as a continuous strand which is called leading strand. In the other strand, short segments of DNA are synthesized. This strand is called lagging strand.
66. Which of this enzyme join the Okazaki fragments?
a) Polymerase
b) Ligase
c) Helicase
d) Primase
Explanation
The short segments of DNA are called Okazaki fragments. The fragments are joined together by the enzyme DNA ligase.
67. At which point the DNA replication stops?
a) Leading strand
b) Terminus
c) Short segments
d) DNA ligase
Explanation
The DNA replication stops when the replication fork of the two sides meet at a site called terminus, which is situated opposite to origin of replication site.
68. What are the significances of the DNA?
a) Responsible for the hereditary information transmission.
b) Information required for the protein formation.
c) Developmental process control and life activities of organisms.
d) All the above
Explanation
Significance of DNA: It is responsible for the transmission of hereditary information from one generation to next generation. It contains information required for the formation of proteins. It controls the developmental process and life activities of an organism.
69. What is known as sex determination?
a) Formation of zygote into male or female sex.
b) Sudden changes in the chromosomes.
c) Inheritance from the mother chromosomes.
d) All the above
Explanation
The formation of zygote into male or female sex during development is called sex determination. Sex is determined by the chromosomes of an individual.
70. How many pair of autosomes is present in the human beings?
a) 22
b) 23
c) 44
d) 20
Explanation
Recall that human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes out of which 22 pairs are autosomes and one pair (23rd pair) is the sex chromosome.
71. The Female gametes or the eggs of the human beings are,
i) Homogametic
ii) Similar chromosome type
iii) Not responsible for the sex of the child.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The female gametes or the eggs formed are similar in their chromosome type (22+XX). Therefore, human females are homogametic.
72. Which of the following statement is not true regarding the male gametes?
a) The male gametes or sperm are of three types.
b) Human males are called as heterogametic.
c) Types of male gametes are produced in equal proportions.
d) The human male sperm bears 22+X and 22+Y chromosomes.
Explanation
The male gametes or sperms produced are of two types. They are produced in equal proportions. The sperm bearing (22+X) chromosomes and the sperm bear (22+Y) chromosomes. The human males are called heterogametic.
73. Choose the correct statements.
i) Both the male and female are the chances of probability of sperm fusing with the egg.
ii) The egg X is fused by the X-bearing sperm to produce the XX female.
iii) The Father and mother are both responsible in determining the sex of the child.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Human male is a chance of probability as to which category of sperm fuses with the egg. If the egg (X) is fused by the X-bearing sperm an XX individual (female) is produced. If the egg (X) is fused by the Y-bearing sperm an XY individual (male) is produced. The sperm produced by the father, determines the sex of the child. The mother is not responsible in determining the sex of the child.
74. How many chromosomes are present in individual male?
a) 22-XY
b) 22+XX
c) 44+XY
d) 44-XY
Explanation
Fertilization of the egg (22+X) with a sperm (22+X) will produce a female child (44+XX). while fertilization of the egg (22+X) with a sperm (22+Y) will give rise to a male child (44+XY).
75. Mutation term was introduced by ______ when he observed phenotypic changes in the ____ plant.
a) Hugo de Vries, Evening Primrose
b) Carolus Linnaeus, Pea plant
c) Gregor Mendel, Oenothera lamarckiana
d) Watson, Hibiscus plant
Explanation
The term mutation was introduced by Hugo De Vries in 1901 when he observed phenotypic changes in the evening primrose plant, Oenothera lamarckiana.
76. Which of the following results in mutation?
a) Long lasting change in DNA.
b) Sudden inheritable change in DNA.
c) Slow non-heritable change in the DNA.
d) None of the above
Explanation
Mutation is an inheritable sudden change in the genetic material (DNA) of an organism.
77. How many types of mutations are classified?
a) 4
b) 5
c) 2
d) 3
Explanation
Mutations are classified into two main types, namely chromosomal mutation and gene mutation.
78. Which of these are caused by the chromosomal mutation?
a) Changes in the structure of the chromosomes
b) Changes in the behavior of the chromosomes
c) Changes in the number of chromosomes
d) Both a and c
Explanation
Chromosomal mutation: The sudden change in the structure or number of chromosomes is called chromosomal mutation. This may result in Changes in the structure of chromosomes and Changes in the number of chromosomes.
79. What are the structural changes occurring in the chromosomal mutation?
a) Deletion of chromosomes
b) Duplication of chromosomes
c) Inversion of chromosomes
d) All the above
Explanation
Structural changes in the chromosomes usually occur due to errors in cell division. The Changes in the number and arrangement of genes takes place as a result of deletion, duplication, inversion and translocation in chromosomes.
80. Define ploidy.
a) Translocation of chromosomes in a cell.
b) Changes in the number of chromosomes.
c) Addition or deletion in the number of chromosomes in a cell.
d) Both b and c
Explanation
Changes in the number of chromosomes: They involve addition or deletion in the number of chromosomes present in a cell. This is called ploidy.
81. How many types of ploidy are classified?
a) 4
b) 2
c) 5
d) 3
Explanation
There are two types of ploidy Euploidy and Aneuploidy.
82. What is the condition of Euploidy?
a) Less than or equal to the number of triploid chromosomes.
b) More than the usual number of diploid chromosomes.
c) Less than usual number of diploid chromosomes.
d) Nullisomy condition.
Explanation
Euploidy: It is the condition in which the individual bears more than the usual number of diploid (2n) chromosomes.
83. Assertion (A): Three haploid set of chromosomes result in the condition called as Triploidy.
Reasoning(R): The triploid plants and animals are typically sterile.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
If an individual has three haploid sets of chromosomes, the condition is called triploidy (3n). Triploid plants and animals are typically sterile.
84. What is the advantage of the tetraploidy condition of plants?
a) Cross pollination
b) Increase in the number of seeds.
c) Increased Fruits and flower size.
d) High yield.
Explanation
If it has four haploid sets of chromosomes, the condition is called tetraploidy (4n). Tetraploid plants are advantageous as they often result in increased fruit and flower size.
85. Assertion (A): Aneuploidy is the loss organ of one or more chromosomes in a set.
Reasoning(R): Down’s syndrome is one of the most commonly known aneuploid conditions in men.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Aneuploidy: It is the loss or gain of one or more chromosomes in a set. In man Down’s syndrome is one of the commonly known aneuploid conditions.
86. Which of the following is not a type of Aneuploidy condition?
a) Nullisomy
b) Disomic
c) Trisomy
d) Monosomy
Explanation
The aneuploid conditions are of three types Monosomy (2n-1), Trisomy (2n+1) and Nullisomy (2n-2).
87. Who identified the Down’s syndrome condition?
a) Louis Pasteur
b) Gregor Mendel
c) Langdon Down
d) James Watson
Explanation
Down’s syndrome: This condition was first identified by a doctor named Langdon Down in1866.
88. State the condition for the Down’s syndrome condition?
a) Trisomy 21
b) Trisomy 13
c) Trisomy 18
d) Trisomy 16
Explanation
Down’s syndrome is a genetic condition in which there is an extra copy of chromosome 21 (Trisomy 21).
89. What are the conditions seen in the Down’s syndrome children?
a) Delayed development
b) Weak muscle tone
c) Mental retardation
d) All the above
Explanation
Down’s syndrome is associated with mental retardation, delayed development, behavioral problems, weak muscle tone, vision and hearing disability are some of the conditions seen in these children.
90. Choose the Incorrect statements about gene or point mutation.
i) Gene mutation is the change occurring in the nucleotide sequence of a gene.
ii) It involves insertion and deletion of single nitrogenous base.
iii) Gene alteration results in abnormal protein formation in an organism.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Gene or point mutation: Gene mutation is the changes occurring in nucleotide sequence of a gene. It involves substitution, deletion, insertion or inversion of a single or more than one nitrogenous base. Gene alteration results in abnormal protein formation in an organism.
91. Which part of hemoglobin molecule is affected in the sickle cell anemia disease?
a) Nuclease
b) Protein
c) Cell wall
d) Cytoplasm
Explanation
Sickle cell anemia is caused by the mutation of a single gene. Alteration in the gene brings a change in the structure of the protein part of hemoglobin molecule. Due to the change in the protein molecule the red blood cell (RBC) that carries the hemoglobin is sickle shaped.
92. Assertion (A): Sickle cell anemia is caused by the mutation of a single gene.
Reasoning(R): The White Blood cell (WBC) is sickle shaped due to the protein change in the molecule.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Sickle cell anemia is caused by the mutation of a single gene. Due to the change in the protein molecule the red blood cell (RBC) that carries the hemoglobin is sickle shaped.
10th Science Lesson 19 Questions in English
19] Origin And Evolution Of Life
1. What are the significant characters of the living organisms?
a) Evolution of diversities
b) Organizational and functional unity
c) Balanced relationship with nature
d) All the above
Explanation
Living organisms possess distinct characteristics, display organizational and functional unity, entail a mechanism of origin and evolution of diversities and maintain a balanced relationship with nature. Most aspects of evolution indicate that the knowledge of the past has become essential for fully understanding the present.
2. Define evolution of life.
a) Adaptations of living organisms throughout the time.
b) Origin and adaptations of life.
c) Knowledge of the past.
d) Changes in the life style on earth.
Explanation
Life since its beginning on earth had changed through time. The history of life comprises of two aspects, one is the origin of life on earth and the other is mechanism involved in the gradual changes and adaptations of living organisms through time which is known as the evolution of life.
3. Assertion (A): The Origin of the Universe is explained by the Big Bang theory.
Reasoning(R): As per Big Bang theory the Universe originated by an explosive mechanism.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Origin of Earth: Origin of life is linked with the origin of earth. The Big Bang theory explains the Origin of Universe. It proposes that the universe had an explosive beginning (Big Bang) and originated 15 billion years ago.
4. Choose the correct statements.
i) The Universe is made up of stars, cloud of gas and dust.
ii) The gaseous clouds collapsed due to own gravity and atoms and particles were formed.
iii) Atoms, dust grains and gaseous disc aggregated to form clumps which gave rise as planets.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
The universe comprised of stars, clouds of gas and dust which form the galaxies. The solar system was probably created when the gaseous clouds started to collapse due to the force of its own gravity forming atoms and particles. Atoms, dust grains and gaseous disc aggregated to form clumps and gave rise to planets. This forms the solar system of the Milky Way galaxy.
5. Assertion (A): Earth was supposed to have formed about 4.5 billion years back.
Reasoning(R): Life appeared 500 million years after the formation of earth.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Earth was supposed to have been formed about 4.5 billion years back. Life appeared 500 million years after the formation of earth.
6. Which of the following ideas or theory supports earth as a divine creation?
a) Special creation
b) Spontaneous generation
c) Cosmic origin
d) Biogenesis
Explanation
Many theories have been postulated to explain the origin of life. The view on the origin of life has been put forth as Special creation: This idea embodies that life on Earth is a divine creation and also attributes to supernatural event at a particular time in the past. It also emphasizes that life has not changed ever since its origin.
7. Which of this theory of life is based on the spontaneous generation?
a) Life came from outer space.
b) Earth is a divine creation.
c) Life originated from lifeless matter.
d) Life originates from pre-existing life.
Explanation
Spontaneous generation (Abiogenesis): According to this theory life originated spontaneously from lifeless matter. It was believed that fishes originated from mud, frogs from moist soil and insects from decaying matter.
8. Who speculated the biogenesis concept of life?
a) Gregor Mendel
b) Louis Pasteur
c) Albert Einstein
d) Carolus Linnaeus
Explanation
Biogenesis: It was speculated by Louis Pasteur (1862) that life originates from preexisting life. He showed that pre-sterilized flasks kept closed airtight, with killed yeast, did not give rise to any life form, while in another flask kept open to air living organisms arose from killed yeast.
9. Which of these were the basis of life in earth and other planets by the Extraterrestrial origin?
a) Dust particles
b) Panspermia
c) Chemical reactions
d) Amoeba
Explanation
Extraterrestrial or cosmic origin: Some scientists still believe that life came from outer space. This states that units of life called spores (Panspermia) were transferred to different planets including earth. This is still an idea of some astronomers.
10. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the Chemical evolution of life.
i) Oparin and Haldane developed the idea of chemical evolution of life.
ii) Life arose by a series of sequential chemical reactions with the conditions prevailing on earth.
iii) The first form of life could have come from a pre-existing living organic molecule.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Chemical Evolution of Life: This idea was developed by Oparin (1922) and Haldane (1929). They proposed that with the conditions prevailing on earth, life arose by a series of sequential chemical reactions. The first form of life could have come from pre-existing nonliving inorganic molecules which gave rise to formation of diverse organic molecules which are transformed into colloid system to produce life. The modern concept on chemical evolution regarding origin of life was accepted.
11. Which of this concept is accepted by the relationship between existing and extinct organisms?
a) Pre-existing non-living inorganic molecules gave rise to diverse organic molecules.
b) All organisms evolved from common ancestors.
c) Life started by a series of chemical reactions.
d) Life originated spontaneously from lifeless matters.
Explanation
Evolution can be better understood only by observing the interrelationship between the existing organisms and also relating the similarities with the extinct organisms. The inter relationship of the organisms is also supported by evidences from different branches of biology. These evidences support the concept that all organisms have evolved from common ancestors.
12. Which of these are the homologous structures in the mammals?
a) Fore limbs
b) Feet
c) Eyes
d) Skull
Explanation
Homologous organs: The homologous organs are those which have inherited from common ancestors with similar developmental pattern in embryos. The fore limbs of mammals are homologous structures. A human hand, a front leg of a cat, flipper of a whale and a bat’s wing look dissimilar and adapted for different functions. Their mode of development and basic structure of bone are similar.
13. Assertion (A): Analogous organs look similar and used to perform similar functions.
Reasoning(R): The wings of a bat and a bird have different origin and development pattern.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Analogous organs: The analogous organs look similar and perform similar functions but they have different origin and developmental pattern. The function of the wings of a bat, the wings of a bird and wings of an insect are similar, but their basic structures are different.
14. Which of the following is not a vestigial organ of a human?
a) Appendix
b) Caudal vertebra
c) Wrist bones
d) Coccyx
Explanation
Vestigial organs: The degenerated and non-functional organs of animals are called vestigial organs. The same organs are found to be well developed and functional, in some of the related forms. Some of the vestigial organs in man are vermiform appendix, nictitating membrane, caudal vertebra, coccyx etc.
15. Define Atavism.
a) Degenerated organs of animals due to improper usage.
b) Reappearance of ancestral characters in some individuals.
c) Organs looking similar and having different structures.
d) Organs inherited from common ancestors with similar development pattern.
Explanation
Atavism: The reappearance of ancestral characters in some individuals is called atavism. E.g Presence of rudimentary tail in new born babies, presence of thick hair on the human body.
16. Choose the Incorrect statements.
i) The comparative study of embryology of different animals supports the evolution concept.
ii) The embryos from fish to mammals are similar in their early stages of development.
iii) The differentiation of the special characters in the animals appears in the early stages of development.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
The study of comparative embryology of different animals supports the concept of evolution. The embryos from fish to mammals are similar in their early stages of development. The differentiation of the special characters appears in the later stages of development.
17. Assertion (A): According to Biogenetic law Ontogeny recapitulates Phylogeny.
Reasoning(R): The Development stage of individuals repeats the evolutionary history of the entire race.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Biogenetic law or Recapitulation theory was given by Ernst Haeckel. According to this theory, Ontogeny recapitulates Phylogeny. The stage of development of the individual animal repeats the evolutionary history of the entire race of the animal.
18. Choose the correct statements.
i) The study of fossils is called as Paleontology.
ii) The study of fossils is used for understanding the evolution line of Invertebrates and Vertebrates.
iii) The Origin of modern birds is supported by the paleontology evidences.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Paleontology deals with the study of fossils. The study of fossils helps us to understand the line of evolution of many invertebrates and vertebrates. Fossil records show that the evolution has taken a gradual process from simple to complex organisms. The origin of modern birds is supported by the evidences from paleontology.
19. Who is known as the Father of Palaeontology?
a) Leonardo da Vinci
b) Jean Baptiste Lamarck
c) Charles Darwin
d) Ernst Haeckel
Explanation
Leonardo da Vinci is called the Father of Palaeontology.
20. Which of the following statement is not true regarding Archaeopteryx?
a) It is the oldest known fossil bird like form found in Jurassic period.
b) This creature links between the reptiles and birds.
c) The reptile features of these form is clawed digits and conical teeth.
d) The small skull is the bird feature of archaeopteryx.
Explanation
Archaeopteryx: Archaeopteryx is the oldest known fossil bird. It was an early birdlike form found in the Jurassic period. It is considered to be a connecting link between reptiles and birds. It had wings with feathers like a bird. It had long tail, clawed digits and conical teeth like a reptile.
21. Assertion (A): Evolution is the formation of new species due to the changes in specific characters over several generations.
Reasoning(R): Evolution is the gradual change occurring in living organisms over a period of time.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Life had evolved along with evolution of earth towards the end of 18th century. Evolution is the gradual change occurring in living organisms over a period of time. Formation of new species due to changes in specific characters over several generations as response to natural selection is called evolution.
22. Which of these theories explain the natural changes in evolution?
a) Ernst Haeckel
b) Lamarck and Darwin
c) Leonardo da Vinci
d) Oparin and Haldine
Explanation
The natural changes occurring are explained through the theories of evolution as proposed by Lamarck and Darwin.
23. Which of the following publication depicted the theory of evolution of Jean Baptiste Lamarck?
a) Origin of Species
b) Philosophic Zoologique
c) The Selfish Gene
d) Species Plantarum
Explanation
Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) was a French naturalist, well known for his theory of evolution. His theory of evolution was published in ‘Philosophic Zoologique’ in the year 1809.
24. Which of the following is the Lamarck’s theory of evolution?
a) Theory of Inheritance of Acquired characters
b) Use and Disuse theory
c) Lamarckism
d) All the above
Explanation
Lamarck’s theory of evolution was published in ‘Philosophic Zoologique’ in the year 1809. It is popularly known as ‘Theory of inheritance of Acquired Characters” or “Use and Disuse theory” or Lamarckism.
25. Which of the following statements is not related to the principles of Lamarckism?
a) Living organisms or their parts tend to increase in size continuously.
b) The study of fossils method is used to study the variations of the living organisms.
c) Environment change brings variations in the need of the organisms.
d) New adaptations of the organisms may develop new body parts.
Explanation
Principles of Lamarckism: Internal vital force, living organisms or their component parts tend to increase in size continuously. This increase in size is due to the inherent ability of the organisms. Environment and new needs, a change in the environment brings about changes in the need of the organisms. In response to the changing environment, the organisms develop certain adaptive characters. The adaptations of the organisms may be in the form of development of new parts of the body.
26. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the concept of Use and Disuse theory.
i) Lamarck’s theory states that if an organ is used constantly that specific organ is developed and strengthened.
ii) Organ which is not used for a long time degenerates immediately.
iii) The continuous stretching of giraffe neck and forelimbs is the example for organ of disuse.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Use and disuse theory: Lamarck’s use and disuse theory states that if an organ is used constantly, the organ develops well and gets strengthened. When an organ is not used for a long time, it gradually degenerates. The ancestors of giraffe were provided with short neck and short forelimbs. Due to shortage of grass, they were forced to feed on leaves from trees. The continuous stretching of their neck and forelimbs resulted in the development of long neck and long forelimbs which is an example for constant use of an organ. The degenerated wing of Kiwi is an example for organ of disuse.
27. Which of the following is called as the acquired character of an animal?
a) Characters developed in response to the environment changes.
b) Characters needed for surviving in the challenging environment.
c) Mutation characters developed during the life time of an animal.
d) Transferred characters from the ancestors without any changes.
Explanation
Theory of Inheritance of acquired characters: When there is a change in the environment the animals respond to the change. They develop adaptive structures. The characters developed by the animals during their life time in response to the environmental changes are called acquired characters. According to Lamarck, the acquired characters are transmitted to the offspring by the process of inheritance.
28. Which of the following statements are not true based on the life history of Charles Darwin?
a) Charles Darwin was one of the great naturalist and philosopher of 18th century.
b) Charles Darwin was born in South America in the year 1809.
c) J.S.Henslow nominated Darwin for the 5 years voyage of exploration on a ship named H.M.S. Beagle.
d) Darwin made elaborate observations on nature of the land, plants and animals worked for a period of 20 years to develop the theory of natural selection.
Explanation
Charles Darwin (1809-1882) was one of the great naturalist and philosopher of 18th century. He was born in England in 1809. While studying in college through his friendship with Professor J.S.Henslow he was fascinated towards nature. At that time the British Admiralty planned a voyage of exploration for 5 years on a ship named H.M.S. Beagle around South America. Dr Henslow was asked to nominate a young naturalist for the voyage. Darwin was given the opportunity. During his five years (1831–1835) voyage he visited many parts of the world, a number of islands including the Galapagos Island and Pacific Island. Darwin made elaborate observations on nature of the land, plants and animals of the regions he visited. He further worked for a period of 20 years to develop the theory of natural selection.
29. Which of these results in the evolutionary transformation according to Darwin theory?
a) Environmental changes
b) Natural selection
c) Need of new species
d) Atmospheric and cosmic variations
Explanation
Darwin published his observations and conclusions under the name ‘Origin of species’ in 1859. The book of Darwin demonstrates the fact of evolution. It elaborates on the theory of Natural selection for evolutionary transformation.
30. Assertion (A): Living beings are able to reproduce more and multiply in a geometrical manner.
Reasoning(R): Overproduction creates an intense competition for food and space leading to struggle.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Principles of Darwinism: Overproduction, Living beings have the ability to reproduce more individuals and form their own progeny. They have the capacity to multiply in a geometrical manner. This will increase reproductive potential leading to overproduction. Struggle for existence, Due to overproduction a geometric ratio of increase in population occurs. The space to live and food available for the organisms remain the same. This creates an intense competition among the organisms for food and space leading to struggle.
31. Which of these is known as the competition among the individuals of same species?
a) Environmental struggle
b) Interspecific struggle
c) Intraspecific struggle
d) Evolution struggle
Explanation
The struggles for existence are of three types:
Intraspecific struggle: Competition among the individuals of same species.
Interspecific struggle: Competition between the organisms of different species living together.
Environmental struggle: Natural conditions like extreme heat or cold drought and floods can affect the existence of organisms.
32. Which of these cause the environmental struggle among the living beings?
a) Heat or cold
b) Flood
c) Drought
d) All the above
Explanation
Environmental struggle: Natural conditions like extreme heat or cold drought and floods can affect the existence of organisms.
33. Choose the Incorrect statements regarding the variations.
i) The Occurrence of variation is a characteristic feature of mammals only.
ii) Small variations are important for evolution.
iii) Favorable variations are useful and unfavorable variations are harmful to the organisms.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Variations: The occurrence of variation is a characteristic feature of all plants and animals. Small variations are important for evolution. According to Darwin favorable variations are useful to the organism and unfavorable variations are harmful or useless to the organism.
34. Which of the following statements are related to the concept of survival of the fittest?
a) Species unable to face challenges are unfit to survive and disappear.
b) All organisms must adapt to the surrounding environment by overcoming a challenging situation.
c) An organ is used constantly then it is developed well and gets strengthened.
d) The process of selection of organisms with favorable variation is natural selection.
Explanation
Survival of the fittest or Natural selection: During the struggle for existence, the organisms which can overcome the challenging situation, survive and adapt to the surrounding environment. Organisms which are unable to face the challenges are unfit to survive and disappear. The process of selection of organisms with favorable variation is called as natural selection.
35. What is the origin of species according to Darwin theory?
a) Gradual accumulation of favorable variations for number of generations.
b) Environment changes lead to the new parts of living organisms.
c) Evolution and variations are not related to each other.
d) Use and Disuse theory is the major reason for the new species.
Explanation
Origin of species: According to Darwin, new species originates by the gradual accumulation of favorable variations for a number of generations.
36. Which of these leads to the differences in the phenotype of off springs from its parents?
a) Adaptation
b) Variations
c) Evolution
d) Environmental changes
Explanation
Sexual reproduction, which involves meiosis, helps in recombination of genes during gametic fusion. This leads to differences in the phenotype of the offspring from its parents. These differences are called variation.
37. Choose the correct statements.
i) Variations play an important role in evolution.
ii) Variations are the difference among the individuals of the same species and the off springs of same parent.
iii) Evolution is not possible without variations.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) All the above
Explanation
Variation is the difference found among individuals of the same species and the offspring of the same parent. Variation is the raw material which plays an important role in evolution. Evolution would not be possible without variation.
38. Which of this variation affects the body cells of the organisms?
a) Somatic variation
b) Germinal variation
c) Discontinuous variation
d) Continuous variation
Explanation
Somatic variation: These are the variations which affect the body (somatic) cells of the organisms. They are not heritable. They occur due to environmental factors.
39. Which of these is not a factor of germinal variation?
a) Variations are produced in germ cells of an organism.
b) Two types of germinal variations are classified.
c) Germinal variations are present in ancestors.
d) These variations are not inherited in organisms.
Explanation
Germinal variation: These variations are produced in germ cells of an organism. They are inherited. They may be present in ancestors or may occur suddenly. They are classified into two types: Continuous variation and Discontinuous variation.
40. Which of these are also known as the continuous variations?
a) Fluctuating variations
b) Sudden variations
c) Accumulating variations
d) Germinal variations
Explanation
Continuous variation: These are small variations which occur among individuals of a population. They are also called as fluctuating variations. They occur by gradual accumulation in a population. e.g. skin color, height and weight of an individual, color of eye, etc.
41. Which of the following statements are not true regarding the discontinuous variation?
a) Sudden changes occur in an organism due to mutations.
b) Discontinuous variation is large and not used for evolution.
c) These variations may have intermediate forms.
d) Discontinuous variation forms the basis for mutation theory proposed by De Vries.
Explanation
Discontinuous variation: These are sudden changes which occur in an organism due to mutations. They do not have any intermediate forms. These large variations are not useful for evolution. E.g. short legged Ancon sheep, six or more digits (fingers) in human, Discontinuous variation form the basis for Mutation theory proposed by De Vries.
42. Choose the correct statements.
i) Mutation and Variation are events involved in the process of evolution.
ii) The Variations leads to Mutation.
iii) Variations bring changes in a single individual.
iv) Mutation arises due to errors occurring in DNA.
a) i, iii only
b) ii, iv only
c) i, iii, iv only
d) iv only
Explanation
Relationship between Mutation and Variation: Mutation and Variation are two events involved in the process of evolution. Mutation arises due to errors occurring in DNA during replication or exposure to UV rays or chemicals. Mutation leads to variation. It brings about changes in a single individual.
43. What is the origin of the word Paleobotany?
a) Greek
b) Persia
c) Latin
d) Rome
Explanation
Paleobotany is derived from Greek words paleon that means “old” and botany the study of plants. It is the branch of paleontology that deals with recovery and identification of plant remains of geological past.
44. Assertion (A): Majority of plants fossils are disarticulated parts of plants that have died long back.
Reasoning(R): Only part of a plant is preserved and it is rare to find preserved form of whole plant.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
A plant fossil is any preserved part of a plant that has died long back. Fossils may be a prehistoric impression that may be hundred to millions of years old. Majority of the plant fossils are disarticulated parts of plants, it is rare to find plants to be preserved as whole.
45. What is the importance’s of Fossils?
a) Historical approach to plant kingdom.
b) Used to classify the plants.
c) Used in descriptive and comparative anatomy.
d) All the above
Explanation
Importance of fossils: They throw light on phylogeny and evolution of plants. Fossil plants give a historical approach to plant kingdom. Fossils are useful in classification of plants. Fossil plants can be used in the field of descriptive and comparative anatomy.
46. Who is known as the Father of Paleobotany?
a) Birbal Sahani
b) J.W.Harshberger
c) Kaspar Maria Von Sternberg
d) W.F.Libby
Explanation
Kaspar Maria Von Sternberg is the “Father of Paleobotany” (1761–1838) was born in Europe. He established the Bohemian National Museum in Prague and is deemed to be the founder of Modern Paleobotany.
47. Assertion (A): Birbal Sahani is the Father of Indian Paleobotany.
Reasoning(R): Birbal Sahani presented his research on the fossil plants of Indian Gondwana formations.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
Birbal Sahani is the “Father of Indian Paleobotany” (1891–1949). He presented his research on two different areas of Paleobotany, the anatomy and morphology of Paleozoic Ferns and the fossil plants of the Indian Gondwana Formations.
48. Which of these methods are the common methods of fossilization?
a) Petrification
b) Molds and cast
c) Carbonization
d) All the above
Explanation
The process of formation of fossil in the rocks is called fossilization. Common methods of fossilization include petrifaction, molds and cast, carbonization, preservation, compression and infiltration.
49. Define petrification.
a) Minerals or sediments fill the hollow depression to form a cast.
b) Organisms are preserved in ice or amber to prevent it from decaying.
c) Minerals like silica penetrate and replace the original organic tissue to form fossils.
d) Organism are buried in sediments and dissolved in underground water.
Explanation
Petrifaction: Minerals like silica slowly penetrate in and replace the original organic tissue and forms a rock like fossil. This method of fossilization can preserve hard and soft parts. Most bones and wood fossils are petrified.
50. Choose the incorrect statements.
i) Mold is a hollow depression formed when an organism is buried in sediments and dissolved in water.
ii) Mold shows the original shape and the internal structure of the organisms.
iii) The Minerals or sediments filling the hollow depression to form a cast.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Mold and Cast: A replica of a plant or animal is preserved in sedimentary rocks. When the organism gets buried in sediment it is dissolved by underground water leaving a hollow depression called a mold. It shows the original shape but does not reveal the internal structure. Minerals or sediment fill the hollow depression and forms a cast.
51. Which of these are used for preserving the original animals or plants?
a) Ice or Amber
b) Alcohol
c) Carbon
d) Mercury
Explanation
Preservation: Original remains can be preserved in ice or amber (tree sap). They protect the organisms from decay. The entire plant or animal is preserved.
52. By which of these process fossils are formed?
a) Replacement
b) Compression
c) Preservation
d) Petrification
Explanation
Compression: When an organism dies, the hard parts of their bodies settle at the bottom of the sea bed and are covered by sediment. The process of sedimentation goes on continuously and fossils are formed.
53. Which of these minerals are used for infiltration or replacement?
a) Calcium carbonate
b) Silica
c) Magnesium carbonate
d) All the above
Explanation
Infiltration or Replacement: The precipitation of minerals takes place which later on infiltrate the cell wall. The process is brought about by several mineral elements such as silica, calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate. Hard parts are dissolved and replaced by these minerals.
54. Which of the following is an example of living fossils?
a) Ammonites
b) Brachiopods
c) Ginko biloba
d) Archaeopteryx
Explanation
Living Fossils: These are living organisms that are similar in appearance to their fossilized distant ancestors and usually have no extinct close features. E.g. Ginko biloba.
55. Which of these radioactive elements is not used to determine the age of fossils?
a) Carbon
b) Mercury
c) Lead
d) Potassium
Explanation
The age of fossils is determined by radioactive elements present in it. They may be carbon, uranium, lead or potassium. It is used in Palaeo botany and anthropology for determining the age of human fossils and manuscripts.
56. Who discovered the Radio-active carbon dating method?
a) W.F.Libby
b) Kaspar Maria Von Sternberg
c) J.W.Harshberger
d) Birbal Sahani
Explanation
Radioactive carbon (C14) dating method: This method was discovered by W.F. Libby (1956). By calculating which of these in a dead animals or plants the time of Carbon consumption of animals and plants stops after death and since then, only the decaying process of C14 occurs continuously. The time passed since death of a plant or animal can be calculated by measuring the amount of C14 present in their body.
57. Assertion (A): The Geological time scale is a system of chronological dating related to the geological rock strata to time.
Reasoning(R): The geological time scale describes the timing and relationships of events occurred during Earth’s history.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
The geological time scale is a system of chronological dating that relates geological rock strata to time, and is used by geologists, paleontologists, and other Earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships of events that have occurred during Earth’s history.
58. Which of the following statements is not true?
a) The organic matter of the trees are replaced by silica and fossilized.
b) The fossilized trees do not retain their original color, shape and texture.
c) The trees are converted into solid rocks and every property of plants is still visible.
d) Thiruvakkarai fossil wood park is located in Villupuram district, Tamil Nadu.
Explanation
Thiruvakkarai fossil Wood Park (Villupuram district, Tamil Nadu): 2 million years ago tree trunks that got buried along the river, in course of time the organic matter was replaced by silica and was fossilized. They retained their color, shape and texture and was converted into solid rocks. The annular rings, the texture, colors of the layers, nodes and every properties of plants are still visible.
59. Choose the incorrect statements regarding Ethno botany.
i) Ethno botany is the study of a region’s plants and their practical usages.
ii) J.W.Harshberger in 1895 coined the term Ethno botany.
iii) Ethno botany emerged as a distinct academic branch of natural science from the ancient times.
a) i only
b) ii only
c) iii only
d) None of the above
Explanation
Ethno botany is the study of a region’s plants and their practical uses through the traditional knowledge of the local culture of people. The term Ethno botany was coined by J.W. Hershberger in 1895 to include the study of plants used by the primitive and aboriginal people. Though this discipline has existed for ages, ethno botany emerged as a distinct academic branch of natural science in 20th century.
60. What are the main aspects of Ethno botany?
a) Economic up liftment
b) Biodiversity conservation
c) Sustainable use of plant resources.
d) All the above
Explanation
Aspects of ethno botany: Ethno botany has relevance with problems of nutrition, health care and life support system, faith in plants, cottage industries, economic up liftment, conservation of biodiversity and sustainable use of plant resources.
61. Which of the following statements is not related to ethno botany?
a) Ethno botany provides the traditional usages known and unknown plants.
b) Synthesized medicines and drugs are made by the various parts of plants.
c) Ethno medicinal data is a useful source of information for the herbal medicine practitioners.
d) Plant parts like bark, stem, root, seeds and oils are used for treating diseases.
Explanation
Importance of Ethno botany: It provides traditional uses of plant. It gives information about certain unknown and known useful plants. The ethno medicinal data will serve as a useful source of information for the chemists, pharmacologists and practitioners of herbal medicine. Tribal communities utilize ethno medicinal plant parts like bark, stem, roots, leaves, flower bud, flowers, fruits, seeds, oils, resins, dyes, gum for the treatment of diseases like diarrhea, fever, headache, diabetes, jaundice, snakebites, leprosy, etc.
62. What are the objectives of Astrobiology or Exobiology?
a) A branch of science deals with presence of extra-terrestrial life in the Universe.
b) Origin, evolution and distribution of life in the Universe.
c) Investigates the possibility of life in other world.
d) All the above
Explanation
Astrobiology/exobiology is the science which looks for the presence of extra-terrestrial life in the universe. Astrobiology deals with the origin, evolution and distribution of life in the universe and to investigate the possibility of life in other world.
63. Which of the following is not a criterion for a habitable zone?
a) A planet must have a right mass to retain an atmosphere.
b) The size of the planet must be small enough to have aquatic zones.
c) The orbit of the planet must be at a right distance from the Star.
d) The distance between planet and the star has to be neither too hot nor not too cold.
Explanation
The major concept in astrobiology is the habitable zone. The theory explains that any planets can support the existence of life, if it fulfills two important criteria. It must have a right mass to retain an atmosphere. It must have an orbit at just the right distance from its star (Sun) that it allows liquid water to exist. Thus, the distance need to be neither too hot nor not too cold and is often referred as Goldilocks Zone for life.
64. Assertion (A): Earth is the only planet in the solar system which is in the Goldilocks zone.
Reasoning(R): Mars planet is likely to have creatures that can survive in extreme environments of Earth.
a) Both A and R is True and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R is True but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is True but R is False.
d) Both A and R is False.
Explanation
In our solar system ‘Earth’ is the only planet in the goldi lock zone. Since, this zone varies at times as the star evolves we know that Mars have also been habitable. The life on Mars is likely to be the creatures, we find in extreme environments on earth.
65. Which of these are called as Extremophiles?
a) Multi cell organisms found in aquatic regions.
b) Organisms living in extreme environmental conditions.
c) Extinct organisms.
d) Single cell organisms.
Explanation
The organisms which live in extreme environmental conditions on earth are called extremophiles. Thus, within our own Solar System, there are many areas that are different from the Earth where it is probable to find the presence of life similar to extremophile bacteria.
66. What are the objectives of the NASA’s Mars 2020?
a) Surface geological process
b) Possibility of past life
c) Preserving bio signatures
d) All the above
Explanation
NASA is developing the Mars 2020 astrobiology to investigate an Astor biologically relevant ancient environment on Mars, its surface geological processes and the possibility of past life on Mars and preservation of bio signatures within accessible geological materials.
10th Science Lesson 20 Questions in English
20] Breeding And Biotechnology
1. Which is the process of increasing food production through high yielding crop varieties and modern agricultural techniques in underdeveloped and developing nations?
- Green revolution
- Blue revolution
- White revolution
- Yellow revolution
Explanation
Green Revolution is the process of increasing food production through high yielding crop varieties and modern agricultural techniques in underdeveloped and developing nations.
2. Who among the following is the “Father of the Green Revolution”, received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1970?
- Norman Borlaug
- Pedro Sanchez
- Salim Ali
- M. S. Swaminathan
Explanation
Dr Norman E. Borlaug, an American agronomist the “Father of the Green Revolution”, received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1970.
3. Which among the following statement is correct
- India’s population is likely to reach 3.7 billion by 2050. Current rate of India’s food production will be able to meet only 39% of the country’s food demand at that time. How can India feed 1.7 billion people by 2050? This can be made possible by ‘Plant breeding’ and ‘Animal feeding’.
- Plant breeding is the art of developing economically important plants with superior quality. Animal husbandry involves the breeding of animals. It aims at improving the genotypes of animals to make them more useful to the welfare of mankind.
- Another breakthrough was the emergence of biotechnology as an entity of modern biology, which paved way to develop advanced healthcare products, diagnostic kits and food production to improve the quality of human life.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
India’s population is likely to reach 1.7 billion by 2050. Current rate of India’s food production will be able to meet only 59% of the country’s food demand at that time. How can India feed 1.7 billion people by 2050? This can be made possible by ‘Plant breeding’ and ‘Animal husbandry’.
4. Who among the following is known as father of Indian green revolution?
- C. v. Raman
- Verghese Kurien
- C. N. Rao
- M. S. Swaminathan
Explanation
Dr. Mankombu Sambasivan Swaminathan is an Indian scientist known for his leading role in India’s Green Revolution. His research on potato, wheat, rice and jute are well known plant breeding experiments. Due to his efforts the wheat production increased from twelve million tonnes in 1960’s to seventy million tonnes now. He is aptly called as the “Father of Indian Green Revolution”.
5. In India Dr M. S. Swaminathan joined with Dr Borlaug in bringing Green Revolution by introducing which wheat variety?
- Russian wheat varieties
- Chinese wheat varieties
- Mexican wheat varieties
- Moroccan wheat varieties
Explanation
In India Dr M. S. Swaminathan joined with Dr Borlaug in bringing Green Revolution by introducing Mexican wheat varieties. This eventually increased wheat and rice production between 1960 and 2000.
6. Which among the following is not semi-dwarf varieties of wheat developed from high-yielding, semi-dwarf, fertilizer responsive wheat varieties from Mexico?
- Sonalika
- Kalyan Sona
- Triguna
- All the above
Explanation
Sonalika, Kalyan Sona are semi-dwarf varieties of wheat developed from highyielding, semi-dwarf, fertilizer responsive wheat varieties from Mexico.
7. In which among the following country International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) is located?
- India
- Indonesia
- Philippines
- Brazil
Explanation
International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) is located in Los Banos, Philippines.
8. Which is a high-yielding semi-dwarf rice variety developed by International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), Philippines?
- Ponni
- IET – 12617
- HMT
- IR – 8
Explanation
IR-8 is a high-yielding semi-dwarf rice variety developed by International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), Philippines.
9. In 1966, in which two country IR-8 was first introduced?
- Philippines and India
- Philippines and Indonesia
- Philippines and Mexico
- Philippines and China
Explanation
In 1966, IR-8 was first introduced in Philippines and India.
10. IR-8 was a hybrid of a which two high yielding rice variety?
- Peta and Dee-geo-woo-gen
- Giho and Dee-geo-woo-gen
- Cisokan and Dee-geo-woo-gen
- Cirata and Dee-geo-woo-gen
Explanation
IR-8 was a hybrid of a high yielding rice variety Peta from Indonesia, and Dee-geo-woo-gen (DGWG) a dwarf variety from China.
11. Who among the following was a Tamil agricultural scientist, environmental activist and organic farming expert?
- Subash Palekar
- Masanobu
- Nammalvar
- Rajiv Kanna
Explanation
Dr. G. Nammalvar (1938-2013) was a Tamil agricultural scientist, environmental activist and organic farming expert. He founded Nammalvar Ecological Foundation for Farm Research and Global Food Security Trust (NEFFFRGFSTVanagam) to create public awareness about the benefits of organic farming.
12. Which among the following pathogen does not affect plant?
- Virus
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- None of the above
Explanation
Plant diseases are caused by pathogens like viruses, bacteria and fungi. This affects crop yield. Hence, it is important to develop disease resistant varieties of crops, that would increase the yield and reduce the use of fungicides and bactericides.
13. Which among the following is the disease resistant variety of wheat?
- Pusa Shubhra
- Pusa Komal
- Himgiri
- All the above
Explanation
Himigiri is the disease resistance variety of wheat. It was resistance to Leaf and stipe rust, hill bunt.
14. Which among the following is the disease resistance variety of cowpea?
- Pusa Shubhra
- Pusa Komal
- Pusa Snowball K-1
- All the above
Explanation
Pusa Komal is the disease resistance variety of Cowpea.
15. Pusa Shubhra is a disease resistance variety of which crop?
- Lemon
- Carrot
- Cauliflower
- Pineapple
Explanation
Pusa Shubhra and Pusa Snowball K-1 are disease resistance variety of cauliflower. It was resistance to Black rot.
16. Which among the following statement is correct
- Undernutrition and protein malnutrition among human population is a major health problem which has been receiving much focus throughout the world. Apart, from humans it also affects the health of farm animals.
- To combat these conditions, human and animal health are to be determined by the nutritional quality of the feed crops. The nutritional quality of crops depends on quality and quantity of nutrients. The nutritional quality may be improved with respect to its 1. Protein content and quality of protein 2. Oil content 3. Mineral content.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
17. Which is the scientific process of developing crop plants enriched with high levels of desirable nutrients like vitamins, proteins and minerals?
- Biotique
- Labiovelars
- Biophilias
- Biofortification
Explanation
Biofortification is the scientific process of developing crop plants enriched with high levels of desirable nutrients like vitamins, proteins and minerals. Some examples are Iron rich fortified rice variety and Vitamin A enriched carrots, pumpkin and spinach.
18. Which among the following is not the lysine rich maize hybrids?
- Protina
- Poorva
- Shakti
- Rathna
Explanation
Protina, Shakti and Rathna are lysine rich maize hybrids (developed in India).
19. Which among the following is the variety of Brassica resistance to Aphids?
- Pusa Gaurav
- Pusa Sawani
- Pusa Sem 2
- All the above
Explanation
Pusa Gaurav is the variety of Brassica that are resistance to Aphids.
20. Which among the following is the protein rich wheat variety?
- Vista
- Caloro-2
- Atlas-66
- Aromatic
Explanation
Atlas 66 is a protein rich wheat variety.
21. Which among the following is not the variety of lady’s finger?
- Pusa Sawani
- Pusa Sem 2
- Pusa A4
- None of the above
Explanation
Pusa Sawani and Pusa Sem-2 are the varieties of lady’s finger resistance to shoot and fruit borer.
22. Which among the following is not the methods of Plant Breeding for Crop Improvement?
- Selection
- Crafting
- Mutation breeding
- Hybridization
Explanation
Methods of plant breeding to develop high yielding varieties are given below: 1. Introduction of new varieties of plants 2. Selection 3. Polyploidy breeding 4. Mutation breeding 5. Hybridization.
23. The process of introducing high yielding varieties of plants from one place to another. Such plants are called as _____
- Endemic species
- Exotic species
- Mids species
- Concentrated species
Explanation
The process of introducing high yielding varieties of plants from one place to another. Such plants are called as exotic species. These imported plant materials may carry pathogens and pests, hence they are thoroughly tested in a plant quarantine before being introduced to the fields.
24. Pusa Sem 2 and Pusa Sem 3 are varieties of which among the following crop?
- Pumpkin
- Tall Radish
- Bottle Gourd
- Flat Beans
Explanation
Pusa Sem 2 and Pusa Sem 3 are varieties of Flat bean.
25. Pusa sem 2 and Pusa sem 3 (varieties of flat bean) are resistance to which among the following pests?
- Leaf hopper
- Aphids
- Fruit borer
- All the above
Explanation
Pusa sem 2 and Pusa sem 3 (varieties of flat bean) are resistance to Leaf hopper, aphids and fruit borer.
26. Which is one of the oldest methods of plant breeding in which individual plants or groups of plants are sorted out from a mixed population based on the morphological characters?
- Breeding
- Selection
- Hybridization
- Termination
Explanation
Selection is one of the oldest methods of plant breeding in which individual plants or groups of plants are sorted out from a mixed population based on the morphological characters
27. how many methods of selection of crops are there?
- Two
- Three
- Five
- Six
Explanation
There are three methods of selection. They are 1. Mass selection 2. Pure line selection 3. Clonal selection.
28. A group of plants produced from a single plant through vegetative or asexual reproduction are called ________
- Clones
- Mutants
- Prophies
- Pales
Explanation
A group of plants produced from a single plant through vegetative or asexual reproduction are called clones.
29. Which among the following statement is correct
- All the plants of a clone are similar both in genotype and phenotype. Selection of desirable clones from the mixed population of vegetatively propagated crop is called clonal selection.
- In mass selection, Seeds of best plants showing various characters are collected from a mixed population. The collected seeds are allowed to raise the second generation. This process is carried out for three or four generations.
- At the end, they will be multiplied and distributed to the farmers for cultivation. Some common examples for mass selection are groundnut varieties like TMV–2 and AK–10.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Seeds of best plants showing desired characters are collected from a mixed population. The collected seeds are allowed to raise the second generation. This process is carried out for seven or eight generations.
30. Pure line selection is also called as __________
- Variety plant selection
- Hybrid plant selection
- Mutant plant selection
- Individual plant selection
Explanation
Pure line is “the progeny of a single individual obtained by self-breeding”. This is also called as individual plant selection. In pure line selection large numbers of plants are selected from a self-pollinated crop and harvested individually. Individual plant progenies from them are evaluated separately. The best one is released as a pure line variety. Progeny is similar both genotypically and phenotypically.
31. Sexually reproducing organisms have two complete set of chromosomes (Diploid) in which cell in plant?
- Xylem cells
- Phloem cells
- Parenchyma cells
- Somatic cells
Explanation
Sexually reproducing organisms have two complete set of chromosomes in their somatic cells. This is called diploid (2n).
32. The gametic cells have only one set of chromosomes. This is called _____
- Amyloid
- Myceloid
- Haploid
- Polyploid
Explanation
The gametic cells have only one set of chromosomes. This is called haploid (n).
33. An organism having more than two sets of chromosomes is called _____
- Amyloid
- Myceloid
- Haploid
- Polyploid
Explanation
An organism having more than two sets of chromosomes is called polyploid. An organism having more than two sets of chromosomes is called polyploid (Greek : Polys = many + aploos = one fold + eidos = form). Such condition is called Polyploidy. It can be induced by physical agents such as heat or cold treatment, X-rays and chemical agents like colchicine.
34. Which among the following about achievement of polyploid breeding is incorrect?
- Seedless watermelons (3n) and bananas (3n)
- TV-29 (triploid variety of tea) with larger shoots and drought tolerance.
- Triticale (6n) is a hybrid of corn and sunflower. To make this plant fertile polyploidy is induced. It has higher dietary minerals and protein.
- Raphano brassica is an allotetraploid by colchicine treatment
Explanation
Triticale (6n) is a hybrid of wheat and rye. To make this plant fertile polyploidy is induced. It has higher dietary fibre and protein.
35. Which is defined as the sudden heritable change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA in an organism?
- Hybridization
- Mutation
- Conjunction
- Poking
Explanation
Mutation is defined as the sudden heritable change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA in an organism. It is a process by which genetic variations are created which in turn brings about changes in the organism. The organism which undergoes mutation is called a mutant.
36. How many types of mutagens are there?
- Two
- Three
- Four
- Six
Explanation
The factors which induce mutations are known as mutagens or mutagenic agents. Mutagens are of two types namely physical mutagens and chemical mutagens.
37. Atomic garden is a concept popularised after World War II for the peaceful use of atomic energy for crop improvement. Atomic garden is also known as _____?
- Alpha garden
- Beta garden
- Gamma garden
- Si garden
Explanation
Gamma garden or Atomic garden is a concept popularised after World War II for the peaceful use of atomic energy for crop improvement. This is a type of induced mutation breeding where radioactive sources particularly gamma rays from Cobalt-60 or Caesium-137 are used to induce desirable mutations in crop plants.
38. Which among the following is not the physical mutagens?
- X-rays
- β rays
- UV rays
- None of the above
Explanation
Radiations like X-rays, α, β and γ-rays, UV rays, temperature etc are which induce mutations are called physical mutagens.
39. Which among the following is not the chemical mutagens?
- Mustards gas
- Nitrous acid
- Sulphuric acid
- None of the above
Explanation
Chemical substances that induce mutations are called chemical mutagens. e.g., Mustard gas and nitrous acid. The utilisation of induced mutation in crop improvement is called mutation breeding.
40. Which among the following achievements of mutation breeding is incorrect
- Sharbati Sonora wheat produced from Sonora-64 by using gamma rays.
- Atomita 2 carrot with saline tolerance and pest resistance
- Groundnuts with thick shells
- None of the above
Explanation
Atomita 2 rice with saline tolerance and pest resistance.
41. Which is defined as the process of crossing two or more types of plants for bringing their desired characters together into one progeny?
- Mutation
- Hybridization
- Poking
- Conjunction
Explanation
Hybridization may be defined as the process of crossing two or more types of plants for bringing their desired characters together into one progeny called hybrid. Hybrid is superior in one or more characters to both parents. Hybridization is the common method of creating genetic variation to get improved varieties.
42. Which is the first man- made cereal hybrid?
- Rye
- Secale
- Spelt
- Triticale
Explanation
Triticale is the first man- made cereal hybrid. It is obtained by crossing wheat (Triticum durum, 2n = 28) and rye (Secale cereal, 2n = 14). The F1 hybrid is sterile (2n = 21). Then the chromosome number is doubled using colchicine and it becomes a hexaploid Triticale (2n = 42).
43. Which among the following statement is correct
- In Hybridization the cycle of crop raising and selection continues till the plants with the desired characters are finally obtained. The development of new varieties is a long-drawn process. Two main aspects of hybridization are to combine the characters of two plants in one plant and to utilize hybrid vigour.
- A breed is a group of animals of common origin within a genus that has certain distinguishing characters that are not found in other members of the same genus like general appearance and others striking features. Breeding involves mating parents of different varieties each having some desired trait which are passed onto the offspring.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
A breed is a group of animals of common origin within a species that has certain distinguishing characters that are not found in other members of the same species like general appearance and others striking features. Breeding involves mating parents of different varieties each having some desired trait which are passed onto the offspring.
44. When breeding takes place between animals of the same breed, it is called ____
- Co-breeding
- Inbreeding
- Outbreeding
- Both Inbreeding and Co-breeding
Explanation
Animal breeding aims at improving the genotypes of domesticated animals to increase their yield and improve the desirable qualities to produce milk, egg and meat. When breeding takes place between animals of the same breed, it is called inbreeding. The cross between different breeds is called outbreeding.
45. Which among the following statement is correct
- Inbreeding refers to the mating of closely related animals within the same breed for about 4-6 generations. Superior males and superior females of the same breed are identified and mated in pairs. It helps in the accumulation of superior genes and elimination of genes which are undesirable.
- Outbreeding is the breeding of unrelated animals. The offspring’s formed are called hybrids. The hybrids are stronger and vigorous than their parents. Cross between two different species with desirable features of economic value are mated.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
46. Which is a new breed of sheep developed in Punjab by crossing Bikaneri (Magra) ewes and Australian Marino rams?
- Hissardale
- Melospiza
- Adactylidium
- Leghorn
Explanation
Hissardale is a new breed of sheep developed in Punjab by crossing Bikaneri (Magra) ewes and Australian Marino rams. Continued inbreeding reduces fertility and productivity. Inbreeding exposes harmful recessive genes that are eliminated by selection.
47. Which is a cross breed produced from horse and donkey, which is superior to horse in strength, intelligence, ability to work and resistance to diseases but they are sterile?
- Hinny
- Liger
- Mule
- Cama
Explanation
Mule is a cross breed produced from horse and donkey, which is superior to horse in strength, intelligence, ability to work and resistance to diseases but they are sterile.
48. Which breed is produced from mating of brown swiss and Sahiwal?
- Gyr swiss
- Rathi swiss
- Malvi swiss
- Karan swiss
Explanation
Karan swiss is produced from mating of brown swiss and Sahiwal. Karan Swiss – yield 2-3 times more milk than indigenous cows.
49. Hybrid fowl that yield more eggs is produced from mating which two breeds?
- White leghorn and Araucana
- Amrock and Welsummer
- White Leghorn and Plymouth Rock
- Araucana and Amrock
Explanation
Hybrid fowl that yield more eggs is produced from mating White Leghorn and Plymouth Rock.
50. The superiority of the hybrid obtained by cross breeding is called as ____
- Selenosis
- Trichosis
- Pycnosis
- Heterosis
Explanation
The superiority of the hybrid obtained by cross breeding is called as heterosis or hybrid vigour. They have increased production of milk by cattle, Increased production of egg by poultry, High quality of meat is produced and Increased growth rate in domesticated animals.
51. Which is the manipulation and transfer of genes from one organism to other organisms to create a new DNA called as recombinant DNA (rDNA)?
- Genetic Selection
- Genetic Engineering
- Genetic Polygon
- Genetic Confetti
Explanation
Genetic engineering is the manipulation and transfer of genes from one organism to other organisms to create a new DNA called as recombinant DNA (rDNA). The term recombinant is used because DNA from two different sources can be joined together. Hence, genetic engineering is also called as recombinant DNA technology.
52. Which is the small circular double stranded DNA molecule found in the cytoplasm of bacterial cell and separated from chromosomal DNA.?
- Pilus
- Plasmid
- Ribosomes
- Cytoplasm
Explanation
Plasmid is the small circular double stranded DNA molecule found in the cytoplasm of bacterial cell and separated from chromosomal DNA. It can replicate independently.
53. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding discoveries that led to the stepping stone of rDNA technology?
- Presence of plasmid in bacteria that can undergo replication independently along with chromosomal DNA.
- Restriction enzymes cuts or break DNA at specific sites and are also called as molecular scissors.
- Restriction enzymes recognises a specific base pair sequence (Aerobic sequence) in DNA called as Production site and cleaves the phosphodiester bond within DNA.
- DNA ligases are the enzymes which help in ligating (joining) the broken DNA fragments.
Explanation
Restriction enzymes recognises a specific base pair sequence (palindromic sequence) in DNA called as restriction site and cleaves the phosphodiester bond within DNA.
54. The carbon copy of an individual is often called a ____
- Mutant
- Clone
- Positron
- Seed
Explanation
The carbon copy of an individual is often called a clone. However, more appropriately, a clone means to make a genetically exact copy of an organism.
55. In gene cloning, a gene or a piece of DNA fragment is inserted into which cell?
- Spores cell
- Virus cell
- Bacterial cell
- All the above
Explanation
In gene cloning, a gene or a piece of DNA fragment is inserted into a bacterial cell where DNA will be multiplied (copied) as the cell divides.
56. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding steps involved in gene cloning?
- Isolation of desired DNA fragment by using restriction enzymes
- Insertion of the DNA fragment into a suitable vector (cytoplasm) to make rDNA
- Transfer of rDNA into bacterial host cell (Transformation)
- Selection and multiplication of recombinant host cell to get a clone. Expression of cloned gene in host cell.
Explanation
Insertion of the DNA fragment into a suitable vector (Plasmid) to make rDNA.
57. Which was the first cloned sheep?
- Dolly
- Knut
- Koko
- Laika
Explanation
Dolly was the first cloned sheep.
58. Dolly was the first cloned female sheep, developed by whom at the Roslin Institute, Scotland in July 1996?
- Ian Wilmut
- Christopher Polge
- Hwang Woo-Suk
- Hans Clevers
Explanation
Dolly was the first cloned female sheep, developed by Dr. Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at the Roslin Institute, Scotland in July 1996. She was created by somatic cell nuclear transfer technique. She lived for 6.5 years and died in 2003 because of lung disease.
59. Which among the following statement incorrect regarding Pharmaceutical products developed by rDNA technique is incorrect
- Development of vaccines against various diseases like Hepatitis B and rabies
- Human growth hormone used for treating children with growth deficiencies.
- Tissue plasminogen activator is used to dissolve blood clots and prevent heart attack
- None of the above
Explanation
Using genetic engineering techniques medicinally important valuable proteins or polypeptides that form the potential pharmaceutical products for treatment of various diseases have been developed on a commercial scale. Includes Insulin used in the treatment of diabetes and Blood clotting factors are developed to treat haemophilia and others.
60. In which country Eli lilly and company in 1979 first started commercial production of human insulin by using rDNA technology?
- United States
- China
- Russia
- France
Explanation
Eli Lilly and Company, United States, in 1979 first started commercial production of human insulin by using rDNA technology.
61. Gene therapy refers to the replacement of defective gene by the direct transfer of functional genes into humans to treat genetic disease or disorder. In which year it was implemented successfully?
- 1990
- 1993
- 1997
- 1999
Explanation
Gene therapy refers to the replacement of defective gene by the direct transfer of functional genes into humans to treat genetic disease or disorder. The genetic makeup of the ‘patient’ cell is altered using recombinant DNA technology. It was first successfully implemented in 1990.
62. Gene therapy conducted till date has targeted only which cell?
- Somatic cell
- Reproductive cell
- Pinner cell
- None of the above
Explanation
Somatic gene therapy is the replacement of defective gene in somatic cells. Germ line gene therapy replacement of defective gene in germ cell (egg and sperm). Gene therapy conducted till date has targeted only somatic (non-reproductive) cells. Correction of genetic defects in somatic cells may be beneficial to the patient but the corrected gene may not be carried to the next generation.
63. Which among the following cell function is to secrete insulin?
- Nerve cells
- Stem cell
- Pancreatic cell
- Heart cell
Explanation
Our body is composed of over 200 specialised cell types, that can carry out specific functions. e.g. neurons or nerve cell that can transmit signals, or heart cells which contract to pump blood or pancreatic cells to secrete insulin.
64. The Specialised cells are called as _________
- Productivity cells
- Differentiated cells
- Undifferentiated cells
- Closet cells
Explanation
The specialised cells are called as differentiated cells.
65. In contrast to differentiated cells, which cells are undifferentiated or unspecialised mass of cells?
- Nerve cells
- Stem cells
- Pancreatic cells
- Heart cells
Explanation
In contrast to differentiated cells, stem cells are undifferentiated or unspecialised mass of cells. The stem cells are the cells of variable potency. Potency refers to the number of possible fates that a cell can acquire.
66. Which among the following is not the property of stem cells
- Its ability to divide and give rise to more stem cells by self-renewal
- Its ability to give rise to specialised cells with specific functions by the process of differentiation
- Its ability to give rise to mutant cells with adaptation to new host
- None of the above
Explanation
The two important properties of stem cells that differentiate them from other cells are: i. its ability to divide and give rise to more stem cells by self-renewal ii. its ability to give rise to specialised cells with specific functions by the process of differentiation.
67. Which among the following is not the type of stem cell?
- Embryonic stem cells
- Adult stem cell
- Somatic stem cell
- None of the above
Explanation
The stem cell are two types. They are Embryonic stem cells and Adult stem cell or somatic stem cell.
68. Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of ____
- Nematocyst
- Blastocyst
- Heterocyst
- Microcyst
Explanation
Embryonic stem cells can be extracted and cultured from the early embryos. These cells are derived from the inner cell mass of blastocyst. These cells can be developed into any cell in the body.
69. Which among the following is not the source of stem cells?
- Amniotic fluid
- Umbilical cord
- Spleen
- Bone marrow.
Explanation
Adult stem cell or somatic stem cell are found in the neonatal (new born) and adults. They have the ability to divide and give rise to specific cell types. Sources of adult stem cells are amniotic fluid, umbilical cord and bone marrow.
70. Sometimes cells, tissues and organs in the body may be permanently damaged or lost due to genetic condition or disease or injury. In such situations stem cells are used for the treatment of diseases which is called ____
- Stem cell cosmetic
- Stem cell therapy
- Stem cell conclave
- All the above
Explanation
Sometimes cells, tissues and organs in the body may be permanently damaged or lost due to genetic condition or disease or injury. In such situations stem cells are used for the treatment of diseases which is called stem-cell therapy.
71. Which among the following is not the neurodegenerative disorders?
- Parkinson’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Arthritis disease
- None of the above
Explanation
In treating neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease neuronal stem cells can be used to replace the damaged or lost neurons.
72. Who among the following developed DNA Fingerprinting Technology?
- Alec Jeffreys
- Colin Pitchfork
- Edmond Locard
- Kary Mullis
Explanation
DNA Fingerprinting Technology was developed by Alec Jeffrey.
73. Which among the following statement is correct
- The human genome has 1.5 billion base pairs. Did you know that the DNA pattern of two individuals cannot be same including their identical twins. Each person’s DNA sequence is unique due to the small difference in the base pairs. Therefore, if we want to compare the genetic difference among the two individuals, DNA fingerprinting is the easier and quicker method.
- The technique analyses each individual’s unique DNA sequences and provides distinctive characteristics of individual which helps in identification. Variable number of tandem repeat sequences (VNTRs) serve as molecular markers for identification.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The human genome has 3 billion base pairs. Did you know that the DNA pattern of two individuals cannot be same except for identical twins. Each person’s DNA sequence is unique due to the small difference in the base pairs. Therefore, if we want to compare the genetic difference among the two individuals, DNA fingerprinting is the easier and quicker method.
74. In human beings, 99 % of the DNA base sequences are the same and this is called as ___
- Caravan DNA
- Bulk genomic DNA
- Scissor cave DNA
- Cocoon genomic DNA
Explanation
In human beings, 99 % of the DNA base sequences are the same and this is called as bulk genomic DNA.
75. In human being, 1 % DNA sequence differs from one individual to another. This 1 % DNA sequence is present as small stretch of repeated sequences which is known as ____
- Satellite DNA
- Caravan DNA
- Marvin DNA
- Captive DNA
Explanation
In human being, 1 % DNA sequence differs from one individual to another. This 1 % DNA sequence is present as small stretch of repeated sequences which is known as satellite DNA. The satellite DNA bring about variation within the population. Variation in DNA banding pattern reveals differences among the individuals.
76. The number of copies of the repeat sequence also called ____
- ATNs
- VNTRs
- PVTMs
- QSMKs
Explanation
The number of copies of the repeat sequence also called as VNTRs differs from one individual to another, and results in variation in the size of the DNA segment.
77. Which among the following is correct regarding applications of DNA Fingerprinting?
- Forensic applications like crime investigation
- Study of genetic diversity of population
- Study of evolution
- All the above
Explanation
DNA fingerprinting technique is widely used in forensic applications like crime investigation such as identifying the culprit. It is also used for paternity testing in case of disputes. It also helps in the study of genetic diversity of population, evolution and speciation.
78. Genetic modification refers to the alteration or manipulation of genes in the organisms using rDNA techniques in order to produce the desired characteristics. The DNA fragment inserted is called?
- Pangene
- Transgene
- Melongene
- Plasmagene
Explanation
Genetic modification refers to the alteration or manipulation of genes in the organisms using rDNA techniques in order to produce the desired characteristics. The DNA fragment inserted is called transgene. Plants or animals expressing a modified endogenous gene or a foregin gene are also known as transgenic organisms.
79. Which gene is required for the synthesis of Vitamin A in human being?
- Alpha carotene
- Beta carotene
- Gama carotene
- Delta carotene
Explanation
Golden rice is produced by inserting Beta carotene gene (In humans, Beta carotene is required for the synthesis of Vitamin A). Genetically modified rice can produce beta carotene, that can prevent Vitamin A deficiency.
80. To improve insect resistance Bt gene from which was inserted in plants?
- Hay Bacillus
- Bacillus Metarhizium
- Bacillus Thuringiensis
- Bacillus Bassiana
Explanation
To increase resistant plants Bt gene from bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis. (Bt gene produces a protein that is toxic to insects) is inserted in plants to increase crop production.
81. To improved wool quality and production in sheep Genes for synthesis of what was inserted?
- Amino acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Chloric acid
- Fermic acid
Explanation
To improve wool quality and production in sheep Transgenic sheep, Genes for synthesis of amino acid, cysteine are inserted.
82. Phaseolus mungo was introduced from which among the following country?
- Japan
- Brazil
- Mexico
- China
Explanation
Phaseolus mungo was introduced from China.
10th Science Lesson 21 Questions in English
21] Health And Diseases
1. Which refers to cruel, violent, harmful or injurious treatment of another human being?
- Abuse
- Caution
- Psychedelic
- All the above
Explanation
Abuse refers to cruel, violent, harmful or injurious treatment of another human being. It includes physical, emotional or psychological, verbal, child and sexual abuses. Abuse can occur within the family and with people who are not associated with the family. These days the use of drugs, alcohol and tobacco has been increasing especially among teenagers and adolescents for adventure, excitement, curiosity and experimentation.
2. Which among the following statement is correct
- Abuses occur in a variety of forms and are deeply rooted in cultural, social and economic practices. Solving this global problem however requires a much better understanding of its occurrence, causes and consequences with context to sexual and childhood abuse, this is followed by substance abuse.
- Smoking cigarettes, alcohol addiction, use of drugs, eating high fat and cholesterol rich diets, excessive intake of junk foods, reduced physical activity are some of the risk factors for illness and early death.
- The role of behaviour in health has been receiving less attention in countries around the world. The health habits of the individuals and their behaviour influence the development of chronic and fatal diseases such as diabetes, obesity, heart disease, cancer and AIDS. These conditions cannot be reduced by changing lifestyles to promote wellness.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
The role of behaviour in health has been receiving increased attention in countries around the world. The health habits of the individuals and their behaviour influence the development of chronic and fatal diseases such as diabetes, obesity, heart disease, cancer and AIDS. These conditions can be substantially reduced by adopting lifestyles that promote wellness and protect their health by taking nutritious diet, regular exercise and by avoiding drugs, alcohol and smoking.
3. Which among the following ministry championed the introduction of the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012?
- The ministry of minority affairs
- The ministry of civil aviation
- The ministry of women and child development
- The ministry of home affairs
Explanation
The Ministry of Women and Child Development championed the introduction of the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012. People who traffic children for sexual purposes are also punishable under the provisions relating to the Act.
4. Which among the following statement is correct
- Child abuse constitutes all forms of physical or emotional ill treatment, sexual abuse, exploitation resulting in child’s ill health, survival and development. Physical abuse of a child is defined as those acts that cause physical harm such as threatening, beating, kicking and hitting the child.
- Sexual harassment is a form of power and dominance of one person over another, which can result in harmful consequence to the victim. It refers to inappropriate or forced sexual contact. Adolescent girls and women encounter sexual harassment in different forms.
- Sexual abuse is more common at work places. Verbal remarks, comments, gestures and looks are the most common forms of abuse. This results in psychological distress, physical illness and eating disorders in the affected individuals.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
5. When National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) was set up?
- 2006
- 2007
- 2009
- 2010
Explanation
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) was set up in March 2007 under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005. This act emphasizes the principle of universality and inviolability of child rights and recognizes the tone of urgency in all the child related policies of the country.
6. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding measures adopted for monitoring and assessment of abused child who have undergone signs and symptoms of distress
- Child Helpline: The Child Helpline provides a social worker who can assist the child by providing food, shelter and protection
- Counselling the child: Psychologists and social workers should provide guidance, counselling and continuous support to a victimized child.
- Family isolation: The victimized child should be isolated by the family members. They should be provided with proper care and attention to overcome their sufferings.
- Medical care: A child victim of sexual offences should receive medical care and treatment from health care professionals to overcome mental stress and depression.
Explanation
Family support: The victimized child should be supported by the family members. They should be provided with proper care and attention to overcome their sufferings.
7. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding measures adopted for monitoring and assessment of abused child who have undergone signs and symptoms of distress
- Legal Counsel: The family or the guardian of the child victim shall be entitled to free assistance of a legal counsel for such offence.
- Rehabilitation: Enrolling in schools and resuming their education is an important step towards rehabilitation of the child. It is essential that the child’s life is gradually returned to normal after the incidence of abuse.
- Community based efforts: Conducting awareness campaign on child abuse and its prevention.
- Protection of all children of all age group up to 16 years of age is of equal importance. Policies define priority actions for the most vulnerable children.
Explanation
Protection of all children of all age group up to 18 years of age is of equal importance. Policies define priority actions for the most vulnerable children.
8. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Instructions to be given by parents and teachers to the child for Prevention of child sexual abuse?
- Do not talk to any suspected person or strangers and to maintain a distance and not to be alone with unknown person
- To be careful while travelling alone in public or private transport.
- Not to receive money, toys, gifts or chocolates from known or unknown person to them without the knowledge of their parents
- All the above
9. The physical and mental dependency on alcohol, smoking and drugs is _____
- Depression
- Rehabilitation
- Addiction
- All the above
Explanation
The physical and mental dependency on alcohol, smoking and drugs is called addiction. The addictive potential of these substances pulls an individual into a vicious cycle leading to regular abuse and dependency. This is of serious concern because abuse of tobacco, alcohol or drugs produce many harmful effects in an individual, to the family and even to the society.
10. Which among the following statement is correct
- Drugs are normally used for the treatment of disease on advice of a physician and withdrawn after recovery. A person who is habituated to a drug due to its prolonged use is called drug addict. This is called drug addiction or drug abuse.
- A drug that modifies the physical, biological, psychological or social behaviour of a person by stimulating, depressing or disturbing the functions of the body and the mind is called compromising drug. These drugs interact with the central nervous system and affect the individual mentally.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
A drug that modifies the physical, biological, psychological or social behaviour of a person by stimulating, depressing or disturbing the functions of the body and the mind is called addictive drug. These drugs interact with the central nervous system and affect the individual physically and mentally.
11. Which drug acts on the brain and alter the behaviour, consciousness, power of thinking and perception?
- Rehabilitation drugs
- Psychotropic drugs
- Abusive drugs
- Pointless drug
Explanation
There are certain drugs called psychotropic drugs which acts on the brain and alter the behaviour, consciousness, power of thinking and perception. They are referred as mood-altering drugs.
12. Which among the following statement is correct
- Persons who consume these drugs become fully dependent on them; they cannot live without drugs. This condition is referred as drug dependence. Psychological dependence is a feel that drugs help them to reduce stress.
- Physical and mental dependence on the drug for normal condition of well-being and to maintain physiological state.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
13. What is the date of International Day against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking?
- January 26
- February 26
- June 26
- September 26
Explanation
International Day against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking – June 26.
14. Which among the following statement on adverse effects of drug use among adolescents is incorrect?
- Drop in academic performance, absence from school or college
- Deteriorating relationship with family and friends
- Lack of interest in personal hygiene, isolation, depression, fatigue and aggressive behaviour
- Increase in food and sleeping habits and decrease in body weight and appetite
Explanation
Change in food and sleeping habits and fluctuation in body weight and appetite. Always looking out for an easy way to get money for obtaining drugs.
15. Adverse effects of drug use among adolescents does not prone to which among the following infection?
- AIDS
- Hepatitis-B
- Chromhidrosis
- None of the above
Explanation
Adverse effects of drug use among adolescents Prone to infections like AIDS and Hepatitis-B.
16. When Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act was introduced?
- 1963
- 1975
- 1985
- 1997
Explanation
Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act was introduced in 1985.
17. The first phase of treatment for drug de-addiction is _____
- Psychotherapy
- Rehabilitation
- Detoxication
- Proliferation
Explanation
Management of de-addiction is a complicated and difficult task. The path to recovery of drug addicts is long and often slow. The first phase of treatment is detoxification. The drug is stopped gradually and the addict is helped to overcome the withdrawal symptoms. The addict undergoes severe physical and emotional disturbance. This is taken care by specific medication.
18. Which among the following statement regarding De-addiction is correct?
- Psychotherapy: Individual counselling is given by psychologists and counsellors not as group counselling. The treatment includes efforts to reduce the addict’s stress, taught traditional ways to solve every day’s problems, adequate diet, rest and relaxation.
- Counselling to family members: Social workers counsel family members in order to change the attitude of rejection so that the addict is accepted by the family and the society
- Rehabilitation: They are given proper vocational training so that they can lead a healthy life and become useful members of the society.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Psychotherapy: Individual and group counselling is given by psychologists and counsellors. The treatment includes efforts to reduce the addict’s stress, taught new ways to solve everyday’s problems, adequate diet, rest and relaxation.
19. Which among the following organisation in 1984 suggested the use of the term drug dependence in place of drug addiction or drug abuse?
- WHO
- IMF
- World Bank
- WTO
Explanation
World Health Organization (WHO) 1984 suggested the use of the term drug dependence in place of drug addiction or drug abuse.
20. Which among the following is obtained from the plant Nicotiana rustica?
- Ricin
- Tobacco
- Coffee
- All the above
Explanation
Tobacco is obtained from the tobacco plant Nicotiana tobaccum and Nicotiana rustica. The dried and cured leaves of its young branches make the commercial tobacco used worldwide. Addiction to tobacco is due to ‘nicotine’ an alkaloid present in it. Nicotine is a stimulant, highly harmful and poisonous substance.
21. When powdered tobacco is taken through nose, it is called _____
- Smoking
- Diluting
- Snuffing
- All the above
Explanation
Tobacco is used for smoking, chewing and snuffing. Inhaling tobacco smoke from cigars, cigarettes, bidis, pipes, hukka is called smoking. Tobacco in powder form is chewed with pan. When powdered tobacco is taken through nose, it is called snuffing.
22. Which among the following Smoking Hazards and Effects of Tobacco is incorrect
- Ergonovine and fermi hydrocarbons present in tobacco smoke is carcinogenic causing lung cancer
- Causes increased gastric secretion which leads to gastric and duodenal ulcers.
- Tobacco chewing causes oral cancer (mouth cancer)
- Increased blood pressure caused by smoking leads to increased risk of heart disease.
Explanation
Benzopyrene and polycyclic hydrocarbons present in tobacco smoke is carcinogenic causing lung cancer.
23. Which among the following organisation issued a directive under which all cigarette advertisements and packs carry a statutory warning “Smoking is injurious to Health”?
- WTO
- United Nations
- WHO
- UNESCO
Explanation
World Health organization (WHO) 1984 suggested the use of the term drug. WHO issued a directive under which all cigarette advertisements and packs carry a statutory warning “Smoking is injurious to Health”.
24. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding Smoking Hazards and Effects of Tobacco
- Causes inflammation of throat and bronchi leading to conditions like bronchitis and pulmonary tuberculosis
- Inflammation of lung alveoli, decrease surface area for gas exchange and cause emphysema.
- Sulphur oxide of tobacco smoke binds to haemoglobin of RBC and decreases its oxygen carrying capacity causing hypoxia in body tissues.
- None of the above
Explanation
Carbon monoxide of tobacco smoke binds to haemoglobin of RBC and decreases its oxygen carrying capacity causing hypoxia in body tissues.
25. When Anti-Tobacco Act was passed _____
- May 1st 2000
- August 1st 2000
- May 1st 2004
- August 1st 2004
Explanation
Anti-Tobacco Act was passed on May 1st 2004. By 2030 tobacco is expected to be single biggest cause of death worldwide accounting for 10 million deaths per year.
26. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- The consumption of alcohol is a social evil practiced by the poorer sections of the society. The dependence of alcohol is called alcoholic and the addict is termed as narcotic. It is called alcohol abuse.
- Drinking of alcohol impairs one’s physical, physiological and psychological functions. Prolonged use of alcohol depresses the nervous system, by acting as a sedative and analgesic substance.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The consumption of alcohol is a social evil practiced by the wealthier and poorer sections of the society. The dependence of alcohol is called alcoholism and the addict is termed as alcoholic. It is called alcohol abuse.
27. Which among the following is correct regarding harmful effect of alcohol?
- Nerve cell damage resulting in various mental and physical disturbances. Lack of co-ordination of body organs and Blurred or reduced vision, results in road accidents.
- Dilation of blood vessels which may affect functioning of the heart. Liver damage resulting in dilate liver which leads to leukaemia and formation of fibrous tissues.
- Body loses its control and consciousness eventually leading to health complications and ultimately to death.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Dilation of blood vessels which may affect functioning of the heart and Liver damage resulting in fatty liver which leads to cirrhosis and formation of fibrous tissues.
28. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Rehabilitation Measures for Alcoholics
- Education and counselling: Education and proper counselling will help the alcoholics to overcome their problems and stress, to accept failures in their life.
- Avoid physical activity: Individuals undergoing rehabilitation should be channelized into healthy mental activities like reading, music, sports not physical activity like sport.
- Seeking help from parents and peer groups: When a problematic situation occurs, the affected individuals should seek help and guidance from parents and peers. This would help them to share their feeling of anxiety, wrong doing and get rid of the habit.
- Only 1
- Only 3
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
Explanation
Physical activity: Individuals undergoing rehabilitation should be channelized into healthy activities like reading, music, sports, yoga and meditation.
29. Alcoholic should seek help from who among the following?
- Psychologist
- Psychiatrist
- Both Psychologist and Psychiatrist
- Godman
Explanation
Alcoholics should seek help from psychologists and psychiatrists to get relieved from this condition and to lead a relaxed and peaceful life. Alcohol de-addiction and rehabilitation programmes are helpful to the individual so that they could get rid of the problem completely and can lead a normal and healthy life.
30. Which among the following is not non-communicable disease?
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Tuberculosis
- Obesity
- Cancer
Explanation
Diseases are prevalent in our society due to our improper way of living, conditions of stress and strain. These diseases are non-communicable (Diabetes Mellitus, Obesity, Cancer, etc.,) and affect the person who are suffering from particular symptoms. It is an impairment of the body tissue or organ, disturbances in metabolic function which require modification of an individual’s normal life.
31. Which is characterised by increased blood glucose level due to insufficient, deficient or failure of insulin secretion?
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Obesity
- Cancer
- Leukemia
Explanation
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder. In Greek (Diabetes – running through; mellitus- sweet). It is characterised by increased blood glucose level due to insufficient, deficient or failure of insulin secretion.
32. Diabetes Mellitus is common due to which endocrine disorder?
- Lungs
- Hypothalamus
- Thyroid
- Pancreas
Explanation
Diabetes Mellitus is the most common pancreatic endocrine disorder.
33. How many types of diabetes mellitus are there?
- Two
- Three
- Five
- Six
Explanation
There are two types of diabetes mellitus. They are Type-1 Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM) and Type-2 Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM).
34. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding Type-1 Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)?
- IDDM accounts for 10 to 20% of the known diabetics. The condition also occurs in elders (mostly old age) and young adults, the onset is usually sudden and can be life threatening. This is caused by the destruction of α-cells of the pancreas.
- It is characterized by abnormally elevated blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) resulting from inadequate insulin secretion. Causes: Genetic inheritance and environmental factors (infections due to virus, acute stress) are the cause for this condition.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
IDDM accounts for 10 to 20% of the known diabetics. The condition also occurs in children (juvenile onset diabetes) and young adults, the onset is usually sudden and can be life threatening. This is caused by the destruction of β-cells of the pancreas.
35. The average age for the onset of diabetes is ____
- 30 years
- 35 years
- 40 years
- 70 years
Explanation
One in every 8 individuals in India is a diabetic. The revised WHO estimates for the year 2025 is 57.2 million diabetics in India. The average age for the onset of diabetes is 40 years, while it is 55 years in other countries. World Health Organization projects that diabetes will be 7th leading cause of death by the year 2030.
36. Which among the following statement is correct
- Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) accounting for 80 to 90% of the diabetic population. It develops slowly, usually milder and more stable. Insulin production by the pancreas is normal but its action is impaired. The target cells do not respond to insulin.
- It does not allow the movement of glucose into cells. The causes are multifactorial which include increasing age (affecting middle aged and older people), obesity, sedentary life style, overeating and physically inactive.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
37. Increased blood glucose level is known as _____
- Polyuria
- Glycosuria
- Polyphagia
- Hyperglycemia
Explanation
Increased blood glucose level is known as Hyperglycemia.
38. Loss of water leads to thirst is known as _____
- Polyphagia
- Glycosuria
- Polydipsia
- Anhidrosis
Explanation
Loss of water leads to thirst (Polydipsia) resulting in increased fluid intake.
39. Which among the following is not the symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus?
- Polyphagia
- Glycosuria
- Anhidrosis
- None of the above
Explanation
Diabetes mellitus is associated with several metabolic alterations. The most important symptoms are Hyperglycemia, polyuria, polydipsia, glycosuria, polyphagia, Fatigue and loss of weight.
40. Which among the following is wrongly matched?
- Polyuria – Increased urine output leading to dehydration
- Glycosuria – Excessive glucose excreted in urine
- Polyphagia – Excess sweat due to loss of glucose in urine.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Only 3
- Both 1 and 3
Explanation
Polyphagia – Excess hunger due to loss of glucose in urine.
41. When diagnosis for confirming diabetes is essential, according to WHO, if the fasting blood glucose is greater than what?
- 90 mg/dl
- 100 mg/dl
- 120 mg/dl
- 140 mg/dl
Explanation
According to WHO recommendation, if the fasting blood glucose is greater than 140 mg/dl or the random blood glucose is greater than 200 mg /dl on more than two occasions, diagnosis for confirming diabetes is essential.
42. Which among the following is not the Millet?
- Sowar
- Wheat
- Bajra
- Ragi
Explanation
jowar, bajra, ragi are millets. Wheat is not a millet
43. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Prevention and Control of Diabetes?
- Diet, hypoglycemic drugs, insulin injection and exercise are the management options based on the type and severity of the condition. The overall goal of diabetes management is to maintain normal blood glucose level.
- Low carbohydrate and fibre rich diets are more appropriate. Carbohydrates should be taken in the form of starch and complex sugars. Refined sugars (sucrose and glucose) should be avoided. Diet comprising whole grains, millets, green leafy vegetables, wheat and unpolished rice should be included in diet regularly.
- Carbohydrates is maintained to about 20- 25% of the total calories. High protein content of 30-35% of the total intake is required to supply essential amino acids. Fat content in the diet should be 5-15% of the total calories. Saturated fat intake should be reduced. Poly saturated fatty acid content should be higher.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Carbohydrates is maintained to about 50- 55% of the total calories. High protein content of 10-15% of the total intake is required to supply essential amino acids. Fat content in the diet should be 15-25% of the total calories. Saturated fat intake should be reduced. Polyunsaturated fatty acid content should be higher.
44. Which is the state in which there is an accumulation of excess body fat with an abnormal increase in body weight?
- Diabetes
- Anxiety
- Obesity
- All the above
Explanation
Obesity is the state in which there is an accumulation of excess body fat with an abnormal increase in body weight. Obesity is a complex multifactorial chronic disease developing from influence of social, behavioural, psychological, metabolic and cellular factors.
45. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Prevention and Control of Diabetes?
- Management with insulin: Commercially available insulin preparations (short and long acting) are also used to maintain blood glucose levels.
- Physical activity: Exercise plays an important role in facilitating a good control of diabetes, in addition to strengthening and toning up the muscles.
- Education and Awareness: People with diabetics should be educated on the nature of disease they have and the possibility of complications of the disease, if blood sugar is not kept under control. Instructions regarding diet, exercise and drugs should be explained.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
46. Which among the following is the formula for Body mass index (BMI)?
- BMI = Weight (kg) / Height (m)2
- BMI = Height (m)2 / Weight (kg)
- BMI = Weight (kg) + Height (m)2
- BMI = Height (m)2 × Weight (kg)
Explanation
Obesity occurs if intake of calories is more than the expenditure of energy. Over weight and obesity are conditions where the body weight is greater than the mean standard weight for age and height of an individual. Body mass index (BMI) is an estimate of body fat and health risk.
BMI = Weight (kg) / Height (m)2.
47. Every how many calories of excess consumption leads to 1 gm fat deposit and increase in body weight?
- 4 Calories
- 7 calories
- 9 Calories
- 12 Calories
Explanation
Every 7 calories of excess consumption lead to 1 gm fat deposit and increase in body weight. Weight due to fat in adipose tissue exceeds more than 20% to 25 % of body weight. An adult weighing 10% more than the standard weight is OVERWEIGHT and 20% more is OBESE.
48. Which among the following is the not risk factors of Obesity?
- Diabetes
- Gall bladder disease
- Arthritis
- None of the above
Explanation
Obesity is due to genetic factors, physical inactivity, eating habits (overeating) and endocrine factors. Obesity is a positive risk factor in development of hypertension, diabetes, gall bladder disease, coronary heart disease and arthritis.
49. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding Prevention and Control of Obesity?
- Diet Management: Low calorie, normal protein, vitamins and mineral, restricted carbohydrate and fat, high fibre diet can prevent overweight. Calorie restriction for weight reduction is safe and most effective.
- Physical exercise: A low calorie diet accompanied by moderate exercise will be effective in causing weight loss. Meditation, yoga and physical activity can also reduce stress related to overeating.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
50. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is associated with diseases of the ____
- Kidney
- Heart
- Lungs
- Neurons
Explanation
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is associated with diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
51. Desirable level for blood cholesterol should be less than what for Indians?
- 200 mg/dl
- 300 mg/dl
- 400 mg/dl
- 500 mg/dl
Explanation
Desirable level for blood cholesterol should be less than 200 mg/dl for Indians. The risk of coronary heart disease increases slowly as blood cholesterol levels increases from 200 to 300 mg/dl.
52. Which among the following statement is correct
- Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the most common form and is caused by deposition of cholesterol in the blood vessels. It usually develops slowly over many years beginning from childhood, they may form a fatty streak to a fibrous complicated plaque.
- It leads to the narrowing of blood vessels leading to Lipoprotein in the large and medium sized arteries that supply the heart muscle with RBC. It leads to sudden ischemia (High blood supply to heart muscle) and myocardial infarction (death of the heart muscle tissue).
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
It leads to the narrowing of blood vessels leading to atherosclerosis in the large and medium sized arteries that supply the heart muscle with oxygen. It leads to sudden ischemia (deficient blood supply to heart muscle) and myocardial infarction (death of the heart muscle tissue).
53. Which among the following is not the major causes and contributing factors for heart disease?
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Hypertension
- Hyperglycemia
- None of the above
Explanation
Hypercholesterolemia (High blood cholesterol) and high blood pressure (Hypertension) are the major causes and contributing factors for heart disease and if untreated may cause severe damage to brain, kidney and eventually lead to stroke.
54. Which among the following is the causes of Heart disease?
- Heredity
- Cigarette smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- All the above
Explanation
Heredity (family history), diet rich in saturated fat and cholesterol, obesity, increasing age, cigarette smoking, emotional stress, sedentary lifestyle, excessive alcohol consumption and physical inactivity are some of the causes.
55. Which among the following is not the symptoms of heart disease?
- Headache
- Hair loss
- Swelling of leg
- Tiredness
Explanation
Shortness of breath, headache, tiredness, dizziness, chest pain, swelling of leg, and gastrointestinal disturbances are symptoms of heart disease.
56. Which among the following has the lowers risk of heart disease?
- Low Density Lipoprotein
- Bad cholesterol
- High Density Lipoprotein
- None of the above
Explanation
HDL (High Density Lipoprotein) or “good” cholesterol lowers risk of heart disease while LDL (Low Density Lipoprotein) or “bad” cholesterol increases risk of heart disease.
57. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Prevention and Control of Heart Disease?
- Reduction in the intake of calories, low saturated fat and cholesterol rich food, low carbohydrates and common salt are some of the dietary modifications. Diet rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) is essential. Increase in the intake of fibre diet, fruits and vegetables, protein, minerals and vitamin are required.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise, walking and yoga are essential for body weight maintenance. Addictive substance avoidance: Alcohol consumption and smoking are to be avoided.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
58. The study of cancer is called _____
- Oncology
- Pulmonology
- Nephrology
- Angiology
Explanation
Cancer causes about 4 million deaths annually throughout the world. In India more than one million people suffer from cancer. Cancer is derived from Latin word meaning crab. The study of cancer is called Oncology (Oncos- Tumor).
59. Cancer is an abnormal and uncontrolled division of cells that invade and destroy surrounding tissue forming _____
- Piroplasm
- Alloplasm
- Bioplasm
- Neoplasm
Explanation
Cancer is an abnormal and uncontrolled division of cells that invade and destroy surrounding tissue forming a tumor or neoplasm (new growth). It is a heterogenous group of cells that do not respond to the normal cell division.
60. The cancerous cells migrate to distant parts of the body and affect new tissues. This process is called _____
- Scoliosis
- Halitosis
- Metastasis
- Katharsis
Explanation
The cancerous cells migrate to distant parts of the body and affect new tissues. This process is called metastasis. The frequent sites of metastasis are lungs, bones, liver, skin and brain.
61. Which type of cancer arise from epithelial and glandular tissues?
- Carcinomas
- Sarcomas
- Candylomas
- Sterigma
Explanation
Carcinomas arise from epithelial and glandular tissues. They include cancers of skin, lung, stomach and brain. About 85% of the tumours are carcinomas.
62. Which type of cancer occur in the connective and muscular tissue?
- Sarcomas
- Candylomas
- Sterigma
- Leucomas
Explanation
Sarcomas occur in the connective and muscular tissue. They include the cancer of bones, cartilage, tendons, adipose tissue and muscles. These form 1% of all tumours.
63. Which among the following are called blood cancers?
- Polycythemia
- Thalassaemia
- Tularemia
- Leukaemia
Explanation
Leukaemia is characterized by an increase in the formation of white blood cells in the bone marrow and lymph nodes. Leukaemia is called blood cancers. Most common type of cancer which also affect children below 15 years of age.
64. Which among the following statement is incorrect
- Benign tumours or Non-malignant tumours: Mass of proliferating cells which grow very rapidly invading and damaging the surrounding normal tissues.
- Malignant tumours: Remain confined in the organ affected and do not spread to other parts of the body.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Benign tumours or Non-malignant tumours: Remain confined in the organ affected and do not spread to other parts of the body.
Malignant tumours: Mass of proliferating cells which grow very rapidly invading and damaging the surrounding normal tissues.
65. Cancer causing agents are called ____
- Antigen
- Kerogen
- Carcinogen
- Pyrogen
Explanation
Cancer causing agents are called carcinogens. They are physical, chemical agents, ionizing radiations and biological agents.
66. Which among the following is not the chemical carcinogenic agent?
- Nicotine
- Pesticide
- Asbestos
- UV rays
Explanation
Chemical agents: Nicotine, caffeine, products of combustion of coal and oil, pesticides, asbestos, nickel, certain dyes and artificial sweeteners induce cancer. Radiations: Ionizing radiations like X-rays, gamma- rays, radioactive substances and non-ionising radiations like UV rays cause DNA damage leading to cancer.
67. Cancer causing viruses are called _____
- Transgenic virus
- Oncogenic virus
- Intragenic virus
- Autogenic virus
Explanation
Biological agents: Cancer causing viruses are called oncogenic viruses.
Cancer control programmes should focus on primary prevention and early detection. To prevent lung cancer tobacco smoking is to be avoided and protective measures to be taken against exposure to toxic pollutants of industries. Excessive exposure to radiation is to be avoided to prevent skin cancer.
68. Heavy smoking causes cancer of ____
- Oral cavity
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- All the above
Explanation
Physical Irritant: Heavy smoking causes lung cancer and cancers of oral cavity, pharynx (throat) and larynx. Betel and tobacco chewing causes oral cancer. Excessive exposure to sunlight may cause skin cancer.
69. Which among the following is incorrect regarding Treatment of Cancer?
- Radiation therapy: Tumour cells are irradiated by lethal doses of radiation while protecting the surrounding normal cells.
- Chemotherapy: Tumours are removed by surgery to prevent further spread of cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Biological response modifiers like interferons are used to activate the immune system and help in destroying the tumours.
- None of the above
Explanation
Chemotherapy: It involves administration of anti-cancerous drugs which prevent cell division and are used to kill cancer cells.
Surgery: Tumours are removed by surgery to prevent further spread of cancer cells.
70. AIDS is a severe viral disease and caused by _____
- ADS
- HIV
- Corona
- Rabies
Explanation
AIDS is a severe viral disease and caused by Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). It is a condition in which immune system fails and suppress the body’s disease fighting mechanism. They attack the lymphocytes and the affected individual is prone to infectious diseases.
71. Who among the following set up the first voluntary testing and counselling centre and an AIDS Research group in Chennai during 80’s?
- Deepa Malik
- Basanti Bisht
- Suniti Solomon
- Anuradha Koirala
Explanation
Dr. Suniti Solomon, pioneered HIV research and treatment in India. She set up the first voluntary testing and counselling centre and an AIDS Research group in Chennai during 80’s. Her team was the first to document evidence of HIV infection in India in 1985 (First Indian AIDS patient in Chennai).
72. AIDS virus has been found in which among the following?
- Tears
- Saliva
- Urine
- All the above
Explanation
AIDS virus has been found in urine, tears, saliva, breast milk and vaginal secretions. The virus is transmitted by an infected patient who comes in contact with blood of a healthy person. HIV/AIDS is not transmitted by touch or any physical contact.
73. Which among the following is incorrect regarding transmission of HIV?
- Sexual contact with infected person
- Use of contaminated needles or syringes especially in case of intravenous drug abusers
- By transfusion of contaminated / infected blood or blood products
- It does not transfer from infected mother to her child through placenta.
Explanation
From infected mother to her child through placenta.
74. What is the date of world cancer day?
- 4th January
- 4th February
- 4th May
- 4th June
Explanation
4th February is world cancer day.
75. Which among the following is not the symptom of AIDS?
- Swelling of lymph nodes
- Loss of memory
- Shedding of nail
- Weight loss
Explanation
Infected individuals become immunodeficient. The person becomes more susceptible to viral, bacterial, protozoan and fungal infections. Swelling of lymph nodes, damage to brain, loss of memory, lack of appetite and weight loss, fever, chronic diarrhoea, cough, lethargy, pharyngitis, nausea and headache.
76. Which among the following is not the diagnosis of AIDS?
- DEXA
- Western Blot
- ELISA
- None of the above
Explanation
The presence of HIV virus can be confirmed by Western Blot analysis or Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA).
77. Which among the following is not the treatment for AIDS?
- Immune stimulative therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Anti-retroviral drugs
- None of the above
Explanation
Anti-retroviral drugs and immune stimulative therapy can prolong the life of the infected person.
78. When was National Cancer Awareness Day?
- 21st February
- 5th May
- 7th November
- 1st August
Explanation
National Cancer Awareness Day -7th November.
79. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding Prevention and Control of AIDS?
- Screening of blood from blood banks for HIV before transfusion.
- Ensuring the use of disposable needles and syringes in hospitals and clinics.
- Advocating safe sex and advantages of using condoms.
- Persons with HIV/AIDS should be isolated from the family and society
Explanation
Persons with HIV/AIDS should not be isolated from the family and society. Creating awareness campaign and educating people on the consequences of AIDS.
80. When “World AIDS Day” is observed every year?
- December 1st
- November 1st
- December 1st
- August 1st
Explanation
Every year December 1st is observed as the “World AIDS Day”.
81. Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) is also called as _____
- Young onset diabetes
- Adult-onset diabetes
- Child onset diabetes
- All the above
Explanation
Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) is also called as Adult-onset diabetes.
82. In our country which among the following organisation are educating people about AIDS?
- NACO
- MICO
- SIIO
- TAO
Explanation
Many people are ignorant about AIDS and it has been said that – “don’t” die of ignorance”. In our country NACO (National AIDS Control Organization) and other NGO’S (Non- Governmental Organizations) are educating people about AIDS.
10th Science Lesson 22 Questions in English
22] Environmental Management
1. Which among the following is not the non-renewable resources?
- Mineral ores
- Wind
- Coal
- Petroleum
Explanation
Resources can be renewed simultaneously along with their exploitation (forests, crops, wildlife, groundwater, wind and solar energy). They can maintain themselves by natural recycling or can be replenished by proper management. Simultaneously, non-renewable resources cannot be recycled and can get exhausted by unlimited and continuous use (mineral ores, coal, petroleum etc). They cannot be replaced easily.
2. Which among the following statement is correct?
- Environmental management deals with the different aspects of environment, its structure, function, its quality and its maintenance including conservation of its living and non-living components. The diversified natural resources on this earth provide the necessities for survival of all forms of life including man.
- Everything that comes from nature has some utility for man but its utilization is possible based on the availability of appropriate technology. Expanding human population resulted in expanding needs of man.
- With scientific and technological advancement man started utilizing natural resources at a much larger scale. Continuous increase in population caused an increased demand for resources. Therefore, conservation of natural resources makes important contributions to the social and economic development of the country.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
3. Which among the following statement is correct
- Natural resources are conserved for their biological, economic and recreational values. The use of natural resources in excess and unplanned way leads to imbalance in the environment. A judicious balance should be maintained between exploitation of resources and its replenishment. It is important that we manage and use our resources carefully so as to preserve for the future generations
- Proper utilization and management of nature and its resources is termed as contamination. We have to build a re-sustainable world, which should last forever. Some of the ways to sustain continuous use of resources are practices to utilise energy efficiently, avoid wastage of water, avoid usage of plastics and other non-biodegradable materials and to take care for the environment we live.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Proper utilization and management of nature and its resources is termed as conservation. We have to build a sustainable world, which should last forever. Some of the ways to sustain continuous use of resources are practices to utilise energy efficiently, avoid wastage of water, avoid usage of plastics and other non-biodegradable materials and to take care for the environment we live.
4. Which among the following movement was a non-violent agitation in 1973 that was aimed at protection and conservation of trees?
- Jungle Bachao movement
- Navdanya movement
- Chipko movement
- Averting movement
Explanation
The Chipko movement was a non-violent agitation in 1973 that was aimed at protection and conservation of trees. The name of the movement ‘Chipko’ comes from the word ’embrace’, as the villagers hugged the trees and encircled them to prevent them from being cut.
5. Which among the following statement is correct
- Forests are an important component of our environment and are dominated by microorganisms, flowering plants, shrubs, climbers, dense trees and provide a vast habitat for wild animals. Forests also contribute to the economic development of our country. Forests are vital for human life it is a source for a wide range of renewable natural resource.
- Forests are major factor of environmental concern. They act as carbon sink, regulate climatic conditions, increase rainfall, reduce global warming, prevent natural hazards like flood and landslides, protect wildlife and also act as catchments for water conservation. They also play a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
6. The Chipko movement originated in which among the following state(Now)?
- Madhya Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
- Rajasthan
- Kerala
Explanation
The Chipko movement originated in the Chamoli district of Uttar Pradesh (now Uttarakhand). The protest of Chipko movement achieved a major victory in 1980 with 15 years ban on cutting trees in the Himalayan forests.
7. India is losing how many million hectares of forest cover every year?
- 1.5 million
- 2.8 million
- 3.6 million
- 5.1 million
Explanation
Deforestation is the destruction of large area of forests. This happens for many reasons like intensive agriculture, urbanization, construction of dams, roads, buildings and industries, hydroelectric projects, forest fires, construction of mountain and forest roads. It is a threat to the economy, quality of life and future of the environment. India is losing about 1.5 million hectares of forest cover every year.
8. Which among the following is not the problem due to Deforestation?
- Floods
- Typhoon
- Drought
- Soil erosion
Explanation
Deforestation gives rise to ecological problems like floods, drought, soil erosion, loss of wild life, extinction of species, imbalance of biogeochemical cycles, alteration of climatic conditions and desertification.
9. How many hectares of forest is classified as reserved forests in India?
- 752.3 lakh hectare
- 576.5 lakh hectare
- 256.9 lakh hectare
- 693.8 lakh hectare
Explanation
India has an area of 752.3 lakh hectare classified as reserved forests and 215.1 lakh hectare as protected forests.
10. Which among the following is the afforestation programme?
- Fasal Bima
- Pashu Kisan
- Van Mahotsav
- Paramparagat Krishi
Explanation
Activities for afforestation programme (Van Mahotsav) includes planting and protecting trees with multiple uses which help in restoration of green cover. Destruction of trees should be curtailed.
11. Which among the following statement is correct
- Social forestry programme should be undertaken on a large scale with active participation of the public and utilization of common land to produce firewood, fodder and timber for the benefit of the rural community. This relieves pressure on existing forests and to safeguard future of tribe.
- Forest Conservation through Laws: Adopting stringent laws and policies to conserve and protect forests are through National Forest Policy, (1972 and 1997) and Forest Conservation Act, 1962.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Forest Conservation through Laws: Adopting stringent laws and policies to conserve and protect forests are through National Forest Policy, (1952 and 1988) and Forest Conservation Act, 1980.
12. Which refer to the undomesticated animals living in their natural habitats (forests, grasslands and deserts) an area without human habitation?
- Den
- Wild life
- Safari
- All the above
Explanation
Wild life refers to the undomesticated animals living in their natural habitats (forests, grasslands and deserts) an area without human habitation. They are needed for maintaining biological diversity. It also helps in promoting economic activities that generates revenue through tourism. Conservation of forest and wildlife is interrelated with each other.
13. Exploitation of wildlife resources has decreased global wildlife population by what percentage between 1970 and 2014?
- 45%
- 52%
- 69%
- 76%
Explanation
Wildlife of India is a great natural heritage. Exploitation of wildlife resources has decreased global wildlife population by 52% between 1970 and 2014. Over exploitation and shrinking of forest cover areas has resulted in animals becoming extinct, some are threatened and some are on the verge of extinction. In recent years, increase in human encroachment has posed a threat to India’s wildlife.
14. Which among the following is incorrect regarding aims of wildlife management?
- To control and limit exploitation of species and to preserve the plants and animals from extinction
- Maintenance of threatened species and protect species which are on the verge of extinction.
- To study the ecological relationship of the plants and animals in natural habitat and preserve the endangered species
- Minimising National parks, Wildlife sanctuaries, protected areas and Biosphere reserves.
Explanation
Establishment of National parks, Wildlife sanctuaries, protected areas and Biosphere reserves. Hunting and poaching should be prohibited.
15. When the Wildlife protection Act was established?
- 1954
- 1962
- 1972
- 1984
Explanation
The Wildlife protection Act was established in 1972.
16. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding wildlife protection act?
- Open trade in wild animals and products obtained from them.
- Constitute sanctuaries, national parks, and closed areas for wildlife conservation.
- Special schemes for preservation of endangered species.
- Constitute Central Zoo Authority and recognition of zoos.
Explanation
Restrict, regulate or prohibit trade in wild animals and products obtained from them. Prohibit killing and hunting of specified animals.
17. Which was the first national park to be established in 1936?
- Pench national park
- Jim Corbett national park
- Keibul-Lamjao national park
- Vansda national park
Explanation
Jim Corbett National Park was the first to be established in 1936.
18. Which among the following is not the Organisations Involved in Conservation of Wildlife?
- Indian Board for WildLife (IBWL)
- World Afforesting Corporate (WAC)
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF) for Nature
- World Conservation Union (WCN)
19. The Corbett National Park was located in which among the following state?
- Assam
- Maharashtra
- Meghalaya
- Uttarakhand
Explanation
The Corbett National Park was established in 1936 in Uttarakhand, India.
20. Which among the following is not the Organisations Involved in Conservation of Wildlife?
- International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural resources (IUCN)
- Convention of International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES)
- Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS)
- Madras National Bird Society (MNBS)
Explanation
The Organisations Involved in Conservation of Wildlife are (i) Indian Board for Wildlife (IBWL) (ii) World Wildlife Fund (WWF) for Nature (iii) World Conservation Union (WCN) (iv) International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural resources (IUCN) (v) Convention of International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) (vi) Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) (vii) Wild life Preservation Society of India, Dehradun.
21. Who among the following was the native of Venkatachalapuram village, Theni District in Tamil Nadu was the first Indian woman to strike an International reputation as wildlife photographer?
- Dayanita Singh
- Anita Venkatesh
- Rathika Ramasamy
- Nalini Malini
Explanation
Rathika Ramasamy, a native of Venkatachalapuram village, Theni District in Tamil Nadu was the first Indian woman to strike an International reputation as wildlife photographer. Her passion is towards bird photography. A photobook on wildlife titled “The best of wildlife moments” was published in November 2014.
22. How many biosphere reserves are in India?
- 10
- 15
- 23
- 28
Explanation
There are 15 biosphere reserves in India. The Nilgiris is a biosphere reserve in Tamil Nadu.
23. Removal of upper layer of soil by wind and water is called _____
- Soil contamination
- Soil possession
- Soil erosion
- All the above
Explanation
The top layers of soil contain humus and mineral salts, which are vital for the growth of plants. Removal of upper layer of soil by wind and water is called soil erosion. Soil erosion causes a significant loss of humus, nutrients and decrease the fertility of soil.
24. Indian Rhino Vision 2020 is to conserve at least 3000 greater one-horned rhinos in which state?
- Assam
- Kerala
- Bihar
- Maharashtra
Explanation
Indian Rhino Vision 2020 is to conserve at least 3000 greater one-horned rhinos in Assam, India by 2020.
25. Match the following Wildlife Conservation Initiatives with its launch year?
- Project Tiger – 1. 1999
- Project Elephant – 2. 1992
- Crocodile Conservation Project – 3. 1976
- Sea Turtle Conservation Project – 4. 1973
- 4 – 2 – 3 – 1
- 3 – 1 – 2 – 4
- 2 – 1 – 4 – 3
- 1 – 4 – 2 – 3
Explanation
Project Tiger and Project Elephant has been launched in 1973 and 1992 respectively. Crocodile Conservation Project was launched in 1976. Sea Turtle Conservation Project was launched in 1999.
26. Which among the following is the agent of soil erosion?
- High velocity of wing
- Farming
- Landslide
- All the above
Explanation
Agents of soil erosion are high velocity of wind, air currents, flowing water, landslide, human activities (deforestation, farming and mining) and overgrazing by cattle.
27. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding Management of Soil Erosion?
- Retain vegetation cover, so that soil is not exposed
- Crop rotation and soil management improve soil organic matter
- Wind speed can be controlled by cutting trees in form of a shelter belt
- Cattle grazing should be controlled and Runoff water should be stored in the catchment.
Explanation
Wind speed can be controlled by planting trees in form of a shelter belt. Reforestation, terracing and contour ploughing.
28. Energy resources can be classified as how many types?
- Two
- Three
- Five
- Six
Explanation
Energy is an important input for development. The expansion of possible energy resources has been directly related with the pace of agricultural and industrial development in every part of the world. Energy resources can be classified two types as non-renewable and renewable.
29. Energy obtained from sources that cannot renew themselves over a short period of time is known as _____
- Renewable energy
- Non-renewable energy
- Inexhaustible energy
- Both Renewable and Inexhaustible
Explanation
Energy obtained from sources that cannot renew themselves over a short period of time is known as non-renewable (Exhaustible) energy. These are available in limited amount in nature.
30. Which among the following is the other term of Renewable energy resources?
- Exhaustible energy resources
- Conventional energy resources
- Inexhaustible energy resources
- Both Conventional and Inexhaustible
Explanation
Renewable (Inexhaustible) energy resources are available in unlimited amount in nature and they can be renewed over a short period of time, inexpensive and can be harvested continuously.
31. The conventional energy resources account for how many percentages of the world’s production of commercial energy?
- 75%
- 80%
- 85%
- 90%
Explanation
The conventional energy resources (Non-renewable energy resources) account for 90% of the world’s production of commercial energy and nuclear power account for 10%.
32. Which among the following is not the Non-renewable energy resource?
- Coal
- Biofuel
- Natural gas
- Petroleum
Explanation
Non-renewable energy resources include coal, petroleum, natural gas and nuclear power. The Renewable (non-conventional) energy resources which include biofuel, biomass energy, geothermal energy, water energy (hydroelectric energy and tidal energy), solar energy, wave energy and wind energy.
33. Which among the following is not the fossil fuel?
- Uranium
- Petroleum
- Coal
- None of the above
Explanation
Fossil fuels are found inside the earth’s crust and are energy rich substances formed by natural process, such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms, over millions of years. As the accumulating sediment layers produce heat and pressure, the remains of the organisms are gradually transformed into hydrocarbons. e.g. petroleum, coal and natural gas.
34. Which among the following statement is correct
- Coal and Petroleum are natural resources. They are called fossil fuels as they are formed from the degradation of biomass buried deep under the earth millions of years ago. Coal is used for generation of electricity at Thermal power plants.
- Petroleum also known as green oil is processed in oil refineries to produce petrol and diesel which are used to run automobiles, trucks, trains, ships and airplanes etc. Macerated oil and LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) obtained from petroleum is used as domestic fuel for cooking food
- The coal and petroleum reserves can get exhausted if we continue using them at a rapid rate. The formation of these fossil fuels is a very slow process and takes very long period of time for renewal.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Petroleum also known as crude oil is processed in oil refineries to produce petrol and diesel which are used to run automobiles, trucks, trains, ships and airplanes etc. Kerosene and LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) obtained from petroleum is used as domestic fuel for cooking food.
35. Which among the following statement regarding Steps to Conserve Coal and Petroleum Resources is incorrect?
- If electricity is saved, it will in turn increase the use of coal
- Using bicycle for covering short distances instead of using cars, scooters or motorcycles
- Using pressure cooker can reduce the consumption of kerosene and LPG while cooking food. Solar cooker and solar heaters can be used wherever possible
- Motor vehicles should be designed with fuel efficient engines to increase efficiency and also reduce air pollution.
Explanation
It is necessary to conserve or save coal and petroleum resources for the future use, which can be done by reducing their consumption. If electricity is saved, it will in turn reduce the use of coal.
36. What is the position of India in the world as the consumer of crude oil?
- First
- Second
- Third
- Fourth
Explanation
India is the third largest consumer of crude oil in the world, after the United States and China.
37. In which among the following state Taj Mahal is present whose white marble became yellow due to air pollution?
- Punjab
- Uttar Pradesh
- Bihar
- Madhya Pradesh
Explanation
The Taj Mahal is one of the seven wonders of the world and is located in Agra, Uttar Pradesh. It is built with white marble. The white marble became yellow due to air pollution. The Government of India has set up emission standards around the monument to protect it from the damage.
38. Which oil refinery owned by Indian Oil Corporation present around Taj Mahal, Agra area produce sulphur and nitrogen oxides cause air pollution?
- Jamnagar oil refinery
- Bina oil refinery
- Mathura oil refinery
- Barmer oil refinery
Explanation
The Mathura oil refinery owned by Indian Oil Corporation present around Taj Mahal, Agra area produce sulphur and nitrogen oxides turns Taj Mahal white marble to Yellow.
39. Which among the following statement is incorrect.
- The energy crisis has shown that for sustainable development in energy sector we must conserve the renewable conventional resources from its rapid depletion and replace them by non-polluting, Non-renewable sources which are environmentally clean.
- Efforts are made to develop new sources of energy which is called non-conventional sources of energy. It would provide greater initiative to local people who could assess their needs and resources and plan a strategy that could be useful to them.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The energy crisis has shown that for sustainable development in energy sector we must conserve the non-renewable conventional resources from its rapid depletion and replace them by non-polluting, renewable sources which are environmentally clean.
40. Which among the following is the energy obtained from the sun?
- Polar energy
- Tidal energy
- Solar energy
- All the above
Explanation
Solar energy is the energy obtained from the sun.
41. Which among the following statement is correct.
- The sun gives out vast amount of light and heat. It is only a little less than half (47%) of solar energy which falls on the atmosphere reaches the earth’s surface. If we could use just a small part of this energy it would fulfil all the country’s need for power.
- Solar energy has advantages and certain limitations. The energy from the sun can be harnessed to provide power. The various devices used for harnessing sun’s energy are called solar energy devices.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
42. Solar cells (Photovoltaic devices) is made up of which element that converts sunlight directly into electricity?
- Phosphor
- Silicon
- Boron
- Carbon
Explanation
Solar cells (Photovoltaic devices) are made up of silicon that converts sunlight directly into electricity. Solar cell produces electricity without polluting the environment. Since it uses no fuel other than sunlight, no harmful gases, no burning, and no wastes are produced.
43. Which among the following is incorrect regarding solar cells?
- Solar cells can be used for street lighting, traffic signals, water pumping, battery charging system etc.
- It is used in artificial satellites and space probes. t is used in calculators, electronic toys and watches.
- It provides radio and TV transmission to remote areas.
- These cannot be installed in remote and inaccessible areas where setting up of power plant is expensive.
Explanation
These can be installed in remote and inaccessible areas (forests and hilly regions) where setting up of power plant is expensive.
44. Which among the following statement is correct.
- Arrangement of many solar cells side by side connected to each other is called solar panel. The capacity to provide electric current is much decreased in the solar panel. The process of manufacture this is very cheap.
- Solar cooker consist of an insulated metal box or wooden box which is painted from outside to absorb maximum solar radiations. A thin silicon sheet forms the cover over the box. The reflector is the plane mirror which is attached to the box. The food is cooked by energy radiated by the sun.
- In solar thermal power plants, many solar panels are used to concentrate sun rays, to heat up water into steam. The steam is used to run the turbines to produce electricity. A capacity of 100 litres solar heater can save up-to 1500 units of electricity per year.
- Only 2
- Only 3
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
Explanation
Arrangement of many solar cells side by side connected to each other is called solar panel. The capacity to provide electric current is much increased in the solar panel. But the process of manufacture is very expensive.
Solar cookers consist of an insulated metal box or wooden box which is painted from inside so as to absorb maximum solar radiations. A thick glass sheet forms the cover over the box. The reflector is the plane mirror which is attached to the box. The food is cooked by energy radiated by the sun.
45. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding solar energy.
- Solar energy is available in abundance in our country and is free of cost.
- Solar energy is a non-renewable source of energy.
- Solar energy can be used for generating electricity or heat.
- Solar energy does not cause pollution.
Explanation
Solar energy is a renewable source of energy.
46. Which among the following is not the part of mixture of Biogas?
- Methane
- Nitrogen
- Hydrogen sulphide
- Carbon dioxide
Explanation
Biogas is the mixture of methane (nearly 75 %), hydrogen sulphide, carbon dioxide and hydrogen. It is produced by the decomposition of animal wastes (cow dung) and plant wastes in the absence of oxygen.
47. Which among the following is the other name of Biogas?
- Gobar gas
- Shale gas
- Gross gas
- Meteor gas
Explanation
Biogas is also commonly called as ‘Gobar gas’ since the starting material used is cow dung which means gobar in Hindi.
48. Which among the following statement incorrect regarding Biogas
- Biogas is used as fuel for cooking and is used to run motors and pump sets.
- Biogas is used to generate electricity and burns with smoke and therefore causes pollution.
- An excellent way to get rid of organic wastes like bio-waste and sewage material and It is safe and convenient to use.
- Left over slurry is a good manure rich in nitrogen and phosphorus and can reduce the amount of greenhouse gases emitted.
Explanation
Biogas is used to generate electricity and burns without smoke and therefore causes less pollution.
49. Which gas is obtained from the compaction of small old rocks containing mud and minerals – such as quartz and calcite, trapped beneath earth’s surface?
- Meteor gas
- Gross gas
- Shale gas
- All the above
Explanation
Shale (Shale gas) refers to the soft finely stratified sedimentary rock that is formed from the compaction of small old rocks containing mud and minerals – such as quartz and calcite, trapped beneath earth’s surface. These rocks contain fossil fuels like oil and gas in their pores.
50. Shale gas is extracted by a technique called ____
- Dynamic cracking
- Hydraulic fracturing
- Crust fracturing
- Plate cracking
Explanation
Shale gas is extracted by a technique called hydraulic fracturing (drilling or well boring of sedimentary rocks layers to reach productive reservoir layers).
51. Which among the following statement is correct regarding shale gas?
- Shale drilling could affect groundwater reserves, which can contaminate the drinking water resources and affect the fertility of the soil.
- Thousand gallons of petroleum is needed to break and release the shale gas, which in turn can affect the ground table.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
Million gallons of water is needed to break and release the shale gas, which inturn can affect the water table.
52. Which among the following is not the identified basins as areas for shale gas exploration?
- Cauvery onshore
- Krishna Godavari onshore
- Narmada onshore
- Gondwana
Explanation
India has identified six basins as areas for shale gas exploration: Cambay (Gujarat), Assam-Arakan (North East), Gondwana (Central India), Krishna Godavari onshore (East Coast), Cauvery onshore and Indo-Gangetic basins.
53. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding wind energy?
- The potential energy possessed by the wind is due to its high speed, that can be converted into chemical power by wind turbines. The rotatory motion of windmill produces wind energy. It can be used for generating electricity, run water pumps, flour mills, draw water from wells etc.
- Windmill is a machine that converts the energy of wind into rotational energy by broad blade attached to the rotating axis. When the blowing air strikes the blades of the windmill, it exerts force and causes the blades to rotate. The rotational movement of the blades operate the generator, and the electricity is produced.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
Explanation
The kinetic energy possessed by the wind is due to its high speed, that can be converted into mechanical power by wind turbines. The rotatory motion of windmill produces wind energy. It can be used for generating electricity, run water pumps, flour mills, draw water from wells etc.,
54. Where world’s largest and tallest wind turbine is situated?
- France
- Madrid
- Hawaii
- Wellington
Explanation
The world’s largest and tallest wind turbine is situated in Hawaii. One wind turbine can produce electricity for 300 homes.
55. Which among the following is incorrect regarding wind energy?
- Wind energy is free, eco-friendly, renewable source of energy.
- Wind energy does not cause pollution.
- Expenses on periodic maintenance is high when compared to the other power sources.
- None of the above
Explanation
Expenses on periodic maintenance is low when compared to the other power sources.
56. Earth’s surface is covered with nearly how many percentages of water?
- 89%
- 53%
- 68%
- 71%
Explanation
Earth’s surface is covered with nearly 71% of water.
57. Which among the following statement is correct regarding water energy?
- Harnessing the energy from the flowing water can be used to produce electricity. The technique to harness the water energy is called Hydropower. The electrical energy is derived from water flow, water falling from a height.
- Hilly areas are suitable for this purpose where there is continuous flow of water in large amounts falling from high slopes. It does not cause environmental pollution or waste generation. Hydropower plants converts the kinetic energy of flowing water into electricity. This is called hydroelectricity.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
58. Which is a technique of collecting and storing rainwater for future use?
- Rainwater harvesting
- Rainwater recementing
- Rainwater plotting
- Rainwater patterning
Explanation
Rainwater harvesting is a technique of collecting and storing rainwater for future use. It is a traditional method of storing rainwater in underground tanks, ponds, lakes, check dams and used in future. The main purpose of rainwater harvesting is to make the rainwater percolate under the ground so as to recharge ‘groundwater level’.
59. Which among the following is not the method of rainwater harvesting?
- Roof top rainwater harvesting
- Ooranis
- Recharge pit
- Incineration
Explanation
Methods of rainwater harvesting are i) Roof top rainwater harvesting, ii) Recharge pit, iii) Digging of tanks or lakes (Eris) and iv) Ooranis.
60. Which among the following statement is incorrect regarding tidal energy?
- Tidal energy is the energy obtained from the movement of water due to ocean tides. Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted on the oceans of the earth.
- A tidal stream is a fast-flowing body of water created by tides. Turbines are placed in tidal streams. When the tides hit the turbine, the turbine rotates and converts the tidal energy into electric energy.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None
61. Which among the following point is incorrect regarding tidal energy?
- Tidal energy does not produce any pollution.
- It does not use any fuel and does not produce any waste.
- Tides are not predictable, so tidal energy can be produced at any time.
- Water is denser than air and therefore can generate electricity at lower speeds than wind turbines.
Explanation
Tides are predictable, so tidal energy can be produced at any time.
62. Which among the following statement regarding Methods of rainwater harvesting is correct.
- Roof top rainwater harvesting: Rooftops are excellent rain catchers. The rainwater that falls on the roof of the houses, apartments, commercial buildings etc. is collected and stored in the surface tank and can be used for domestic purpose.
- Digging of tanks or lakes (Eris): It is one of the traditional waters harvesting system in Tamil Nadu. Eris are constructed in such a way that if the water in one eri overflows, it automatically gets diverted to the eri of the next village, as these eris are interconnected.
- Ooranis: In this method, the rainwater is first collected from the roof tops or open spaces and is directed into the percolation pits through pipes for filtration. After filtration the rainwater enters the recharge pits or ground wells.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Recharge pit: In this method, the rainwater is first collected from the roof tops or open spaces and is directed into the percolation pits through pipes for filtration. After filtration the rainwater enters the recharge pits or ground wells.
Ooranis: These are small ponds to collect rainwater. The water is used for various domestic purposes (drinking, washing, and bathing). These ponds cater the nearby villages.
63. Who among the following build the kallanai Dam, also known as Grand Anicut?
- King Raja Raja Chola
- King Rajendra Chola
- King Karikala Chola
- King Adhithya Chola
Explanation
kallanai Dam, also known as Grand Anicut, is the fourth oldest dam in the world, constructed by King Karikala Chola of the Chola Dynasty in the 2nd century A.D.(CE). It still serves the people of Tamilnadu, the dam is located on the River Kaveri, approximately 20 km from the city of Tiruchirapalli.
64. Which among the following point is incorrect regarding rainwater harvesting?
- Overcome the rapid depletion of ground water levels.
- To Meet the increase demand of water.
- Reduces flood and soil erosion.
- Water stored in ground is contaminated by human and animal wastes so examined before drinking purpose.
Explanation
Water stored in ground is not contaminated by human and animal wastes and hence can be used for drinking purpose.
65. Which among the following produce Electricity or electric power?
- Motor
- Generator
- Compressor
- All the above
Explanation
Electricity or electric power is produced by generators. The generators are operated by the turbines attached to it. The turbines are rotated by steam, moving water or wind power to produce electricity.
66. Which among the following point is incorrect regarding Conservation of electrical energy?
- Use energy efficient appliances to save electricity like Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFL), Light Emiting Diode (LED) bulbs and other electric equipments.
- Switch off the lights and fans, television and other electrical appliances when not in use.
- Minimise the use of solar radiation. Electric geyser can be used instead of Solar water heating system.
- Switch of the mobile phone chargers when not in use and Minimise the use of air conditioners.
Explanation
Maximise the use of solar radiation. Solar water heating system can be used instead of electric geysers.
67. E-wastes are generally called as ______
- Engineering wastes
- Electronic wastes
- Elite wastes
- Economical wastes
Explanation
E-wastes are generally called as electronic wastes, which includes the spoiled, outdated, non-repairable electrical and electronic devices. These wastes contain toxic metals like lead, cadmium, chromium, and mercury, though also contain iron, copper, silicon, aluminum and gold which can be recovered.
68. How many percentages of e-wastes produced are recycled?
- 5%
- 10%
- 15%
- 25%
Explanation
Only 5 % of e-wastes produced are recycled.
69. Which among the following is not the Sources of e-wastes?
- Electronic devices
- Household electrical appliances
- Accessories
- None of the above
Explanation
Electronic devices: Computers, laptops, mobile phones, printers, monitors, televisions, DVD players, calculators, toys, sport equipment’s, etc.
Household electrical appliances: Refrigerators, washing machine, microwave oven, mixer, grinder, water heater, etc.,
Accessories: Printing cartridges, batteries, and chargers.
70. E-waste includes how many percentages of computer components?
- 45%
- 58%
- 66%
- 72%
Explanation
E-wastes include 1. Computer components – 66%, 2. Telecommunication components – 12 %, 3. Electronic components – 5 %, 4. Biomedical components – 7 % and Other components – 6 %. Disposal of any kind of electrical and electronic devices without knowledge can become the landfill and water pollutants.
71. Which among the following Damages central and peripheral nervous system; affect brain development in children?
- Lead
- Chromium
- Cadmium
- Mercury
Explanation
Lead: Damages central and peripheral nervous system; affect brain development in children.
72. Which among the following accumulates in kidney and liver; neural damage?
- Chromium
- Cadmium
- Mercury
- Polyvinyl Chloride
Explanation
Cadmium: Accumulates in kidney and liver; neural damage.
73. Which among the following is correctly matched with Health Effects of E- Wastes?
- Mercury – Asthmatic bronchitis
- Chromium – Chronic damage to brain and respiratory system
- Polyvinyl Chloride – Burning produces dioxin which can cause developmental and reproductive problems, damages the immune system.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Only 3
- Both 1 and 3
Explanation
Chromium – Asthmatic bronchitis, Mercury – Chronic damage to brain and respiratory system.
74. Which among the following is the sources of Sewage/wastewater?
- Leather industries
- Paper and pulp industries
- Household activities
- All the above
Explanation
Untreated sewage or wastewater generated from domestic and industrial process is the leading polluter of water sources in India. Sewage water results in agricultural contamination and environmental degradation. Sources of sewage are • Domestic purpose or household activities • Dye and textile industries • Leather industries • Sugar and breweries industries • Paper and pulp industries.
75. Which among the following is not conventional wastewater treatment methods?
- Pre-screening
- Aeration
- Water Reuse
- Incineration
Explanation
The conventional wastewater treatment methods involve the following steps (a) Pre-screening (b) Aeration (c) Sludge Management and (d) Water Reuse.
76. Which among the following statement is correct regarding Sewage/wastewater treatment method?
- Pre-screening: Wastewater generated from domestic and industrial activities is screened to remove soil and solid particulates.
- Aeration: Screened wastewater is then pumped to an aeration tank. Here the microbial contaminants are removed by the biological degradation that occurs in the presence of air.
- Water recycling: The water will then be supplied for domestic or industrial purposes.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
77. In Sedimentation process method (Sewage treatment method) the solid particles in suspension form are allowed to settle. The particles that settle out from the suspension is known as _____
- Posh
- Sludge
- Raven
- All the above
Explanation
In Sedimentation process the solid particles in suspension form are allowed to settle. The particles that settle out from the suspension is known as sludge. The sludge generated by the degradation process is transferred periodically from the tank for safe disposal.
78. Which among the following is not used to remove any microorganism contamination in Sewage/wastewater treatment method?
- Chlorination
- Ultraviolet radiation
- Infrared
- None of the above
Explanation
Chlorination and ultraviolet (UV) radiation of treated water is required to remove any microorganism contamination.
79. Which among the following is not the solid waste?
- Hospital wastes
- Industrial wastes
- E- wastes
- None of the above
Explanation
Solid wastes mainly include municipal wastes, hospital wastes, industrial wastes and e- wastes etc. The solid wastes are dumped in the soil which results in landscape pollution. Solid-waste management involves the collection, treatment and proper disposing of solid material that is discarded from the household and industrial activities.
80. Which among the following methods of solid wastes disposal is incorrect?
- Aeration
- Segregation
- Sanitary landfill
- Incineration
Explanation
Methods of solid wastes disposal are 1. Segregation, 2. Compositing, 3. Incineration and 4. Sanitary landfill.
81. Which among the following statement is correct regarding methods of solid wastes disposal?
- Segregation: It is the separation of different type of waste materials like biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes
- Composting: Solid wastes are dumped into low lying areas. The layers are compacted by trucks to allow settlement. The waste materials get stabilised in about 2-12 months. The organic matter undergoes decomposition.
- Incineration: It is the burning of non-biodegradable solid wastes (medical wastes) in properly constructed furnace at high temperature.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Sanitary landfill: Solid wastes are dumped into low lying areas. The layers are compacted by trucks to allow settlement. The waste materials get stabilised in about 2-12 months. The organic matter undergoes decomposition.
82. In Compositing method, Biodegradable matter of solid wastes is digested by microbial action or earthworms and converted into _____
- Pores
- Cymath
- Humus
- Spike
Explanation
In Composting method Biodegradable matter of solid wastes is digested by microbial action or earthworms and converted into humus.
83. Which among the following statement is incorrect.
- Papers from old books, magazines and newspapers are recycled to produce papers in papermills.
- Agricultural wastes like coconut shells, jute cotton stalk, bagasse of sugarcane can be used to make paper and hard board. Paddy husk can be used as livestock fodder.
- Cow dung and other organic wastes can be used in shale gas plant to provide natural gas and manure for fields.
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
- All 1, 2 and 3
Explanation
Cow dung and other organic wastes can be used in gobar gas plant to provide biogas and manure for fields.
84. Which among the following is not the 4R approach?
- Recovery
- Remove
- Recycle
- Reduce
Explanation
The 4R approach such as Reduce, Reuse, Recovery and Recycle may be followed for effective waste management.